Unit 2 - Molecular biology
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Chemical properties of carbon
Carbons are able to form covalent bonds. This is when there is a sharing of two electrons between two atoms. Carbons can form up to four single bonds or a combination of single and double bonds with other carbon atoms or atoms of other non-metallic elements. This allows carbon to form long, stable chains and rings.
It can form single rings, multiple rings, branched chains and unbranched chains.
Single rings: Glucose
Multiple rings: Cholesterol
Branched chains: Glycogen
Unbranched chains: Amylose
Condensation
Chemical process where two or more molecules join together to form a more complex molecule, often eliminating another molecule, like water. An example in carbohydrates is that when two molecules join, one molecule loses a hydroxyl group (−OH) and the other loses a hydrogen atom (−H), forming a water molecule and resulting in formation of a new covalent bond.
Examples of production of macromolecules by condensation reactions that link monomers to form a polymer.
Polysaccharides: Cellulose (plant cell wall), Glycogen (energy reserve)
Polypeptides: Peptide hormones, component of snake venom (Natriuretic peptides)
Nucleic acid: DNA, RNA
Hydrolysis
A chemical process that breaks down proteins into peptides and amino acids by addition of water and presence of enzymes. In the human body, larger polymers are broken down into individual monomers to build new monomers because macromolecules are too large too be absorbed and used by cells.
Macromolecule
Large molecules made up of smaller building blocks known as monomers. Most macromolecules are polymers, with the exception being lipids.
Monosaccharide
A monosaccharide is the simplest form of a carbohydrate, consisting of a single sugar unit that cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis.
Types of monosaccharides
Glucose: Very common in nature and is an important energy source for many organisms
Fructose: Type of sugar normally found in fruits
Galactose: Typically found in dairy products
Properties of glucose
Glucose has two isomers like alpha glucose and beta glucose. For example, glycogen and starch are made out of alpha glucose molecules, cellulose is composed of beta glucose molecules. As a result it plays a critical role in the formation of polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and cellulose.
Glucose is soluble. Can dissolve in water due to it being polar. This allows it to be transported in blood because it can dissolve in plasma.
Glucose can be oxidised. Important process in many biological systems as it involves production of ATP through cellular respiration.
Starch
Main form of energy storage in plants. There are two types of starch: amylose and amylopectin.
These polysaccharides are mostly insoluble, which helps to maintain the osmotic balance within an organism.
It is compact in its structure because of its coiling and branching during polymerisation, which allows for efficient storage in small place.
Can be broken down to release glucose molecules through hydrolysis.
Glycogen
It is a branched polymer of glucose molecules that form a highly compact, coiled structure in cells.
The coiled structure of glycogen is due to the branching pattern of the molecule, which allows for efficient storage and mobilisation of glucose when energy is needed.
Like starch, glycogen is relatively insoluble due to its large molecular size, helping maintain osmotic balance within an organism.
The liver stores glycogen primarily to maintain blood glucose levels, as the liver can break down glycogen and release glucose into the bloodstream when blood glucose levels drop.
Can also be found in muscle cells as glycogen can be quickly mobilised and broken down into glucose molecules when the body needs it.
What is the bond called that is links monosaccharides to form polysaccharides?
Glycosidic bond. It is a covalent bond and there are different types of glycosidic bonds such as alpha and beta.
Polysaccharides as structural compounds: cellulose
Cellulose forms a straight chain because the beta glucose molecules alternate in orientation.
This unique structure allows the cellulose molecules to form long, unbranched chains that can be grouped into bundles called microfibrils. Hydrogen bonding gives the cellulose a lot of tensile strength.
This is important because if the plant did not have this the plant cells would be unable to withstand the forces of osmosis and would collapse under their own weight.
Glycoproteins
Proteins that have one or more carbohydrates attached to them. Found in many cellular structures, extra cellular matrix, cell membranes, secreted proteins.
Roles of glycoproteins
Cell to cell recognition. Receptors, ligands, structural support.
Antigens
Identifying markers (recognizing blood cells). Main ones: AB. The compatibility of blood types is based on recognition and interaction of specific glycoproteins on the surface of red blood cells. When incompatible blood types are mixed, the immune system can recognize the other glycoproteins as foreign molecules and attack.
Hydrophobic properties of lipids
Lipids repel water and tend to dissolve in non polar solvents. Examples include: Wax (can be found on leaves, slows down rate of transpiration), triglycerides (three fatty acid chains attached to one glycerol), steroids that composed of four carbon rings that are fused together.
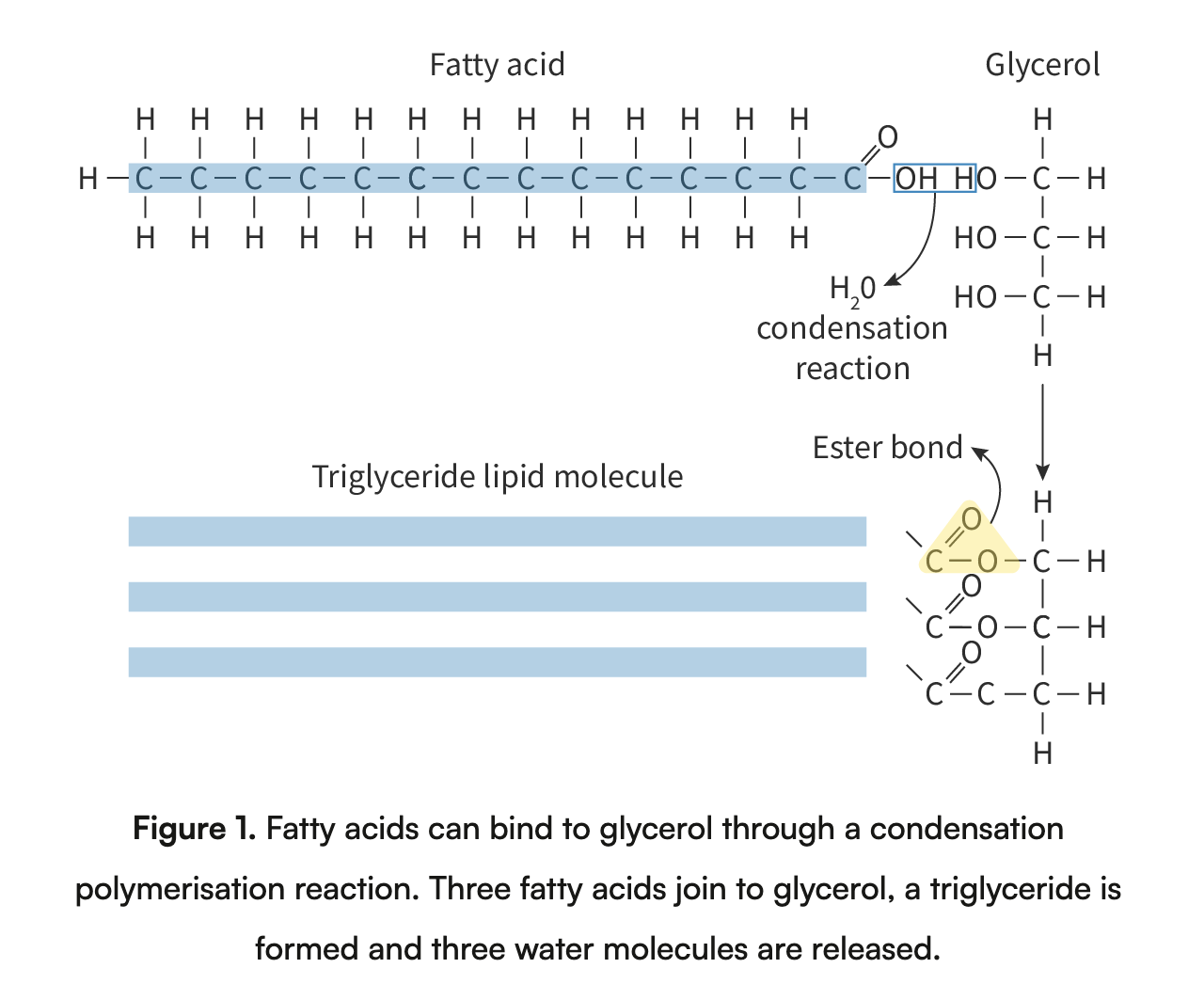
Formation of triglycerides and phospholipids by condensation reactions
Triglycerides: Formed by condensation of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules. Whenever a fatty acid molecule joins the glycerol molecule, a water molecule is released. Bond between the glycerol molecule and the fatty acid molecule is called an ester bond.
Phospholipids: Consists of a glycerol molecule with a phosphate group and two fatty acids. Similarly to triglycerides, when two fatty acids join the glycerol phosphate molecule, and ester bond is made and water is released.
Difference between saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated fatty acids
Can be classified as either depending on the number of double bonds in the chain.
Saturated fatty acids: Straight, linear shape, no double bonds between carbon atoms. Allows them to pack tightly together which is why they are solid at room temperature.
Monounsaturated fatty acids: One double bond which forms bends or kinks in the fatty acids chain, prevents the fatty acids from packing tightly together, which is why they are liquid at room temperature.
Polyunsaturated fats: They have two or more double bonds, examples include fatty fish like salmon.
Cis unsaturated fat vs trans unsaturated fat
In cis unsaturated fat, the hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the double carbon bond. Whereas in a trans unsaturated fat, the hydrogen atoms are located on the opposite side of the carbon double bond. Thus creating a more linear structure, not found naturally.
Properties of tryglycerides to life
Energy reserve: They are the primary form of energy reserves in fat cells. They are created from excess calories. These triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids when body is in need of energy like during physical exercise, fasting etc.
Insulation: Play a role as thermal insulators in many organisms, helping to regulate body temperatures and protect against the cold. One example is the whale, which has a thick layer of blubber that protects the whale from the cold. It also serves as an energy reserve for the whale.

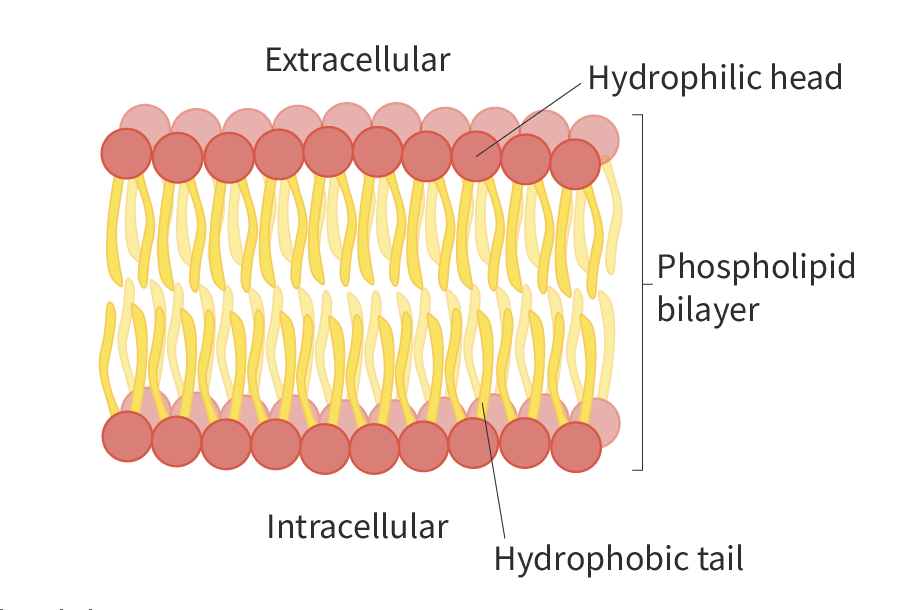
Phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipids have a head that is considered to be hydrophilic and they have a tail that is hydrophilic. The head is positioned on the outside while the tail is on the inside. The head is composed of hydrophilic phosphate groups, while the tails are mainly hydrophobic fatty acids. Therefore, they are considered to be amphipathic. As a result, they may spontaneously form a phospholipid bilayer in a aqueous solution.
Non polar steroids with the ability to pass through the phospholipid bilayer
Steroids are naturally occurring hormones that are important in regulating physiological functions in the body. They are organic compounds that are composed of four carbon-based rings as the basic structure but the difference in functional groups is vast allowing steroids to have a diverse array of functions. They also provide stability and flexibility to the phospholipid bilayer.
As steroids are hydrophobic molecules, they are capable of passing through the phospholipid bilayer of cells. This allows these cells to have a faster response to the presence of these steroids allowing the signal to occur more efficiently.
Examples of steroids
Oestradiol and testosterone are important to the development in male and female reproductive development.
Role of cholesterol in phospholipid bilayer
Provides stability and flexibility
Lipid bilayer as an effective barrier between aqueous solutions
The phospholipid bilayer has a low permeability to larger molecules and hydrophilic particles, including ions and polar molecules, thus the membranes function as effective barriers between aqueous solutions.
Proteins
Complex macromolecules composed of one or more chains of amino acids.
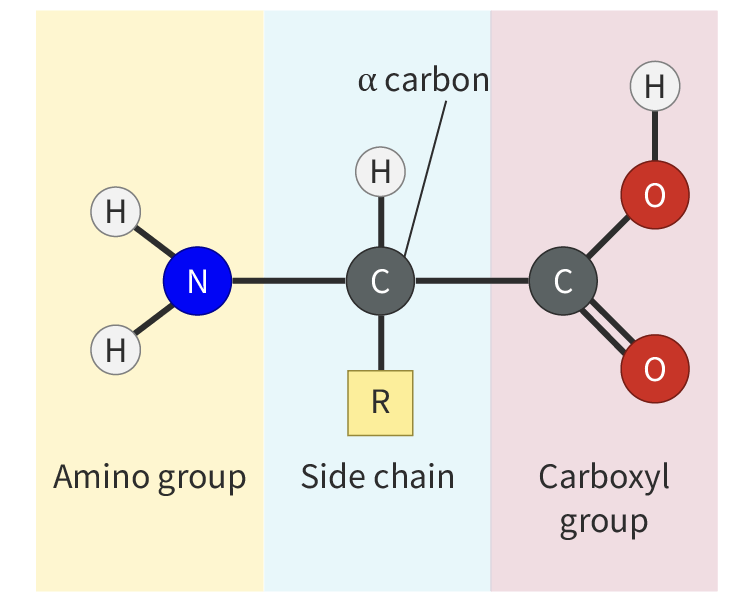
Amino acid
They are the monomers that build proteins. There are twenty different amino acids, but each has the general structure.
Generalized structure of an amino acid
The central carbon is known as the alpha (α) carbon and it is covalently bonded to four different chemical groups:
a carboxyl group (–COOH)
an amino group (–NH2)
a hydrogen atom (–H)
a unique organic side chain called the R - group
.
Condensation reactions forming dipeptides and longer chains of amino acids
Amino acids can join together through a condensation reaction. A peptide bond is formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acids joins with the amino group of another amino acid to form a dipeptide. A water is released as the product. Since a peptide bond is a covalent bond, they are very stable.
Word equation for condensation reaction forming dipeptides and longer chains of amino acids
amino acid + amino acid → dipeptide + 1 water molecule
Polypeptide
A long chain that is composed of more than 2 amino acids. It is a chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. There is an infinite variety of possible peptide chains as the 20 amino acids can be composted into any sequence, which allows for the complexity and diversity for life.
Essential amino acids
The amino acids that cannot be synthesized inside the body and needs to be consumed through foods. Therefore it is necessary for a vegan to consume a diet that is composed of a variety of plants to ensure that all of the essential amino acids are consumed.
Non - essential amino acids
The amino acids that can be synthesized in the human body but can also be found in food.
Protein
A complex, three dimensional structure, that is made up of one or more polypeptide chains. In a protein composed of only one polypeptide chain, the amino acids will interact with each other, folding the chain into a functional protein. In proteins composed of more than one polypeptide, the polypeptide chains can additionally interact with each other, contributing to the overall structure of the protein.
Single chain polypeptides
Lysozyme: An enzyme made out of 129 amino acids. Can be found in saliva and tears. Has antimicrobial properties which can disrupt cell wall of bacteria, allowing it to defend against microbial infections.
Glucagon: Hormone made out of 29 amino acid residues. The hormone regulates blood sugar levels. It is secreted from the pancreas when there is low levels of glucose in blood which stimulates liver to release more glucose into bloodstream which raises blood sugar levels.
Myoglobin: is an oxygen-binding protein, mainly found in muscle tissues, which is composed of 153 amino acid residues. It facilitates the storage and release of oxygen to muscle fibres, particularly during periods of low oxygen availability, such as strenuous physical activity.
Effect of PH and temperature on protein structure
The structure of proteins is extremely important for their biological function and any changes can result in loss of activity. Denaturation is the process in which a protein loses it’s original shape, causing it to lose its function.
PH: Can make it alter the proteins solubility and shape because PH affects the charge of the protein. This can cause permanent changes in protein structure. One example is pepsin, which thrives in acidic environment.
Temperature: Can break the hydrogen bonds (which are a bit weak) which leads to the unfolding of the protein and thus lose its function. Most proteins in the body function the best at around 37 celsius.
Chemical diversity in the r-groups that gives huge diversity in protein form and function
Amino acids are linked together by ribosomes. The r-group gives the amino acid its unique properties/characteristics. The R groups of the amino acids present in a polypeptide determines properties of assembled polypeptides.
R-groups can either be hydrophilic or hydrophobic. Hydrophilic r-groups (they are usually polar or charged, acidic or basic) tend to attract water molecules while hydrophobic r-groups tend to repel water molecules (they are mostly non-polar). Polar R-groups contain partial charges that interact with water molecules, while charged R groups can be either positively charged (basic) or negatively charged (acidic).
Primary structure
Refers to the specific sequence of amino acids that are joined together to form a polypeptide chain. The different structure determines how the polypeptide will fold, thus creating the three dimensional structure of the protein
Secondary structure
Refers to the local folding patters within the polypeptide chains. Two common structures are beta pleated sheets and alpha helices.
Alpha helices: A type of secondary protein structure that forms coils or helix with a right-hand twist.
Beta pleated sheets: A type of secondary protein structure that forms pleats.
Can be achieved through the hydrogen bonding between carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid n a different part of the polypeptide chain.
Tertiary structure
The overall three dimensional structure of a single polypeptide chain due to the folding of the secondary structure (beta pleated sheets and alpha helices.)
Stabilising forces:
Hydrogen bonding between polar r groups in the tertiary structure of a protein plays a crucial role in stabilising the three dimensional shape by holding distant regions of the polypeptide chain together. This preserves the proteins functional integrity.
Ionic bonding can be formed between oppositely charged ions. R-group may become charged because it loses or binds with hydrogen ions. These charged R- groups can then form ionic bonds with other molecules. This can contribute to the overall stability and function of the protein.
Disulfide covalent bonds can form between pairs of cysteine amino acids residues that contain sulfur atoms. The bonds are important for stabilising the tertiary and quaternary structures of the proteins by forming covalent bonds that maintain the proteins three dimensional shape, further contributing to its stability and function.
Hydrophobic interactions happen between non polar amino acids. Non polar amino acids tend to bunch up in the middle of the protein to minimize the contact with surrounding water molecules. This stabilises the protein’s tertiary structure and quaternary structures.
Globular proteins
Proteins that are compact and spherical in shape. They play important roles as enzymes, transporters and regulators.
Fibrous proteins
Long structural proteins that are insoluble in water, provides strength and support to tissues.
Effect of polar and non-polar amino acids on tertiary structure of proteins
Hydrophilic amino acids position themself outside to the environment while hydrophobic amino acids position themself inwards. As a result the folded confirmation exposes the hydrophilic surfaces to the solvent and the hydrophobic residues in the protein’s interior, thereby contributing to the overall protein stability and function.
Examples: Myoglobin and haemoglobin are both examples globular proteins with hydrophobic cores. Integral proteins have regions with hydrophobic amino acids allowing them to embed in membranes more easily.
Quaternary structure