Periodic Table - Chem. KAP
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What are three important factors to consider when examining periodic trends?
Nuclear charge, shielding effect, octet rule
How is nuclear charge increased?
When a proton is added.
Why does nuclear charge increase when a proton is added?
Electrons are pulled in to the nucleus even more.
T/F: Nuclear charge increases across a row/period
True
T/F: Elements in the same period have the same nuclear charge.
False, as you go down a period, nuclear charge increases
What happens when a proton is added to he nucleus?
It creates a strogner nuclear charge
An energy level is the same thing as
A period
In adding a period or energy level, you also add a
shield
As energy levels are added, the atom becomes larger/smaller in radius
Larger
Does the pull of a nucleus for the valence electrons increase or decrease under the shielding effect?
Decrease
Why does the pull of a nucleus for the valence electrons increase or decrease under the shielding effect?
Because there are more shields and because the valence electrons are also further from the nucleus (proton pull is less)
As energy levels are added/removed, it becomes easier to add/remove a valence electron
As energy levels are added, it becomes easier to remove a valence electron
What is the most important thing to remember about shields?
The number of shields is always one less than the number of periods or energy levels!!!!!!! So if a period is 4, the shield number is 3.
Atoms will lose, gain or share _____ so they can achieve the electron configuration of the closest noble gas.
lose, gain, or share electrons
T/F: As atoms get closer to the nobles gases on the periodic table (further to the right), their attraction for electrons is greater
True
Where is atoms attraction for electrons the greatest?
Right next to noble gases (increase along a period)
Why is attraction greatest to the right?
Atoms to the left want to lose electrons, so they won’t have as much attraction.
What are the two definitions of atomic radius?
Technically: the distance from the center of the nucleus to the edge of the electron cloud.
Literally: ½ the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms in a diatomic molecule.
How is atomic radius measured?
Picometers (pm), 10^-12 m, or Angstroms (A), 10^-10m
What does atomic radius indicate?
Relative volume or size of the atom
Atomic radius increase/decreases as you move down a group.
Atomic radius increases as you move down a group (down a column).
Why does atomic radius increase as you move down a group?
Succeeding energy levels are being filled.
Atomic radius generally increases/decreases as you move along a period from left to right.
Atomic radius generally decreases as you move along a period from left to right.
Why does atomic radius decrease as you move down a period?
Nuclear charge is increasing (proton pull is larger, things get pulled in more)
What is a group trend?
A pattern or trend from within a group
What is a period trend?
A pattern or trend from within a period
A cation is a positive/negative ion that is a metal/nonmetal atom that has lost/gained electrons
A cation is a positive ion that is a metal atom that has lost electrons
An anion is a positive/negative ion that is a metal/nonmetal atom that has lost/gained electrons
An anion is a negative ion that is a nonmetal atom that has gained electrons
Positive ions are always bigger/smaller than neutral metal atoms.
Smaller
Negative ions are always bigger/smaller than neutral nonmetal ions
Bigger
Why are positive ions smaller than neutral metal ones?
When metal ions form, the outer energy level is emptied so the electron cloud is smaller. Also, excess of protons will draw remaining electrons closer
Why are negative ions bigger than neutral nonmetal ones?
There is more repulsion in the cloud due to the added electrons (so things get more spread out) and there are no extra protons to pull it closer
For both cations and anions, ionic radius generally increases/decreases as you move down a group. Why?
For both cations and anions, ionic radius generally increases as you move down a group because energy levels are filled.
For both cations and anions, ionic radius increases/decreases as you move across a period from left to right. Why?
For both cations and anions, ionic radius decreases as you move from left to right across a period because of increasing nuclear charge.
T/F: Anions within one period are larger than cations within the same period. Why?
True! The cations lost an energy level.
What is ionization energy?
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from a gas atom, producing a cation.
What is the formula for the ionization energy of sodium?
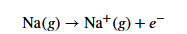
Ionization energy increases/decreases as you move down a group.
Ionization energy decreases as you move down a group.
Why does ionization energy decrease as you move down a group?
Ionization energy decreases as you move down a group because of the shielding effect.
Which period is ionization energy lower? Period 1 or 7?
Period 7
Ionization energy increases/decreases as you move left to right across a period.
Ionization energy increases as you move left to right across a period.
Why does ionization energy increase/decrease as you move left to right across a period.
Increasing nuclear charge and the octet rule (elements on the right will have higher attraction because they want to gain electrons to be a noble gas).
What is the energy required to remove the first outermost electron called? The second outermost electron?
First ionization energy, second ionization energy
Once stability is reached…(reason for sharp IE increase)
the atom will strongly resist further loss of electrons
What is electronegativity?
The tendency of atoms of an element to attract bonding electrons when they are chemically combined with atoms of another element
Electronegativity increases/decreases as you move down a group
Electronegativity decreases as you move down a group
What is the reason that electronegativity increases/decreases as you move down a group?
The distance from the nucleus is greater (they’re more shields away, so they become difficult to attract and pull).
Electronegativity increases/decreases as you move left to right across a period.
Electronegativity increases as you move left to right across a period.
What is the reason that electronegativity increases/decreases as you move left to right across a period?
Increasing nuclear charge (more protons = stronger pull) and the octet rule (closer to right side = WANT to gain).
T/F: Noble gases have electronegativity
FALSE!!!! Noble gases DO NOT HAVE ELECTRONEGATIVITY.
Why don’t noble gases have electronegativity?
They don’t attract electrons.
What is metal reactivity caused by
Greater tendency to lose electrons across periods from R to L, and due to the shielding effect down a group. Metal reactivity decreases from left to right (increasing nuclear charge = harder to lose) and increases down a group (shielding effect—> it’s easier to lose electrons w/ more shields).
What is non-metal reactivity caused by
Greater tendency to gain electrons across periods and due to the lack of shielding effect (up a group). Nonmetal reactivity increases across a period (increasing nuclear charge and octet rule), and decreases down a group (shielding effect)
Who is the father of the periodic table? How did he organize it?
Dmitri Mendeleev. Organized it according to chemical and physical properties (which let him predict existence/properties of missing elements) and increasing atomic mass.
What does periodic mean?
Repeating pattern
Who is Henry Mosely?
Rearranged Mendeleev’s PT in order of increasing atomic number.
Whose PT is the modern one?
Mosely.
How did Mosely die?
Enlisted in the British army during WW1 and died in the battle of the Gallpoll campaign—super short science career.
Who did Mosely work with?
Rutherford—found wavelengths of x-rays emitted by an element are related to its atomic number, which lead to realization that atomic number is better than atomic weight to arrange.
What is another name for the Periodic Law?
Law of Chemical Periodicity
What does the Periodic Law or the Law of Chemical Periodicity say?
Properties of the elements are periodic functions of an atomic number. When elements are arranged in order by atomic number, within a group their chemical and physical properties are similar to each other.
Who is Seaborg?
The discoverer of the ten transuranium elements and the name behind Element 106. He also broke out the Inner Transition elements.
What did Seaborg do in the Wartime Metallurgical Laboratory at UChicago?
Figure out how to prepare and purify plutonium-293 in useful quantities for the Manhatten Project, the making of the atomic bomb.
Which document was Seaborg a signer of?
The Franck Report, recommending a safe demonstration test of the atomic bomb might persuade Japan to surrender without the bomb actually being used.
Seaborg’s discovery of ___ at ____ followed the at the ___ same site by Edwin McMillan, who shared the 1951 Nobel Prize in chemistry with Seaborg for these accomplishments.
Seaborg’s discovery of plutonium at UC Berkely followed the at the synthesis of neptunium at the same site by Edwin McMillan, who shared the 1951 Nobel Prize in chemistry with Seaborg for these accomplishments.
Which two scientists have elements named after them?
Mendeleev and Seaborg
Which is solid at room temp except Mercury, which is a liquid?
Metals
Which metal is the only metal liquid at human body temperature?
Gallium
Who is this describing? Traits: soft, silvery metals with a low density. They are the most reactive metals and are not found by themselves in nature (always found in compounds). Explosive when exposed to air/water.
Alkali Metals
Where are Alkali Metals used?
Soap, lights, and present in body (electrolytes)
Who is this describing? Traits: harder, denser and stronger than the Alkali metals. Silvery in color. Second most reactive metals and not found by themselves in nature.
Alkali Earth Metals
What are the uses of Alkaline Earth Metals?
Gemstones, limestone, marble, alloys for aircraft, truck bodies, fireworks, flares, calcium for bones/teeth
What does this describe? Traits: hard, sivlery, solid metals that have a high density. High luster (shiny), malleable (can be hammered or pressed), ductile (stretchable, can be drawn our into a thin wire), good conductors of heat and electricity. Less reactive than groups 1 or 2 and many are found by themselves in nature.
Transition Metals (NOT to be confused with Inner Transition Metals)
What are the uses of inner transition metals?
Paint, steel, coins, electrical wiring, plumbing, jewelry, construction
Which group does this describe? Traits: shiny, silvery, reactive metals with high melting points. If _____, found in compounds. If ____ all radioactive (unstable), many artificially produced, only Th, PA, U and Np found in nature.
Inner Transition Metals. Lanthanides = found in compounds, Actinides = all radioactive, artificially produced usually
What does this describe? Traits: have properties of both metals and nonmetals. Semiconductors. Good electrical conductors at high temperatures, good insulators and low temps.
Metalloids
What are metalloids used for?
Computer chips, glass
What does this describe? Traits: poor electrical conductors but good insulators, don’t have luster and are brittle in the solid form, nonductile, exist in various phases of matter
Nonmetals
What are nonmetals used for?
Many are needed for your health
What are the diatomics?
All the halogens except for At, and plus the two to the left of F.
What does this describe? Traits: Fluorine + Chlorine = yellow-green bases, Bromine = dark red liquid, Iodine = purple-black crystalline solid, the most reactive group of nonmetals. Unpleasant odor, will burn flesh. Strongly electro negative. Oxidizing agents.
Halogens
What are halogens used for?
Med treatment, gemstones, bones, teeth, DNA, medicine, organic compounds, Xerox copying, bleach, antiseptics.
What does this describe? Traits: No chemical reactivity (inert), all are gases, outer energy level is full
Noble gases
What are noble gases used for
Hot air balloons, glowing lights
What are the properties of metals?
Physical: good electrical conducts and heat conductors, malleable, ductile, possess luster, opaque as thin sheet, solid at room temperature.
Chemical: Usually 1-3 electrons in their outershell, lose their valence electrons easily, form oxides that are basic, good reducing agents, have lower electronegativities.
What are the properties of nonmetals?
Physical: bad conductors of heat and electricity, brittle (if a solid), nonductile, no luster, transparent, solid or liquid or gas at room temp
Chemical: 4-8 electrons in outer shell, gain or share valence electrons easily, form oxides that are acidic, good oxidizing gents.
Which group has exceptions found to e- config?
Transition metals
What are the soft metals?
Alkali metals
See #17 on SG