Intro to Challenge and Change in Society - Unit Test #1
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Social Science Inquiry Model
Steps for conducting social science investigations.

Closed Questions
Questions with yes or no answers.
Open Questions
Require longer, elaborative responses.
Ethical Research
Collecting data while avoiding bias and ensuring objectivity.
Milgram Experiment
Study measuring obedience to authority figures.
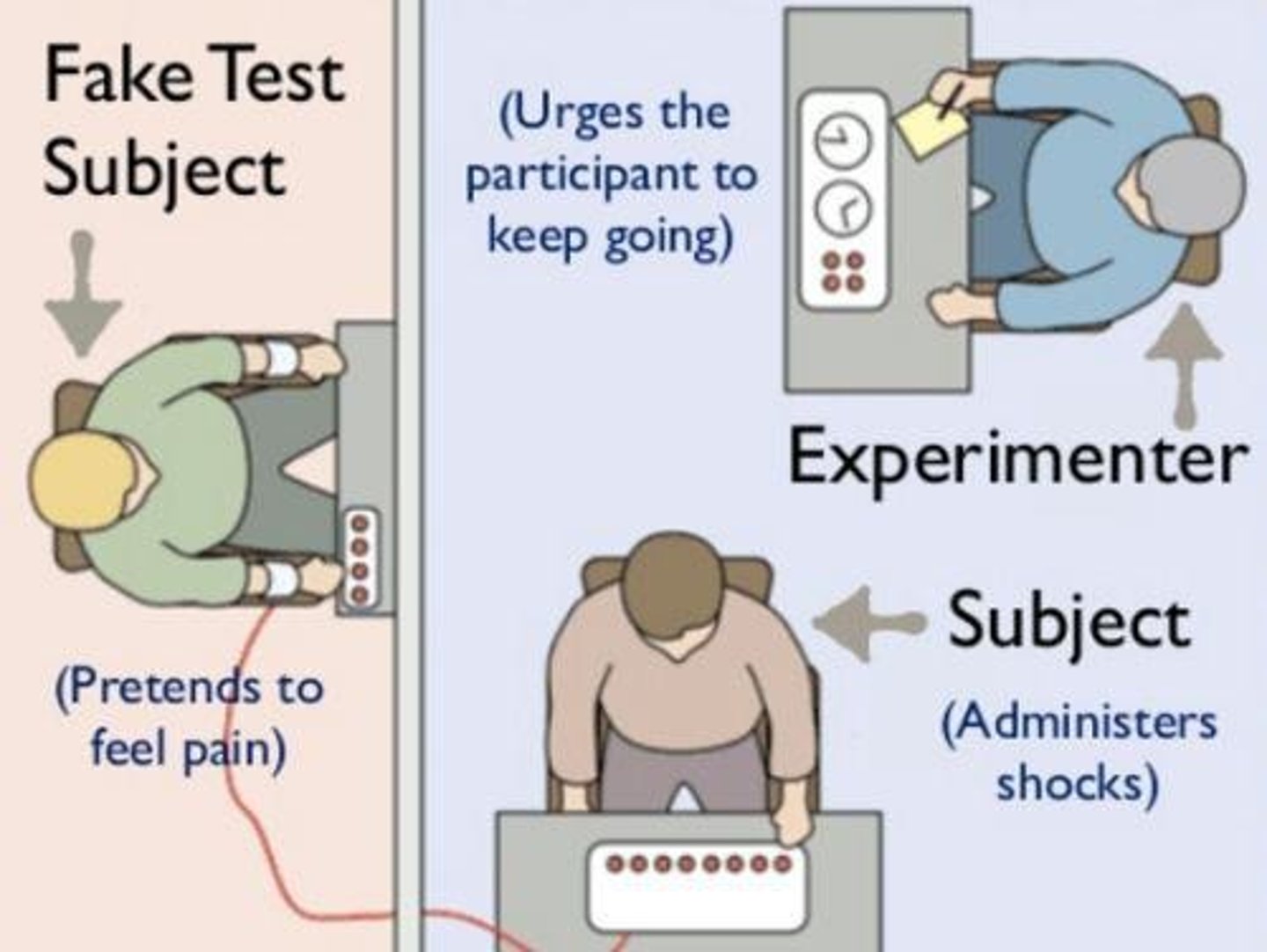
Obedience
Compliance with an authority's commands.
Research Question
Identifies the focus of the inquiry.
Hypothesis
Proposed answer based on preliminary evidence.
Data Gathering
Collecting information through various methods.
Data Analysis
Examining and organizing collected data.
Drawing Conclusions
Assessing research accuracy and communicating results.
Theories
Frameworks to explain and predict observations.
Characteristics of a Theory
Must explain reality and withstand scrutiny.
Good Theory
Concise, precise, testable, and productive.
Anthropological Theories
Explain cultural change through internal and external factors.
Internal Change
Inventions addressing societal needs.
External Change
Diffusion and acculturation between cultures.
Psychological Theories
Describe behaviors and predict future actions.
Sociological Theories
Examine social changes and predict future events.
Participant Observation
Research method involving immersion in a group.
Experiments
Controlled studies to test hypotheses.
Surveys
Questionnaires to gather data from participants.
Ethnography
Comparative cultural analysis through fieldwork.
Longitudinal Studies
Analysis over an extended period.
Quantifiable Results
Data that can be measured and compared.
Social Change
Transformation in society's beliefs and structures.
Agents of Change
Individuals influencing or challenging the status quo.
Status Quo
Existing state of affairs in society.
Social Movement
Collective effort to promote social change.
Cultural Values
Beliefs and norms shaping a society's behavior.
Historical Perspectives
Understanding change through past societal contexts.
Suffrage Movement
Campaign for women's right to vote.
Tipping Point
Moment when an idea gains significant popularity.
Social Epidemic
Rapid spread of ideas or behaviors like a virus.
Law of the Few
Influence of a small group on social change.
Stickiness Factor
Memorable presentation of ideas for effective communication.
Power of Context
Influence of environment on human behavior.
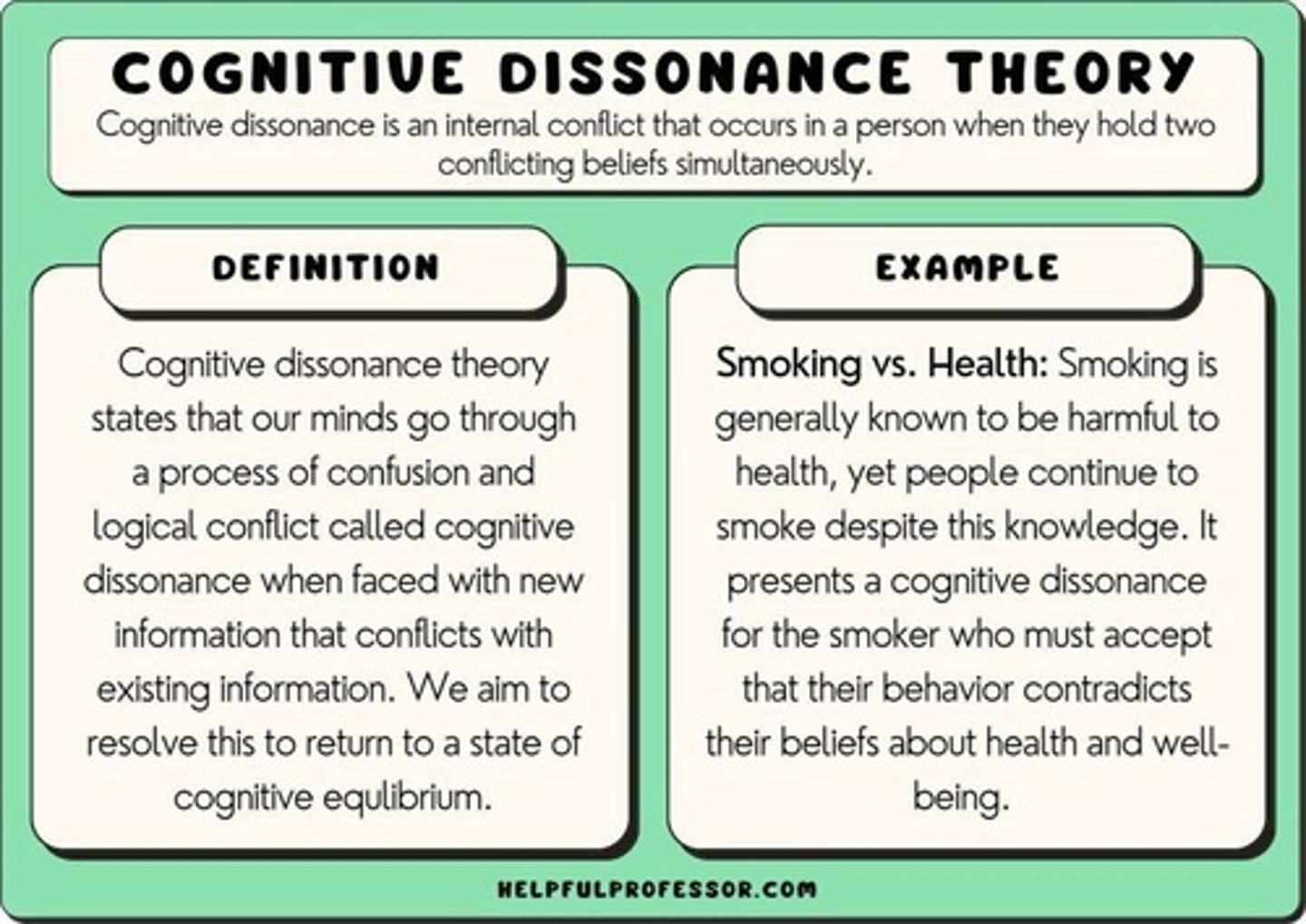
Cognitive Dissonance
Mental discomfort from holding conflicting beliefs.
Technological Change
Impact of technology on societal transformation.

Socialization
Process of internalizing societal norms and values.
Public Support
Community backing for social movements or changes.
Long-View Perspective
Analyzing social change over extended periods.
Resistance to Change
Opposition to new ideas or practices.
Social Scientists
Researchers studying societal dynamics and changes.
Complexity of Change
Multiple factors influencing a single social change.
Historical Change
Evolution of societal norms over time.
Environmental Influence
Effect of surroundings on societal behaviors.
Socialization Agents
Influencers like family, education, and media.
Anthropology
Systematic study of humanity, with the goal of understanding our evolutionary origins, our distinctiveness as a species, and the great diversity in our forms of social existence across the world and through time.
Cultural Relativism
Studying other cultures and values with acceptance and respect.
Ethnology
Studying and comparing past with contemporary cultures.
Ethnography
The in-depth description of a particular culture through extensive field work.
Participant Observation
The effort of an investigator to gain entrance into and social acceptance by a foreign culture so as better to attain a comprehensive understanding of the internal structure of the society.
Biological (Physical) Anthropology
The study of human-environmental adaptation (evolution) within the context of human cultures and behaviours.
Cultural Anthropology
The study of the learned behaviours of groups of people in specific environments.
Archaeology
The study of human past by careful uncovery & examination of material remains in order to interpret the experiences of peoples throughout history.
Linguistic Anthropology
The study of how language influences social life and how people use it for social and cultural purposes.
Ruth Benedict
Anthropologist known for the quote, 'The Purpose of Anthropology is to make the World Safe for Human Differences.'
Alfred L. Kroeber
Anthropologist known for the quote, 'Anthropology is the most humanistic of the sciences and the most scientific of the Humanities.'
Methodology
Rely heavily on fieldwork and the detailed observations.
Archaeologists
Professionals who excavate sites where ancient societies once lived.

Cultural Anthropologists
Professionals who interact with modern social groups in order to better understand them or their distant ancestors.
Fieldwork
Commonly consists of interacting with modern social groups to better understand them or their distant ancestors.
Prehistoric Cultures
Cultures that existed before the invention of writing.
Artifacts
Material remains left behind by cultures that can be interpreted to reconstruct a prehistoric culture's way of life.
Evolution
The process of change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations.

Social Existence
The diverse ways in which humans live and interact within societies.
Human Differences
The variations among human beings in terms of culture, behavior, and social structures.
Culture
Is the full range of learned human behaviour patterns; the beliefs, attitudes, values and ideals of a society.
Components of Culture
1) material objects that we might possess or desire, 2) attitudes that are considered acceptable, 3) behaviours that are considered proper.
Characteristics of Culture
Culture is learned, shared with others, shapes how we understand the world, and has patterns.
Ethnocentrism
Term applied to the cultural bias (conscious or unconscious) in which an individual views the world from the perspective of his or her own group, establishing the in-group as the norm and rating all other groups with reference to this ideal.
Consequences of Ethnocentrism
Results in an inability to adequately understand cultures that are different from one's own and value judgments that preference the in-group and assert its inherent superiority.
Cultural Relativism
The antithesis of ethnocentrism, actively countered through education.
Universal Emotions
Emotions that are recognized across different cultures.
Ethnography
Comparative study of two or more cultures by using data taken from research and applying it to a single cultural topic.
Culture Writing
Refers to a type of documentation commonly used by Anthropologists, that uses detailed first hand descriptions based on first hand research.
Holism in Anthropology
The idea that culture can be best understood through the understanding of as many aspects of the culture as possible.
Functionalism
Culture functions to meet the needs of individuals rather than the needs of society as a whole.
Micro Level Orientation
Focuses on individuals' feelings and motives as crucial to understanding the way society functions.
Structuralism
Involves analyzing something (person, society, etc.) by breaking it down into its most basic elements and exploring how these elements are related to each other and to the whole.
Macro Level Orientation
Focuses on the broader structures and systems within society.
Cultural Materialism
Based on the premise that human life is a response to the practical problems of existence that the physical world impacts and sets constraints on human behavior.
Material Conditions
Prioritized as more likely than ideas to be causal in human societies.
Sociology
The study of social life, social change and the social causes and consequences of human behaviour.
Socialization
Process of learning to behave in a way that is acceptable to society.
Values
A person's principles or standards of behaviour.
Norms
A pattern of social behavior typical or expected of a group.
Demographics
Statistical studies of population and particular groups within it.
Pure Sociology
To gain knowledge. Ex. Studying the social structure of disadvantaged communities.
Applied Sociology
Find solutions to social problems. Ex. How to prevent criminality in disadvantaged communities.
Clinical Sociology
The application of theories, research, and interventions to social issues and problems presented by clients.
Primary Groups
Small groups with members hard to replace, who frequently meet face-to-face and share in-depth things together.
Secondary Groups
Impersonal and informal groups where members know minimal personal information.
Deviance
Behaviour that is different from the social norm.

Status
A term used to describe our position in an institution.
Hierarchy
Ranking of authority and power.
Role
A socially expected behavior pattern usually determined by an individual's status in a particular society.
Structural-Functionalism
The theory that societies need certain things to function (education, reproduction, socializing, certain goods).
Conflict Theory
The theory that economic power equals political power and to understand society, one must look at the economy and the great differences in power created by money.