Quiz 4
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
1
New cards
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
-nucleic acid (polymer)
-macromolecule
-nucleic acid (polymer)
-macromolecule
2
New cards
central dogma
DNA is transcribed to RNA; RNA is translated to proteins
DNA --> RNA --> proteina
DNA --> RNA --> proteina
3
New cards
nuclear DNA (nDNA)
found in the nucleus
4
New cards
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
found in the mitochondria
5
New cards
supercoiling
DNA is packed by this process, wound tightly around histones to form nucleosomes
6
New cards
histones
offer level of protection to DNA
7
New cards
chromatin
densely packed DNA found in the nucleolus of nucleus
8
New cards
human karyotype
consists of 22 matched pairs of autosomes (non-sex cells) and a pair of two sex chromosomes (XX-F and XY-M)
9
New cards
genome
complete set of instructions for making an organism (entire DNA within cell), consists of DNA in all of its chromosomes
10
New cards
functions of genome
-complete set of genetic information
-includes coding DNA (exons- extrovert/express)
-non-coding DNA (introns- introvert/no express)
-includes coding DNA (exons- extrovert/express)
-non-coding DNA (introns- introvert/no express)
11
New cards
genes
genetic information that is coded and packaged
12
New cards
genotypes
set of genes
13
New cards
phenotypes
observable characteristics
14
New cards
hybridization
DNA is linked together
15
New cards
nucleotide
individual unit (building block) of DNA, pair with complementary base via hydrogen bonds (A --> T (U) double bond) (G --> C triple bond)
16
New cards
nucleotide components
-pentose sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA)
-nitrogenous base (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine-DNA ; Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil- RNA)
-phosphate group
-nitrogenous base (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine-DNA ; Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil- RNA)
-phosphate group
17
New cards
nucleoside components
-nitrogenous base
-pentose sugar
**bases and pentose sugars are heterocyclic compounds
-pentose sugar
**bases and pentose sugars are heterocyclic compounds
18
New cards
Nitrogenous base
4 possibilities at each position (A, G, C, or T)
- trillions of combinations are possible
- ** the info content in the DNA is encoded in the order
(sequence) of the bases **
ex: cats --> scat, snn, cell #
- trillions of combinations are possible
- ** the info content in the DNA is encoded in the order
(sequence) of the bases **
ex: cats --> scat, snn, cell #
19
New cards
dATP
deoxyadenosine 5'-triphosphate or deoxyadenylate
20
New cards
gametes
or germ cells (egg or sperm) have haploid or single set of chromosomes
21
New cards
somatic: body cells
any cell other than germ cell
22
New cards
haploid cells
3 picograms, one set of chromosomes, n
23
New cards
diploid cells
6 picograms, two sets of chromosomes, 2n
24
New cards
RNA
carries messages encoded in DNA sequence to the cytoplasm (specifically mRNA) since DNA cannot leave nucleus, proteins are translated in cytoplasm
25
New cards
forms of RNA
-ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
-messenger RNA (mRNA)
-transfer RNA (tRNA)
-microRNA (miRNA)
-messenger RNA (mRNA)
-transfer RNA (tRNA)
-microRNA (miRNA)
26
New cards
microRNA
(miRNA) small non-coding RNA and can be used for body fluid identification (tissue specific), HTS (sequencing) of miRNA of interest and comparison to reference
27
New cards
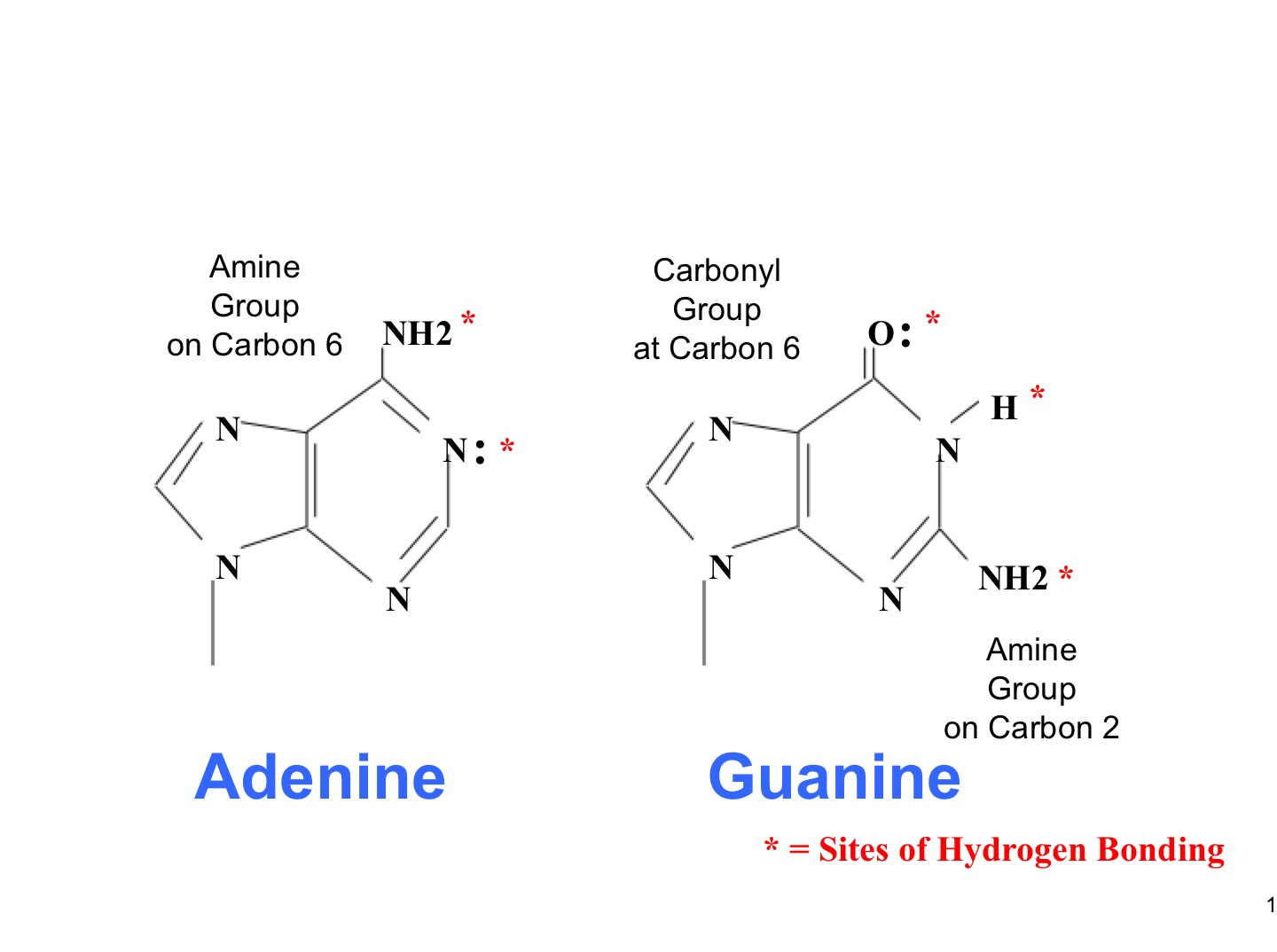
purine
Adenine and Guanine
have a double-ring structure with six-carbon ring fused to five-carbon ring
have a double-ring structure with six-carbon ring fused to five-carbon ring
28
New cards
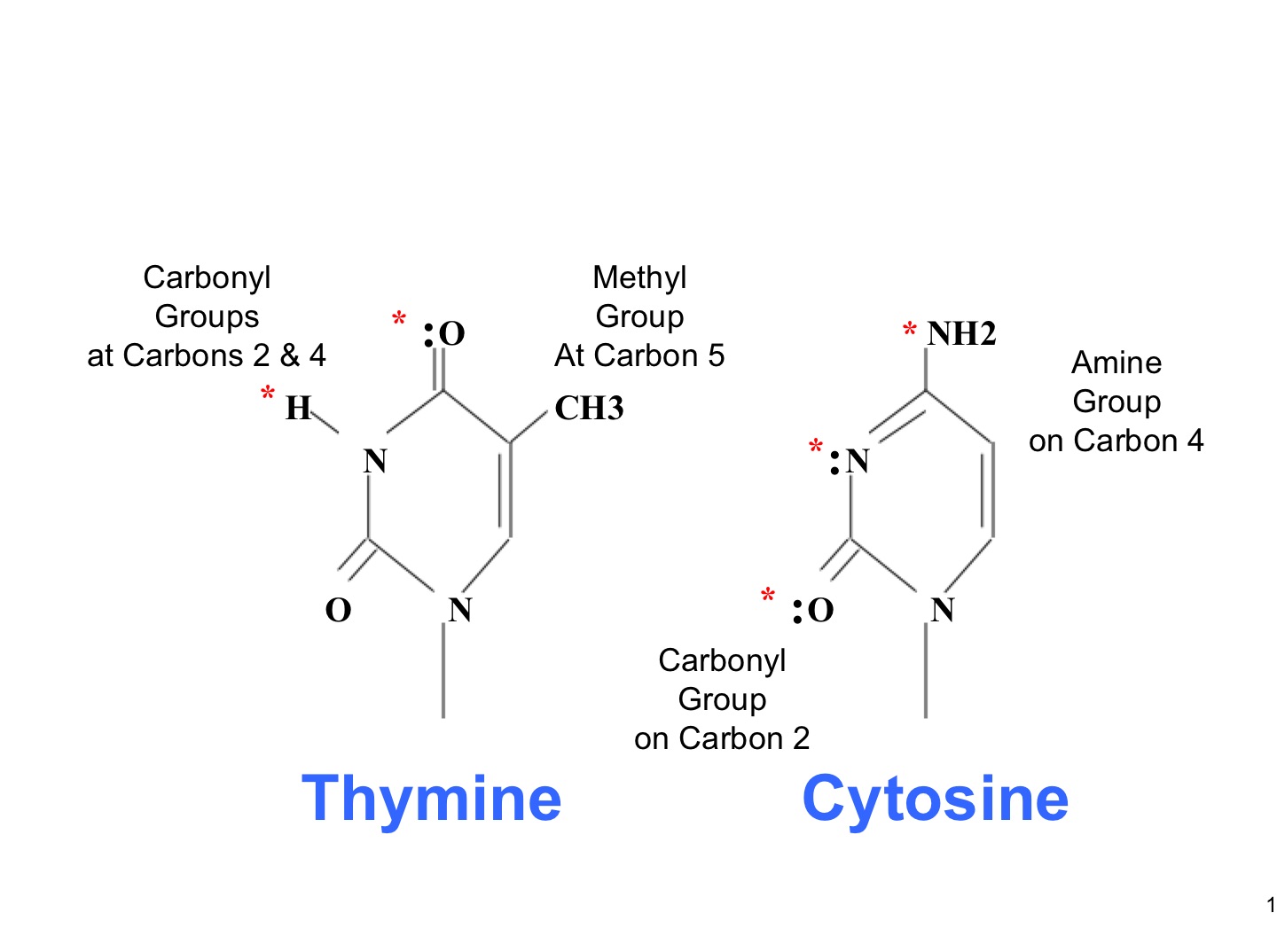
pyrimidine
Cytosine and Thymine
smaller bases that only have a six-carbon ring structure
smaller bases that only have a six-carbon ring structure
29
New cards
gene locus
specific location on a chromosome where a coding region exists (in forensic science look at non-coding region)
singular- locus
plural- loci
singular- locus
plural- loci
30
New cards
allele
form of the gene locus or an alternate form of a gene***
***bolded in notes
# of repeats exhibited in a particular STR marker, resulting in different length
***bolded in notes
# of repeats exhibited in a particular STR marker, resulting in different length
31
New cards
homozygote
two copies of the same allele or form of the gene locus, individual has two alleles of the name # of repeats, both alleles same length
32
New cards
heterozygote
different alleles or forms of the gene locus, individual has two alleles with different # of repeats, alleles differ and can be resolved from one another
33
New cards
STR
short tandem repeat
regions of DNA that are repeated (typically in non-coding region)
single stranded DNA
regions of DNA that are repeated (typically in non-coding region)
single stranded DNA
34
New cards

locus
specific STR marker
35
New cards
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
(RFLP) early technology, required a lot of DNA and high quality DNA to work (started with this analysis technology)
Dr. Alex Jeffries ?
Dr. Alex Jeffries ?
36
New cards
HLA DQA1
(reverse dot blot SNP assay) first PCR-based technology, the later addition of Polymarker (PM) made the technique more discriminatory
37
New cards
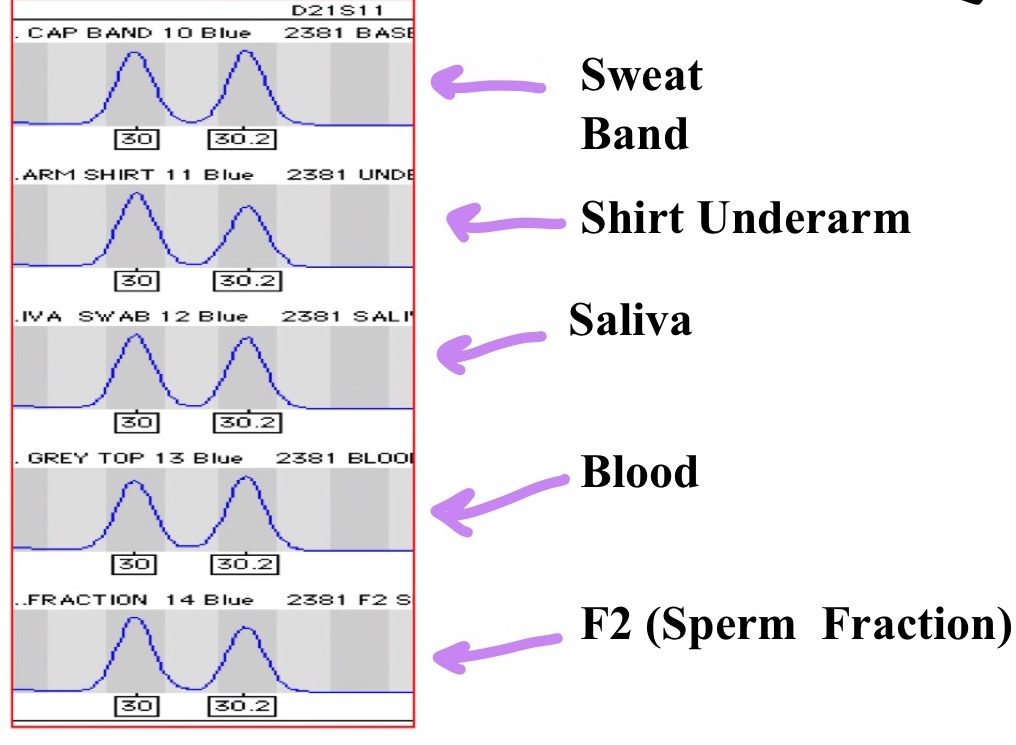
STR analysis
more discriminatory, faster, requires less DNA, can analyze degraded samples; autosomal
38
New cards
challenges of DNA rape case
-mixtures must be resolved
-DNA is often degraded
-inhibitors to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) are often present- heme can be an inhibitor
-DNA is often degraded
-inhibitors to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) are often present- heme can be an inhibitor
39
New cards
forensic cases
matching suspect with evidence
40
New cards
paternity testing
identifying father
41
New cards
mass disasters
putting pieces back together
42
New cards
human identity testing
-forensic cases
-paternity testing
-historical investigations
-missing persons investigations
-mass disasters
-military DNA "dog tag"
-convicted felon DNA databases
-paternity testing
-historical investigations
-missing persons investigations
-mass disasters
-military DNA "dog tag"
-convicted felon DNA databases
43
New cards
Y-STR analysis
Y chromosome, number of male contributors, paternal inheritance
44
New cards
mtDNA features
shape: circular
genetic alphabet: 16,569 base pairs
copies per cell: 100's-1000's
inherited: 100% mother
location in cell: mitochondrion
unique: no
genetic alphabet: 16,569 base pairs
copies per cell: 100's-1000's
inherited: 100% mother
location in cell: mitochondrion
unique: no
45
New cards
nucDNA features
shape: linear
genetic alphabet: ~3 billion base pairs
copies per cell: 2
inherited: 50% mother, 50% father
location in cell: nucleus
unique: yes
genetic alphabet: ~3 billion base pairs
copies per cell: 2
inherited: 50% mother, 50% father
location in cell: nucleus
unique: yes
46
New cards
nuclear and mtDNA specimen type
-blood
-tissue
-hair (w/ root)
-fresh bone/teeth
-body fluids
-stamps/envelopes
-tissue
-hair (w/ root)
-fresh bone/teeth
-body fluids
-stamps/envelopes
47
New cards
mtDNA only specimen types
-skeletal remains (not flesh)
-hair shafts
-fingernails
-hair shafts
-fingernails
48
New cards
steps in DNA (STR) analysis
1) extraction
2) quantification
3) amplification
4) separation
5) analysis and interpretation
6) report conclusions (and statistics)
ADD CHART
2) quantification
3) amplification
4) separation
5) analysis and interpretation
6) report conclusions (and statistics)
ADD CHART
49
New cards
extraction
isolate DNA
50
New cards
quantification
how much DNA is in extract
51
New cards
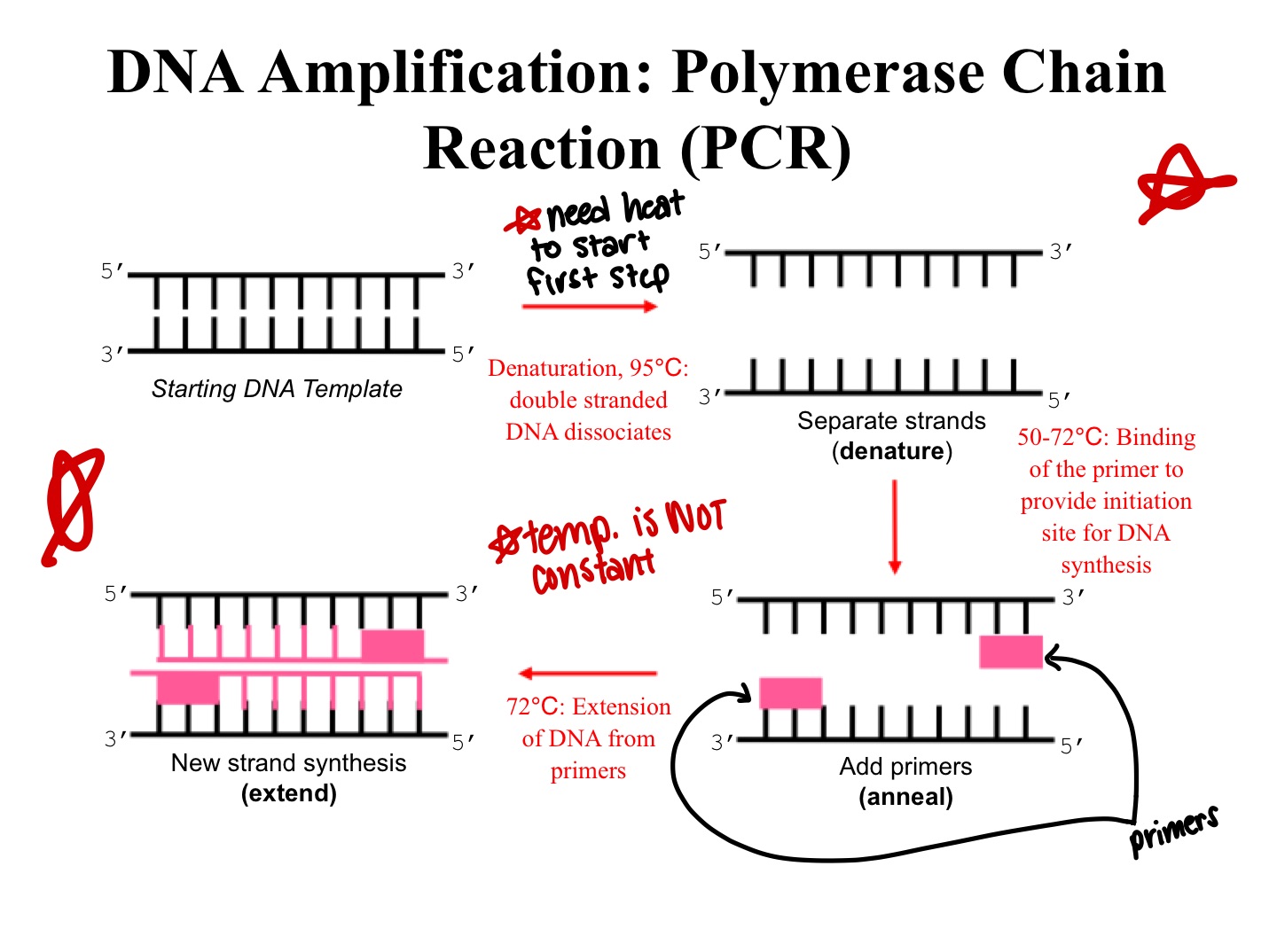
amplification
make many copies of DNA sample (at different STR markers) for analysis, polymerase chain reaction is used
52
New cards
separation
(capillary electrophoresis) separate DNA fragments
53
New cards
interpretation
determine DNA profile of a sample by analyzing electropherogram from the Capillary Electrophoresis
54
New cards
statistics
IF MATCH, is there reference to profile and/or database
55
New cards
Human nuclear DNA is not found in which of what cell type?
red blood cells
56
New cards
impurities
-protein
-ionic species
-compounds
-cell debris
-carbohydrate
-internal cellular structures
-ionic species
-compounds
-cell debris
-carbohydrate
-internal cellular structures
57
New cards
steps for isolation of DNA
1) open organism/ cell that contains DNA
2) separation of DNA from other cellular components
2) separation of DNA from other cellular components
58
New cards
organism/cell with DNA
-any human biological specimen
-non-human biological specimen
-plants, seeds, leaves
-microbial specimen (terrorism)
-non-human biological specimen
-plants, seeds, leaves
-microbial specimen (terrorism)
59
New cards
cellular components
remove inhibitors
- heme from blood
- humic acid, fulvic acid, calcium and collagen (bone
samples)
- melanin in hair, skin
- inhibitors can inhibit enzyme polymerase, or Mg
- heme from blood
- humic acid, fulvic acid, calcium and collagen (bone
samples)
- melanin in hair, skin
- inhibitors can inhibit enzyme polymerase, or Mg
60
New cards
chelex
simple system for neat samples
Ex: saliva reference samples
compound you use 1 tube, extract DNA from same tube
Ex: saliva reference samples
compound you use 1 tube, extract DNA from same tube
61
New cards
FTA
card based extraction system
62
New cards
robotic
simple, magnetic bead extraction technique
-Dr. Roy uses for her research
-Dr. Roy uses for her research
63
New cards
organic
more challenging samples, gets rid of impurities
Ex: blood, etc
gold standard, get double stranded DNA
Ex: blood, etc
gold standard, get double stranded DNA
64
New cards
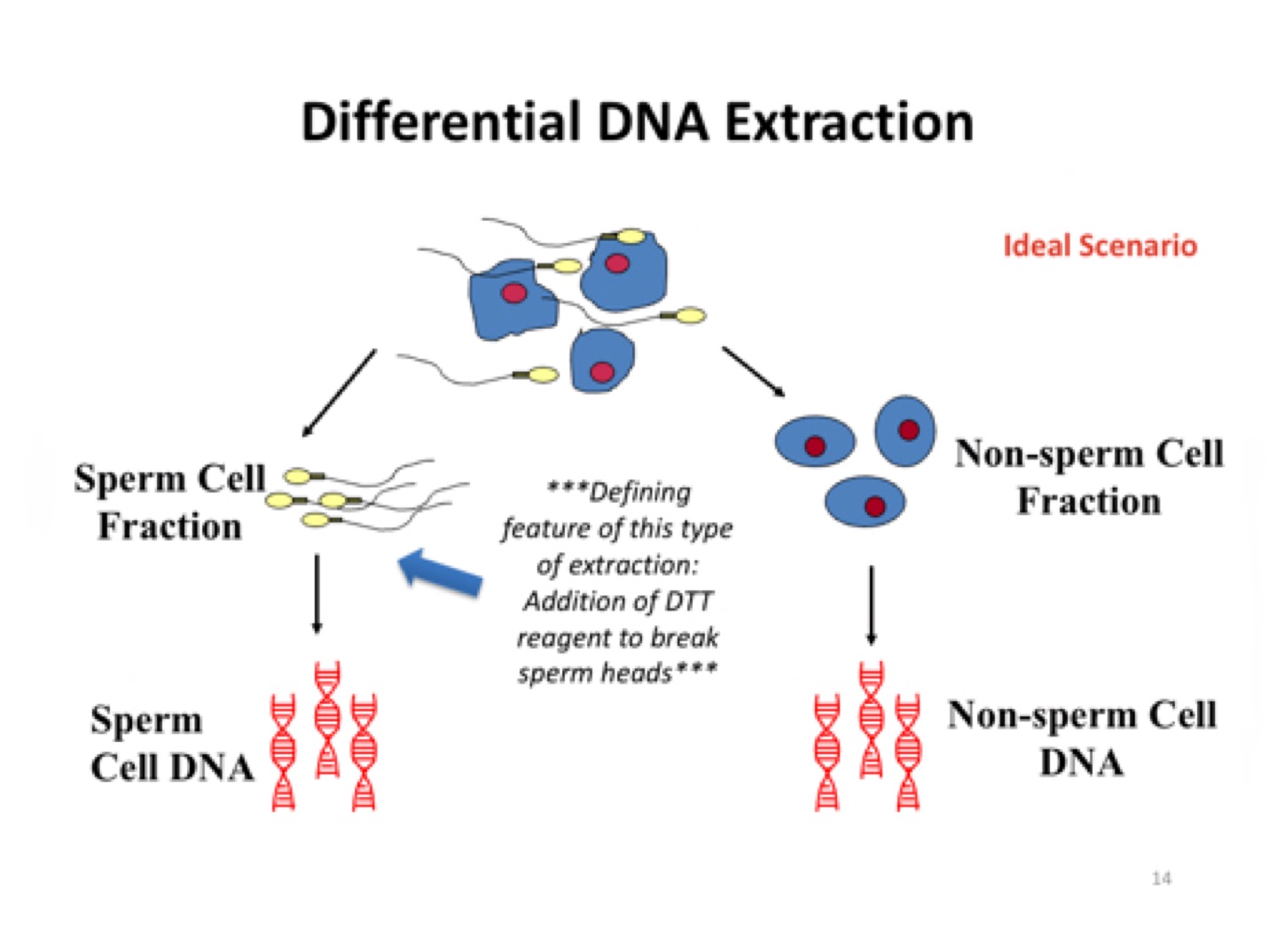
differential extraction
complex samples with possible mixture, used in sexual assault cases (separate sperm from other cells)
65
New cards
solid-phase extraction method
qiagen
66
New cards
chelex-100
ion-exchange column resin, iminodiacetic acid
- binds magnesium and removes them from the reaction
mixture = DNA stabilized and preserved, extracted DNA is
partially single stranded (due to heat)
- metal ions Zn, Mg, Ca, can act as catalysts or cofactors for
nucleases and thus help degrade DNA by enzymatic
degradation of hydrolysis
- binds magnesium and removes them from the reaction
mixture = DNA stabilized and preserved, extracted DNA is
partially single stranded (due to heat)
- metal ions Zn, Mg, Ca, can act as catalysts or cofactors for
nucleases and thus help degrade DNA by enzymatic
degradation of hydrolysis
67
New cards
iminoacetate ion
chelating characteristics
68
New cards
chelating
binding of ions or molecules to metal ions (gives single stranded DNA)
69
New cards
RFLP
double stranded DNA
70
New cards
reagents in differential extraction
- lysis buffer
- SDS (Sodium dodecyl sulfate)
- Pro K (Proteinase K)
- DTT (Dithiothreitol)
- EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)
- buffer/ions
- SDS (Sodium dodecyl sulfate)
- Pro K (Proteinase K)
- DTT (Dithiothreitol)
- EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)
- buffer/ions
71
New cards
Lysis buffer
chemicals and proteins added to the sample that facilitate lysis of the cell membrane and effective removal of impurities
72
New cards
SDS
sodium dodecyl sulfate (detergent)
- why shampoo forms
- why shampoo forms
73
New cards
Pro K
proteinase K (digests proteins and chops it up)
- need to get rid of proteins
- need to get rid of proteins
74
New cards
DTT
dithiothreitol (differential extraction, breaks the S-S bonds and allows the protein to break apart)
- sperm heads broken down
- sperm heads broken down
75
New cards
EDTA
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (chelates metal ions that can degrade DNA and cause hydrolysis of DNA molecule
- acts like chelex
- acts like chelex
76
New cards
buffer/ions in differential extraction
maintains pH, ions helps later in the downstream
Ex: Tris-HCl and NaCl
- basic rudimentary DNA
Ex: Tris-HCl and NaCl
- basic rudimentary DNA
77
New cards
quantitative PCR (qPCR)
real time PCR
determine the amount (quantity) of DNA present in the extract to assist in determining the appropriate amount of the extract to add for amplification
determine the amount (quantity) of DNA present in the extract to assist in determining the appropriate amount of the extract to add for amplification
78
New cards
thermal cycler
polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is performed by this, repeated cycles of heating and cooling like a copy machine
79
New cards
steps of PCR
- denature
- anneal
- extend
DAE
- anneal
- extend
DAE
80
New cards
PCR reagents
- template DNA (single stranded)
- short primers (initiate synthesis of new DNA)
- dNTPs (add to growing strand of DNA)
- polymerase (perform synthesis of new DNA)
- MgCl2 (activate polymerase)
Old Faithful w/ hot --> cold --> hot
- short primers (initiate synthesis of new DNA)
- dNTPs (add to growing strand of DNA)
- polymerase (perform synthesis of new DNA)
- MgCl2 (activate polymerase)
Old Faithful w/ hot --> cold --> hot
81
New cards
DNA amplification steps
1) starting DNA template (heat needed to start first step)
- denaturation, double stranded DNA dissociates
2) separate strands (denature)
- binding of the primer to provide initiation site for DNA
synthesis
3) add primers (anneal)
- extension of DNA from primers
4) new strand synthesis (extend)
- denaturation, double stranded DNA dissociates
2) separate strands (denature)
- binding of the primer to provide initiation site for DNA
synthesis
3) add primers (anneal)
- extension of DNA from primers
4) new strand synthesis (extend)
82
New cards
multiplex PCR
- started with 10 markers
- over 26 markers can be copied at once
- sensitivities to levels less than 1 ng of DNA
- ability to handle mixtures and degraded samples
- different fluorescent dyes used to distinguish STR alleles with
overlapping size ranges
- over 26 markers can be copied at once
- sensitivities to levels less than 1 ng of DNA
- ability to handle mixtures and degraded samples
- different fluorescent dyes used to distinguish STR alleles with
overlapping size ranges
83
New cards
separation by capillary electrophoresis (CE)
like liquid gel electrophoresis
- separation of fragments by size using applied electric
voltage
- DNA is negatively charged = small fragments move towards
positive charge faster than larger fragments
fragments tagged with dyes, captured by camera as they migrate
instrument: 3130 xL genetic analyzer
- separation of fragments by size using applied electric
voltage
- DNA is negatively charged = small fragments move towards
positive charge faster than larger fragments
fragments tagged with dyes, captured by camera as they migrate
instrument: 3130 xL genetic analyzer
84
New cards
TH01
human tyrosine hydroxylase gene
01-repeat region is located within intron 1 of tyrosine hydroxylase gene
01-repeat region is located within intron 1 of tyrosine hydroxylase gene
85
New cards
HUM
human genome prefix
86
New cards
STR locus TH01
HUMTH01
87
New cards
gene name
-IF marker WITHIN gene or PART of gene, gene name used
-marker OUTSIDE gene regions, designated by CHROMOSOMAL position
-marker OUTSIDE gene regions, designated by CHROMOSOMAL position
88
New cards
example of locus not w/in gene regions
D5S818
D- DNA
5- chromosome 5
S- DNA marker is a single copy sequence
*S represents unique DNA segment
818- order of discovery/ order in which locus was identified
**ALL OF THE ABOVE MAKES LOCUS UNIQUE
DYS19
D- DNA
Y- y chromosome
s- single copy sequence
19- order discovered
D- DNA
5- chromosome 5
S- DNA marker is a single copy sequence
*S represents unique DNA segment
818- order of discovery/ order in which locus was identified
**ALL OF THE ABOVE MAKES LOCUS UNIQUE
DYS19
D- DNA
Y- y chromosome
s- single copy sequence
19- order discovered
89
New cards
do we need to add DTT (dithiothreitol) to non-sperm samples?
no, do not need to be broken?
90
New cards
single source
typically for each locus, expect to see 2 alleles ( 2 peaks)
- 2 alleles ~ heterozygote
-1 allele ~ homozygote
- 2 alleles ~ heterozygote
-1 allele ~ homozygote
91
New cards
mixture
when more than 2 alleles are see at two or more loci
contributors- 3 peaks - 2 cont., 5 peaks - 3 cont., 6 peaks - 3 cont., 7 peaks - 4 cont., 8 peaks - 4 cont.
contributors- 3 peaks - 2 cont., 5 peaks - 3 cont., 6 peaks - 3 cont., 7 peaks - 4 cont., 8 peaks - 4 cont.
92
New cards
amelogenin
sex determining locus
gene on the x-chromosome that codes for proteins associated with tooth enamel
gene on the x-chromosome that codes for proteins associated with tooth enamel
93
New cards
x-homologous amelogenin gene region
exists on y-chromosome, region has 6 bp deletion, so x and y products differ in size
94
New cards
factors that can complicate interpretation
- stutter
- pull up
- spikes
- dye blobs
- degradation
- low DNA template amount (can lead to stochastic-random
effects, drop out)
- pull up
- spikes
- dye blobs
- degradation
- low DNA template amount (can lead to stochastic-random
effects, drop out)
95
New cards
stutter
during PCR DNA is improperly replicated so one repeat is shorter than parent strand, slipped strand mispairing model
come together out of sync, shows up as little peaks
come together out of sync, shows up as little peaks
96
New cards
conclusion
made after comparing a profile to a reference
- inclusion ** (must always provide statistics)
- exclusion
- inconclusive
- inclusion ** (must always provide statistics)
- exclusion
- inconclusive
97
New cards
inclusion
evidence profile and reference profile appear to match
weight of the match must be reported in conclusion via statistic, how strong of a reference profile to evidence profile
weight of the match must be reported in conclusion via statistic, how strong of a reference profile to evidence profile
98
New cards
single source profiles
random match probability (RMP)
weight between single source and evidence court order
STRONGEST STATISTIC TO USE
weight between single source and evidence court order
STRONGEST STATISTIC TO USE
99
New cards
mixture profiles
- modified random match probability (mRMP)
- combined probability of exclusion (CPE)
- combined probability of inclusion (CPI)
- likelihood ratio (LR)* - becoming very popular
- combined probability of exclusion (CPE)
- combined probability of inclusion (CPI)
- likelihood ratio (LR)* - becoming very popular
100
New cards
CODIS
combined DNA index system, represents the software
software stores data, interpol can see w/ permission to look
- used for linking serial crimes and unsolved cases w/ repeat
offenders at local, state and national level
- US national DNA database
- launched oct 1998
- links all 50 states
- when started required >4 RFLP markers
- currently 20 core LOCI (STR) markers, STR core loci at the
beginning started with 13
software stores data, interpol can see w/ permission to look
- used for linking serial crimes and unsolved cases w/ repeat
offenders at local, state and national level
- US national DNA database
- launched oct 1998
- links all 50 states
- when started required >4 RFLP markers
- currently 20 core LOCI (STR) markers, STR core loci at the
beginning started with 13