MC: practice questions (week 2)
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
muscles of hindlimbs, muscles of the trunk, structure/function of forelimb + hindlimb joints, spinal column, clinically important joints, inflammation of joints
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Which hamstring muscle’s primary action is to extend the hip, stifle, & tarsus as well as flex the stifle & is innervated by both the caudal gluteal + ischiatic nerve?
Biceps femoris m.
Which hamstring muscle’s primary action is to flex the stifle & is innervated by the ischiatic nerve?
Semitendinosus m.
Which craniolateral crus muscle’s primary action is to flex the tarsus & is innervated by the fibular/common peroneal nerve?
Peroneus tertius m.
Which stifle muscle’s primary action is to extend the stifle & is innervated by the femoral nerve?
Quadriceps femoris m.
Which muscle’s primary action is to rotate the thigh laterally & is innervated by the obturator nerve?
External obturator m.
What nerve innervates the craniolateral crus muscles?
Fibular/common peroneal nerve
Which craniolateral crus muscle’s primary action is to extend the digits as well as flex the tarsus & is innervated by the fibular/peroneal nerve?
Long digital extensor m.
Which two caudal crus muscles’ primary action is to extend the tarsus & are innervated by the tibial nerve?
Gastrocnemius + Soleus m.
Which two caudal crus muscles’ primary action is to flex the digits/stifle as well as extend the tarsus & are innervated by the tibial nerve?
Deep digital flexor + Superficial digital flexor m.
What are the three main muscles that make up the gluteal (rump) muscles that extend from the ilium to the thigh?
Superficial gluteal m.
Gluteobiceps m.
Middle gluteal m.
Which gluteal (rump) muscle’s primary action is to extend the hip joint as well as extend the stifle/tarsus & is innervated by the caudal gluteal nerve?
Superficial gluteal m.
In ruminants, what two gluteal (rump) muscles fuse to form the gluteobiceps m.?
Superficial gluteal + Biceps femoris m.
Which gluteal (rump) muscle is the largest & most powerful extensor of the hip as well as retractor/abductor of the limb & is innervated by the cranial gluteal nerve?
Middle gluteal m.
What gluteal (rump) muscle blends with the longissimus lumborum m. in the horse to assist in rearing?
Middle gluteal m.
What is the synovial bursa present between the cranial part of the greater trochanter & the aponeurotic attachment of the accessory gluteal m.?
Trochanteric bursa
What is the cause of Whorlbone lameness?
Inflammation of the trochanteric bursa (trochanteric bursitis)
What two hamstring muscles are extra important in the formation of the common calcanean tendon (Achilles tendon)?
Gastrocnemius + Superficial digital flexor m.
If a dog is experiencing partial disruption of the common calcanean tendon, what will the lower limb look like? What about in complete disruption?
Partial: weight bearing on flexed toes
Complete: weight bearing on fully extended toes, hock dropped completely to floor (plantigrade stance)
What are the three main medial muscles of the thigh that are primarily responsible for adduction of the pelvic limbs & are innervated by the obturator nerve?
Gracilis m.
Pectineal (Pectineus) m.
Adductor m.
If there is damage to the obturator nerve, what effect will this have on an animal?
Abduction of hindlimbs (ex: down cow → paralysis)
What three structures make up the femoral triangle?
Femoral artery
Femoral vein
Saphenous nerve
What are the cranial, caudal, & dorsomedial boundaries of the femoral triangle?
Cranial: Sartorius m.
Caudal: Pectineus m. belly
Dorsomedial: Inguinal ligament
If there is damage to the femoral nerve, what effect will this have on an animal?
Inability to extend the stifle (just flexes)
-no sensation on medial surface of the foot
What are the four major tendinous muscles of the crus in the horse that store elastic energy, support joints, & return the leg to position?
Peroneus tertius m.
SDF m.
DDF m.
Interosseous m.
What is the medial (dorsal) tendon branch of the peroneus tertius m. that may be resected in cases of osteoarthritis of the tarsus in horses?
Cunean tendon
In horses, what structure allows for synergistic/simultaneous movement between the stifle & the hock?
Reciprocal apparatus
-peroneus tertius m./third fibular m. plays important role in it
How would a ruptured/torn peroneus tertius tendon affect a horse?
Hock will overextend
-stifle joint flexes independently from the hock joint (in health, they should move simultaneously)
The term “Pes” is used for which specific part of the animal body?
Lower part of the hindlimb
What craniolateral crus muscle flexes the tarsus only?
Cranial tibial m.
The __________ nerve innervates most of the medial thigh adductor muscles.
Obturator
What structures form the borders of the abdominal cavity?
Lateral/ventral: abdominal muscles
Dorsal: thoracolumbar/sacral vertebra
Caudal: pelvic girdle
What are the important muscles of the abdominal cavity as well as their topography?
(Most superficial) External abdominal oblique m. → caudoventrally
Internal abdominal oblique m. → cranioventrally
Rectus abdominis m. → craniocaudally
(Deepest) Transversus abdominis m. → dorsoventrally
What abdominal muscle extends from the ribs & thoracolumbar fascia, & its fibers travel caudoventrally to the ventral midline?
External abdominal oblique m.
What is the rectus sheath?
Wrapping around the rectus abdominis m.
What structure separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity?
Diaphragm
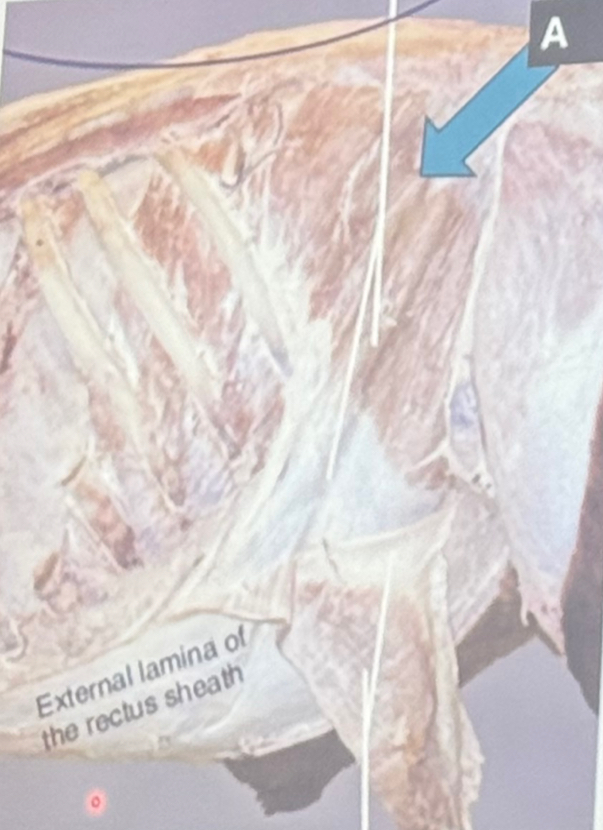
Identify the structure labelled A.
Internal abdominal oblique m.
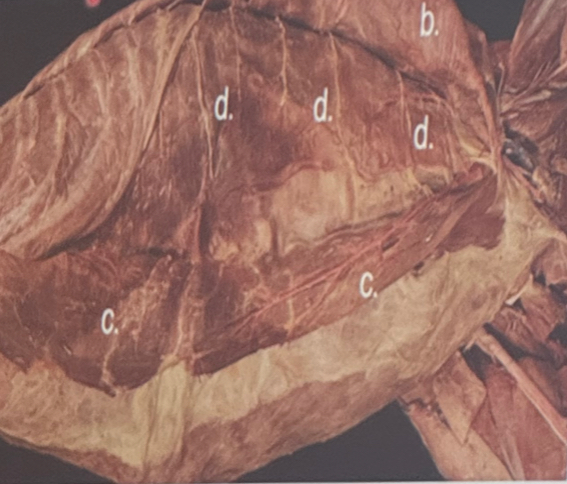
Identify the structure labelled D.
Transversus abdominis m.
What structures form the linea alba (raphe)?
Aponeurosis of abdominal muscles
What structures form the external rectus sheath?
External abdominal oblique m. + internal abdominal oblique m.
What are the important vessels that supply the abdominal wall?
Cranial abdominal artery
Deep circumflex artery
Cranial + caudal epigastric arteries
Cranial + caudal superficial epigastric arteries
What abdominal vessel vascularizes the caudo-dorsal quadrant of the abdominal wall?
Deep circumflex iliac artery
What spinal nerve in bovine courses along the tips of the transverse process of L2?
Iliohypogastric n.
What are the nerves that innervate the paralumbar fossa in ruminants?
T13: costoabdominal
L1: iliohypogastric
L2: ilioinguinal
L3: genitofemoral
What forms the cranial border of the paralumbar fossa?
Last rib
What paravertebral nerve block targets nerves close to where they immerge from their respective intervertebral foramina?
(a) or Farquharsen paravertebral nerve block
What is the result of expansion of the thoracic cage/walls & contraction of the diaphragm?
Increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity
What are the muscles of inspiration in the thoracic cavity?
Scalenus m.
Serratus dorsalis cranialis m.
External intercostal m.
What are the muscles of expiration in the thoracic cavity?
Serratus dorsalis caudalis m.
Internal intercostal m.
What is the direction of the muscle fibers that produce inspiration?
Caudoventral
What is the direction of the muscle fibers that produce expiration?
Cranioventral
What two large arteries travel along the ventral surface of the thoracic cavity & supply the ventral portion of the thoracic wall?
Internal thoracic arteries
How are joints in dogs primarily classified?
By function & structure
What is an example of a fibrous joint in dogs?
Suture in the skull
_________ joints have a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid & are the most __________ type of joint in dogs.
Synovial, movable
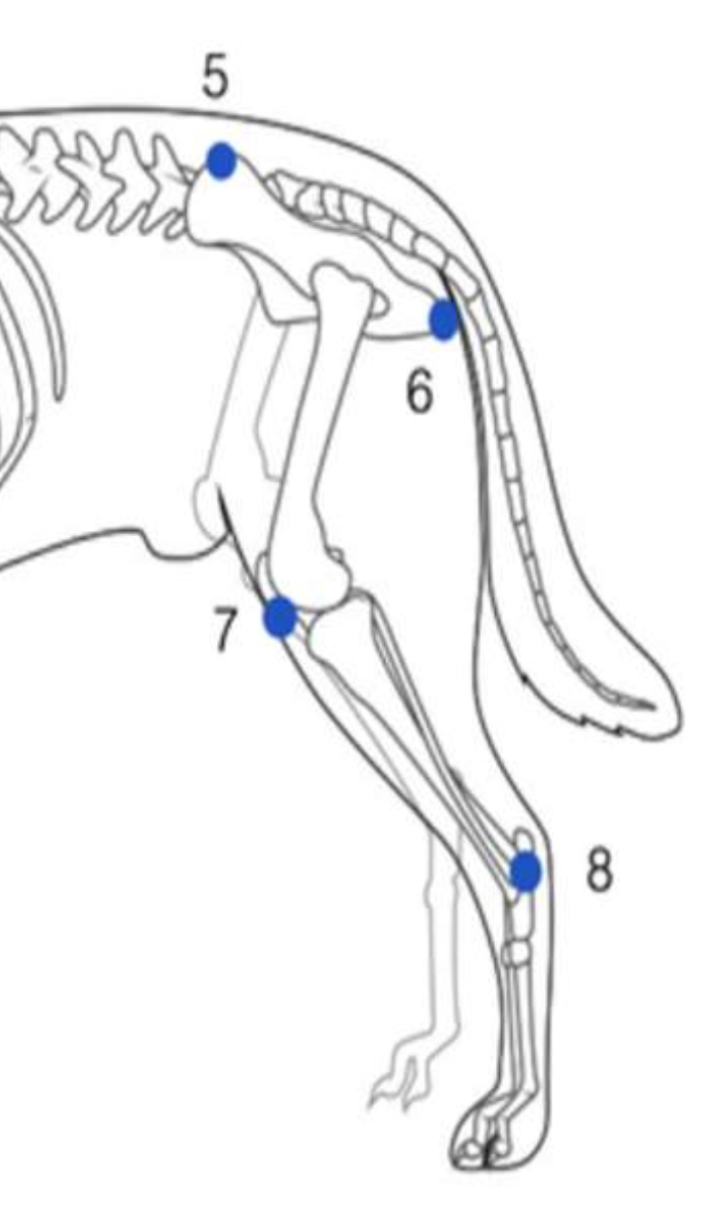
Identify the hindlimb joints indicated by numbers 7 & 8 respectively.
7: stifle/genual joint
8: hock/tarsal joint
The flexor surface of the stifle joint is located on the _______side of the joint.
Caudal
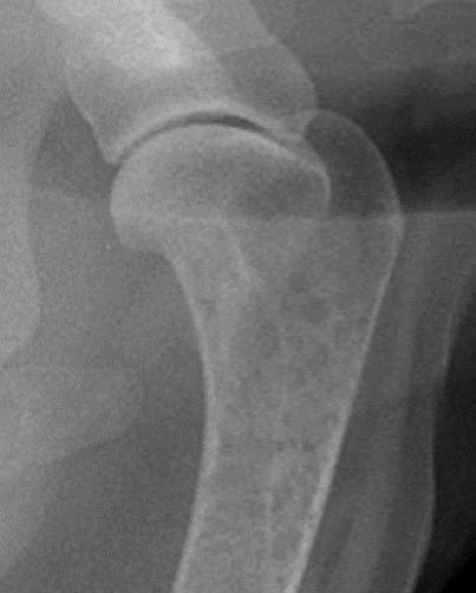
What type of joint is shown in this radiograph?
Simple Synovial joint
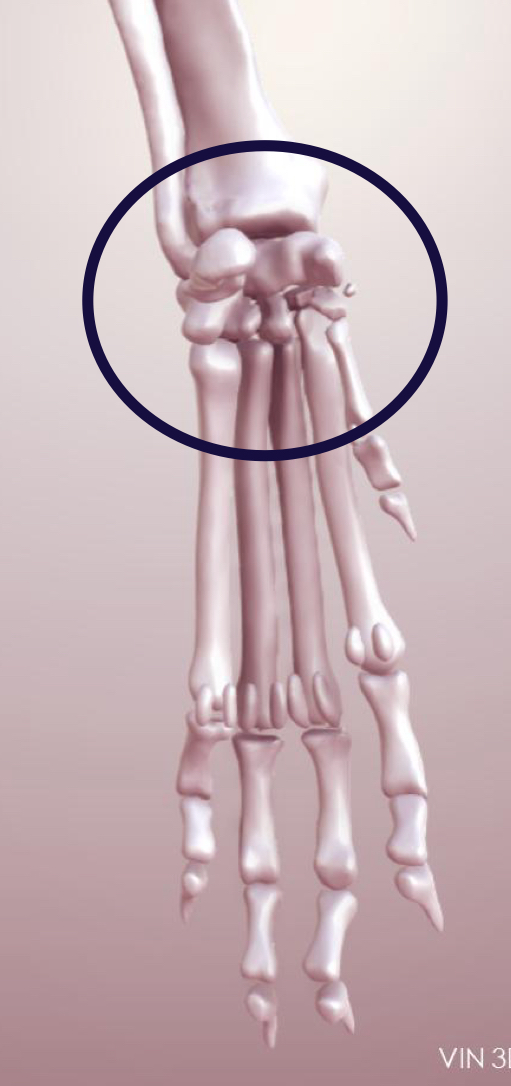
What type of joint is in this photo?
Compound Synovial joint (carpal joint)
What joint is otherwise known as the metacarpophalangeal joint in horses?
Fetlock joint
What joint is otherwise known as the proximal interphalangeal joint in horses?
Pastern joint
What joint is otherwise known as the distal interphalangeal joint in horses?
Coffin joint
What feature of the humerus allows gliding movements & helps to absorb shock absorption in horses?
Larger head of humerus than glenoid cavity
What structure extends from the glenoid lip to the neck of the humerus & is an extension of the shoulder joint in dogs, but an isolated cavity in horses?
Bicipital bursa
Which ligament holds the tendon of the biceps brachii m. in the intertubercular groove on the proximal end of the humerus?
Transverse humeral ligament
Atrophy of which muscles/active ligaments render the shoulder unstable?
Supraspinatus + Infraspinatus m.
-also damage to suprascapular nerve
What ligament secures the head of the femur to the acetabulum & is unique to horses?
Accessory ligament
What feature is always present in all synovial joints?
Articular capsule
What is an additional feature of a synovial joint?
Ligament
Which bones join to form the elbow/cubital joint (compound synovial condylar joint/hinge joint)?
Distal humerus + Proximal radius + Proximal ulna
Which type of ligaments stabilize the joint & limit movement to ONLY flexion + extension?
Collateral ligaments
Which ligament of the elbow/cubital joint prevents hyperflexion?
Olecranon ligament (elastic)
Which ligament of the elbow/cubital joint prevents hyperextension?
Oblique ligament
Which collateral ligament of the elbow/cubital joint in the horse is a component of the stay apparatus?
La
Which bones make up the carpal joint (compound synovial/hinge joint) in the dog?
Distal radius/ulna + 7 carpal bones + 5 metacarpal bones
Which bones make up the carpal joint (compound synovial/hinge joint) in the horse?
Distal radius + 7 carpal bones + 3 metacarpal bones
Which carpal joint cavity is most movable (opens widest upon flexion) but is isolated?
Antebrachiocarpal joint cavity
Which carpal joint cavities communicate with each other?
Middle carpal + Carpometacarpal joint cavities
Which ligaments are very important for stabilization of the accessory carpal bone?
2 accessory metacarpal ligaments
What feature prevents hyperextension of the carpus in the horse?
Palmar carpal ligament
-also shape of bones involved & flexor muscles of the carpus
Which bones make up the fetlock/metacarpophalangeal/metatarsophalangeal joint (compound synovial/hinge joint)?
Distal 3rd metacarpal (cannon bone) + Proximal 1st phalanx + Proximal sesamoid bones
What is the most stressed & frequently damaged joint of equine limbs?
Fetlock joint
What is the major proximal sesamoidean ligament that prevents hyperflexion of the fetlock joint?
Interosseus muscle (suspensory ligament)
What is the unpaired middle sesamoidean ligament that provides a smooth gliding surface for the digital flexor tendons?
Intersesamoidean ligament (proximal scutum)
What are the paired middle sesamoidean ligaments that hold the sesamoid bones in place?
Collateral sesamoidean ligaments
What is the unpaired distal sesamoidean ligament that prevents hyperextension of both the fetlock & pastern?
Straight (superficial) sesamoidean ligament
Which bones make up the pastern/proximal interphalangeal joint (simple synovial saddle joint)?
Distal proximal phalanx + Proximal middle phalanx
Why is the pastern joint called the Middle Scutum?
Fibrocartilage provides a gliding surface for the DDF tendon
What two structures prevent buckling forward of the pastern joint when the foot hits the ground?
Oblique sesamoidean ligament of fetlock + Superficial digital flexor tendon
Which bones make up the coffin/distal interphalangeal joint (compound synovial/hinge joint)?
Distal middle phalanx + Proximal distal phalanx
What ligament of the coffin joint extends from the proximal phalanx to the cartilage?
Chondrocompedal ligament
What ligament of the coffin joint extends from the middle phalanx to the cartilage?
Chondrocoronal ligament
What ligament of the coffin joint extends from the distal phalanx to the cartilage?
Chondroungular ligament
What synovial bursa lies between the navicular bone & the Deep Digital Flexor tendon?
Navicular bursa
What ligaments of the distal limb wrap around the flexor tendons & other ligaments on the palmar/plantar surface of the manus/pes?
Annular ligaments
What is the annular ligament that supports the fetlock joint?
Palmar annular ligament
What is the annular ligament that supports the long pastern & pastern joint?
Proximal digital annular ligament
What is the annular ligament that supports the coffin joint?
Distal digital annular ligament
What occurs when the interosseus muscle ruptures?
Fetlock sinks
What occurs when the superficial digital flexor tendon ruptures?
Fetlock sinks slightly, not fully grounded
What occurs when both the digital flexors & interosseus muscle ruptures?
Complete grounding (collapse) of fetlock