psyc 211 - the action potential
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the golgi stain
It is a mixture of silver nitrate and potassium chromate which crystallizes 2% of neurons and causes them to become black and easier to see

What is crystallization
it is the process where atoms or molecules arrange into a well-defined rigid crystal lattice in order to minimize their energetic state
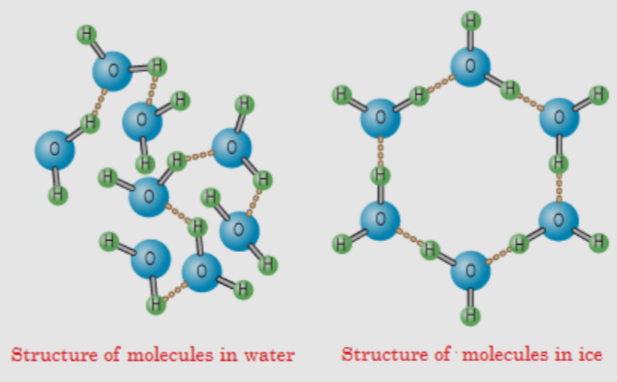
When they freeze, water molecules crystallize, which causes the ice to arrange itself larger than water
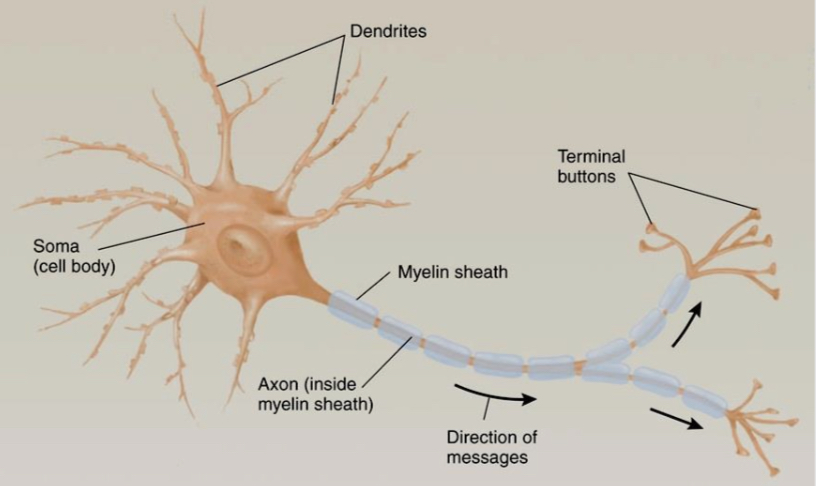
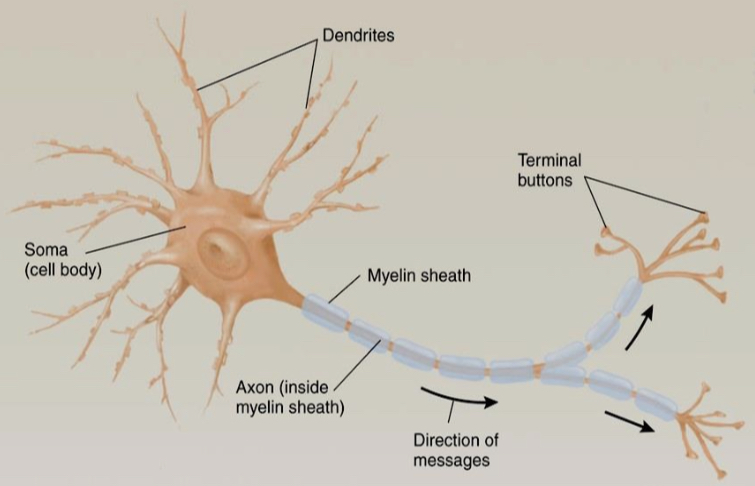
Structure of the neuron
1- the soma or cell body of a neuron is where its nucleus is located
2- dentrites are branched, treelike extensions of the soma. They are responsible for collecting information relevant to the cell, like sensing neurotransmitters and other stimuli in the extracellular space
3- each neuron has one axon, but it can branch many times.
4- these branches are called axon collaterals
5- there is an axon terminal at the end of every axon
6- axons send information downstream cells by releasing signaling molecules from the axon terminal.
7- the synapse is the junction between the axon terminal and a downstream cells
What is voltage
it is an electric charge difference beteeen two points
ir is measured with a voltmeter
When there is a charge difference, ions naturally want to move to neutralize the differcne, but they cannot cross the membrane, unless there is an open door for them. The cell memebrane prevents this movement
When measuring voltage, there will always be a point that has a charge of 0mV (“the ground”). In the brain, this is extracellular fluid
What is the resting potential of neurons
-40 to -90 mV
This means that the voltage across the cell membrane makes positively charged ions want to enter the cell and negatively charged ions want to leave the cell
What is an ion
an atome or molecule that has a net electrical charge.
They move freely in water
Cation → positively charged
Anion → negatively charged
What is electrostatic pressure
It is the attractive force between ions that are oppositely charged and the repulsive force between ions that are similarly charged
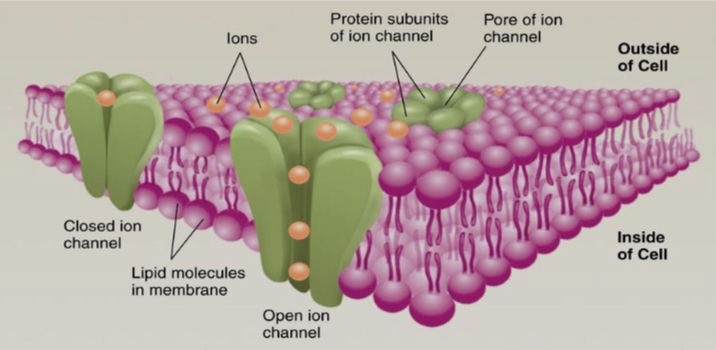
What are ion channels
They are proteins that form at the pore through which atoms can pass
They are placed in the cell membrane
When open, they let specific ions freely flow in and out of the cell.
Most ion channels are bidirectional
What is a leak channel
it is an ion channels that stays permanently open
Potassium leak channels selectively let potassium ions flow freely in and out of the cell
Which neurons are important for understanding how neurons work?
Positively charged ions:
monovalent cations:
sodium (Na+) ( abundant in extracellular space)
Potassium (K+) ( abundant inside of the cells)
Divalent cations:
Calcium (Ca2+) (abundant extracellularly)
Magnesium (Mg2+) (abundant extracellularly)
negatively charged ions:
monovalent anions:
Chloride (Cl-)
these all form salts when dry and separate into ions when in water
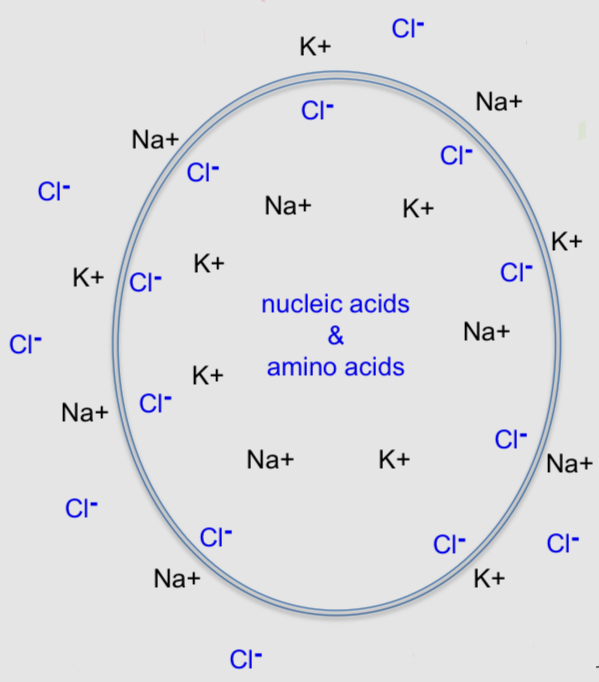
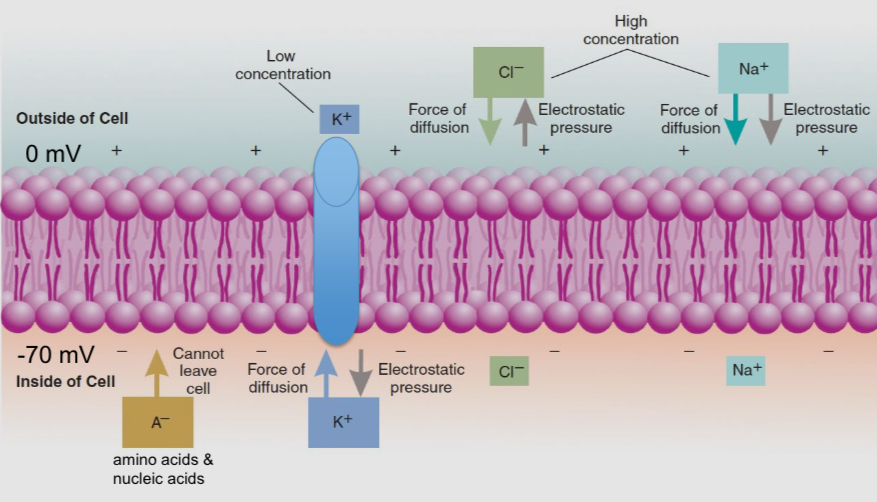
What is found in intracellular and extra cellular fluid
Intracellular fluid contains negatively charged nucleic acids and amino acids
There are dissolved salts outside and inside the cell
There are more negative charges in a cell than outside, which causes intracellular Cl- ions to hug the cell membrane
Most cells in the world are like this and have a membrane potential around -20 mV
Why do neurons have a negative membrane potential
to be able to communicate quickly from one end of the cell to the other
They do so by creating a strong electrical potential across the membrane using the sodium potassium pump and the potassium leak channel
The electrical potential makes it possible for a neuron to rapidly propagate information down the length of its axon. This is called an action potential and involves voltage gated sodium channel and voltage gated potassium channel
at the end of the axon, neurotransmitter réalisés is triggered by the voltage-gated calcium channel
What is the sodium potassium pump
it is a protein that continually pumps sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell.
It uses ATP for energy, which forces these ions to move where they otherwise wouldn’t
Neurons fill their cell membrane with this protein
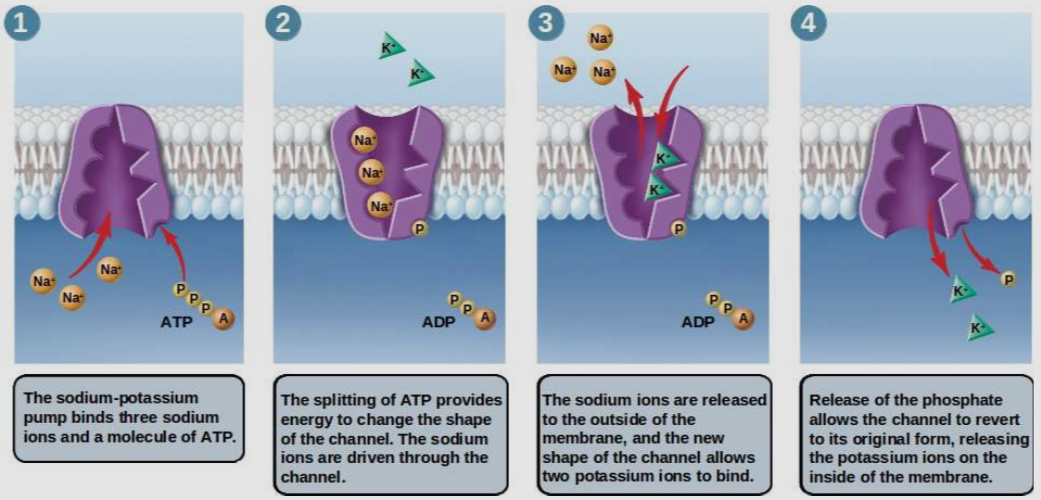
How does the sodium potassium affect the concentration of K+ and Na+ ions
It makes the concentration of K+ ions 30 x higher inside the cell than out
It makes the concentration of Na+ ions 15x more concentrated outside the cell than inside
These concentration gradients never change, they are always constant
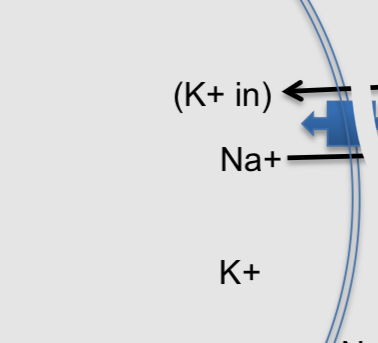
What do sodium potassium pumps create
They don't change the membrane potential very much on their own
They create concentration gradients: potassium is concentrated in and potassium is concentrated
Both these concentration gradients generate the force of diffusion
What is diffusion
it is when atoms or molecules will move from a area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, when there is no concentration gradient or force barriers
What is a potassium leak channel
They are channels permanently open to potassium ions freely move in or out of the cell
Since K+ ions are 30x more concentrated inside the cell than out, they are more likely leave the cell than enter it
This is the force of diffusion, which competes with force of electrostatic pressure
K+ ions leave the cell because of diffusion and they enter the cell because it is negatively charged inside rather than outside
The forces because equal and opposite when the membrane potential falls to -90 mV
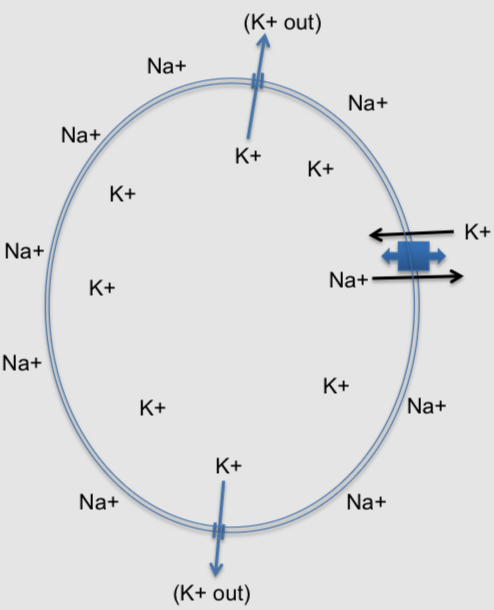
What happens when a neuron's membrane potential is -90 mV
There is no movement of K+ ions: The amount leaving is equal to the amount entering
What happens when the membrane potential is less negative than -90 mV
More K+ ions will leave the cell than enter: the force of K+ ions diffusion oucompletes its electrostatic pressure
What happens when the membrane potential is more negative than -90mV
More K+ ions enter the cell than leave it; it’s electrostatic pressure outcompetes the force of diffusion
What is the resting memebrane of most neurons
it is somewhere between -40 mV and -80 mV
This is because other ions continuously flow into neurons through other ion channels and pumps
What is the cause of the variability of membrane potentials
it is due to differences of neurons in their permeability to K+
Neurons that express a lot of K+ leak channels have a membrane potential close to -90mV
Neurons with few K+ leak channels have more depolarized membrane potential, up to -40 mV
What is a membrane potential
it is the electrical charge across a membrane
Most cells in the world have a membrane potential around -20mV. The membrane potential of non-neuronal cells is often irrelevant to their function
what is the resting membrane potential
it is when the neuron is not actively receiving or transmitting messages
Neurons have a stable membrane potential when they are at rest. It is between -40 and -80 mV
What are the two proteins responsible for setting up and maintaining the resting membrane potential of neurons
Sodium potassium transporters (use ATP to concentrate potassium inside the cell and sodium outside the cell
Potassium leak channels ( are always open; the number of these ion channels largely determines the resting membrane potential
What is the purpose of receptors
many proteins on the cell membrane act as receptors (sensors). They are sensitive to some aspects of the extra cellular environment
Cells use receptorsto detect and pul in nutrients (sugars, fats, vitamins,etc.)
Neurons put receptors on their cell membranes, primarily on dentrites, to sense these stimuli, to gain a better understanding of the world around them
How do neuron's ion channel receptors work-
Dendrites of most neurons are full of receptors that are ion channels
Once activated, the receptors change shape and a pore through which ions flow in and out
These leak channels are gated by something.
If an activated receptor allows positively charged Na+ ions to flow freely, they rush into the cell on account of diffusion and electrostatic pressure. A large rapid influx of Na+ ions through a bunch of activated receptors will depolarize the membrane potential (make less negative)
What is depolarization
it is when the membrane potential of a neuron becomes less negative than it normally is a rest
The activation of a receptor that allows positively charged Na+ ions to enter a neuron will cause its membrane to depolarize from -70 mV to -60 mV
How are changes to the membrane potential affected-
Changes are always transient (short-lived)
neurons are Wuxi to return to their resting state because K+ leak channels are always open.
The abundance of K+ leak channels ensures that neurons never deviate from their resting membrane potential very long
An influx of Na+ ions through an activated receptor will only transiently depolarize the membrane since K+ ions immediately react and leave the cell through leak channels, thus restoring the resting membrane potential
What are voltage gated ion channels
they are gate channels with an electrical charge, so it opens and closes in response to changes in the membrane potential
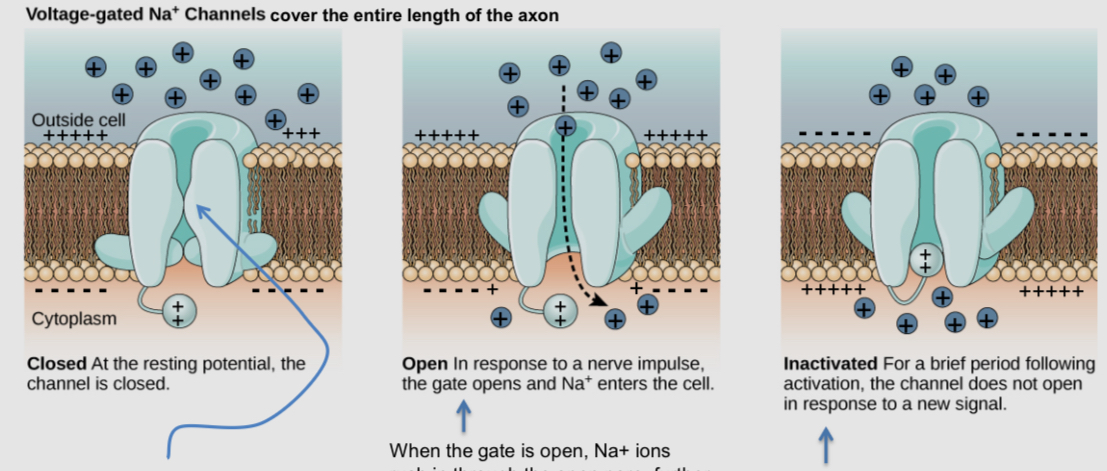
What is a voltage-gated sodium channel
it is used to initiate and propagate the action potential
They line the length of the axon, it is rare to find them anywhere else
There are any where the axon connects to the Soma (the axon hillock) where action potential starts
If recomptons let enough Na+ ions to significantly depolarize the membrane of the axon hillock (to around -40 mV), then voltage-gated channels will start opening, allowing more Na+ to enter and further depolarizing the membrane
The influx of Na+ through voltage gated sodium channels starts a chain of reaction that propagates down the entire length of the axon. Na+ influx through the first channels in the axon hillock trigger next ones to open, etc.
What is a voltage-gated potassium channel
it quickly restores the resting membrane potential
It lines the entire length of the axon, it is rare to find it anywhere else
What is a voltage-gated calcium channel
it trigger the realize of neurotransmitters
It is primarily found at the end of the axon (axon terminal)
What happens when voltage-gated sodium channels open
the membrane briefly becomes more permeable to sodium than potassium
Sodium ions are 15x more concentrated outside the cell than inside, so they want to enter a neuron due to diffusion and electrostatic pressure
Sodium ions keep entering until the membrane potential reaches +60 mV, at which point the forces of diffusion and electrostatic pressure acting on Na+ cancel out
Although, they are never able to reach that value because they get clogged. In the ½ millisecond they are open, the membrane portential reaches +40 mV
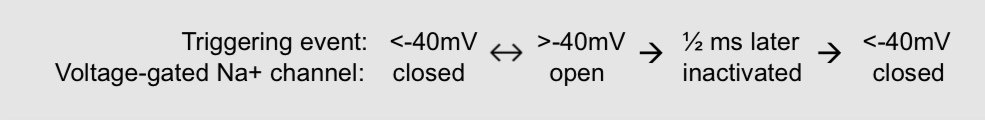
What are the two ways to prevent current flow through a voltage-gated sodium channels start
the pore closes whenever the membrane is more negative than -40 mV
the pores get clogged within a ½ after opening. When this happens, the ion channel is said to be deactivated. Inactivation persists until the membrane potential returns to rest
Define the action potential and its cause
It is a brief electrical impulses that propagates down the length of the axon due to the opening of voltage- gated sodium channels
It is triggered when the membrane potential reaches the treshold of excitation
The initial depolarization of an action potential usually comes from a small influx of Na+ ions through an activated receptor on a dendrite
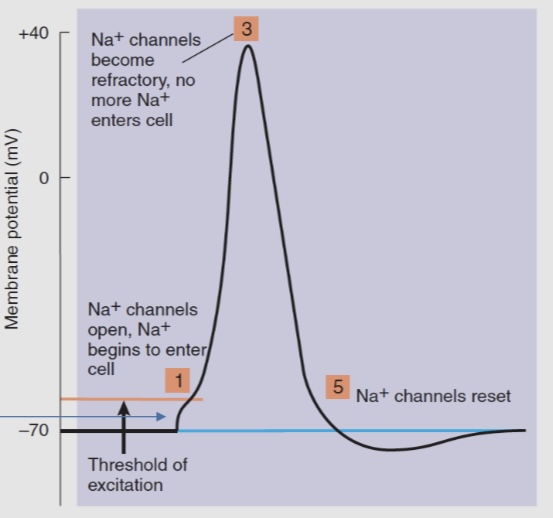
What happens when the action potential reaches its peak
when the membrane potential reaches + 40 mV, all voltage gated sodium channels become inactivated by their ball and chain. They won’t be able to,e to open again until the membrane potential gets back down to reset
Potassium leak channels are always open and they will restore the resting membrane potential eventually, which can take up to 10 millisecond. Although, this is to long to support the rapid action potential
To speed up the restoration of the membrane potential, neurons use the voltage-gated potassium channel
What is the refractory period
This is when it is hard to trigger another action potential when the membrane is that hyperpolarized
On which animal was the first action potential done?
a squid
It was done using microelectrodes
What happens when the action the end of the axon
it triggers the opening voltage-gated calcium channels
Calcium is 1000x more concentrated outside the cell than in, so it rushes into the cell
This influx triggers the fusion of neurotransmitter-filled vesicles
Neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, where they activate receptors on the downstream cell
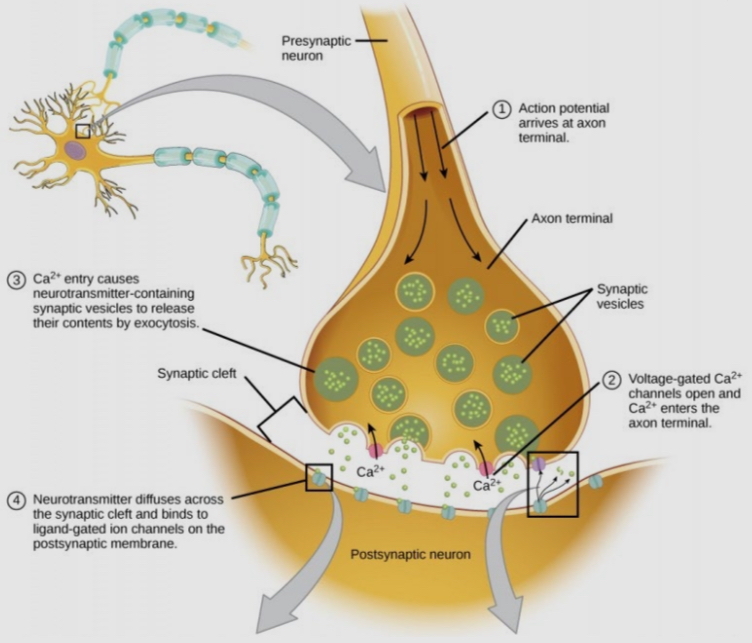
What is the primary source of communication between neurons
synaptic transmission: the transmission of a chemical message from one neuron to another via synaptic connection
Released neurotransmitters activate receptors on downstream neurons, and this may allow Na+ ions to enter those cells, perhaps triggering more action potentials
In which direction does the action potential go
it is unidirectional. It starts in the soma and travels down the axon terminal
The ball and chain inactivation mechanisms of the voltage-gated sodium chanel prevents the action potential from reversing direction
When the action potential propagates Down the axon, the amplitude of it remains constant
what is the all or none law
It states that an action potential can occur or not, but once triggered, it propagates down the length of the axon without growing or diminishing in size
What is the rate law
It states that the rate of the message is represented by the rate of firing ( the number of action potential rather than the size or speed of an action potential