Cells and Control - Cell Division and Stem Cells
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
Describe cell cycle completely.
Interphase - DNA spread out in long strings. Cell grows and increases amount of subcellular structures. DNA is duplicated and forms X - shaped chromosomes.
Mitosis
Prophase - Chromosomes condense. Membrane around nucleus breaks down, exposing the chromosomes
Metaphase - Chromosomes line up at centre of cell
Anaphase - Spindle fibres pull chromosomes apart. Chromatids pulled to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase - Membranes form around each set of chromosomes, forming 2 nuclei of 2 new cells
Cytokinesis - Before telophase ends, cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to form two separate cells.
Final result: 2 genetically identical daughter cells .
Describe adaptations of the following:
Red blood cell
Nerve cell
Muscle cell
Red blood cell - contains haemoglobin which carries oxygen. Has no nucleus in order to carry more oxygen. Flat disc shape = wider surface area = absorb more oxygen in lungs
Nerve cell - thin and long. Contains fatty myelin sheath that increases speed at which messages can travel
Muscle cell - Look at the photo attached
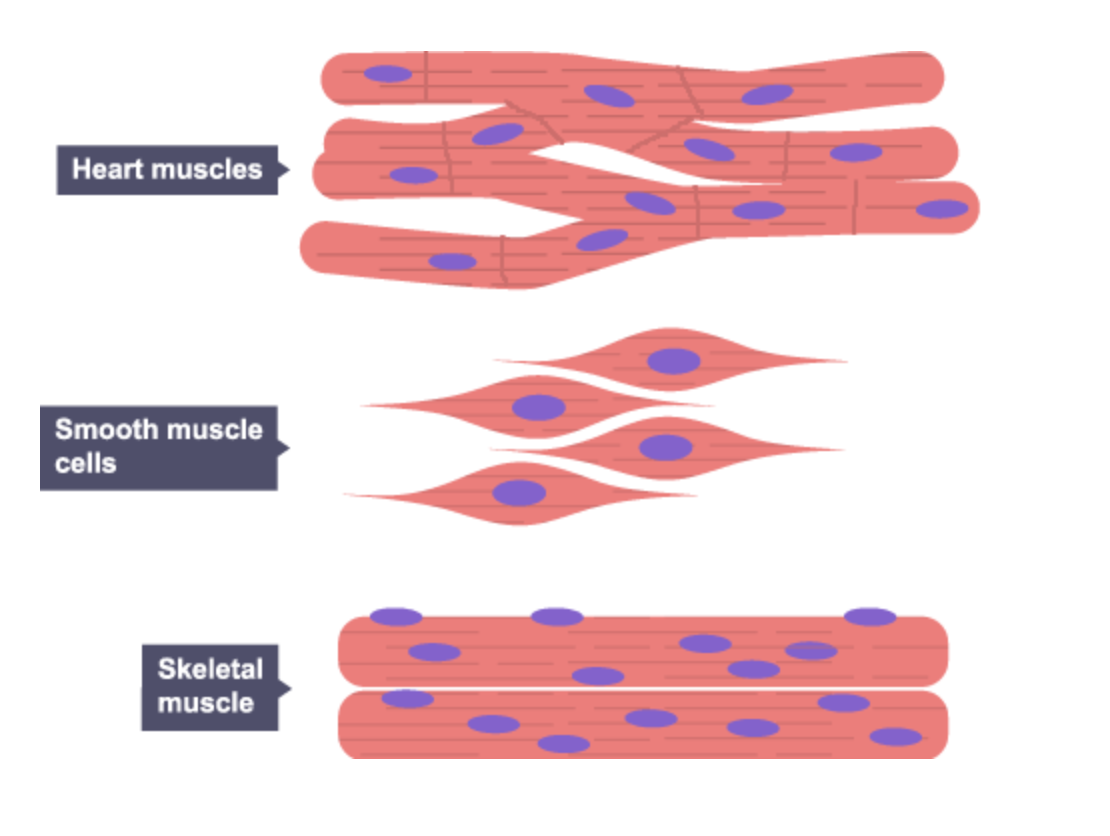
Where are stem cells found?
Early human embryos. Bone marrow. Meristems of plants
Where can stem cells be used in medicine?
Used to treat paralysis. Embryonic stem cells can be used to produce nerve cells to replace damaged spinal tissue in paralysed people.
Used to treat diabetes. Embryonic stem cells used to produce insulin - producing cells, to replace the faulty ones in people with diabetes
Benefits and risks of using stem cells in medicine?
Issues:
Tumour development. Disease transmission. Rejection. Ethical issues.
Benefits:
Can be used in research and to cure diabetes and paralysis.