4/5- salivary glands + GI motility
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
3 phases of digestion
cephalic (reflex): prior to food entry, salivary glands major component
gastric: arrival of food into stomach
intestinal: arrival of food into duodenum
how is the cephalic phase triggered
thought, site, sound, smell of food → parasympathetic outflow → salivation, gastric + pancreatic secretion, release of bile into GI tract
liver releases 1 L of bile that is completely absorbed by what
ileum of small intestine
which CN is responsible for parasympathetic outflow in the cephalic phase
CN 7 + 9
5 positive regulators (stimulators) of saliva production
thought of food
smell of food
sight of food
act of chewing
nausea
4 negative regulators (decrease) of saliva production
dehydration
sleep
fear
anticholinergic drugs
T/F: positive regulators of saliva production can cause a 10x increase in saliva
true
6 causes of xerostomia
meds like anticholinergics
nerve damage
autoimmune destruction (Sjogrens)
infection (HIV)
radiation
severe dehydration
4 consequences of xerostomia
dental caries + disease
infections like thrush
difficulty speaking + swallowing
decreased taste
3 functions of bicarbonate (HCO3-) secretion in the GI tract
buffering pH
neutralizing gastric acid + provide optimal pH for digestive enzymes in duodenum
solubilizes macromolecules (mucin, bile acids)
3 sources of bicarbonate
plasma
carbonic anhydrase (CA): converts H2O + CO2 → H+ + HCO3-
GI lumen
what 4 things secreted in saliva by acinar cells
alpha-amylase: begins carbohydrate digestion + inactivated by low pH
lipase: beings lipid digestion by converting triglycerides → fatty acids + monoglycerides
mucin: involved in bolus formation + swallowing
extracellular fluid: similar ionic composition to plasma
pH must be ___ in order for alpha-amylase + lipase to be active
neutral
what cells in salivary glands modify the ion content of saliva by absorption + secretion
ductal cells
T/F: most salivary ductal cells do not express aquaporin (water) channels in their apical membrane + are impermeable to water
true
saliva is hyper or hypotonic
hypotonic, so that it aids the detection of salt in the diet
what’s responsible for the hypotonic saliva that enters the mouth
lack of aquaporin channels (AQP) in the apical membrane of most ductal cells
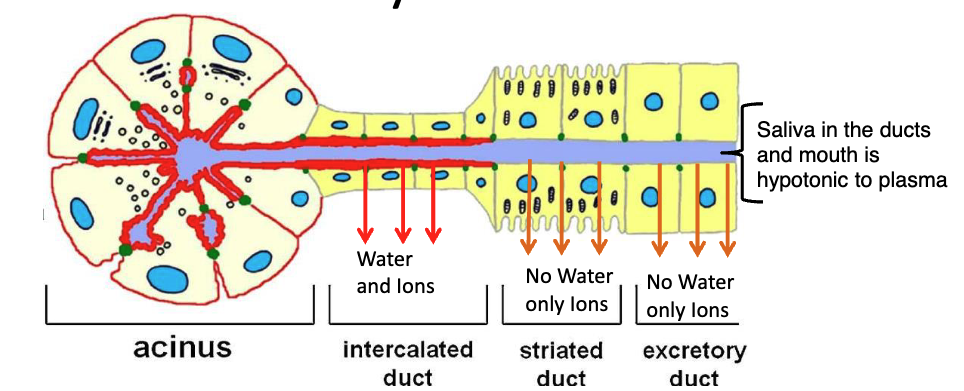
describe parasympathetic stimulation of salivary glands
increased secretion of fluid + ions from the acinar + ductal cells
describe sympathetic stimulation of salivary glands
increased fluid, ion, protein secretion but a minor contributor to increase in fluid volume
T/F: GI hormones play a role in salivary secretion regulation
false
which major salivary gland contributes the most saliva during no stimulation (fasted state)
submandibular gland: 69%
parotid gland: 26%
sublingual gland: 5%
which major salivary gland contributes the most saliva during stimulation (started eating something)
parotid gland: 69%
submandibular gland: 26%
sublingual gland: 5%
what’s the most common disorder of salivary glands
stones (sialoliths)
7 sphincters of the GI
upper esophageal (UES)
lower esophageal (LES)
pyloric
oddi
ileocecal
internal anal
external anal
which sphincter malfunctions in GERD
lower esophageal (LES)
where does the smooth muscle that continues through the GI tract start
lower 1/3 of esophagus
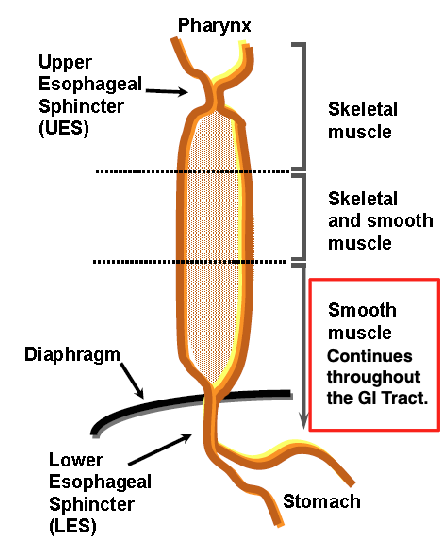
what happens during swallowing
pharynx constricts
UES opens
LES + proximal stomach relax
what is movement of the bolus as it goes down the esophageal body
primary peristalsis
what happens if there’s some food leftover in the esophagus
secondary peristalsis
esophageal peristalsis is caused by
sequential contraction of circular muscles of muscularis propria, mediated by acetylcholine
describe neurotransmitter mechanism of esophageal peristalsis
nitrergic inhibition: NO acts as an inhibitor to relax the smooth muscle as the bolus is traveling down
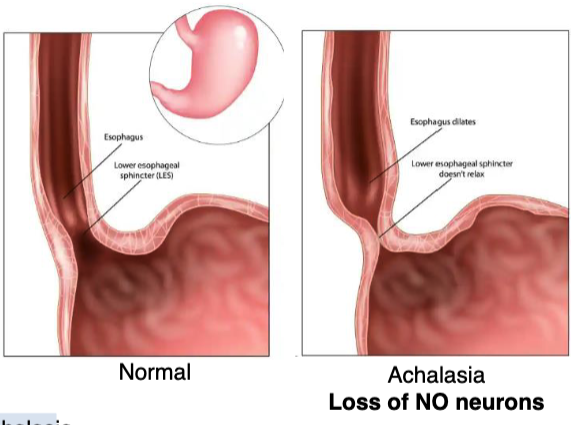
what’s achalasia
loss of nitrergic neurons (neurons that release NO) in distal esophagus → constriction of LES → pt has difficulty swallowing
which stimulates the enteric nervous system (ENS): sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic
how does the parasympathetic nervous system stimulate the ENS
via dorsal motor nucleus of CN X using ACh
how does the sympathetic nervous system inhibit the ENS
via sympathetic nerves using norepinephrine
2 distinct features of smooth muscles
dense bodies: point of attachment for myofilaments
gap junctions: electrically link sheets of muscle cells to contract as 1 unit
5 things that can modulate smooth muscle of the GI
autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters
hormones
intrinsic properties that produce spontaneous electrical activity
changes in local chemical composition
stretch (distention)
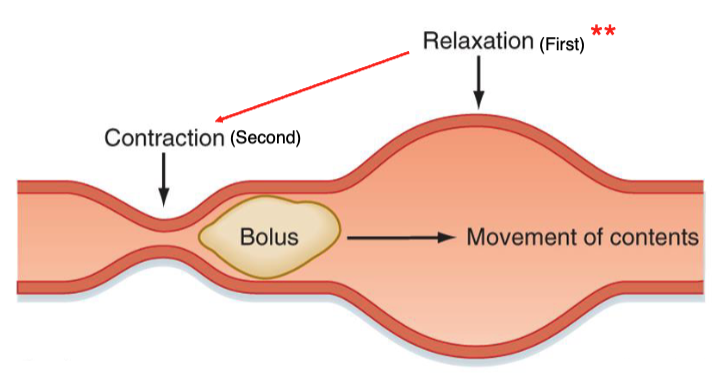
what happens first during GI tract perstalsis: contraction or relaxation
relaxation, then followed by contraction
distinguish the 2 branches of CN X for esophageal innervation
nucleus ambiguus → striated muscle in upper esophagus
dorsal motor nucleus → smooth muscle in lower esophagus
2 positive regulators of esophageal smooth muscle
acetylcholine (ACh)
substance P (SP)
2 negative regulators of esophageal smooth muscle
nitric oxide (NO)
vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
what’s the valve between the small + large intestine
ileocecal valve (ICV)
2 primary functions of the ileocecal valve (ICV)
control flow between small + large intestine
prevent bacteria from large intestine contaminating small intestine
excessive motility of the large intestine results in
less fluid absorption + diarrhea/loose stool
2 main types of movement in the large intestine
haustral contractions
mass movements
where do the primary movements of the large intestine occur
ascending + transverse colon
differentiate between haustral contractions vs. mass movements
haustral contractions: occur every 30 min + last ~1 min, stimulated by stretch when food fills haustra
mass movements: long, slow, powerful that move over the colon 3/4x a day usually after meals, stimulated by gastrin release when food arrives in stomach