Waves - Double Slit Experiment & Electromagnetic Waves
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
if light behaves like a wave., it should have
dark areas (DI) and bright areas (CI)
young experiment involved a
monochromatic light
narrow slits (one in front, two after that)
the light leaving the double slits acted as 2 sources and was essentially IN PHASE and exhibited the same wave properties
interference of light waves visual
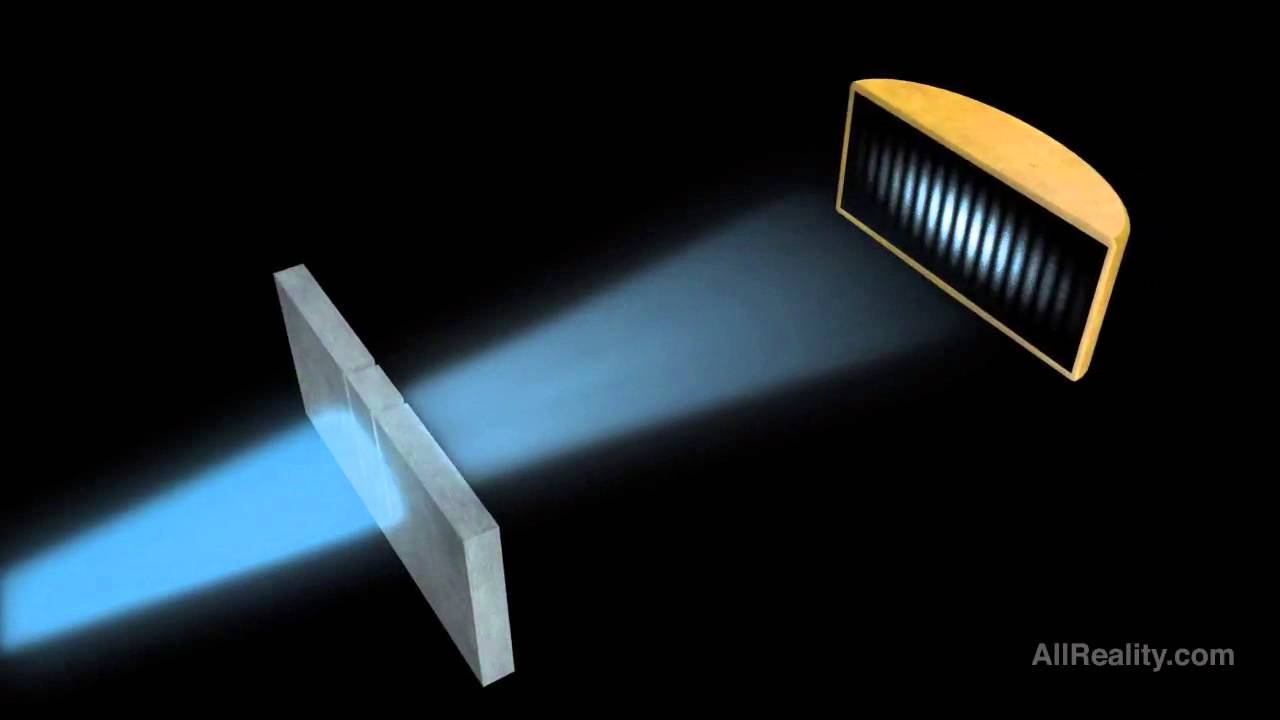
the bands of bright bands are otherwise refered to as
maxima (CI)
interference fringe
the bands of dark bands are otherwise refered to as
minima (DI)
interference fringe
to det the wl of the light, you have to first det the
path length difference between each slit and the screen.
the bands were created on the screen bc
of the light waves diffracting from going thru the small slit
zero-order maxima
the central maxima
the eqn with m is for
maximas
maximas occur at the location given by that eqn w the sin function
m =
0,1,2,3 → 0 would be the central maxima and the maxes are counted outwards
this is where CI happens
to get DI, the second wave len must trav
an extra dist behind or in front of the other wave to reach the screen
→ must be a mult of wl/2 but cannot bea whole number
to find where minimas occur
use the formula w (n - 1/2), wl, d, and sin func (see notes)
where n = 1, 2, 3 → first order min, second order min and so on
to calc the fringe width
the eqn w Xm and m is for bright fringes
the eqn w Xn, (n - 1/2 ) is for dark fringes
the fringe width and intensity of the fringes is
uniform
to calc the sep b/w any two adjacent fringes
use the eqn w no angle
the central fringe (zero-order max) =
2(x1)
EM waves are
complex transverse waves
particles move in every dir that is perpen to the trajectory of trav
how EM waves work
vibrating electric charges in space produce an electric field
moving charges set up a magnetic field perpendicular to motion of charge
changing magnetic field induces an electric field perpendicular to the magnetic field AND they continuously change
interacting electric and magnetic fields will travel through a vacuum in the form of EM waves at c=3.0x108 m/s
Electromagnetic propagation
ε induces changing B, which induces changing ε, which induces changing B, and so on that are
oscillating in phase perpendicular to each other
and at 90° to the direction of the wave
Wave-Particle Duality
Light energy propagates as a wave BUT when it interacts with matter behaves like a particle
Photons are discrete bundles of energy that do not have mass and exhibit interference effects like electrons (from Einstein’s Quantum Thy of Light)
EM waves can
interfere, diffract, refract, polarize, and have linear and angular momentum
All EM waves travel through a vacuum at
c= 3.00 x 108 m/s and obey the universal wave eq’n 𝒗 = 𝒇𝝀