NLE Roman culture, etc for Latin (Latin 1 NLE) real
1/430
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
431 Terms
Curia
building where Roman senators met
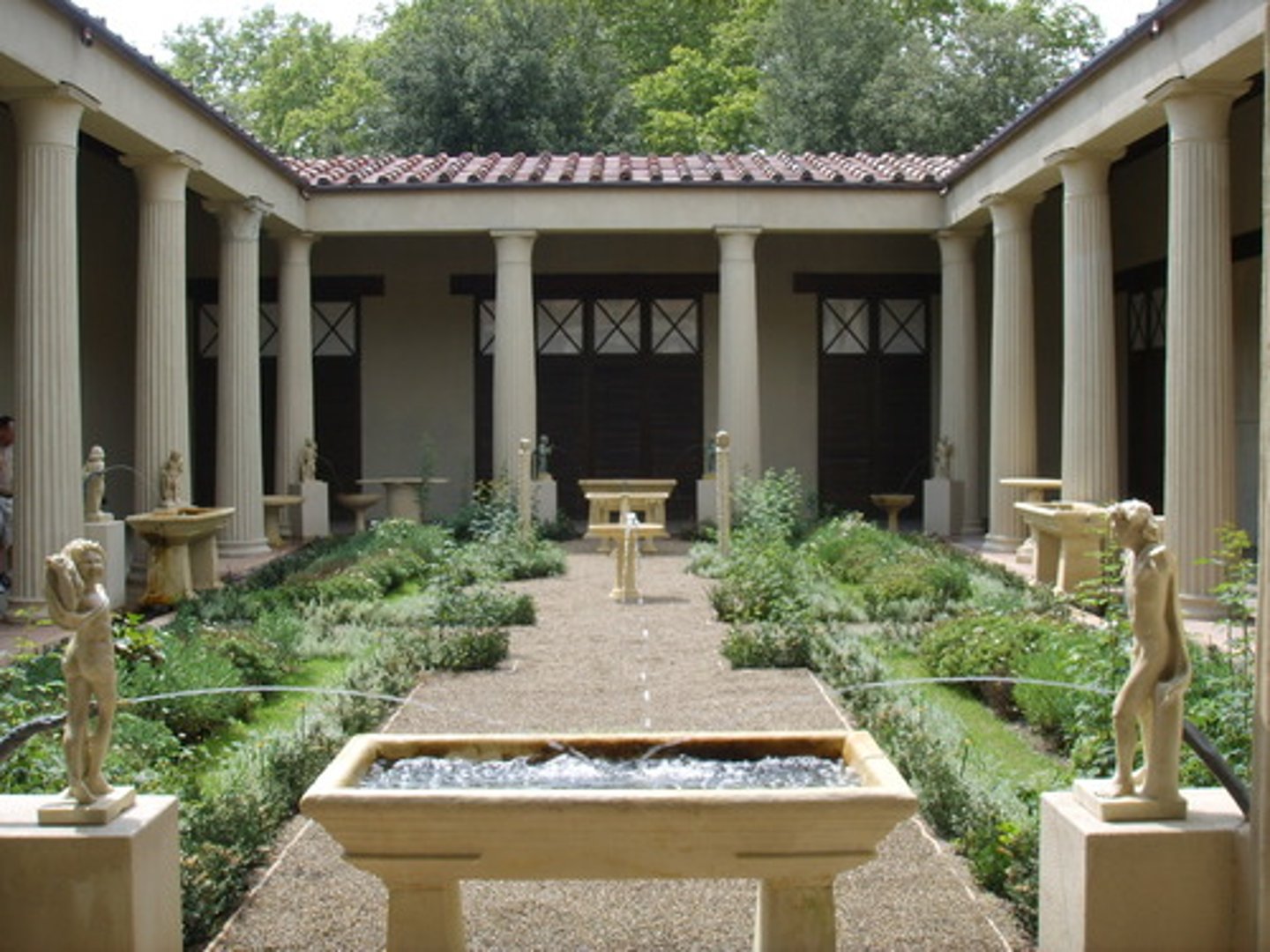
peristylium
Roman garden surrounded by columns

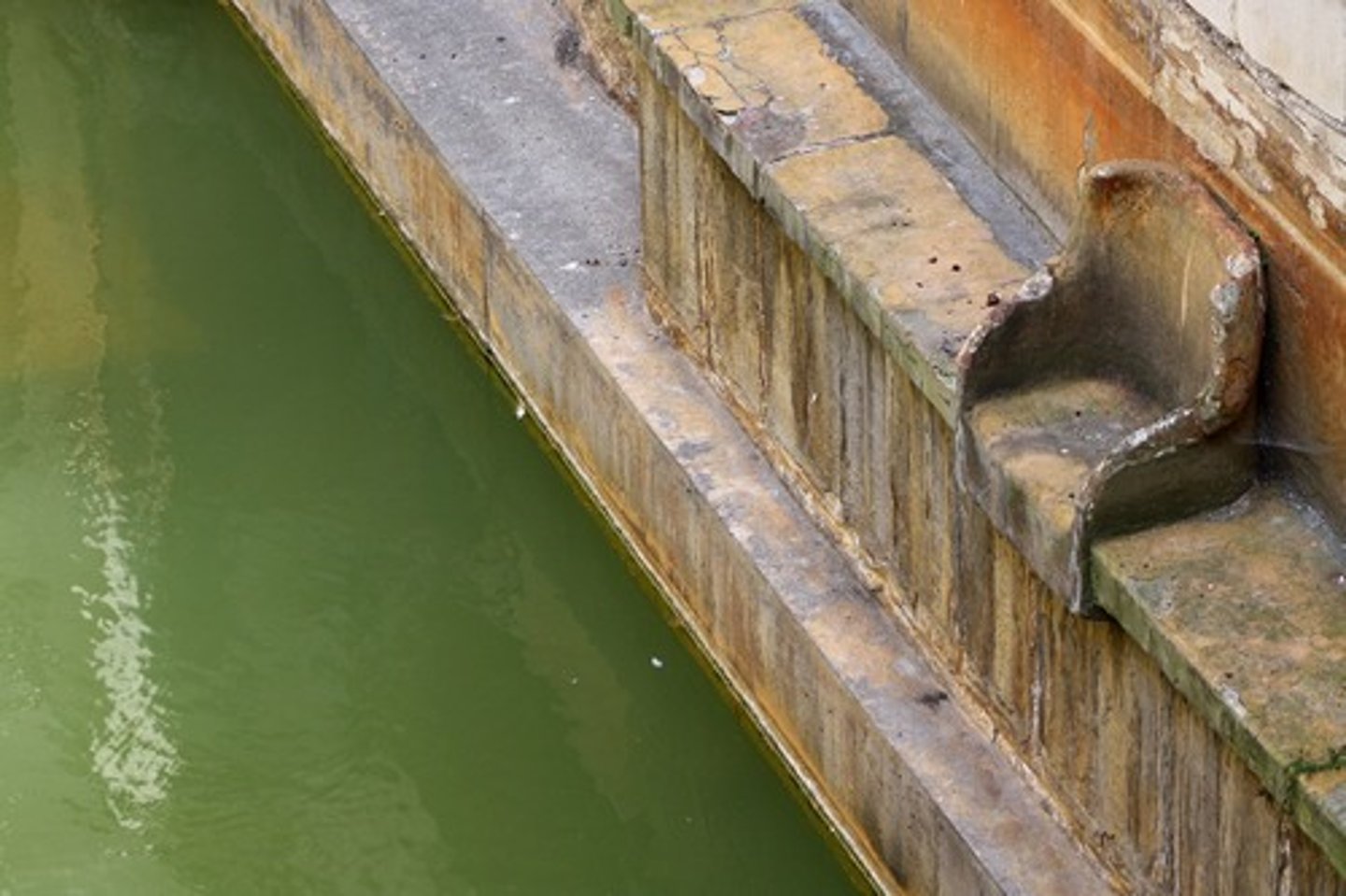
Thermae
baths. (these were large buildings where many could bathe at once. There was a caldarium (hot water room) a tepidarium (warm water room) and a frigidarium (cold water room). People might also rub olive oil on themselves and them scrape it off, which served as moisturizer and exfoliant.)

toga
worn only by male Roman citizens. (Togas did not look like what these fraternity clowns are wearing -- but while we're on the topic, where do we get the word fraternity?)

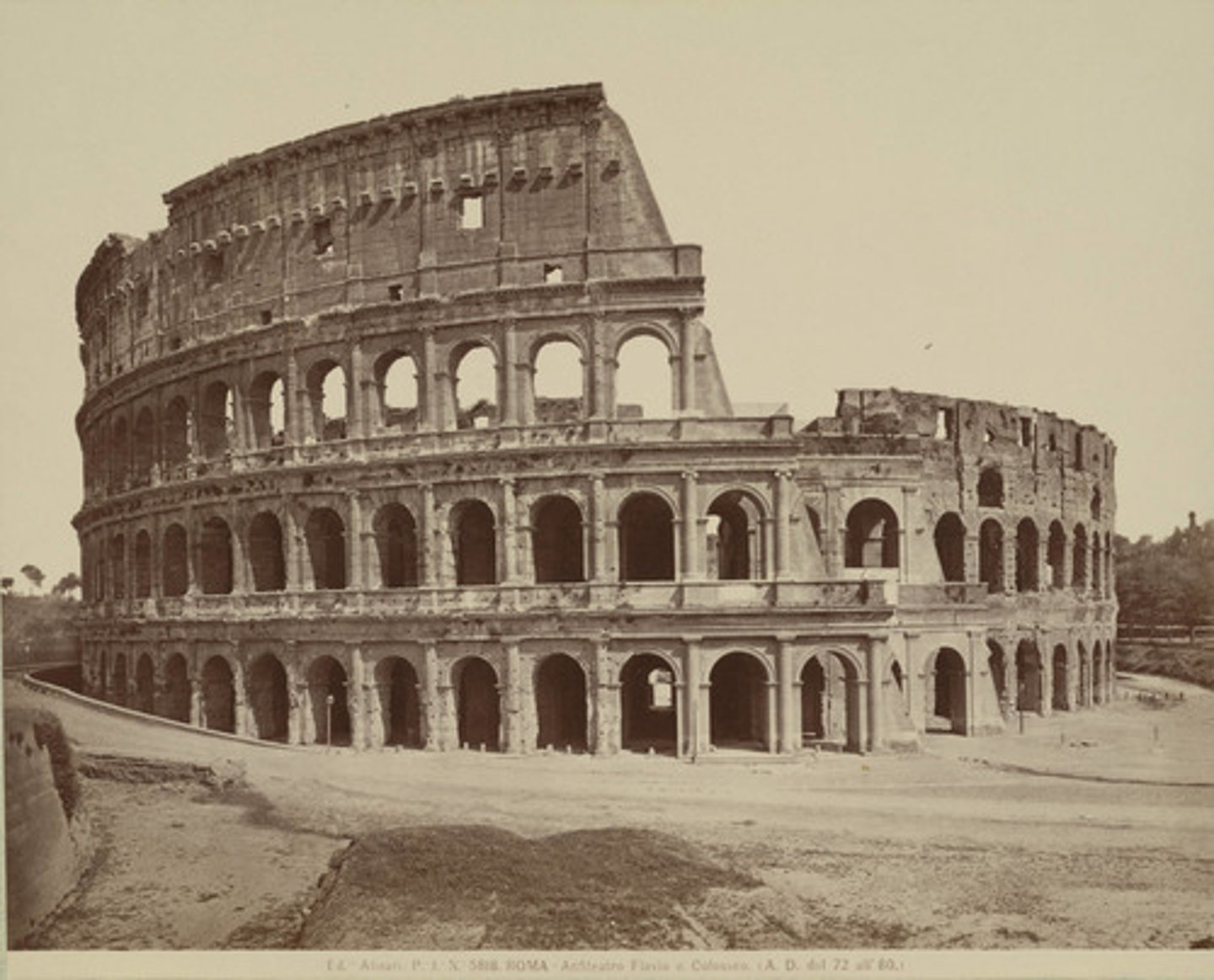
Colosseum
famous Roman amphitheater known for great size and clever design that allowed large numbers of spectators to quickly enter and exit the building without excessive congestion or delay

culina
Roman kitchen
basilica
Roman courthouse. Imagine lawyers eating basil?
cena
the third meal of the day; equivalent to modern dinner
ientaculum
the first meal of the day; equivalent to breakfast
stola
dress worn by a Roman woman (baby at heel is an optional accessory)

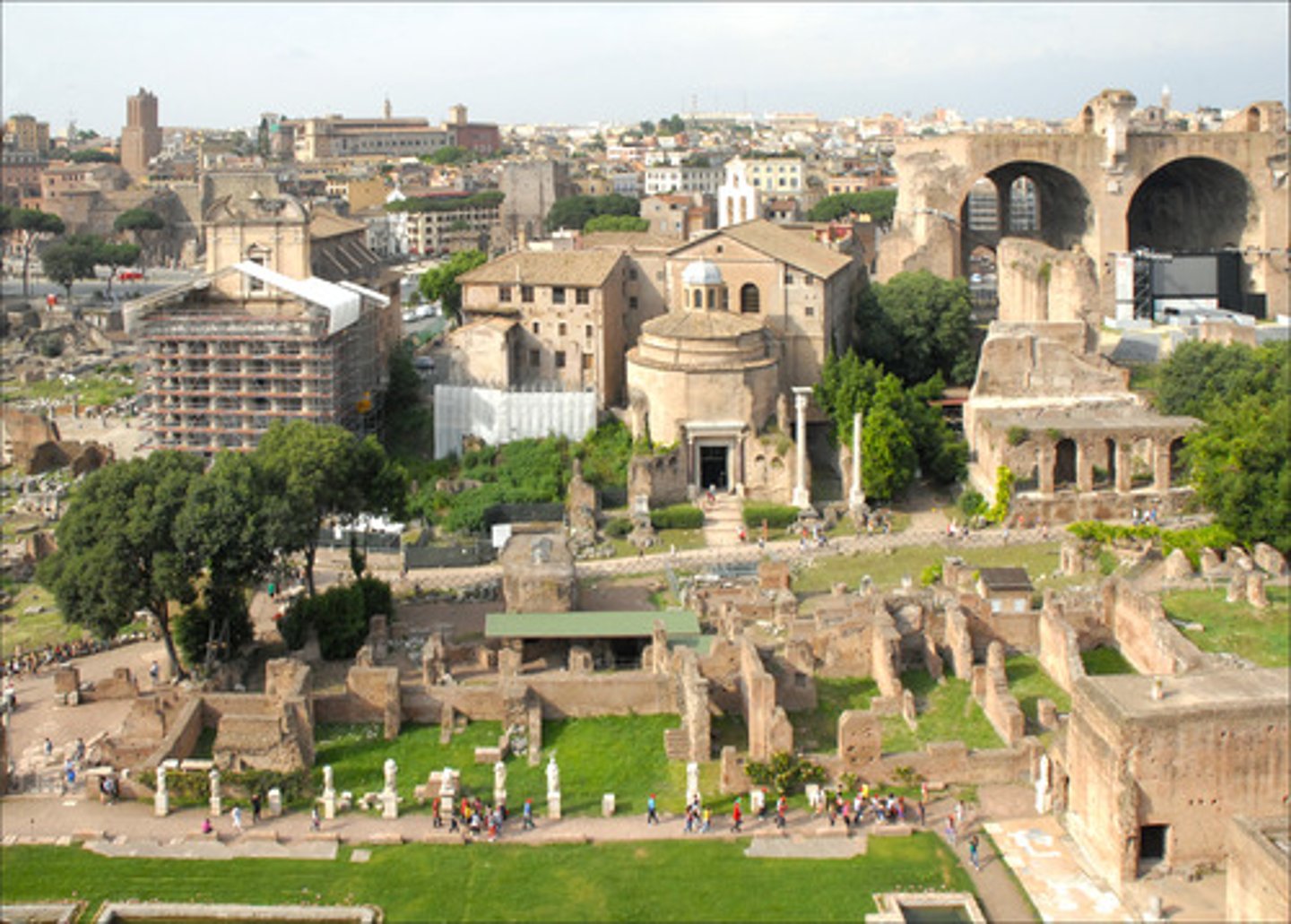
forum
main part of town where shops and government buildings were located

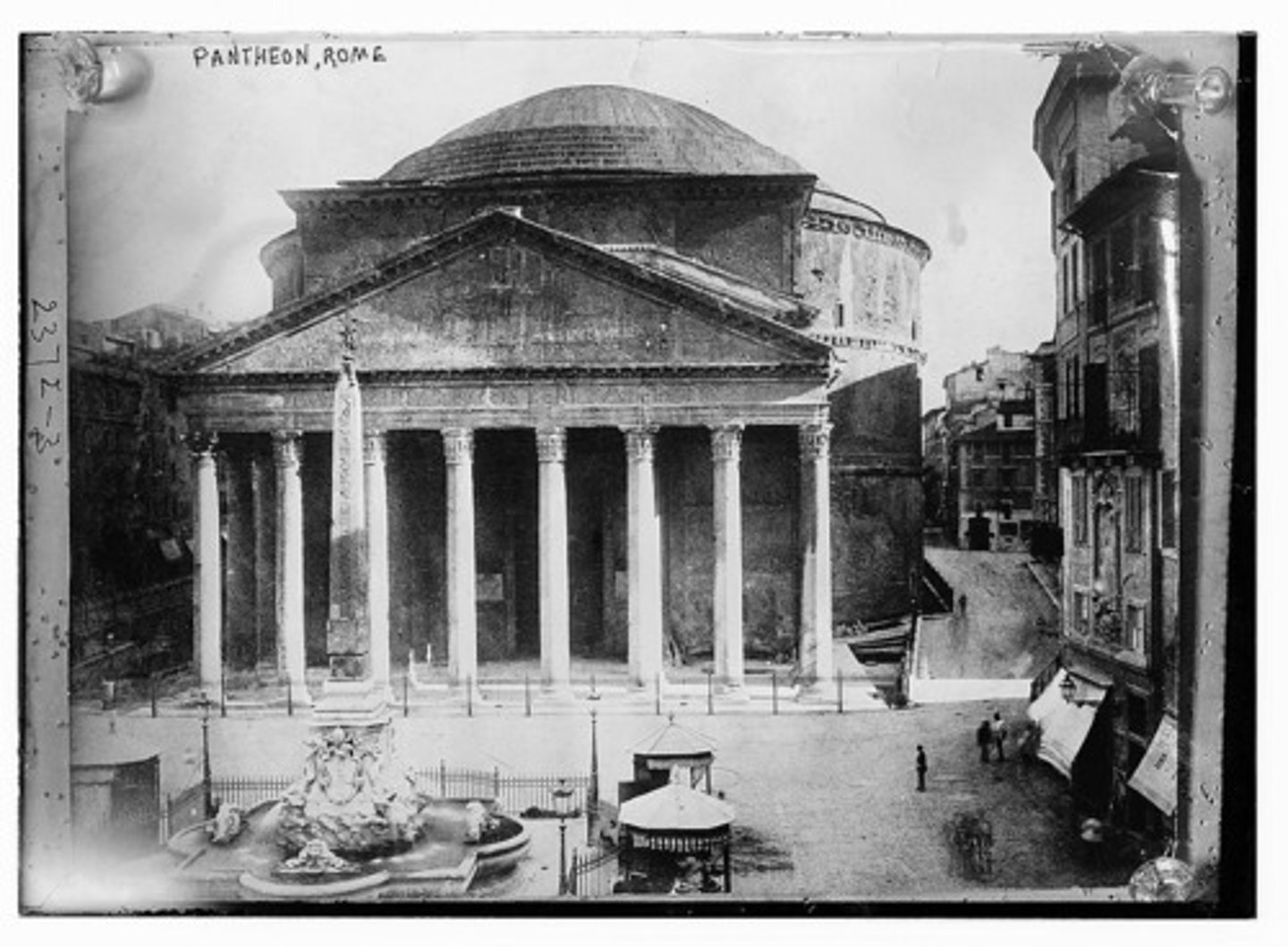
Pantheon
dome-shaped temple in Rome that houses statues to 12 major Roman gods/goddesses

prandium
second meal of the day; equivalent to lunch. (this gives us the fancy English word 'postprandial', meaning "after a meal".
templum
temple. where gods/goddesses were worshipped
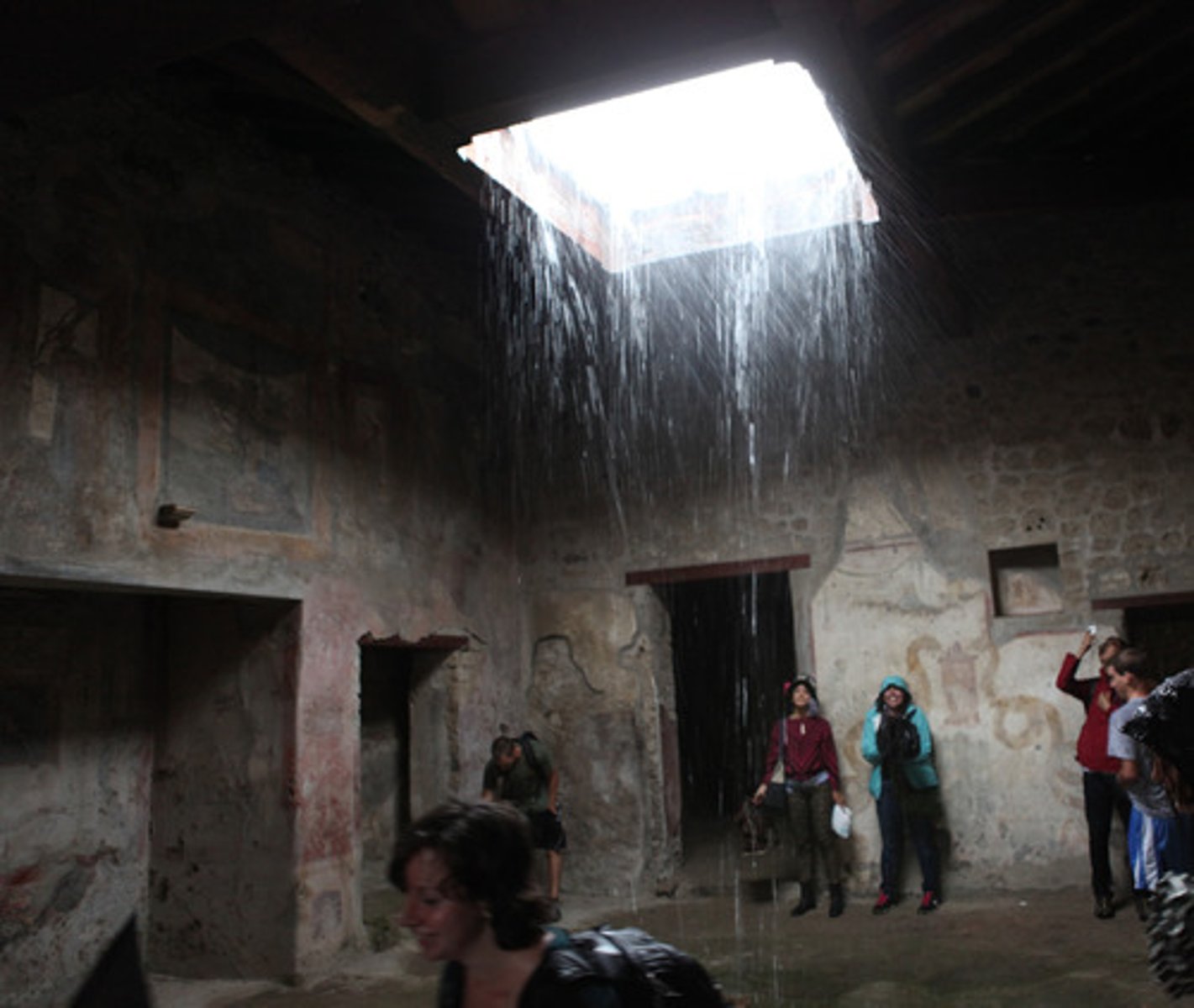
compluvium
opening in the roof of a Roman atrium that let in light, and also rainwater, which would then fall into the impluvium: a pool in the floor.

Acropolis
trick answer that's in Greece; not Rome! It's the 'high city' in Athens. From Greek: Acro (high: acrophobia) plus Polis (city: political; Neapolis=Naples)

Campus Martius
Latin for "the field of Mars". Public, open field where soldiers exercised and held military drills. elections were sometimes held there.
Circus Maximus
large oval course where chariots were raced. (Associated vocab: aurigae, carceres, metae, spina. a 'circus' is a place for horse-chariot racing.)

insulae
Roman apartment buildings (this also means 'islands' and is where we get vocab like 'peninsula' and 'insulate')
paedagogus
slave who escorted Roman boys to school. (This is where we get the fancy word 'pedagogy' -- which essentially means 'the art of teaching'.)
Palatine
centermost of the seven hills of Rome, and the hill on which legend says Romulus and Remus founded Rome.

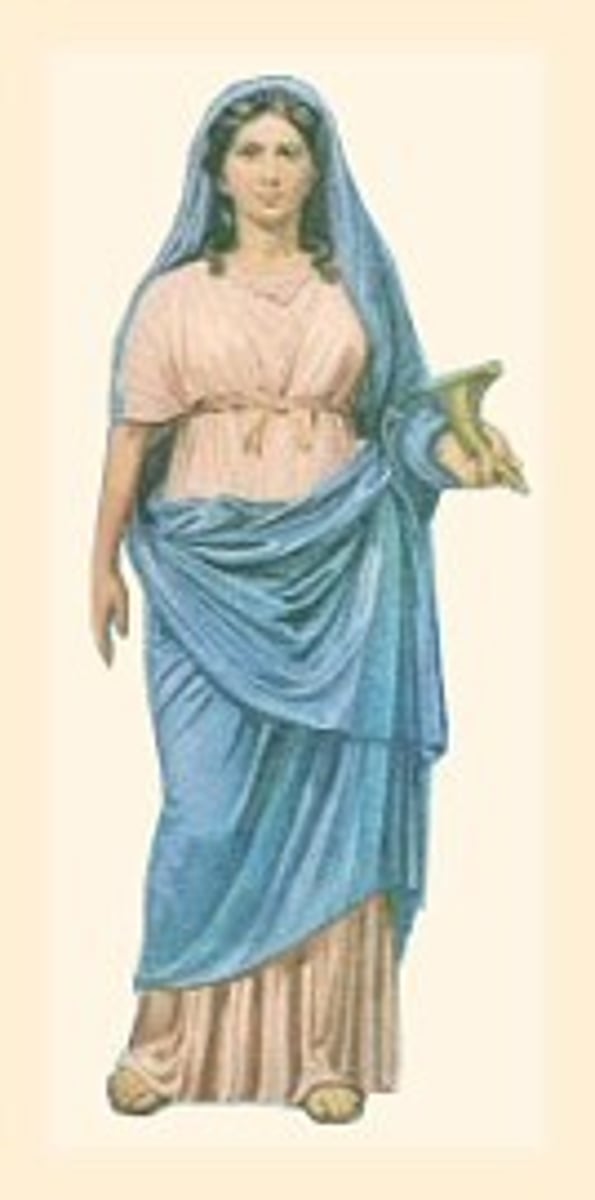
palla
woman's cloak, which she could wear as a shawl, or to cover her head.

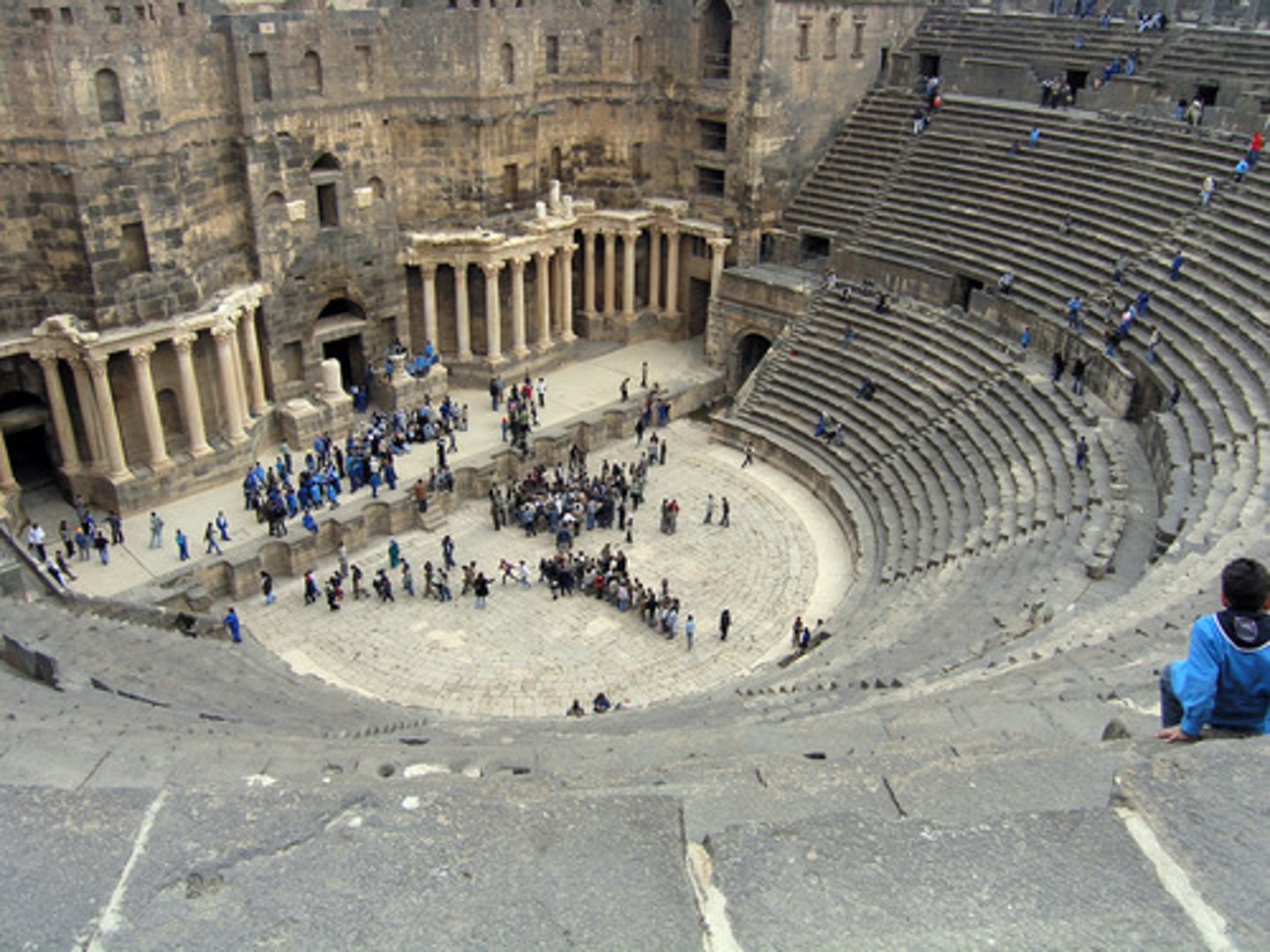
theaters
where actors put on shows. notice that a Roman theater was basically half of an amphitheater, even though very different things took place there.

tunica
a basic garment, worn by both men and women. A man might wear it under his toga, a woman under her palla. Even slaves wore a tunica.

cubiculum
bedroom
Lares and Penates
Roman household gods. Yes, individual household had their own little minor deities. Talk about polytheism!
aves
birds -- Romans watched them to tell the future and seek guidance from the gods
amphitheater
where gladiatorial contests were held. The colosseum (aka Flavian amphitheater) is an amphitheater, for example. these were like modern sports arenas, with seating on all sides.

Apenninus Mons.
The Appenine Mountains: mountains that run down the middle of Italy
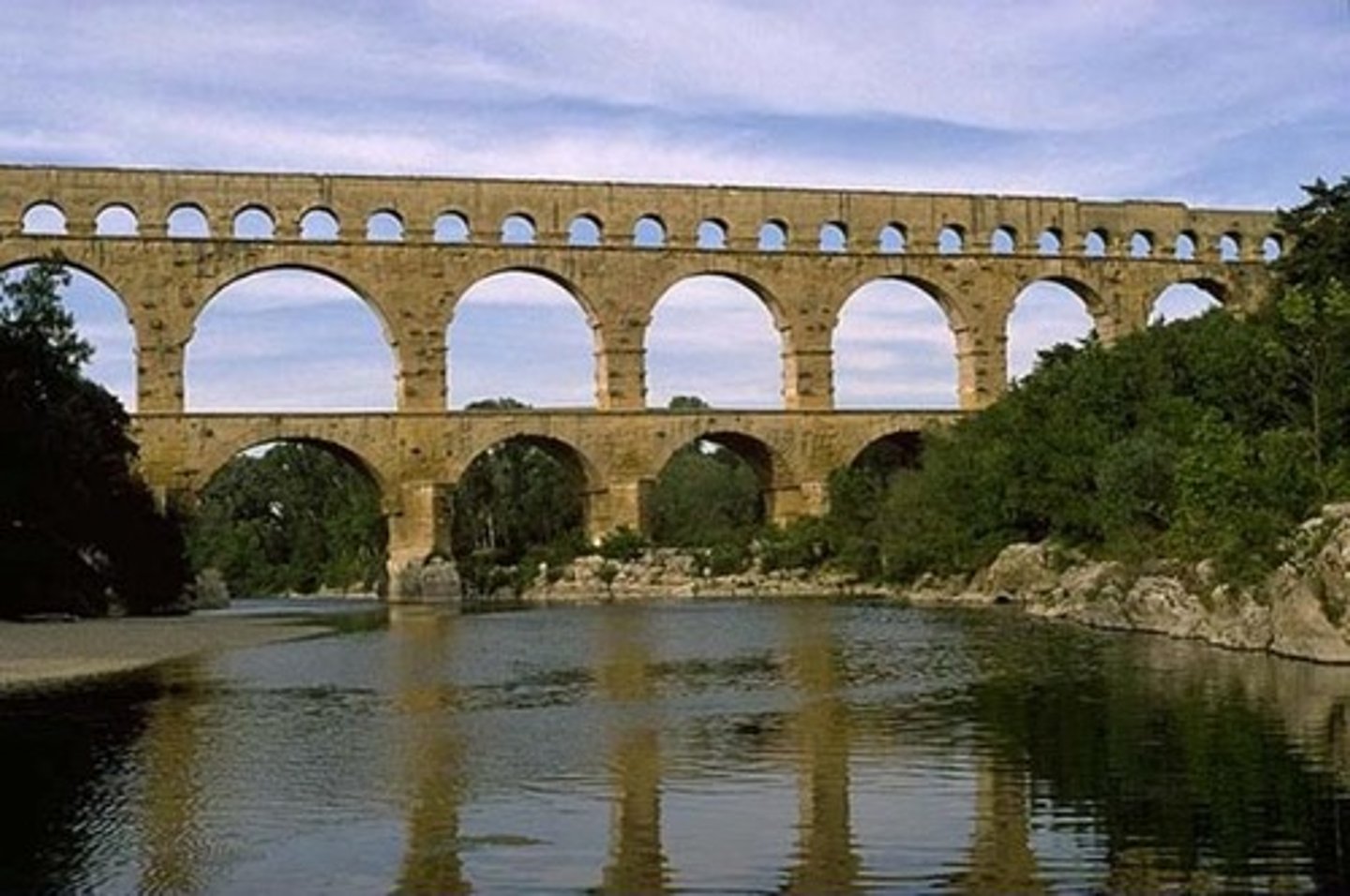
aqueduct
used for transporting water efficiently to Rome from far-off places

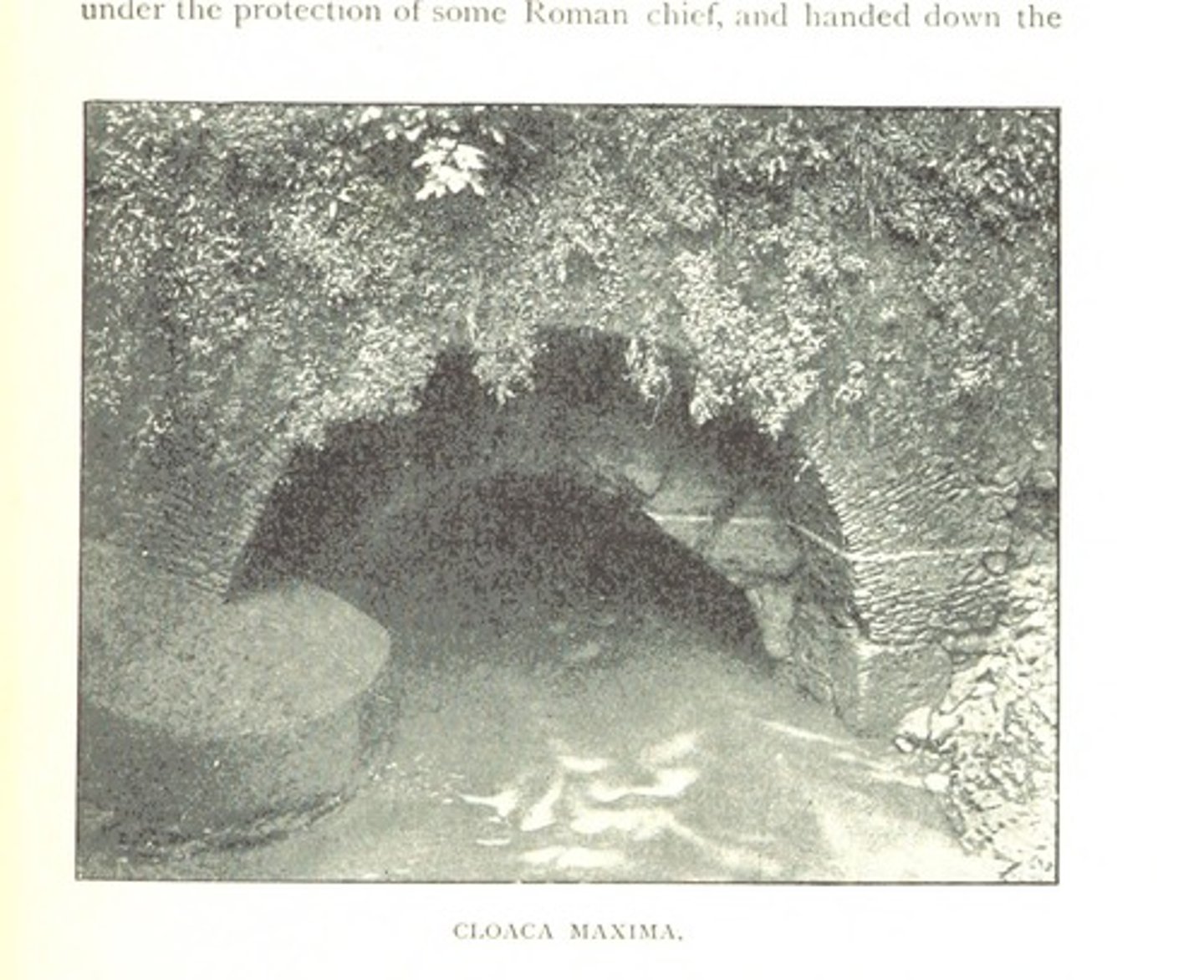
cloaca maxima
Roman sewer. A really massive, complex, underground sewer. Some of it still survives.
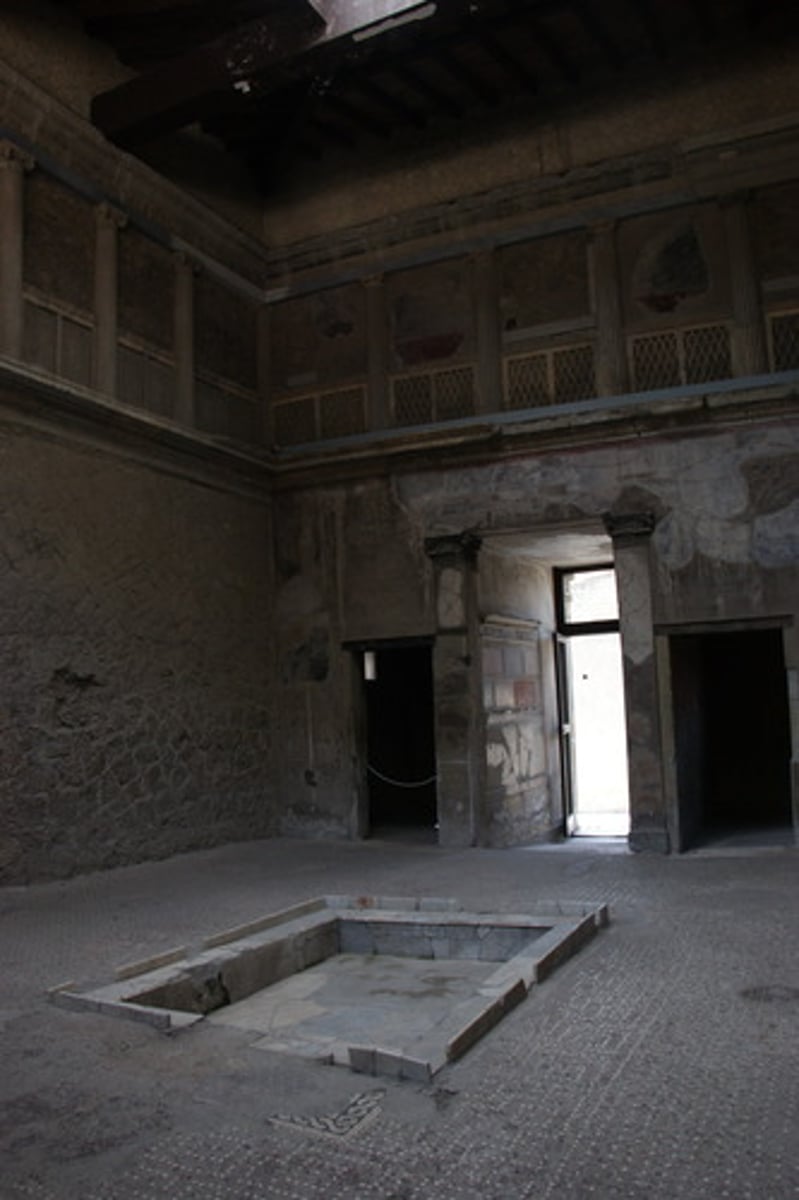
impluvium
pool that collected rainwater from an atrium's compluvium (which was a square rain-hole in the middle of the entrance hall's ceiling in a fancy Roman house).

domus
House. Another word for villa
Seven Hills
The seven hills of Rome are: Viminal Aventine Esquiline Palatine Caelian Quirinal Capitoline. "Women have asked my pal Caelius for his queer cap" is the goofy mnemonic for this one (in which 'queer' of course means 'unusual').
palaestra
exercise area in Roman baths
secunda mensa
followed cena (dinner); equivalent to dessert
tabella
writing tablet used by Roman schoolboys; also refers to a voting ballot
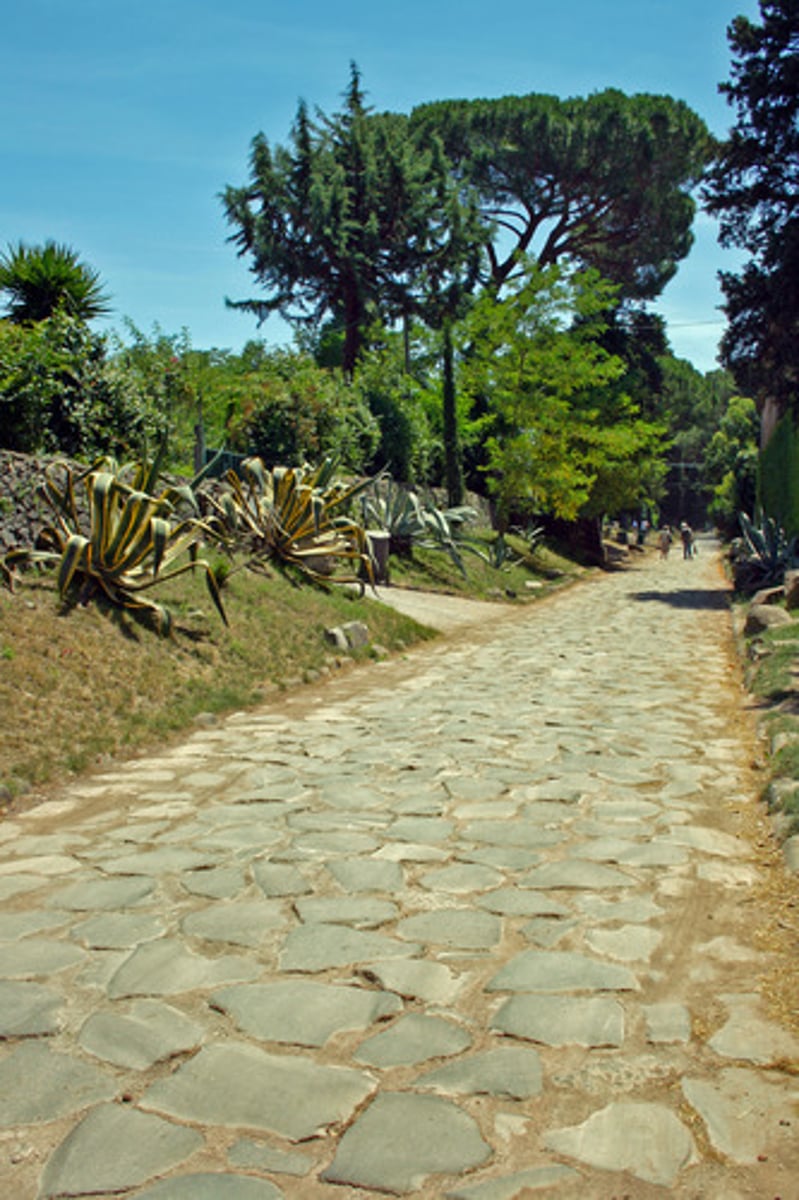
Via Appia
Via means 'road'. the most famous was the Via Appia, which leads from Rome to Brundisium, from where one could sail to Greece.

aedificia
buildings
school
ludus; or schola
taberna
a shop
aedile
official in charge of public buildings and religious festivals
apodyterium, caldarium, tepidarium, frigidarium, strigiles
all associated with Roman baths (aka thermae)
Capitoline
smallest; but most sacred of Rome's 7 hills. Holds lots of temples. What are the other hills?
toga praetexta
purple-striped toga that indicates political and social importance
Cincinnatus
Roman politician who became dictator with absolute power when Rome was having difficult times, and as soon as he had helped fix the problems he was humble enough to give up his power and return to being a simple citizen, plowing his own fields. What a guy! This happened around 450BC.
Hannibal
Carthaginian general who fought against Rome in the Punic Wars ("we battled Carthage in 3 wars from 264 to 146...")
Tarquinius Superbus
The last of the Etruscan Kings. "They say that Rome was born in 753 -- with Romulus then the Etruscan Kings as royalty. But then Lucretia was taken by that damned Etruscan lout: we threw them out -- and then SUPERBUS had no clout!"
Period of Kings
753bc till 509bc
(the names of the kings, which you don't need to memorize but should be familiar with, were:
Romulus 1st king
Numa Pompilius 2nd king
Tullus Hostilius 3rd king
Ancus Marcius 4th king
Tarquinius Priscus 5th king
Servius Tullius 6th king
Tarquinius Superbus 7th and last king)
Period of the Republic
509bc till 27bc (at which point Augustus becomes first emperor)
Period of Empire/Emperors
27bc till... 1453? you just need to know it starts in 27bc.
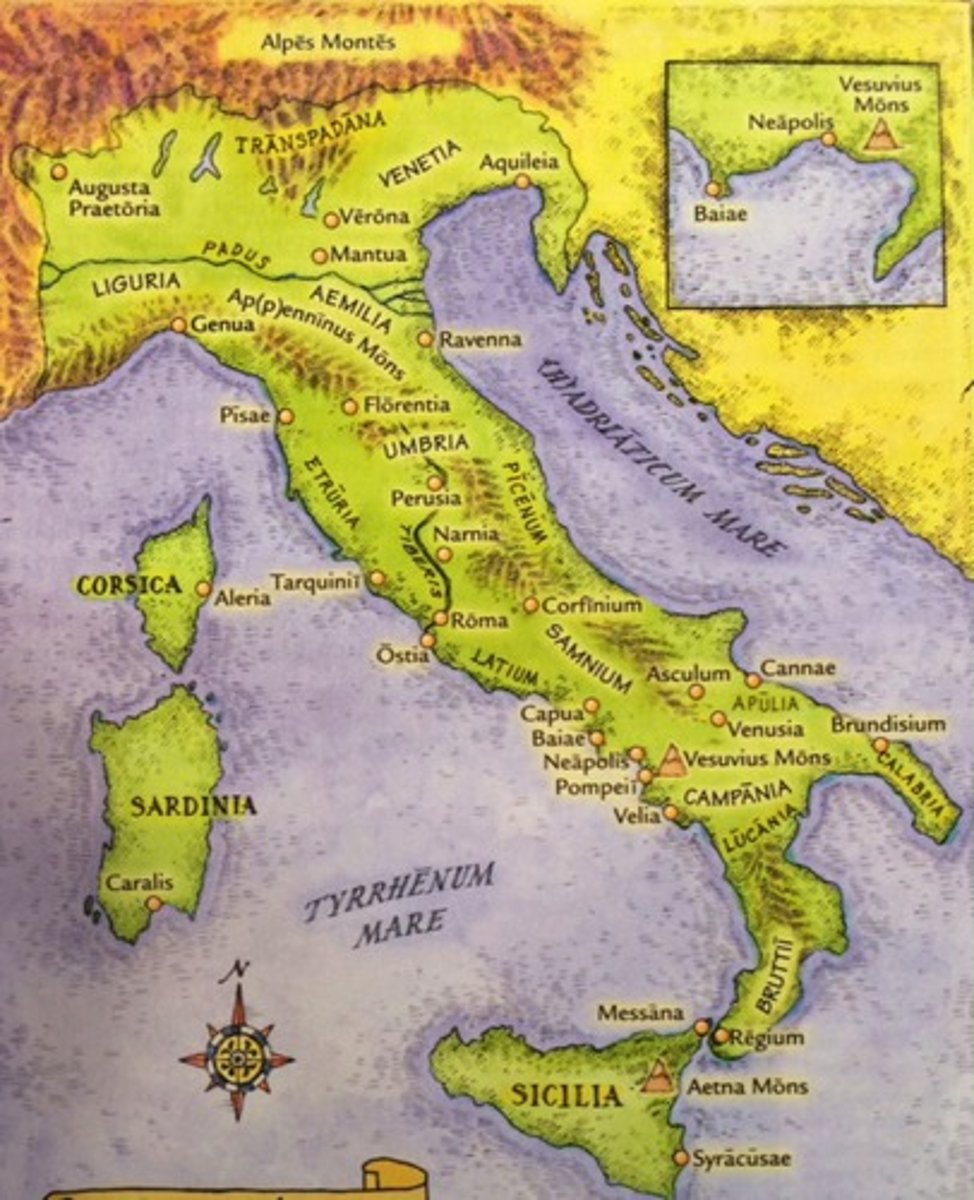
Ostia
The port city of Rome, on the seacoast, a few miles down the Tiber river from Rome. You can still visit it to this day.
Herculaneum
Covered in 79ad by the eruption of Mt. Vesuvius, just like Pompeii.
Carthage
City on the north coast of Africa, which was involved in the Punic Wars against Rome.
aestuosus a um
hot
caelum
sky
frigus frigoris n
cold (noun -- as in 'come in from the cold'
fulget
there is lightning
calidus
-a -um hot
frigidus a um
cold (adjective -- as in 'cold water')
fulmen fulminis n
lightning
imber
imbris m. rain
nix
nivis f. snow
nubilus
-a -um cloudy
pluit
pluere pluit it is raining
lucet
it is shining (as in 'the sun ...')
ningit
it is snowing
nubes
cloud
pluvia
rain (as in the names of certain parts of the Roman atrium, right?)
sol
sun
tonat
'it is thundering'
hiems hiemis f
winter
aestas aestatis f
summer
tepidus
-a -um warmish
ventus
wind
autumnus
autumn
ver veris n
spring
quota hora est?
what time is it?
Horatius Cocles
one-eyed Roman superstar who heroically defended the bridge so opposing forces could not make it across the Tiber and into Rome, very early Republic
morituri te salutamus
"we, about to die, salute you!" gladiators would apparently say this to the emperor. I would imagine there were a few who muttered something slightly different, right?
Mucius Scaevola
Essentially, a young Roman who burned off his right hand to show his enemy how tough he was -- thereby earning himself the nickname Scaevola (essentially meaning 'Lefty'). This was around the year 508 (ie, very early Republic).
With the help of the wingéd horse Pegasus, ______________ was able to kill the monster ______________
Bellerophon killed the Chimera, with the help of what wingéd horse?
What was the first triumvirate?
Caesar, Pompey and Crassus (an alliance formed in 60 bc)

What was the second triumvirate?
Octavian, Lepidus and Marc Anthony (an alliance formed in 43 bc)

When did Caesar invade Gaul
58 bc
what was the Campus Martius used for?
a training ground for Roman soldiers, and for certain elections.
Actium?
"at Actium, in 31, the big O beat Anthony -- and then Octavian's named Augustus in 27 bc!"
Philippi?
"at Philippi in 44 bc Brutus and Cassius take their lives" after Octavian and Marc Anthony humble them.
Scipio Africanus...
defeated Hannibal in the Punic Wars
When was the Roman calendar revised?
several times, but most notably around the time of Augustus.
what is a 'sine qua non'?
something necessary or essential ("without which, no")
Constantine
This Emperor adopted Christianity as official religion, moved head of empire to Constantinople, all around the year 300AD.

L Junius Brutus
helped expel the Tarquin Kings, ushering in the period of the Republic, around 509. nb: this is NOT the same Brutus from the time of Caesar (et TWO Bruti? ha!), but is meant to be an ancestor of his: both of them supposedly "got rid of tyrants".
Where are the Atlas mountains?
North Africa
Spartacus
an escaped gladiator who lead an army of slaves in revolt against the Romans, around 73 bc.

in absentia
"although not present" or "while absent"
pm (post meridiem)
"in the afternoon"
quid
"what"
etc
"et cetera" = "and other things"
S.P.Q.R
Senatus Populusque Romanus = the Senate and the People of Rome. These initials represented the Roman political leadership, especially during the Republic.
