urogenital
1/248
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
249 Terms
3 types of imaging to eval kidneys
survey rads
EU
compression studies
Which view best separates the kidneys
right lateral
which view is best for eval of SIZE and shape of kidneys
VD
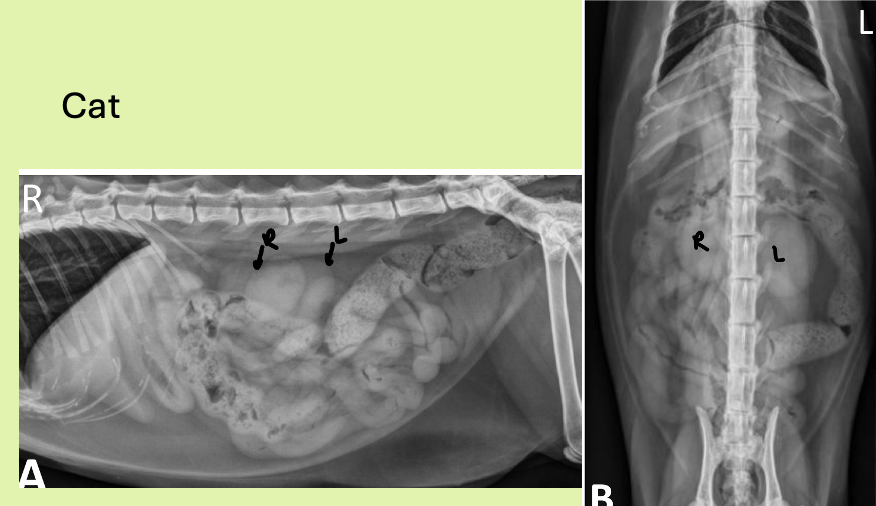
where are right and left kidney located
R kidney - 13th rib where cr. pole touches caudate lobe of liver
L kidney - more cd. than right kidney. Just behind gastric fundus, cd/med to splenic head
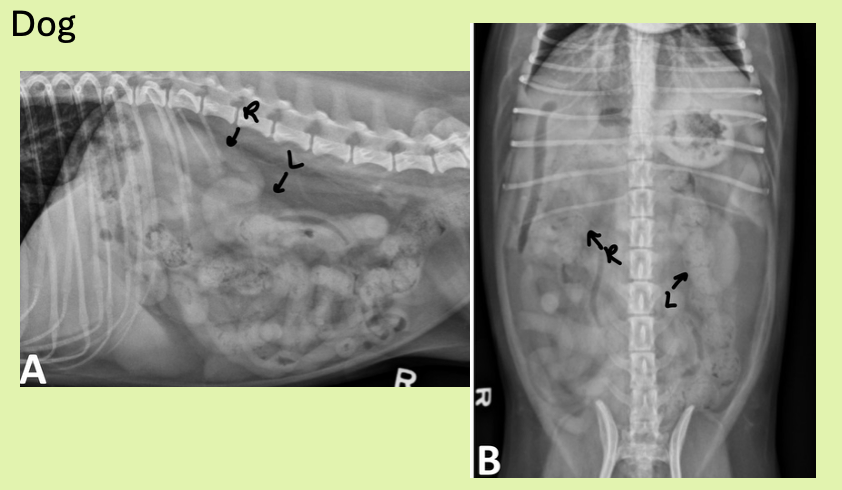
how are cat kidneys located differently from dog
more cd (same thing with right kidney more cr.)
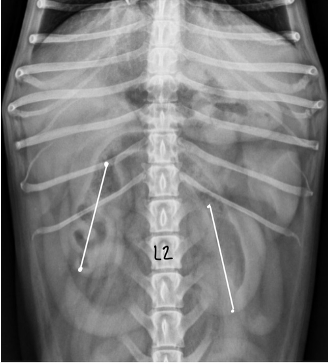
dog kidney size vs cat kidney size
dog - 2.5-3.5 x length L2
cat - 1.9-3.2 x length L2
shape of kidneys dog vs cat
dog - bean
cat - oval
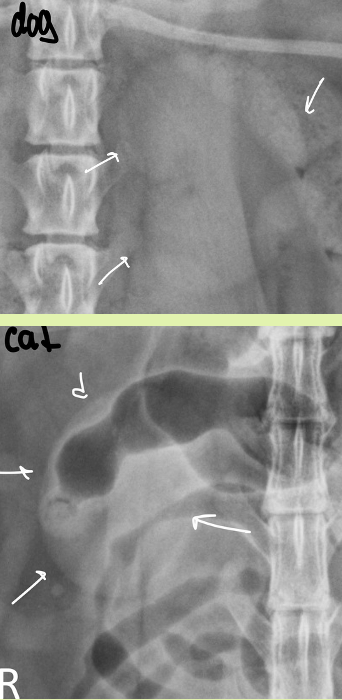
what might you see in the renal pelvis region of cat that is different from dog kidneys
peripelvic fat

5 reasons why we see less than 2 kidneys (don’t think dz)
pyelonephrectomy
lack of RP fat
summate with RP fluid
superimpose with GI and other viscera
poor exposure technique
3 reasons why we see more than 2 kidneys
congenital anomaly
artifact/interp error
renal transplant
4 reasons we see abnormal position of kidneys
incidental
lots of RP fat, distended stomach, postural changes
ectopic kidneys
masses (liver, spleen, adrenal, ovaries)
6 reasons for generalized increase in kidney size
comp hypertrophy
hydronephrosis - can be severe
acute inflam
toxic renal
neoplasia
PSS
3 reasons for focal multifocal increase of kidney size
neoplasia
large renal cysts/PCRD
FIP
5 reasons for decreased kidney size
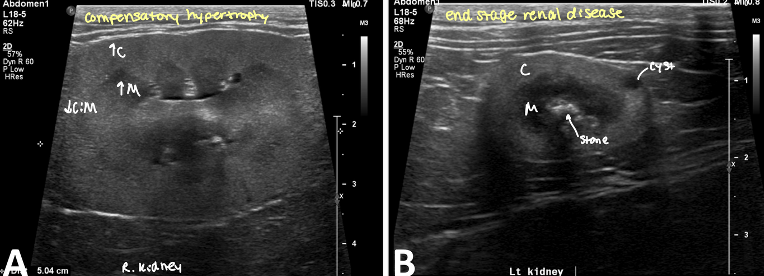
chronic inflam
end stage renal disease
infarcts
familial dysplasia, congenital disease
renal hypoplasia
5 focal irregular shape changes kidneys
infarcts
neoplasia
end stage renal or chronic inflam
renal cysts/PCRD
FIP
5 reasons for weird margination around kidneys
acute inflam
toxicity
acute obstruct
trauma
aggressive neoplasia
3 causes of focal increased opacity of kidneys
renal calculi
dystrophic calcification
mineralized cyst, calcified tumors
2 reasons for diffuse increased opacity of kidneys
IV contrast administration
diffuse calcification (nephrocalcinosis)
2 reasons for decreased renal opacity
vesiculoreteral ureflux
infection with gas bacteria
4 indications of EU
incontinence
indistinct RP space
renal/ureteral calculi
cannot find kidneys on rads
4 contraindications for EU
clinical dehydration
sensitive to contrast media
multiple myeloma
combined renal and hepatic failure
6 reasons for Diffuse increase in cortical echogenicity kidneys
Normal in cats – fat deposition in the tubules
inflam disease - glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis
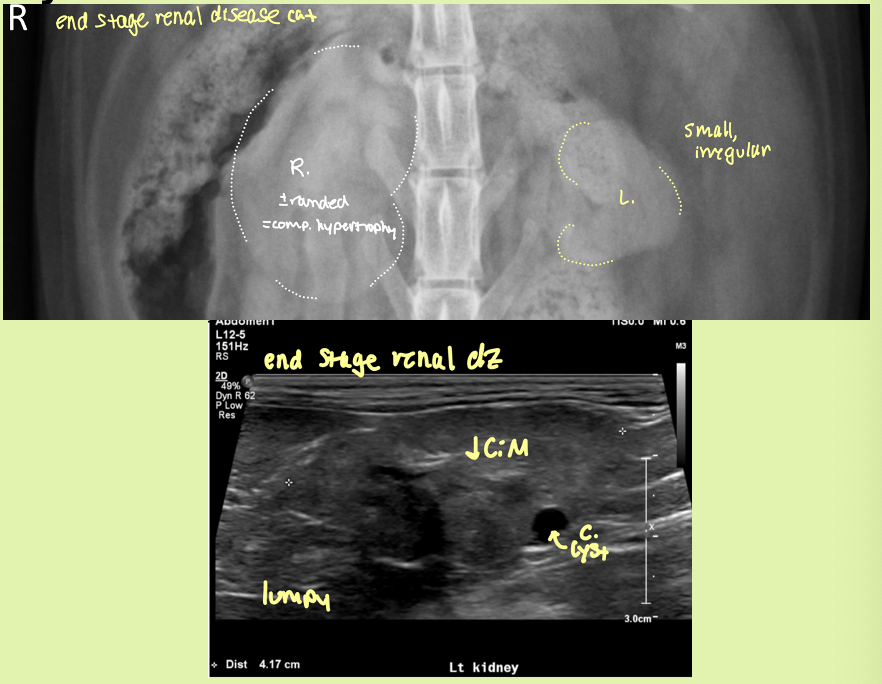
End-stage renal disease – kidneys also small and irregular
Toxic - ethylene glycol tox
Renal dysplasia – kidneys also small and irregular
Neoplasia
what are the 3 ways to describe CM junction distinction
retained - both equally bright
enhanced - medulla normal, cortex bright
decreased -medulla also bright
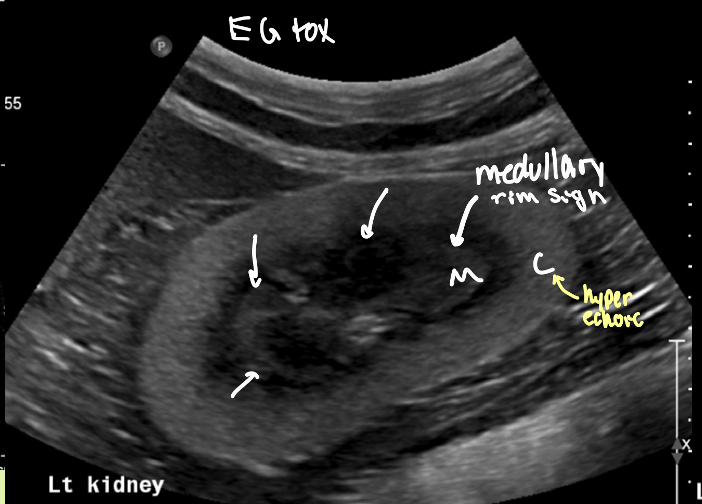
is the medullary rim sign something to be worried about
no! can see in both normal small dogs and diseased kidneys
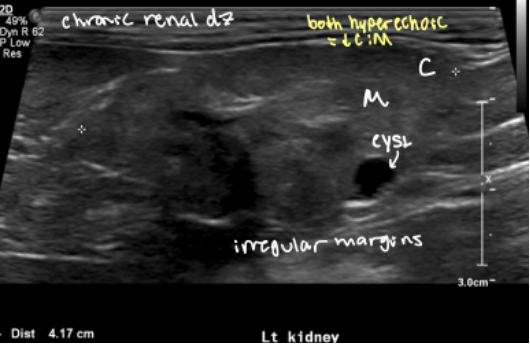
2 reasons for decreased CM junction distinction
chronic renal disease
renal dysplasia
3 things that are abnormal and anechoic in kidneys
cysts
abscess
neoplasia
4 things abnormal and hypo/hyperechoic in kidney
neoplasia
infarct
abscess, granuloma
hematoma
2 reasons you might see mineralization in kidneys
dystrophic
calculi
what are 2 reasons for mild and severe distension of renal pelvis
mild - full bladder, diuresis/PU
severe - pyelonephritis, obstruction
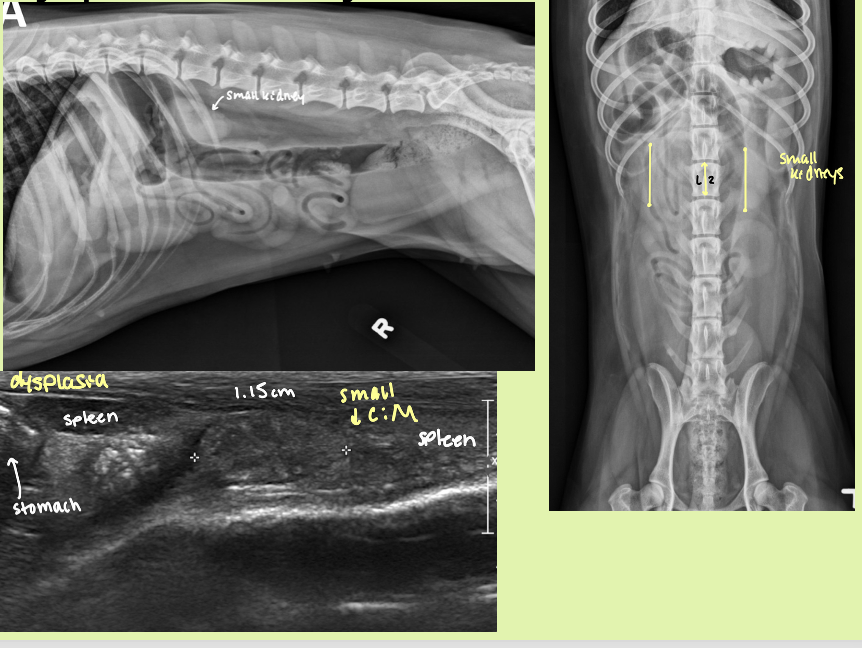
YOUNG animal with renal disease that results in 2 small kidneys
hypoplastic/dysplastic kidneys
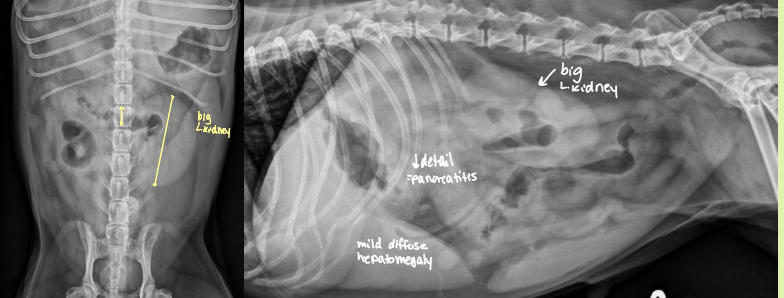
condition where one kidney becomes enlarged to compensate for a down kidney
compensatory hypertrophy
kidney preserved architecture
decreased CM distinction
when in the disease process can you see pyelonephritis on rads
chronic or healed
2 causes of pyelonephritis
hematogenous or ascending infxn
acute vs chronic pyelonephritis rad and ultrasound findings
acute
slight enlargement of kidneys ± RP effusion
smooth contours and diffusely hyperechoic
↓CM distinction
pus/echogenic content in pelvis
pyelectasia
Chronic
small to normal sized kidneys with irregular shape
pelvis distorted
↓CM distinction
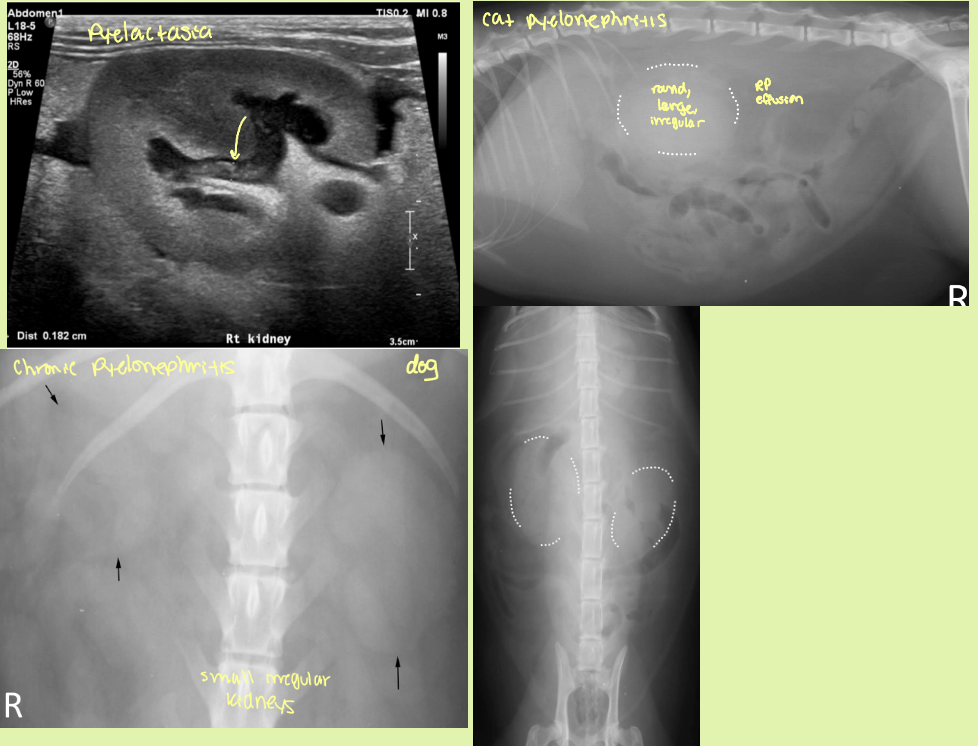
small, irregularly lumpy, bumpy shaped kidneys, ↓CM distinction ± mineralization
end stage kidneys
hydronephrosis is caused by
partial or complete obstruction of urine outflow in renal collecting system or ureters
4 causes of congenital vs acquired hydronephrosis
Congenital
kinking or partial obstruction of ureters 2° to kidney or ureteral malposition
Stenosis
compression from ureterocele
associated with ectopic ureters or other congenital malformations without true obstruction
Acquired
Obstruction from urinary calculi, neoplastic or inflam masses
accidental ligation
ureteral stricture
parasites (dioctophyma renale)
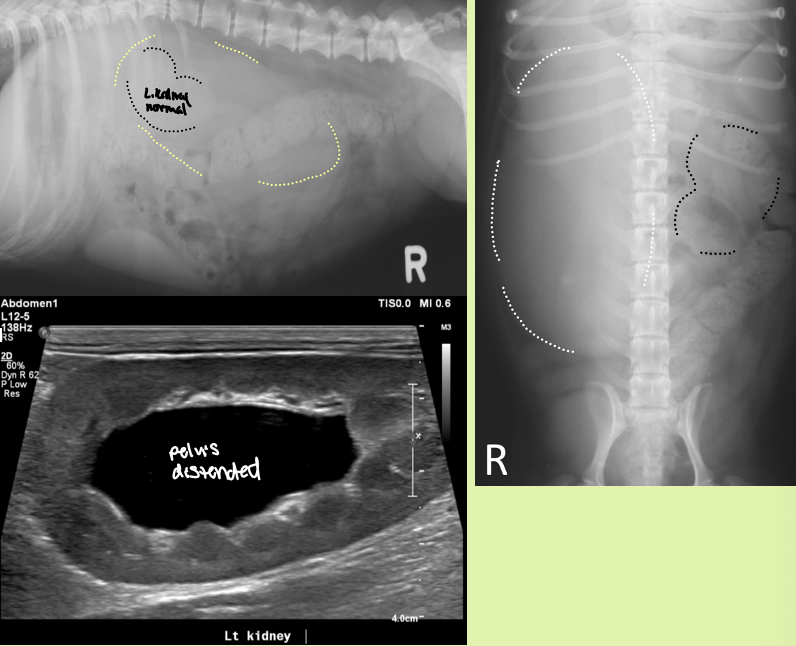
enlarged smooth kidneys with distended pelvis ± distended ureters
hydronephrosis
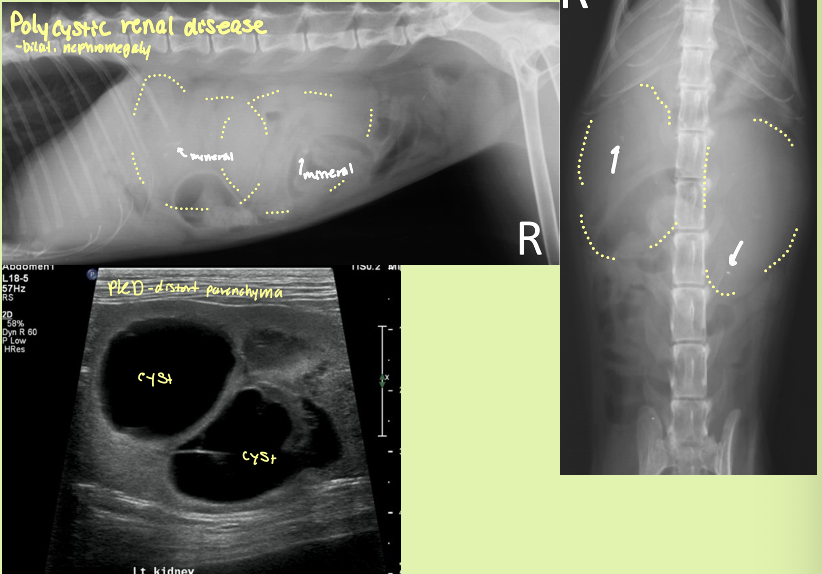
polycystic renal disease (PCRD) is heritable in what species and breed
persian cats - autosomal dominant
what organ likes to accumulate cysts with PCRD
kidneys and liver
what is the sequela of severe PCRD
chronic renal failure - parenchyma distorted and non-fxn
bilateral renomegaly with irregular margins with many cysts in the cortex that are anechoic with distal acoustic enhancement
PCRD
What is dog and cat #1 kidney neoplasia
dog = carcinoma
cat = LSA
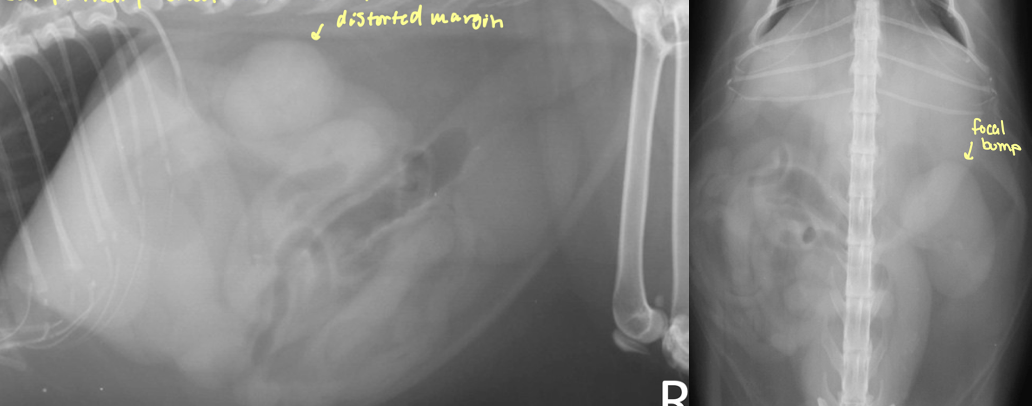
cat renal carcinoma
focal enlargement
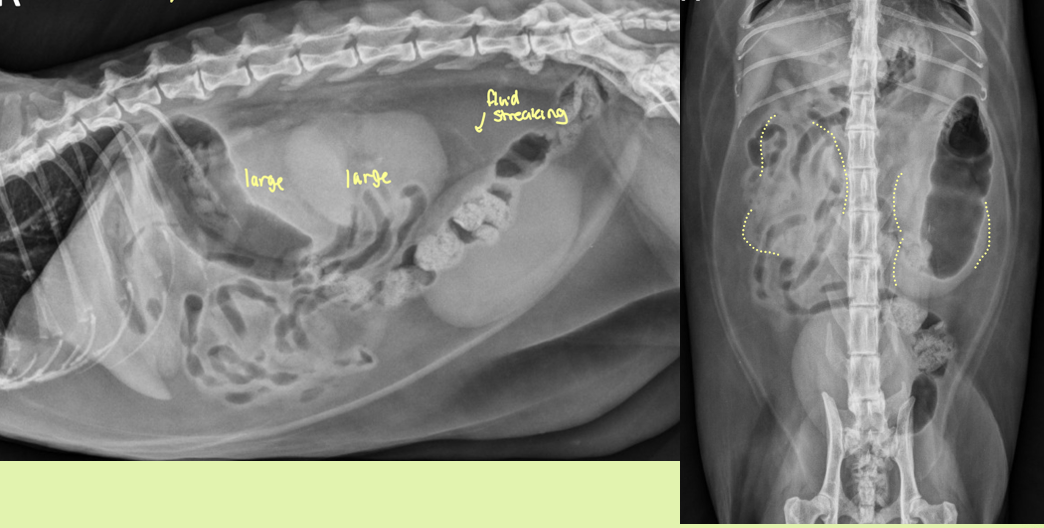
cat renal lymphoma
generalized enlargement
which is more characteristic of lymphoma vs mets
lymphoma = left
mets = right
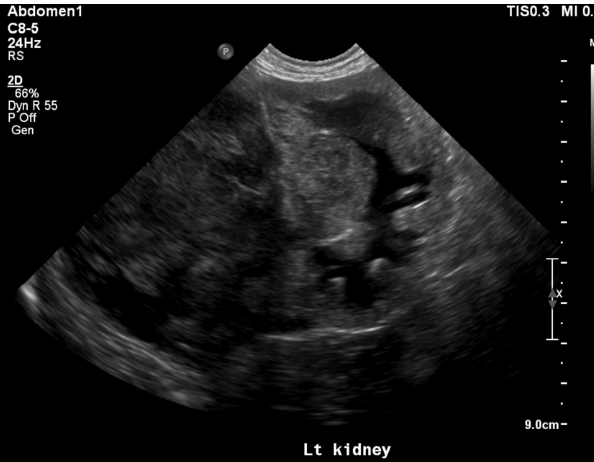
what is going on with this kidney
mass - neoplasia
focal/multifocal nodules with renal enlargement
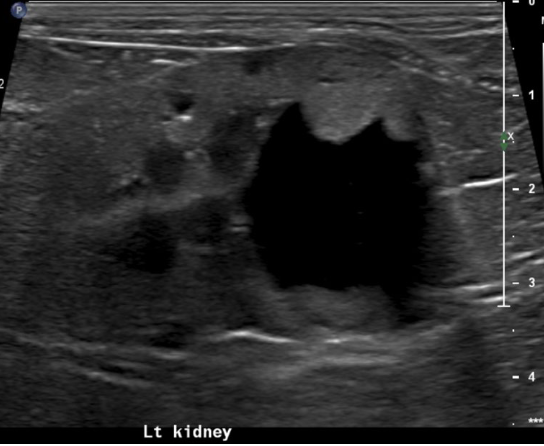
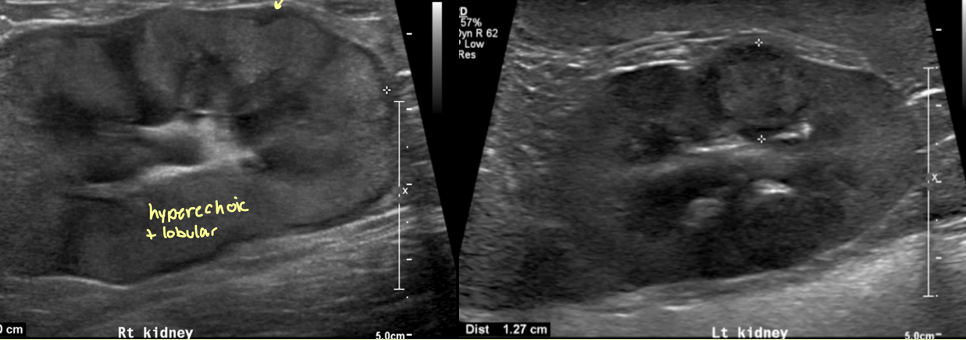
what is going on with this kidney
mass - cystic carcinoma
hypo/iso/hyperechoic ill defined mass ± cysts and mineralization
what types of stones are typically nephroliths
calcium oxalate
struvite
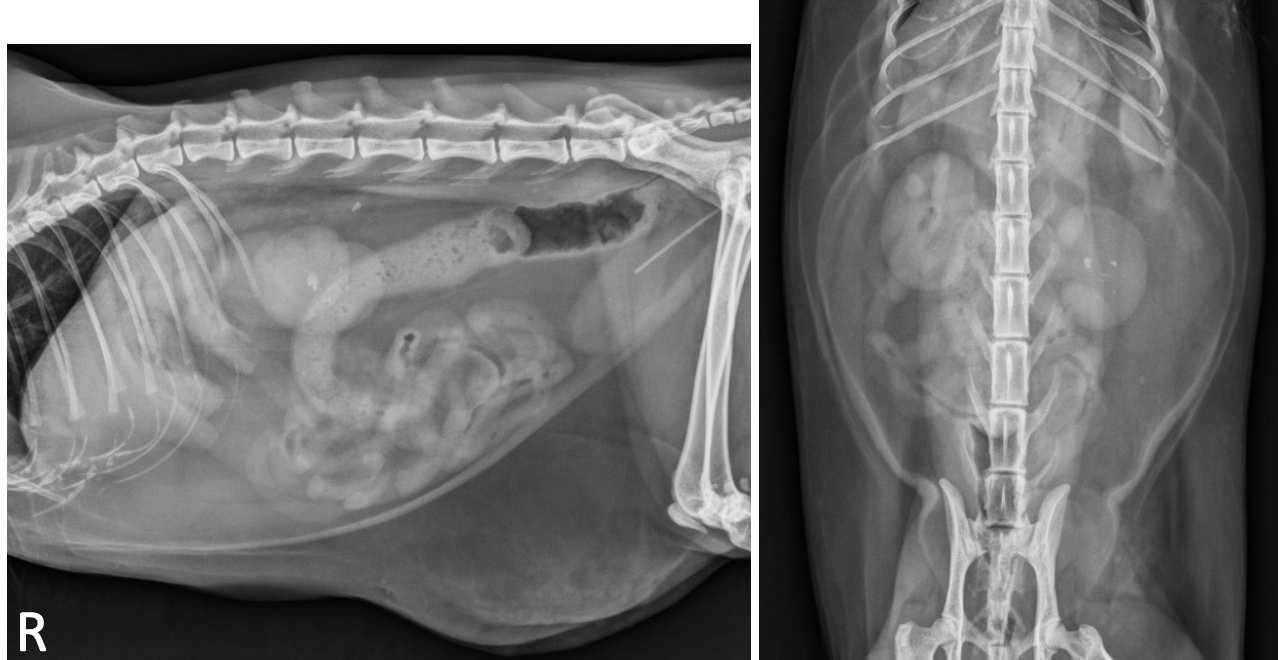
nephrolith and ureterolith
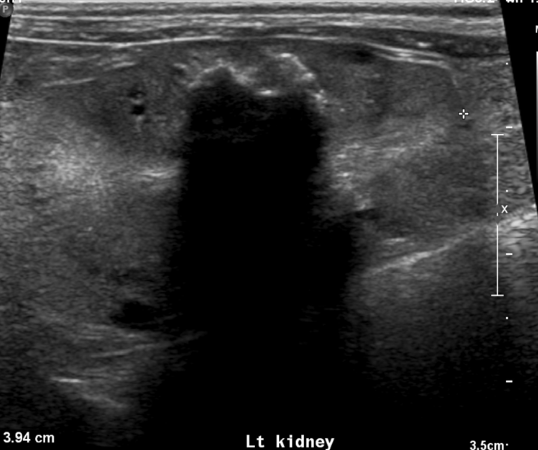
what is creating this shadow
nephrolith
on lateral radiographs you find these mineral opacities in the kidneys and ureters. You probe an ultrasound over it and find a mineral opacity that has a distal acoustic shadow
Nephrolith
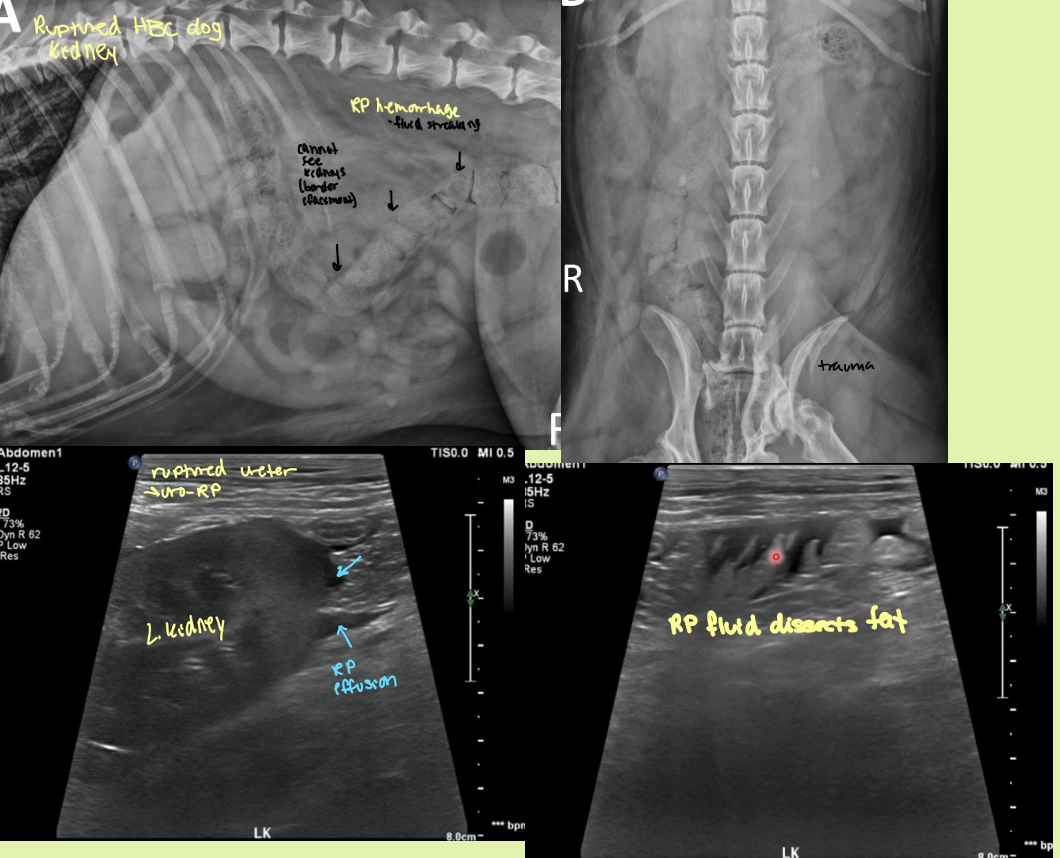
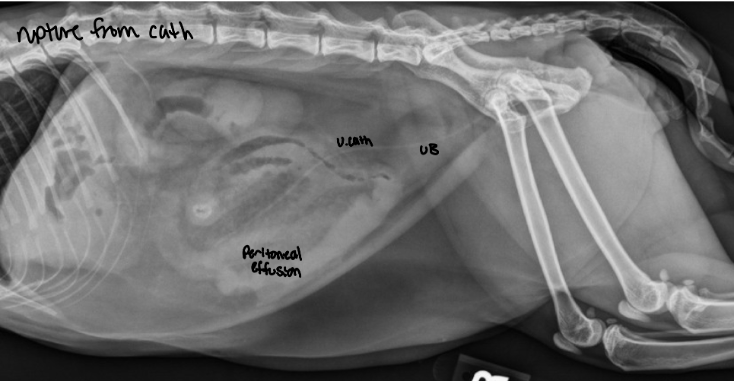
what is the best mode of imaging for a ruptured kidney
EU
fluid opacity in the RP region that makes it hard to make out the kidneys. EU has leakage of contrast into RP space and a hematoma is seen on ultrasound
ruptured kidney
normal location of the ureters
arise from renal pelvis —> dorsal to mid point to trigon level of bladder as enter peritoneal cavity —> turn ventrally and empty bladder at trigon
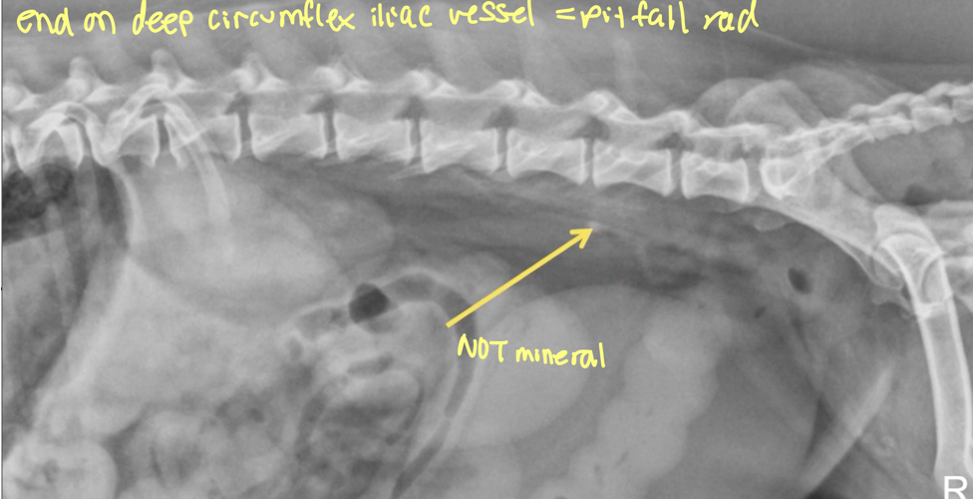
what is a structure often confused for ureteral mineral (PITFALL)
end on deep circumflex iliac vessel
ureters are not normally visible on rads, what do you need to see ureters
EU/IVP
rad and ultrasound findings of ureteroliths
Rad findings - Can be seen
Ultrasound findings
hyperechoic structures with distal acoustic shadowing
Variable size
If obstruction—> hydronephrosis and hydroureter prox. and a normal ureter distally
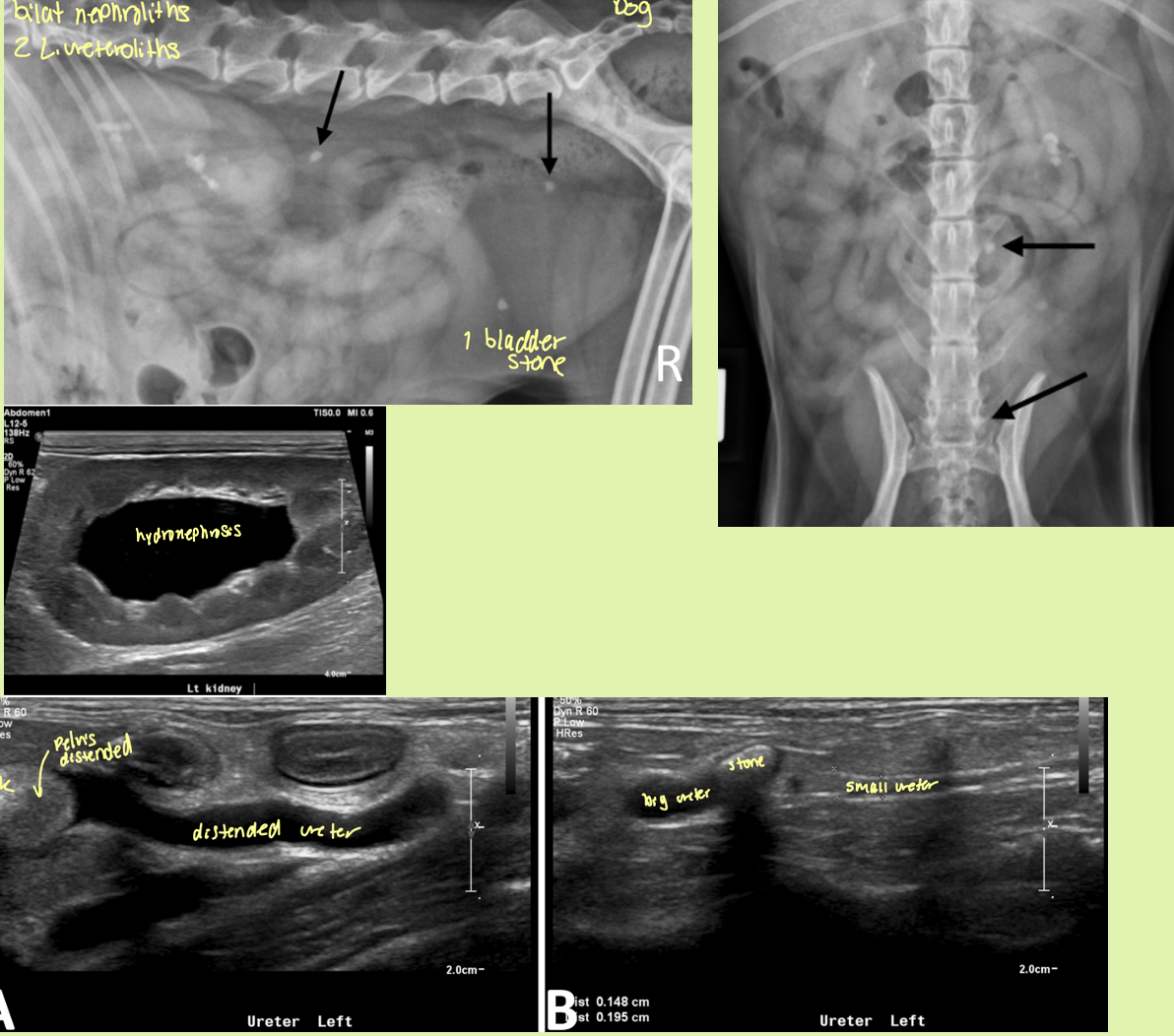
degree of distension of renal pelvis and ureter depend on what 2 factors
degree of severity
chronicity of obstruction
preferred method to ID ureteral rupture
EU/IVP
dog with trauma hx has decreased RP detail and leakage of contrast material into both the peritoneal and RP space
ruptured ureter
avulsion — peritoneal space
rupture — RP space
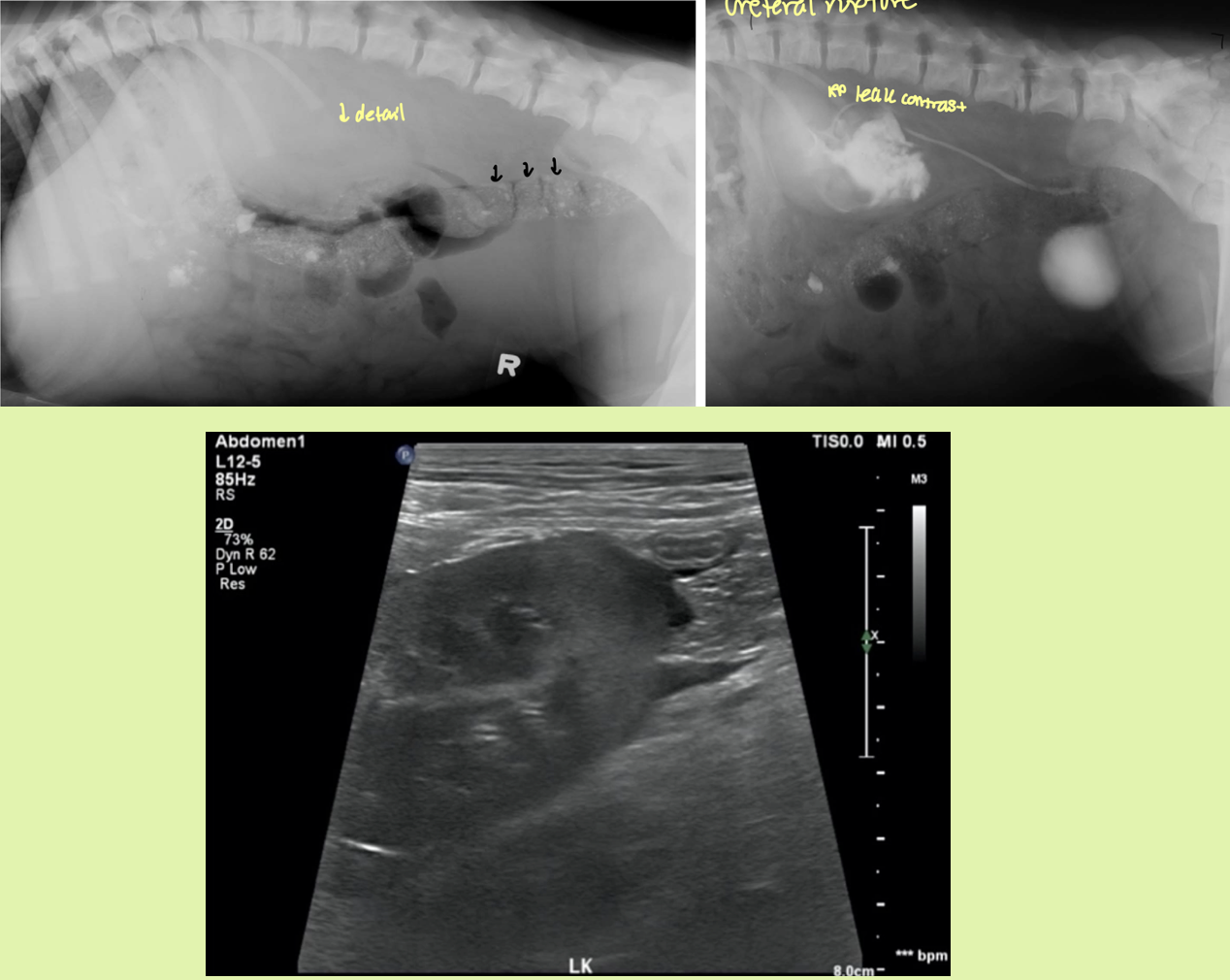
how would you be able to differentiate a ruptured kidney vs ureter
kidney rupture - injured kidney with opacify inhomogenous
ureter rupture -only one ureter will light up with contrast and deposit into bladder
congenital defect that affects females more and results in urinary incontinence since birth
ectopic ureters
2 common locations for ectopic ureters
prox urethra - after sphincter (IUS)
vaginal vault
**can have multiple or fenestrated openings
what combo of imaging modalities is the best way to view ectopic ureters
negative contrast cystogram (make bladder black) + EU (highlight ureters)
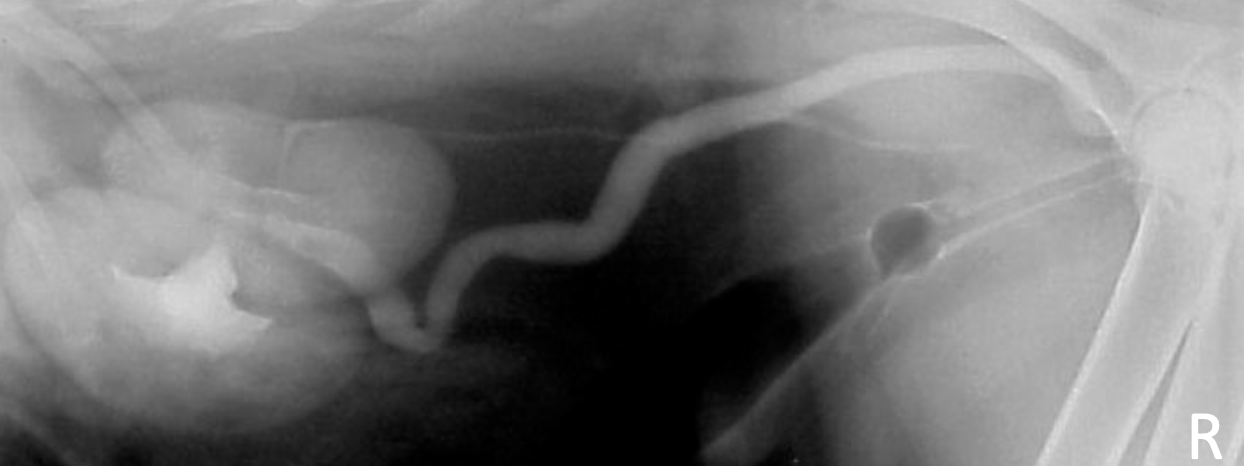
female dog with history of incontinence since birth
ectopic ureters
normal non-distended bladder
hydroureter
accumulation of contrast not in bladder
abnormal termination location of ureters
ureters and kidneys may appear normal - trace to abnormal termination site
± hydroureter/hydronephrosis if cause obstruction
3 ways to do contrast cystography on bladder
Positive Contrast Cystogram -bright
Negative Contrast Cystogram –dark/gas
Double Contrast Cystogram –both
T/F bladder changes are seen on rads normally
FALSE - need cystogram or ultrasound for dx
what are the 3 parts of the bladder
The vertex-blunt cr. Aspect (round)
The body- middle
The neck (trigone) – cd. aspect
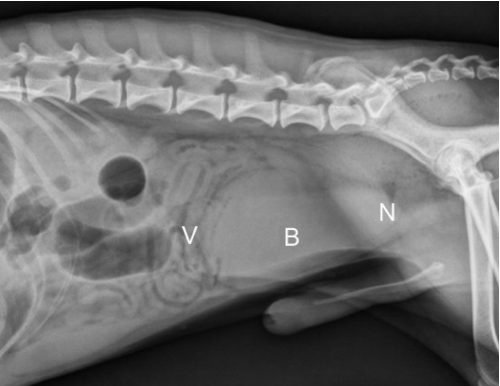
what 4 things that could make the bladder hard to see on rads
insufficient fat
not distended
superimposed intestinal loops
pelvic muscles
what organs border the bladder dorsally in female and male
male = colon
female = uterus
how does a cat bladder look different from dog
further into abd and longer neck than dog
what are the 3 distensible organs
bladder
stomach
uterus
describe opacity of normal bladder
less opaque at periphery (less fluid), thicker looking in the center
3 abnormalities that will make the bladder disappear
empty bladder
lack visceral contrast
displacement of bladder
what 2 organs can displace the bladder
colon and uterus
4 places the bladder can be displaced to abnormally
perineal hernia
inguinal hernia
abdominal wal hernia
entire bladder into pelvic canal (not always clinically significant)
3 reasons for distended bladder and small bladder
distended
normal
obstruction
neurogenic
small bladder
empty bladder
cystitis
ectopic ureters
what 2 things can alter shape/margin of bladder
adjacent mass/structure
primary bladder abnormality
**eval at complete distention with contrast
4 reasons for increased opacity of bladder
radiopaque calculi
IV contrast admin for something else
dystrophic mineral of neoplasia
dystrophic mineral of chronic inflam
2 reasons for decreased opacity in the bladder
air opacity in bladder wall - emphysematous cystitis (diabetes mellitus)
air opacity in lumen - gas bact diabetes, iatrogenic cath/cysto
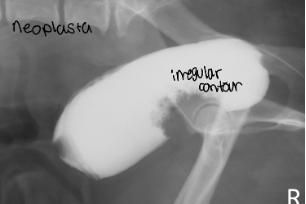
positive contrast cystography best highlights
position and wall integrity
negative conrast cystography in combination with EU highlights what 3 conditions
ectopic ureter
localize bladder we not seen on rads
non-opaque bladder calculi
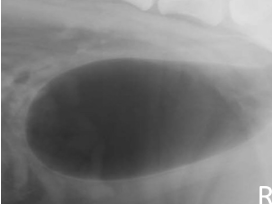
double contrast cystography highlights
mural diseases and intramural filling defects
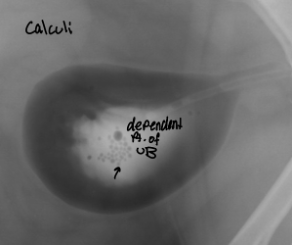
what are 9 indications to use cystography
Suspect urinary bladder rupture**
Localization of urinary bladder relative to suspected hernia**
Non-observable urinary bladder and differentiation of bladder from caudal abdominal mass lesions*
Stranguria, dysuria*
Hematuria
Pyuria
Proteinuria
Crystalluria
Persistent or recurrent UTI
what 3 lab values will contrast effect
USG
sediment
inhibition of growth of culture pathogen
what are 4 things to eval when looking at cystography
wall thickness > 2 mm
wall integrity
mucosal surface
intraluminal filling defects
5 examples of attached intraluminal defects bladder
neoplasia
blood clot
polyps
hematoma
ureterocele
3 types of free intraluminal defects bladder
calculi
hematoma, blood clot
gas bubbles
6 complications of cystography
air embolism
trauma
bladder rupture
hemorrhage from distention of diseased bladder wall
catheter kinking/knot
bacterial contamination
3 etiologies that might distort bladder wall
neoplasia
artifact due to small bladder size
cystitis
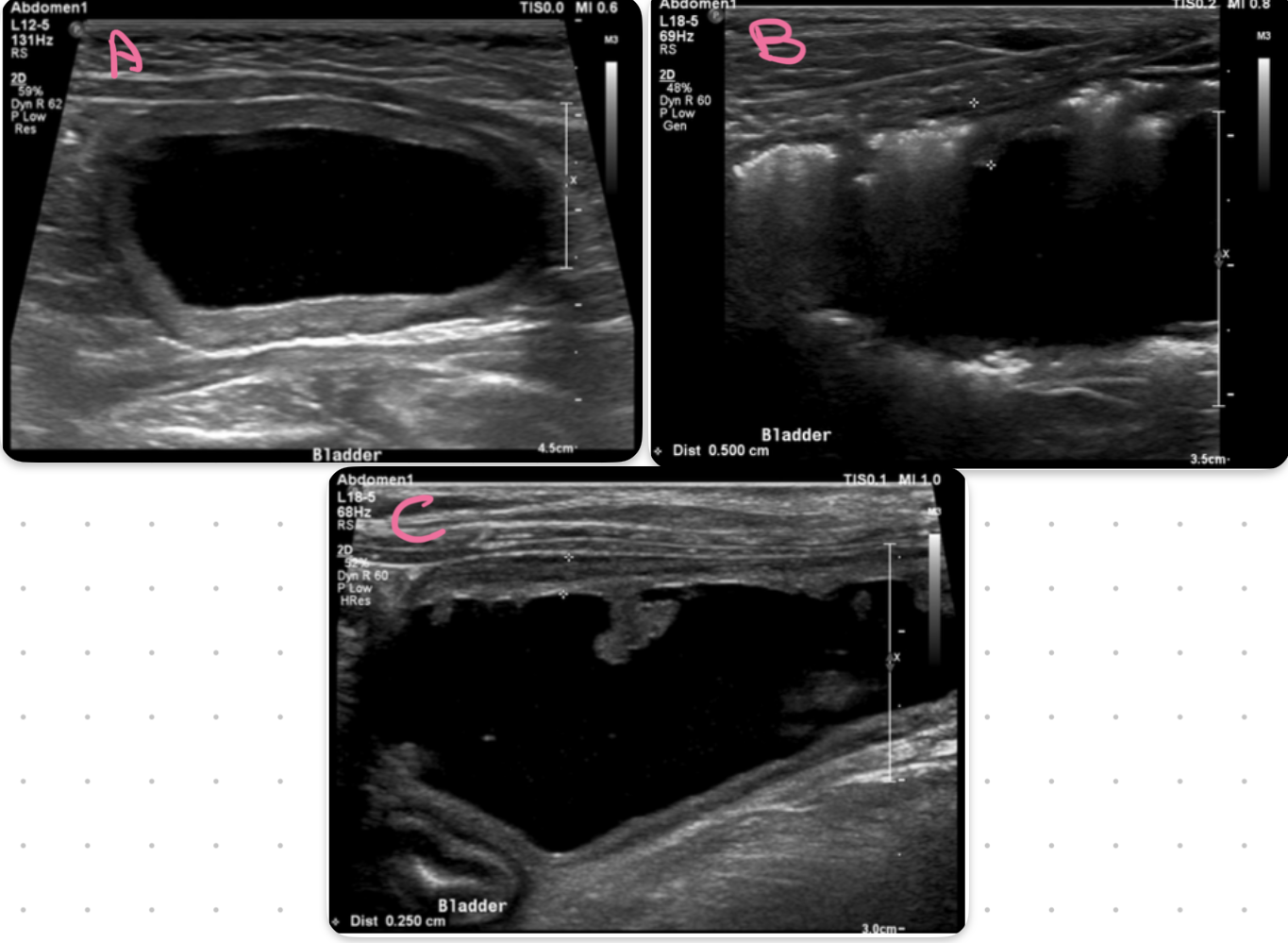
bladder
A = cystitis
B = emphysematous cystitis
C= polypoid cystitis
key ultrasound feature of cystitis
irregular thickened hypoechoic urinary bladder wall
what part of the bladder is most affected by cystitis
cranioventral aspect
neoplasia of the bladder likes to affect what region
trigon and dorsal wall
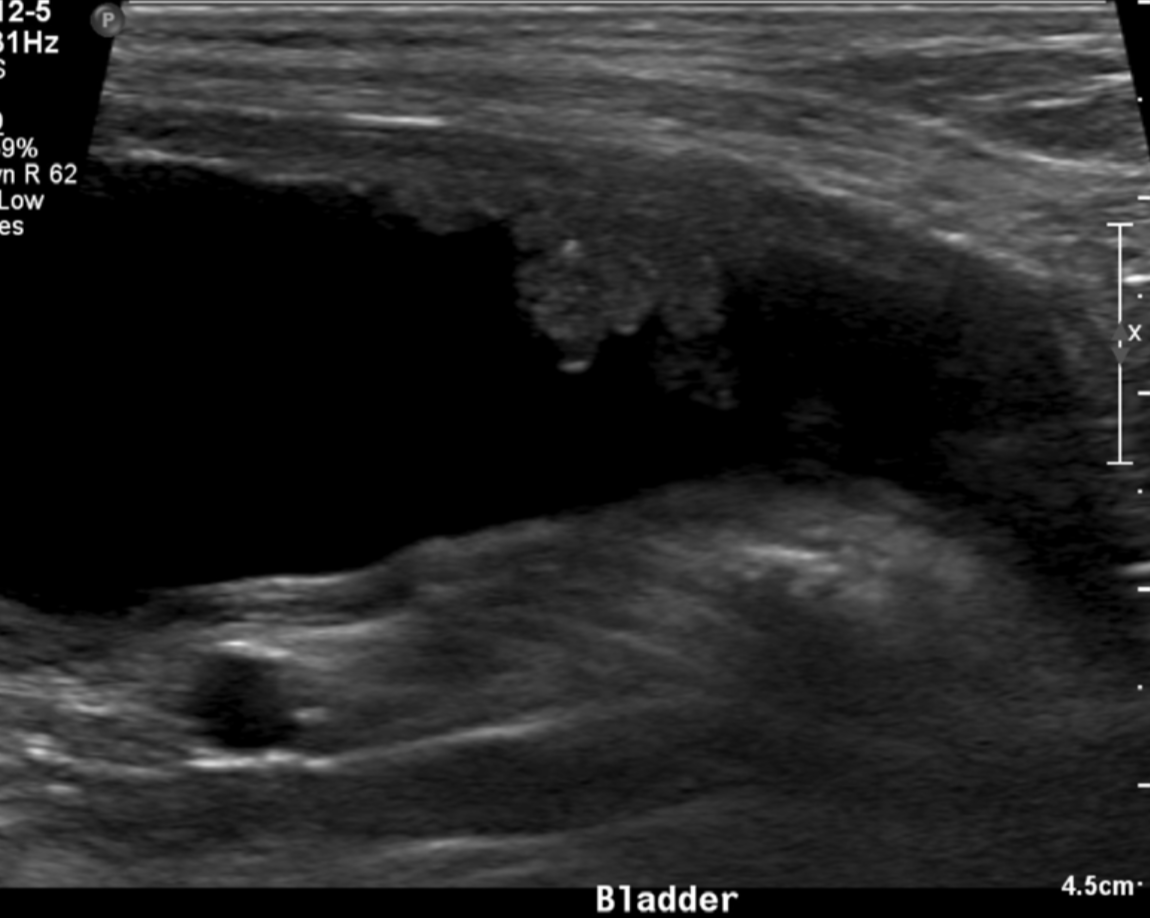
OLD DOG bladder
TCC/neoplasia
key feature of bladder neoplasia on ultrasound
mass or polyp lesion in the trigon or dorsal wall
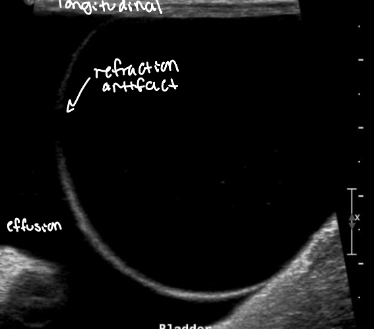
when dx urinary bladder rupture, what artifact often looks like a hole in the wall
refraction artifact at apex of bladder
5 etiologies that can distort bladder content
pseudosludge
sediment
iatrogenic gas bubbles
calculi
blood clot
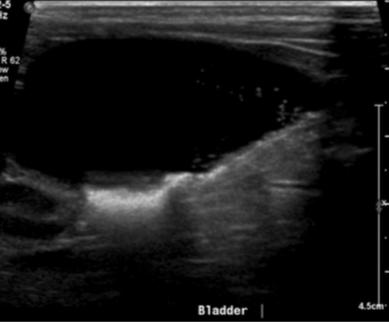
bladder
sandy calculi