Periodontal Ligament, Cementum, and Alveolar Bone
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What layers makes up the attachment apparatus?
periodontal ligament, cementum, alveolar bone
What is the periodontal ligament?
ligaments that surround the teeth
What are the functions of the periodontal ligament? (7)
absorbs excess pressure from grinding
allow teeth to float in bony cavity
Supportive
Sensory (pain, pressure)
Nutritive (transport of nutrients)
Formative (formation and maintenance of fibrous and calcified tissue)
Resorptive
Where is the periodontal ligament located and what is its size?
apical to JE, 0.15-0.25 mm wide
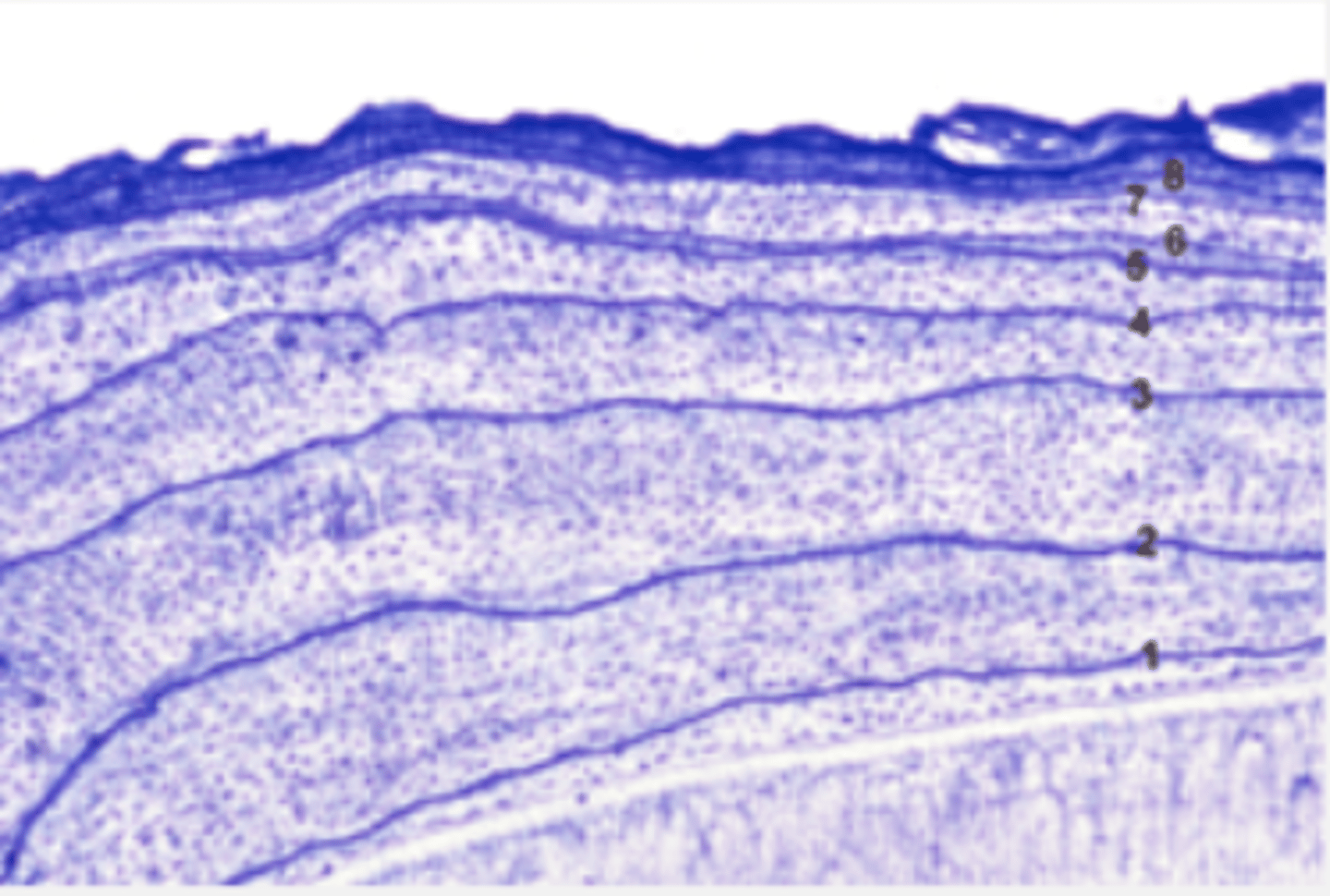
Describe the histologic view of PDL space (purple in picture)
Fibers are not elastic, but elongate with pressure exerted on tooth
Wavy configuration
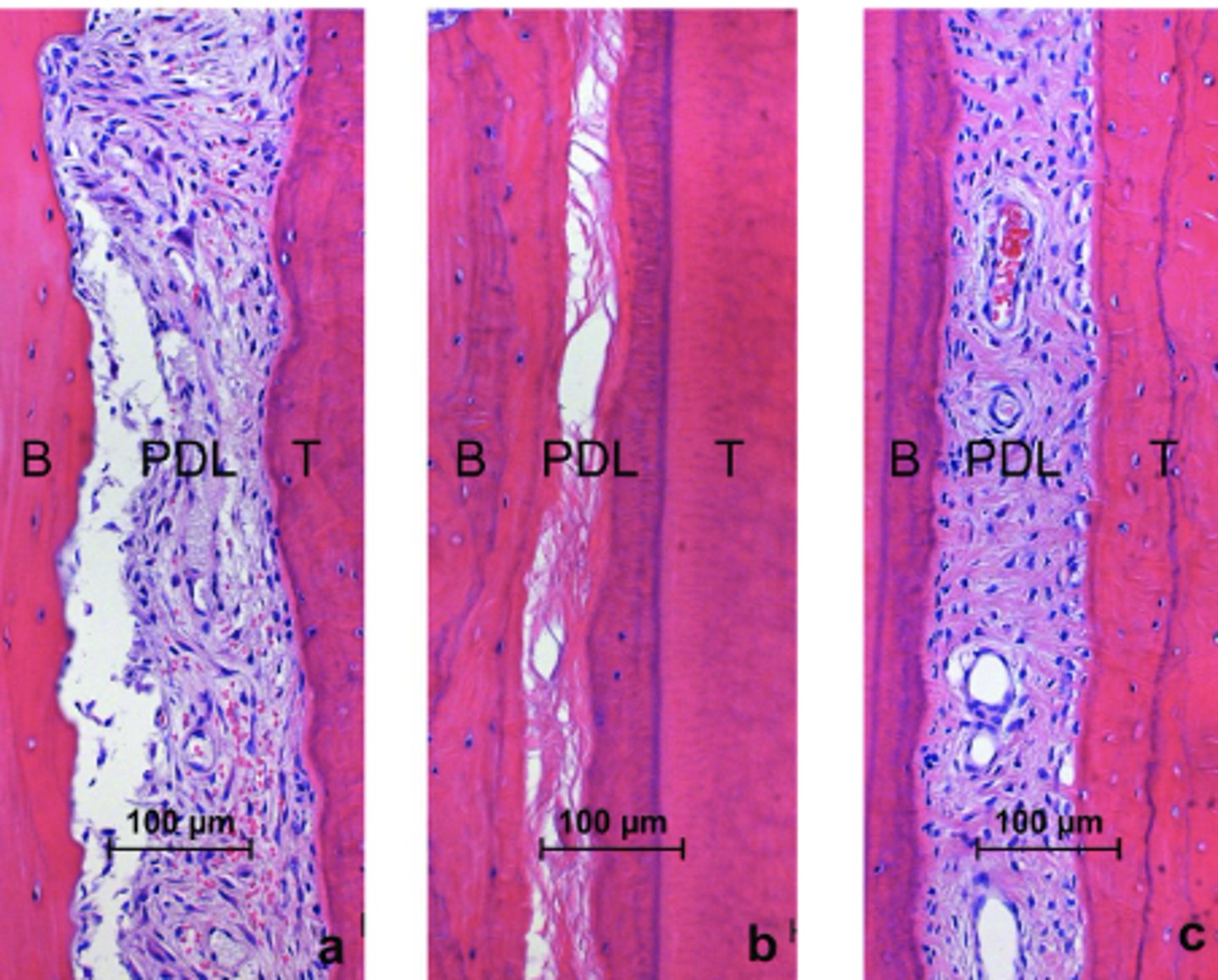
What is the composition of PDL space?
fibers (Those attached to bone and cementum (principal fiber groups))
ground substance, cells
Describe the fibers of the PDL space
heavy fibers that form the basic structure of the periodontal ligament
collagen fibers that have great resistance to forces exerted on teeth (occlusal, proximal, facial/lingual)
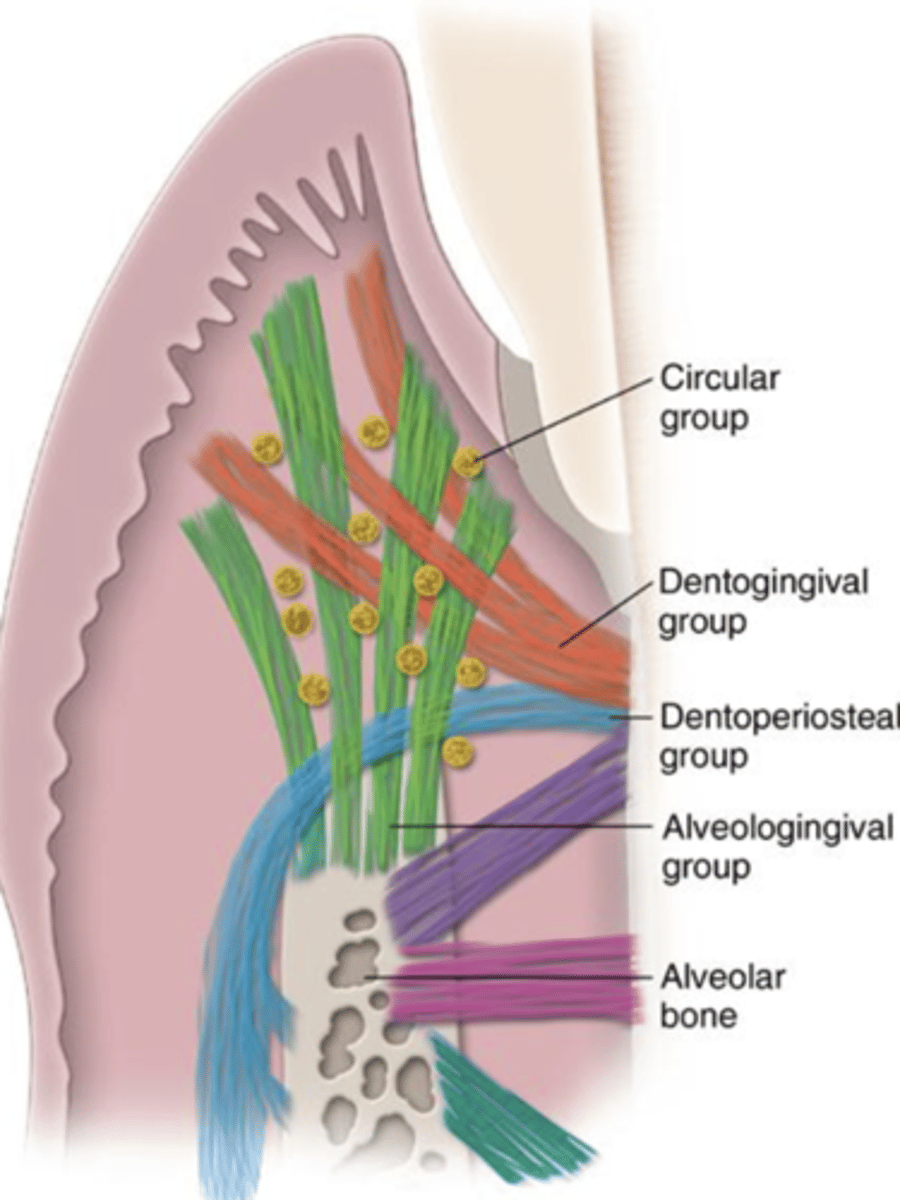
What are the types of principal fiber groups?
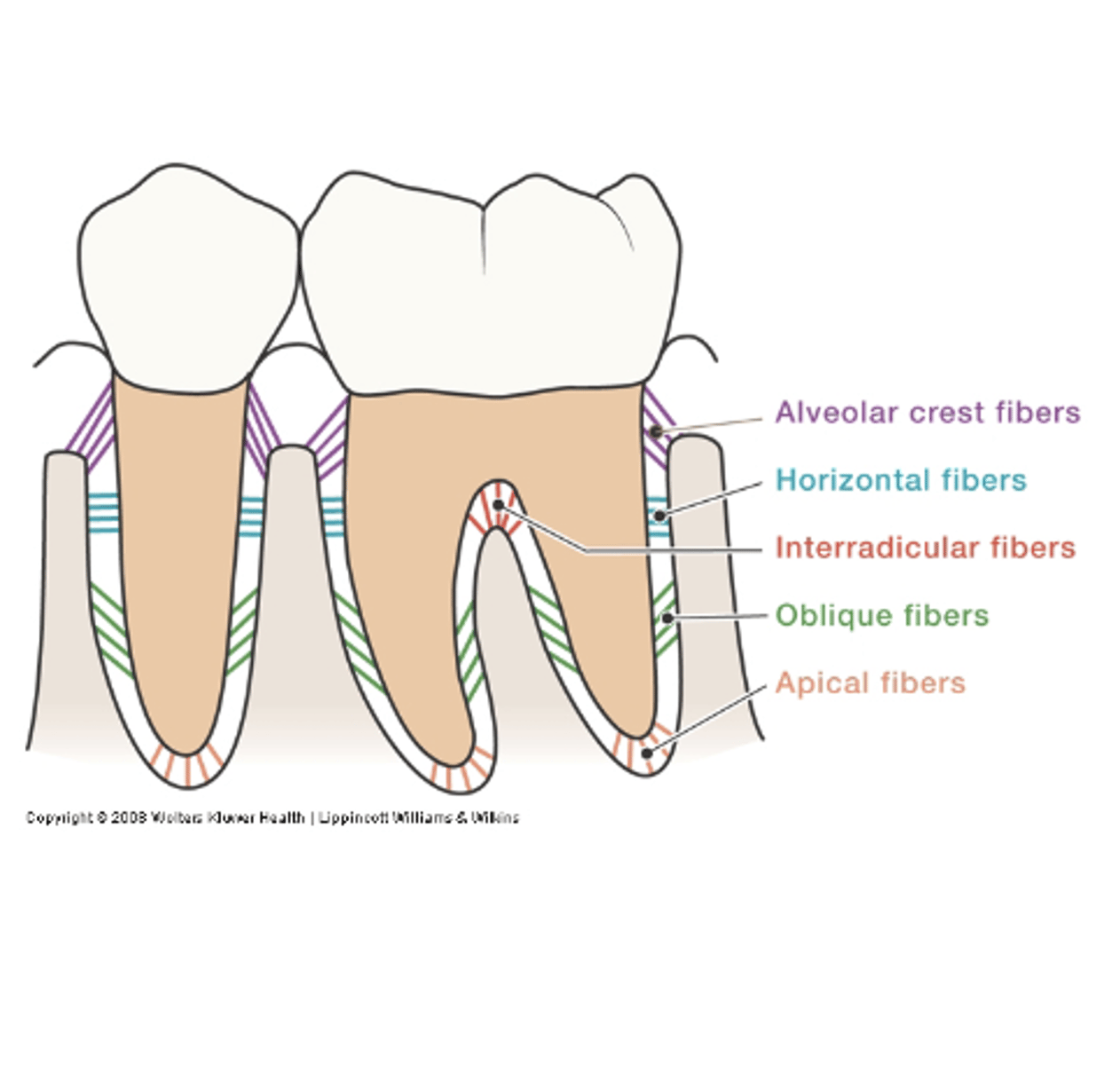
alveolar crest, horizontal, oblique, apical, interradicular, transseptal
Describe the alveolar crest fibers
Run in apical direction
Counterbalance coronal thrust
Describe the horizontal fibers
Horizontal direction
Resist lateral pressures
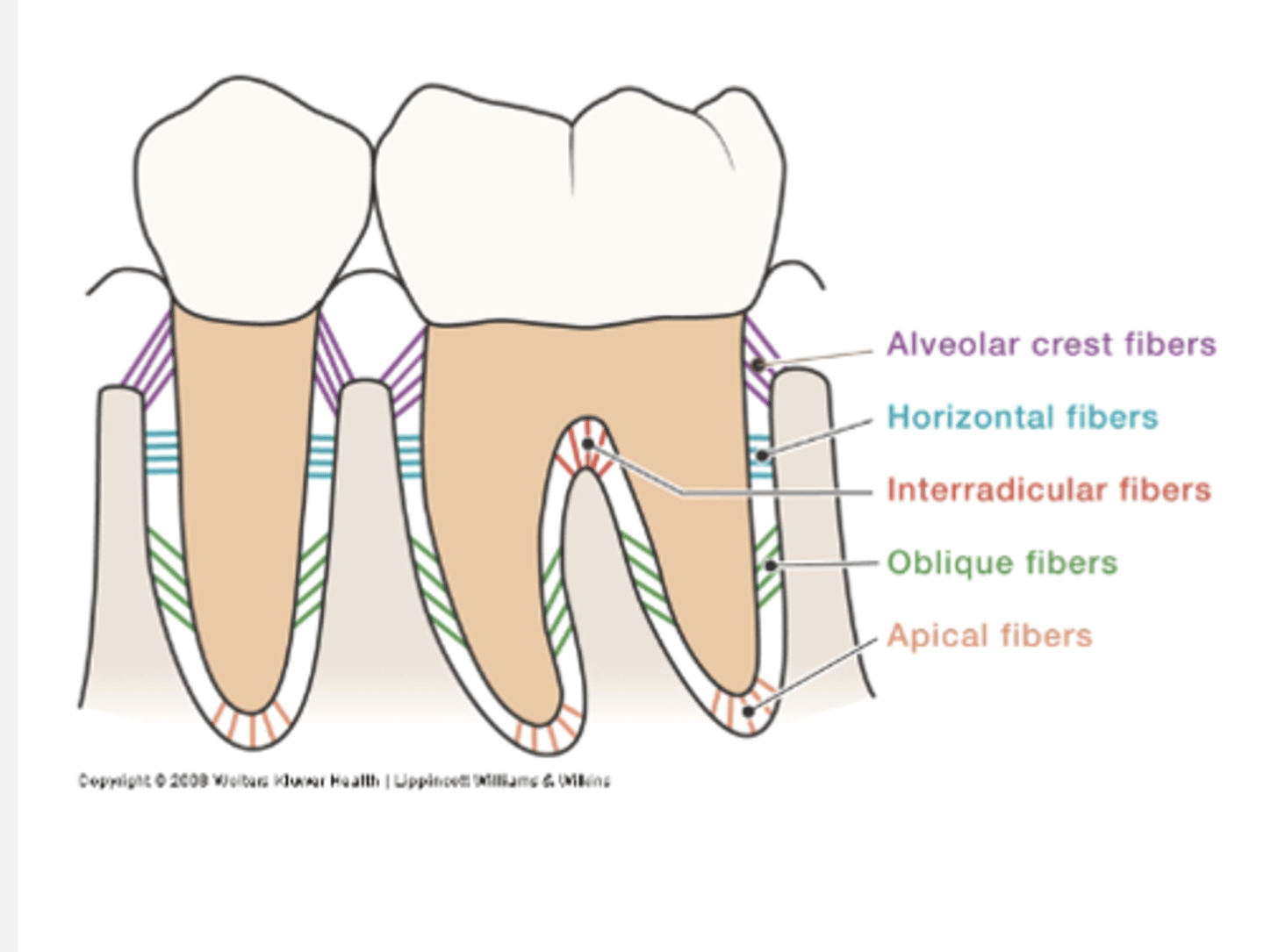
Describe the oblique fibers
Cover 80-85% of cemental surface
Run obliquely
Bear vertical/ apical forces; chewing forces
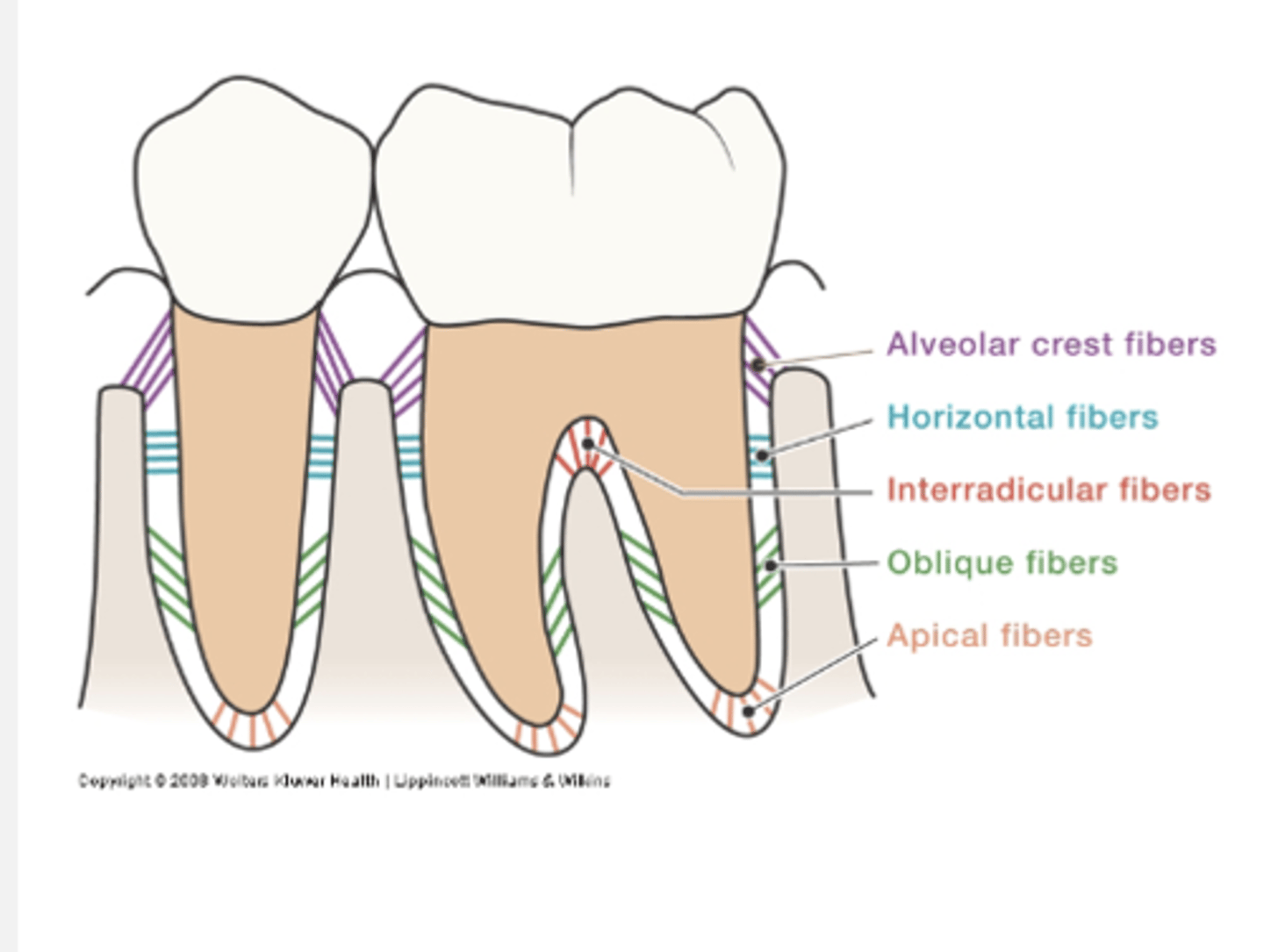
Describe the apical fibers
At apex of root
Resist tilting forces
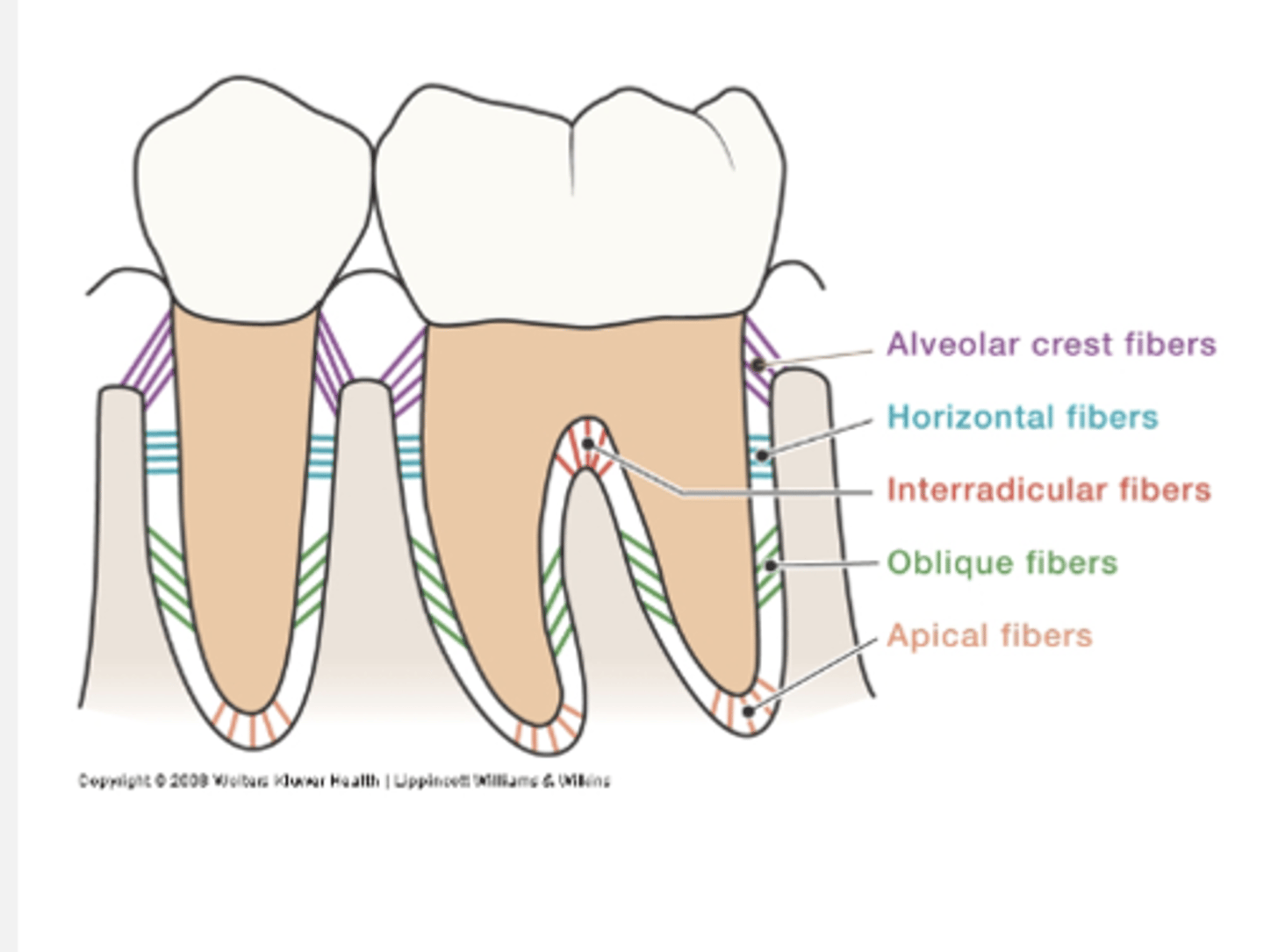
Describe interradicular fibers
only in multi-rooted teeth, between the fibers (In furcations)
Resist tilting forces
Describe the transseptal fibers (extend, imbed, function, considered)
Extend over the alveolar bone crest interproximally
Imbedded into cementum of adjacent teeth to form an interdental ligament
Function to maintain properly aligned teeth and preserve contacts
Considered to be part of the gingival tissues as no osseous attachment
What is the overall function of the PDL fiber groups?
Helps maintain varied forces, for optimal resistance and bone protection
Fibers transform forces into evenly distributed tension on the bone
What are sharpey's fibers and their function?
anchor fibers
Terminal ends of principal fibers (in bone and cementum) outer surface becomes calcified as cementum and bone are formed
Help maintain support because of attachment in bone and cementum
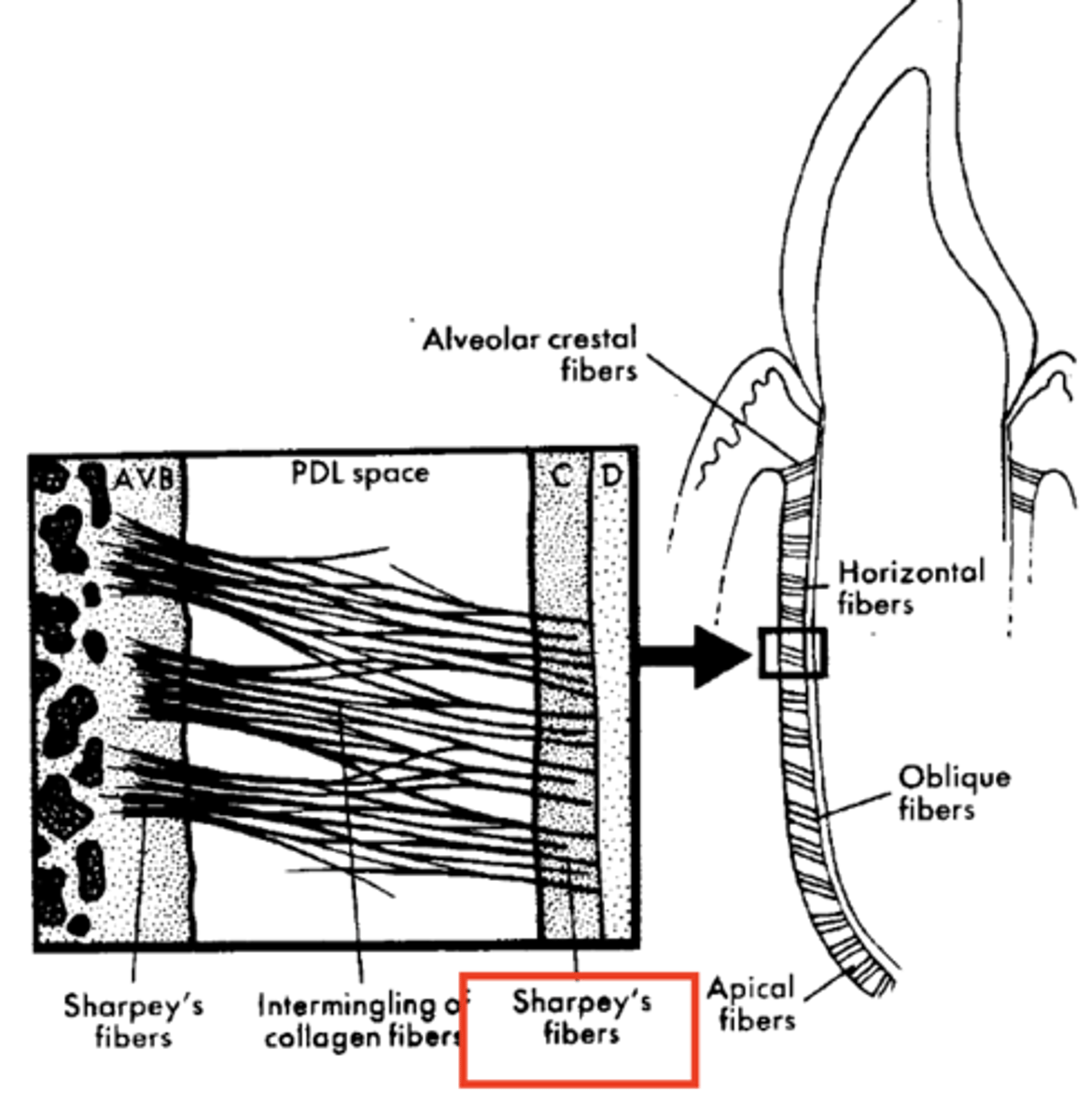
How to blood vessels enter the PDL?
from apex of tooth or bone
What is true when PDL is not intact?
continuous deposition of cementum and bone are not possible
What are the types of cells within the PDL space?
Fibroblasts: both "blast" and "clast" activity
Cementoblasts/clasts
Osteoblasts/clasts
What is the width of the PDL? How does it change over time?
Hourglass shape --> narrow at center of root, thinnest near the middle of the root
mesial thinner than distal
width decreases with age, always remodeling
What is the width of the PDL affected by?
whether or not the tooth is in function/in normal use
not in function: thinner PDL, disorganized
over function: thick/wide PDL
What causes the destruction of PDL? (5)
1. loss of antagonist tooth (not in function)
2. occlusal trauma (over function)
3. periodontal disease
4. recession
5. orthodontic forces
Identify cementum
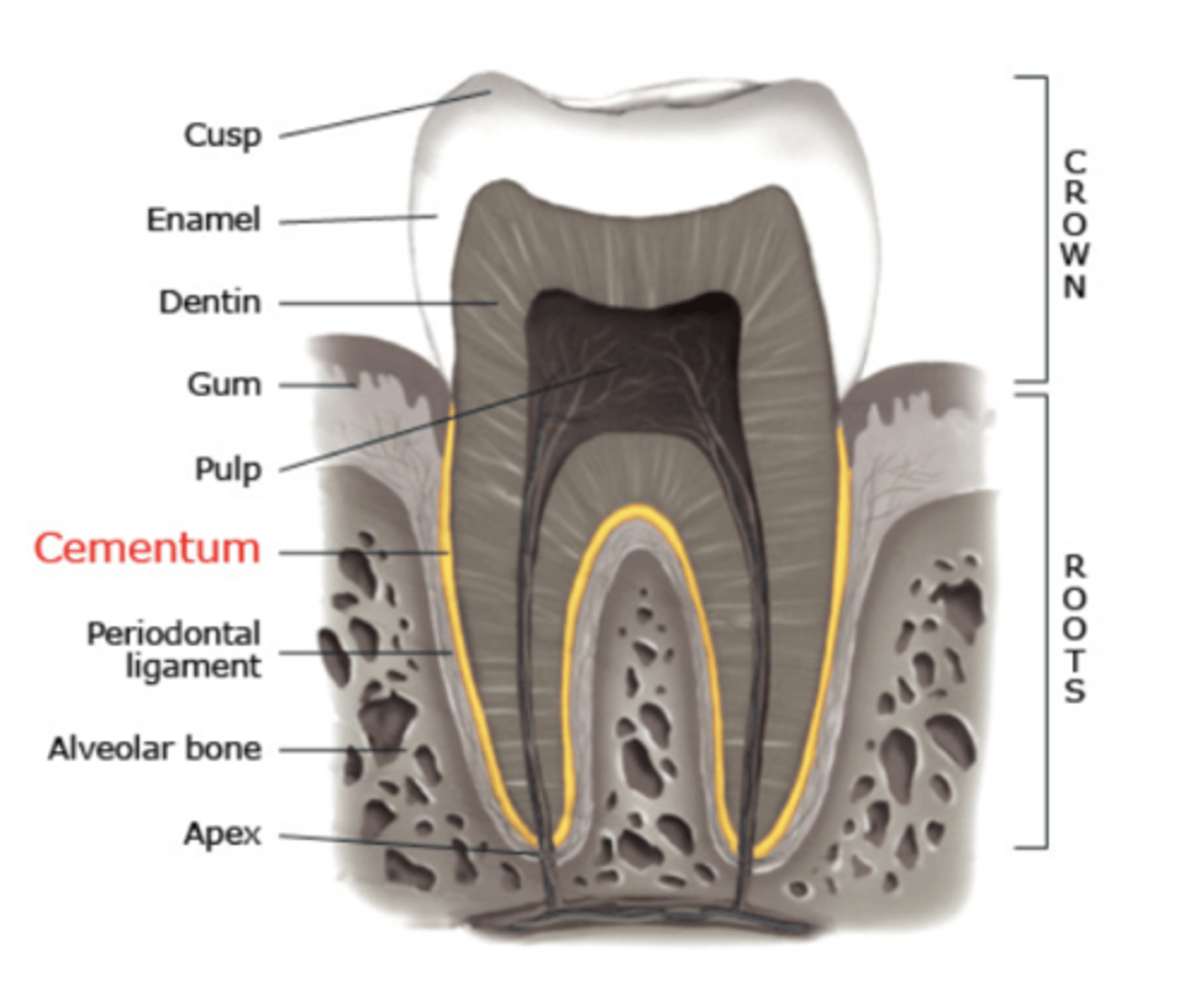
What are the characteristics of cementum? (attachment, color, hardness, types, nutrients)
Overlies and attaches to dentin on the root
Yellow in color
Softer than dentin and enamel --> "bone-like"
2 types:
cellular
acellular
Nutrients from PDL
What are the functions of cementum? (3)
Anchor for Sharpey's fibers (attachment apparatus)
Covers dentin
Compensates for tooth wear and continual eruption
What is the composition of cementum? (%)
50-55 % = organic (fibers and cells)
45-50% = inorganic (hydroxyapatite crystals)
What is the organic fiber content of the cementum?
sharpey's fibers and fibers of the cementum
What is the organic cell content of the cementum?
cementoblasts (forms)
cementoclasts (destroys)
Where is cementum thinnest and what is the width like?
thinnest at CEJ with increasing thickness toward the apex
width is approximately the thickness of a strand of hair
Describe the cementoenamel junctions?
Less than 15 % - cementum overlaps enamel
33% - cementum and enamel do not meet
52-76% - meet end-to-end
Describe the acellular cementum (location, what is it made of, width, what makes it acellular)
located on coronal half
made of mainly sharpey's fibers
thinner and more calcified
no cementocytes which make it acellular
width does not increase with age
Describe the cellular cementum (location, what is it made of, width, what makes it cellular)
located on apical half
made of less Sharpey's fibers
thicker and less calcified
cementocytes present which make it cellular
width does increase with age
What is deposition in regards to cementum?
formation of cementum on root surface (blast cells)
purple is arrest lines that occur in intervals
only adjacent to vital connective tissue
What is the purpose of deposition?
Compensates for tooth eruption
Maintains PDL space
Repair, over lifetime
What is resorption in regards to cementum?
removal of cementum on root surfaces (clast cells)
located in microscopic concavities, usually apical third; clast-cell activity (so- in PDL space)
What is affected by cementum resorption? Describe the process
mostly cementum affected, but dentin could be affected as well
Generally a localized process
Painless
Not a continuous process, but
alternates with repair
What are the causes of cementum resorption? (6)
Occlusal trauma
Orthodontic movement
Malaligned erupting teeth
Cysts/ tumors
Replanted teeth
Periodontal disease
What are the clinical considerations associated with cementum?
1. Exposed cementum - hypersensitivity (recession can lead to this)
2. Periodontal disease process destroys attachment and alters cementum
3. Toothbrush abrasion causes exposed cementum resulting in cemental caries
What are the functions of the alveolar process?
Supports entire dentition
Pathway for nutrients
Deposition to compensate for continuous tooth eruption and wear
What is alveoli?
spaces where root fit in
What is the alveolar bone/process made of? Located?
all bone
alveolar bone proper is adjacent to the root
What are other names for the alveolar bone proper?
cribriform plate
lamina dura (on radiographs)
What is the supporting alveolar bone?
all other bone
includes:
1. cortical plates/bone (compact)
2. trabeculae --> cancellous bone, spongy
What is the occlusal function? (forces being exerted)
affects thickness of cancellous bone
increase occlusal function, increase density and vice versa
What is the periosteum?
can't see clinically, covers cortical plate
dense, fibrous CT that attaches gingiva to bone and contains osteoblasts
highly vascular
What is the organic composition of bone?
35% of composition
fibers: collagen (resist tension, provide support)
cells: osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes
What is the inorganic composition of bone?
hydroxyapatite (calcium, phosphate)
What is the morphology (shape) of bone?
follows position of tooth contacts and contour of roots (influenced by tooth contacts and alignment)
anteriors - peaked
posteriors - blunted
Gingiva follows shape of bone
What is the height of alveolar crest?
height is 1-2 mm apical to cej (normal)
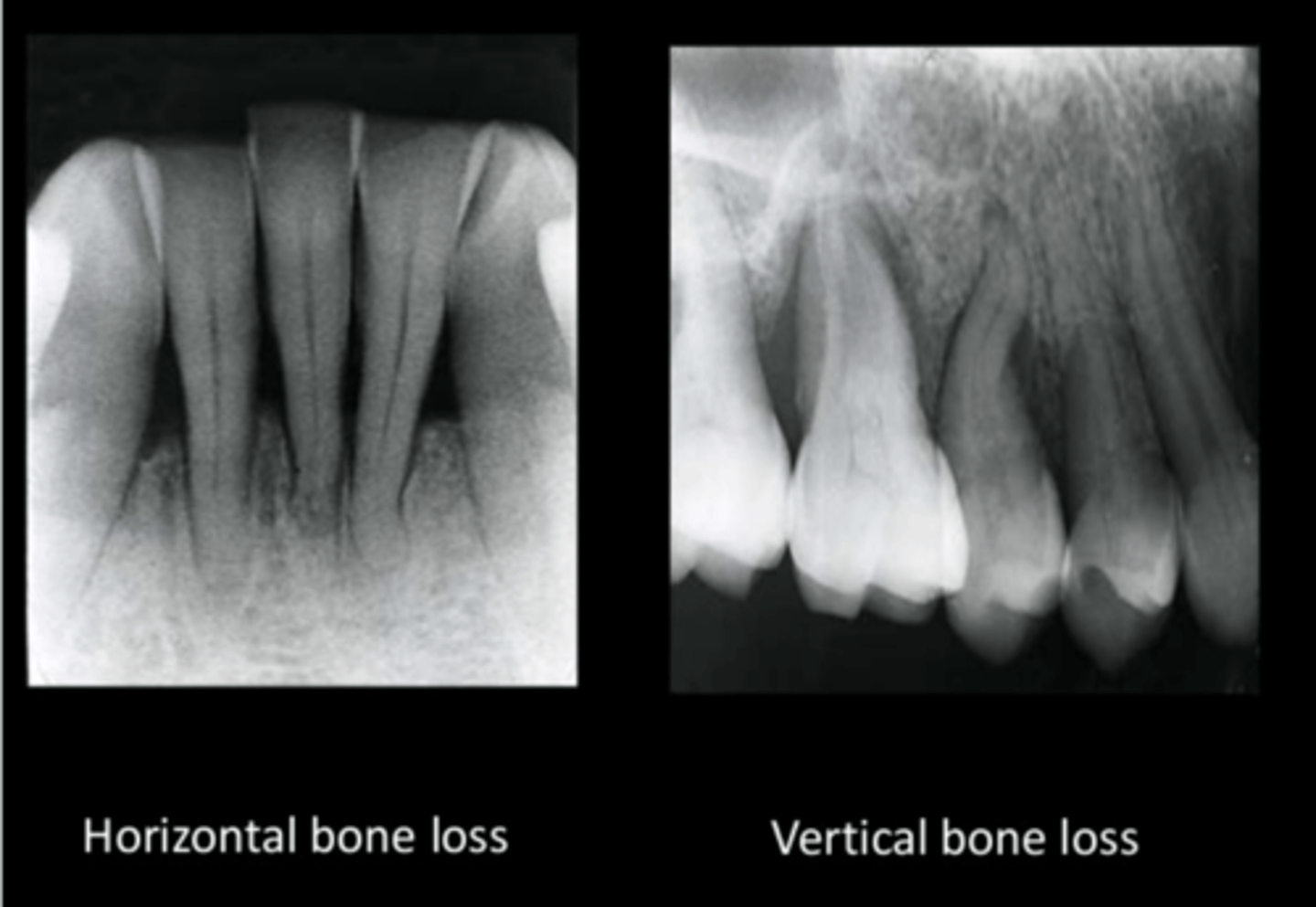
Describe bone loss
Initial bone changes shows crest of bone as fuzzy, not a definite shape
vertical bone loss
horizontal bone loss
What are the bony defects?
dehiscence: cleft in bone
fenestration: hole or window in bone