Biological molecules Alevel P1
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Define Polymer
Large complex molecule made up of repeating units called monomers
define a monomer
small basic molecular unit that joins together in long chains to form polymers
what reaction causes polymers to form
condensation reactions
examples of polymers
DNA/RNA, Carbohydrates, Proteins
define a condensation reaction
chemical process where a chemical/covalent bond forms between monomers which releases a molecule of water (H2O)
what monomer makes up the polymer of protein
amino acids
which monomer makes up the polymer of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
what is a hydrolysis reaction
reaction that breaks the chemical bond between monomers by adding a water molecule.
what are the 3 main biological molecules
carbohydrates, proteins and lipids/fats
define a monosaccharide
simplest form of a carbohydrate, basic subunit making up the polymer carbohydrate consisting of a single unit of sugar
what chemical elements do monosaccharides contain
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
give 3 examples of monosaccharides
fructose, galactose and glucose
what’s the chemical formula for glucose
C6 H12 O6
describe the basics of glucose
glucose is a hexose sugar (has 6 carbon atoms) and there are 2 isomers (types of glucose)
what are the names for the two different types of glucose
alpha and beta
give examples of some monomers and the polymer that they form
amino acids form proteins
monosaccharides form carbohydrates
nucleotides form DNA and RNA
what’s the monomer of a carbohydrate
monosaccharides
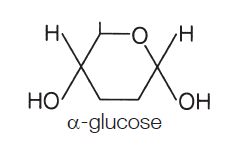
where is the OH (hydroxyl group) in alpha glucose
bottom right
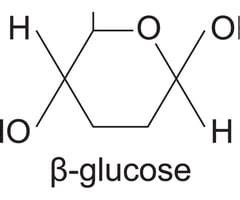
where is the OH (hydroxyl group) in beta glucose
top right
define a disaccharide
when two monosaccharides join together
when monosaccharides join together what reaction takes place and what happens
condensation reaction meaning a bond of water (H2O) forms and is released leaving oxygen by itself
Because Oxygen is left due to a condensation reaction when monosaccharides join- what bond does it make
glycosidic bond
what’s the word sequence to help remember what monosaccharides join together to make disaccharides
GOOD LUCK , MATE, FOOD SUCKS
Good Luck (alpha g+ galactose= lactose)
Mate (alpha g+ alpha g= Maltose)
Food Sucks (alpha g+ fructose= sucrose)
what monosaccharides join to form maltose
alpha glucose and alpha glucose
what monosaccharides join to form lactose
alpha glucose and galactose
what monosaccharides join to form sucrose
alpha glucose and fructose
define a polysaccharide
complex carbohydrates made up of many monosaccharides joined via glycosidic bonds
what are the 3 main polysaccharides
starch, glycogen and cellulose
where is starch found
only found in plant cells
how do plant cells make glucose - what’s it stored as
make glucose in photosynthesis where its stored as starch
What’s the chemical formula for photosynthesis
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂.
why is glucose stored as starch in plants
because glucose is soluble so can effect osmosis causing cells to loose water therefor its stored as starch which is insoluble
when starch is eaten to provide energy what’s it broken down into and stored as
broken down back into glucose to be stored as glycogen
what two different polysaccharides is starch made off
amylose and amylopectin
what are the main points about starch
suited for an energy store
compact
insoluble
easily hydrolysed
what are the monosaccharides of amylose and amylopectin
alpha glucose
What’s the main points about amylose (polysaccharide that makes up starch)
linear structure made of alpha glucose
glycosidic bonds
twist into helix shape making it compact to store more glucose
what are the main points about amylopectin (polysaccharide that makes up starch)
chains of alpha glucose linked by glycosidic bonds
branched molecule meaning its easily hydrolysed for use during respiration
Where is Glycogen stored
stored in muscles and liver
is glycogen found in animal cells, plant cells, both or neither
only animal cells
what is glycogen made up of
made of alpha glucose
describe the structure of glycogen
similar structure to amylopectin but has more branches making it more compact and so because it has more free ends condensation and hydrolysis reactions occur more rapidly
main function of glycogen
main carbohydrate storage product of animals
where is cellulose found
found in the cell wall of plant cells only
what is cellulose made of
made of Beta glucose linked by glycosidic bonds
what does cellulose provide
provides strength and rigidity to the cell wall
describe the structure of cellulose
straight unbranched chains that run parallel to each other, each Beta glucose molecule is inverted in respect to its neighbour causing hydrogen bonds to form between the adjacent chains known as cross links which make it really strong
what chemical elements does protein contain
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen
amino acids are the monomers of……
proteins
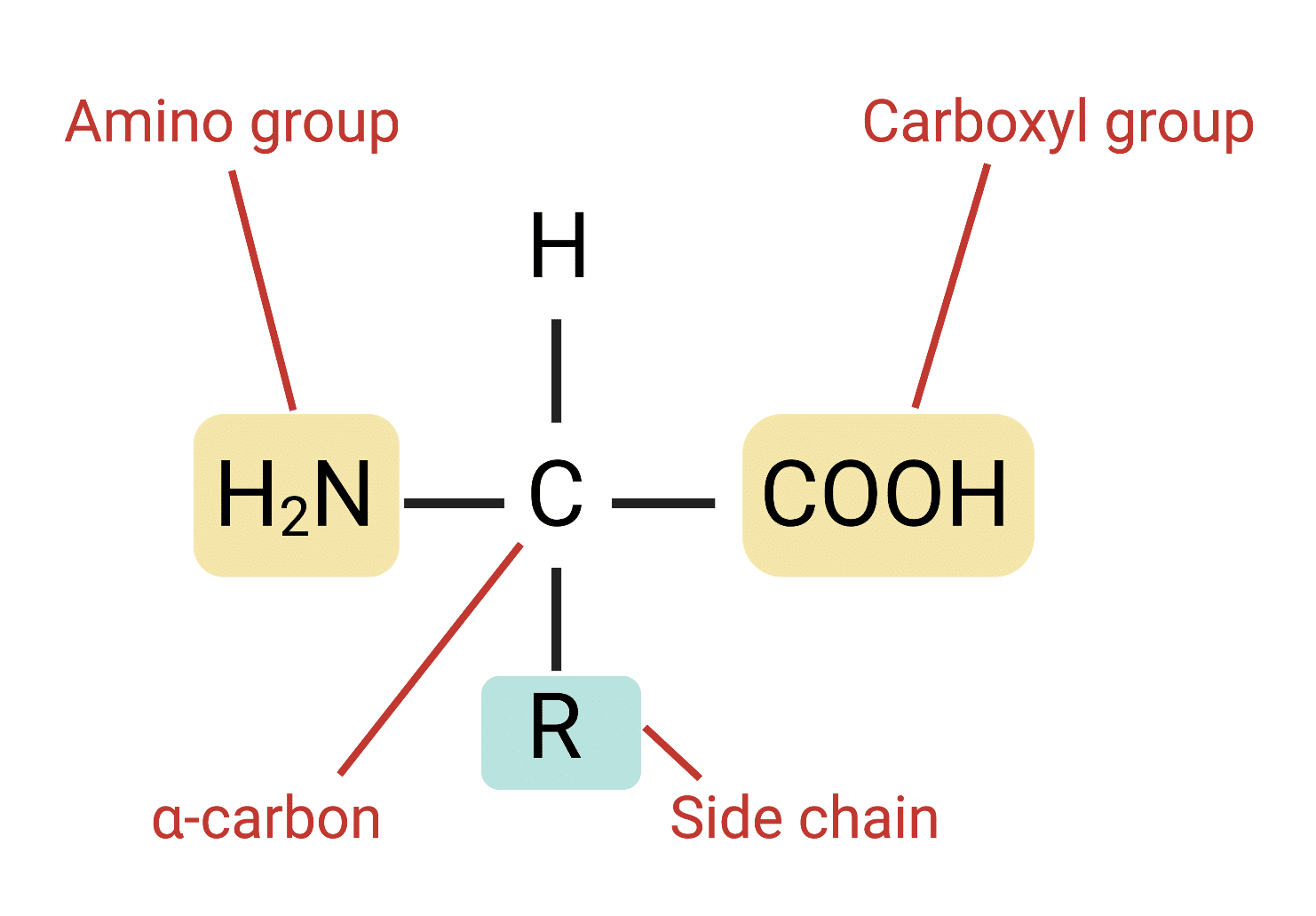
What are the 3 groups that amino acids have
amino group, carboxyl group and variable group
whats in the amino group
H-N-H
what’s in the carboxyl group
COOH
what letter represents the variable group
R
why is there a variable group
some amino acids will have a different element to create a different type of amino acid
whats the full structure of a pro
what’s it called when two amino acids join together
Dipeptide
when a dipeptide forms through a condensation reaction creates what type of bond
peptide bond
what reaction needs to take place to break down a dipeptide
hydrolysis reaction
what is a polypeptide
is the polymer of many monomers of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds
what 4 structures do proteins have
primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary
what is the primary structure
sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
what’s a secondary structure
chain doesn’t remain straight- hydrogen bonds form between amino acids in the chain
forms either a coil of alpha helix or fold into a beta pleated sheet
what’s a tertiary structure
coiled or folded chains are folded/coiled more
more bonds form between different parts of polypeptide chain including hydrogen, ionic bons and disulfide bridges
proteins made of single polypeptide chain tertiary structure forms their final 3D structure
what’s the quaternary structure
some proteins are made of several different polypeptide chains - quaternary structure is the way chains are assembled together
proteins final 3D structure
what are lipids made from
from different components and contain hydrocarbons : carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
what are the two types of lipids
triglyceride and phospholipid
what’s the structure of a triglyceride
a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid chains
how do the fatty acids attach to the glycerol molecule
attach in a condensation reaction where 3 h2o molecules are lost to form bonds
what bonds are formed between fatty acids and glycerol
Ester linkage/ bonds
what properties do a Triglyceride lipid have
long hydrocarbon fatty acid tails, when broken down lots of energy is released
insoluble in water - doesn’t affect osmotic potential
bundle together as insoluble droplets in cells - fatty acid tails face inwards shielding themselves from water with their glycerol head
what does unsaturated fatty acids mean
has one or more double carbon to carbon bond (C=C) causing a kink in chain
what does saturated fatty acid mean
single carbon to carbon bond (C-C) creating a straight chain
what is the test for lipids
emulsion test
what are the fatty acid tails made of
hydrocarbons
what are the fatty acid tails known as + what does this mean
hydrophobic - repel water/cant mix
where are phospholipids found
found in cell membranes
what is the structure of a phospholipid
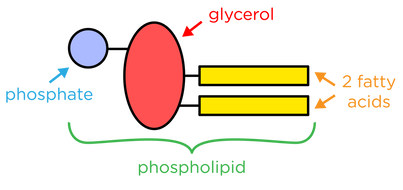
contain a phosphate, glycerol molecule and 2 fatty acid chains
the phospholipids head contains what
phosphate and glycerol
the head of phospholipids are what
hydrophilic - attracts water
what are the properties of phospholipids
-make up the phospholipid bilayer of cell membrane which controls what goes in and out
-heads are hydrophilic and tails are hydrophobic so form a double layer
-centre of bilayer is hydrophobic so water soluble substances cant easily pass through it
-channels made of proteins to allow water molecules across
what are the stages for the emulsion test
shake test substance with ethanol for about a minute then pour the solution into water
any lipid will show up as a milky emulsion
enzymes are known as…..
biological catalysts
what does it mean by enzymes being a biological catalyst
they speed up chemical reactions, they catalyse metabolic reactions both at a cellular level and for whole organism
enzyme action can be both what?
intracellular (within the cell) or extracellular (outside cells)
enzymes are a type of what
type of protein
what is the active site
is the part of the enzyme where the substrate molecule bind to
what is important about the active site
it has a specific shape
what causes enzymes to have a highly specific shape
because they are a tertiary structured protein
when talking about the active site and substrate binding you would say they are…
complimentary
when substrate joins active site what forms
a enzyme substrate complex
define activation energy
minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to occur
what do enzymes do to the activation energy
lower amount of activation energy needed to speed up the rate of reaction
why does the enzyme substrate complex lower activation energy
if two molecules need to be joined together being attached to enzyme holds them close reducing any repulsion so they can bond easily
if enzyme is catalysing a breakdown reaction, fitting into active site puts stain on bonds in substrate so substrate molecule breaks up more easily
what is the older model called of enzymes
lock and key theory/model
what does the lock and key theory state
one substrate fits one specific active site of an enzyme just like a key fits into a specific lock
as new evidence rose what was the newer version of the lock and key theory
the induced fit model
what does the induced fit model state
substrate doesn’t only have to be the right shape to fit active site, it has to make the active site change shape in the right way as well