how to get a girlfriend in 10 days
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Software change is inevitable because:
A key problem is:
new requirements emerge
business environment changes
errors must be repaired
new computers and equipment are added to the system
performance/reliability of system may have to be improved
-implementing/managing change to existing software systems
What is program evolution dynamics?
the study of the processes of system change
What are lehman’s laws
continuing change
increasing complexity
large program evolution
organisational stability
conservation of familiarity
continuing growth
declining quality
feedback system
Lehman’s law generally apply to what?
It is not clear how they should be modified for:
large, tailored systems
- shrink-wrapped products
- systems that incorporate a significant # of COTS (commercial off the shelf)
- small orgs
- med. sized systems
What is software maintenance? (EXAM)
Modifying a program after it has been put into use
Why is maintenance inevitable?
environment is changing
systems are tightly coupled with their environment
systems MUST be maintained if they want to stay useful
What are the types of maintenance? (EXAM)
repair software faults
adapt software to different operating enviornment
add/modify system’s functionality
Distribution of maintenance effort is:
65% functionality addition/modification
18% software adaptation
17% fault repair
Maintenance Cost Factors:
Team stability (cost reduce if same staff are present)
Contractual responsibility (no incentive to design for future change)
staff skills (staff often inexperienced and have limited knowledge)
program age and structure (programs age, structure degrades and become harder to understand and change)
Complexity depends on:
Complexity of control structures
complexity of data structures
object, method and module size
Process measurements used to assess maintainabilty:
number of requests for corrective maintenance
average time required for impact analysis
average time to implement change request
number of outstanding change requests
Evolution processes depend on:
the type of software being maintained
development processes used
skills and experience of the people involved
The system evolution process: (EXAM)
System release → change requests → impact analysis → release planning → change implementation → release planning or system release
release planning → change implementation or
fault repair, platform adaptation, system enehancement
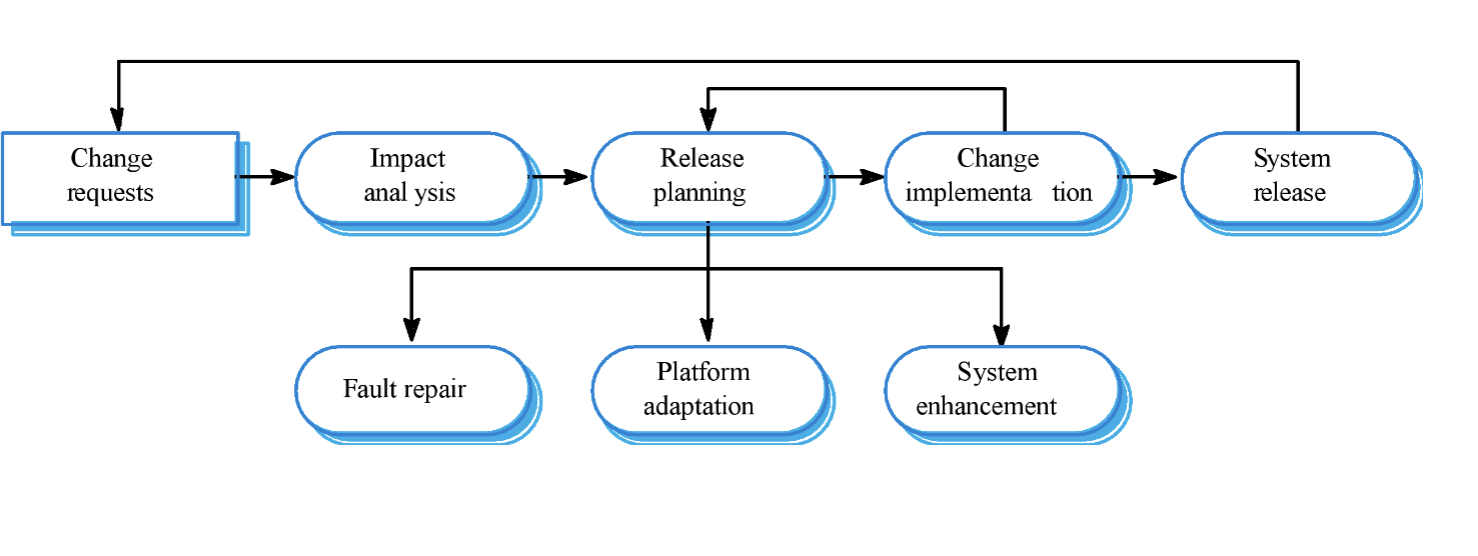
Urgent change requests happen when:
serious fault has to be repaired
changes to system’s environment have unexpected effects
if there are business changes that require a very rapid response
What is security engineering? (EXAM)
method to support development/maintenance of systems that resist malicious attacks that are intended to damage a computer-based system or its data
What are the security dimensions?
confidentiality: made accessible to unauthorized users
integrity: make data un-usable
availabilty: make accessible data unaccessible
Details of Security
security of system is a system property that reflects the system’s ability to protect itself from accidental or deliberate external attack
essential as most systems are networked
essential pre-requisite for availability, reliability, and safety
Asset (EXAM)
something of value which has to be protected
attack (EXAM)
exploitation of a system’s vulnerability
control (EXAM)
protective measure that reduces a system’s vulnerability
exposure (EXAM)
possible loss or harm to a computing system
threat (EXAM)
circumstances that have potential to cause loss or harm
vulnerability (EXAM)
weakness in a system that may be exploited to cause loss or harm
What are the threat types? (EXAM)
interception: allow attacker to gain access to asset
interruption: allow attacker to make part of system unavailable
modification: allow attacker to tamper with system asset
fabrication: allow attacker to insert false information into a system (MOST DANGEROUS)
What are types of security requirement?
identification
authentication
authorizaiton
immunity
integrity
intrusion
non-repudiation
privacy
security auditing
system maintenance
security requirement classificatoin
risk avoidance (set out the risks that should be avoided)
risk detection (define mechanisms that identify risk and neturalise)
risk mitigation (how system should be designed to recover from loss)
What is a bot?
Automated software app that performs repetitive tasks over a network
faster at these tasks than humans
can be malicious and come in the form of malware
Main cybersecurity threats
viruses
worms
trojan horses
social engineering
phishing
ransomware
pharming
zombie botnets
rootkits
mitm
What is a virus? (EXAM)
program that spreads by injecting files and then making copies of itself
some are harmelss, others may damage or destroy files
require some sort of user action
What are worms?
type of virus that can spread w/o human interaction
take up valuable memory and network bandwidth
allow attackers to gain access to your computer remotely
what are trojan horses?
computer program that hides a virus or other damaging programs.
masquerades as a benign program while quietly destroying data or damaging your system
What is social engineering?
tactic of manipulating, influencing, or deceiving a victim in order to gain control over a comptuer system, or to steal personal and financial information.
What is Phishing? (EXAM)
scam emails/texts that contain links to malicious websites
Spear Phishing: targets specific individuals through emails
Whaling: aimed at senior executives, designed to encourage victims to perform a secondary action, such as initating a wire transfer
Vishing (EXAM): defrauding people over the phone
Email Phishing: scam emails/texts that contain links to malicious websites (is this not the definition of phishing?)
What is ransomware?
prevents you from accessing your device and the data stored on it by encrypting your files
criminals will demand ransom in exchange for it back
Crypto-Ransomware: encrypts files in order to extort money.
Locker ransomware: prevents users from using their device for extortion
What is Pharming?
redirects internet users to fake websites to steal personal info
What is zomebie botnet?
botnet is # of compromised computers used to create and send spam viruses or flood network with messages as DoS attack.
compromised computers are called zombies
malware includes component that allow attacker to control infected computers remotely
What is a rootkit?
malware program that enables cyber criminals to gain access to machines without being detected
may enable keystroke logger, etc
it eliminates evidence of break-in
modifies the operating system
What is man in the middle attack?
cyber attack in which threat actor puts themselves between user and an application, to intercept their communications and data and use them for malicious purposes
Dependable programming guidelines are:
limit visibility of info in a program
check inputs for validity
provide handler for all exceptions
minimize use of error-prone constructs
provide restart capabilities
check array bounds
include timeouts when calling external components
name all constants that represent real world values
What are the System Types?
personal systems
embedded systems
distributed systems
Distributed system characteristics:
resource sharing
openness
concurrency
scalability
fault tolerance
Distributed System disadvantages:
complexity
security
manageability
unpredictability
Distributed Systems architectures: (EXAM)
Client-server architectures
called on by clients
servers that provde services treated differently from clients that use services
Distributed object architectures
no distinction b/w clients and servers. any object on system may provide and use services from other objects
Middleware:
software that manages and supports different components of a distributed system.
examples:
transaction processing monitors
data converters
communication controllers
Client-server architectures:
modelled by set of services provided by servers and set of clients that use these services
clients know of servers but servers need not know of clients
clients and servers are logical processes
mapping is not necessarily 1:1
Layered application architecture:
presentation layer
application processing layer
data management layer
Thin Client model
all of application processing and data management is carried out on the server
used when legacy systems are migrated to client server architectures
disadvantage: places heavy processing load on both server and network
Fat client model
server only responsible for data management
more processing delegated to client
most suitable for new C/S systems where capabilites are known in advance
more complex than thin client model
3-Tier architectures:
each application architecture layers may exectue on a separate processor
allows for better performance than thin-client approach and simpler to manage than fat-client approach
more scalable
Distributed Object architectures
no distinction b/w client and server
each entity is an object that provides services to other objects and receives from other objects
communicatoin is b/w middleware system called object request broker (important)
more complex to design
Distributed object architecture advantages:
allows designer to delay decisions
very open system
flexible and scalable
possible to reconfigure system dynamically
CORBA (EXAM) f
common object request broker architecture
middelware for distributed computing required at 2 levels
logical communication
component
CORBA application structure (EXAM)
gotta draw it for the exam
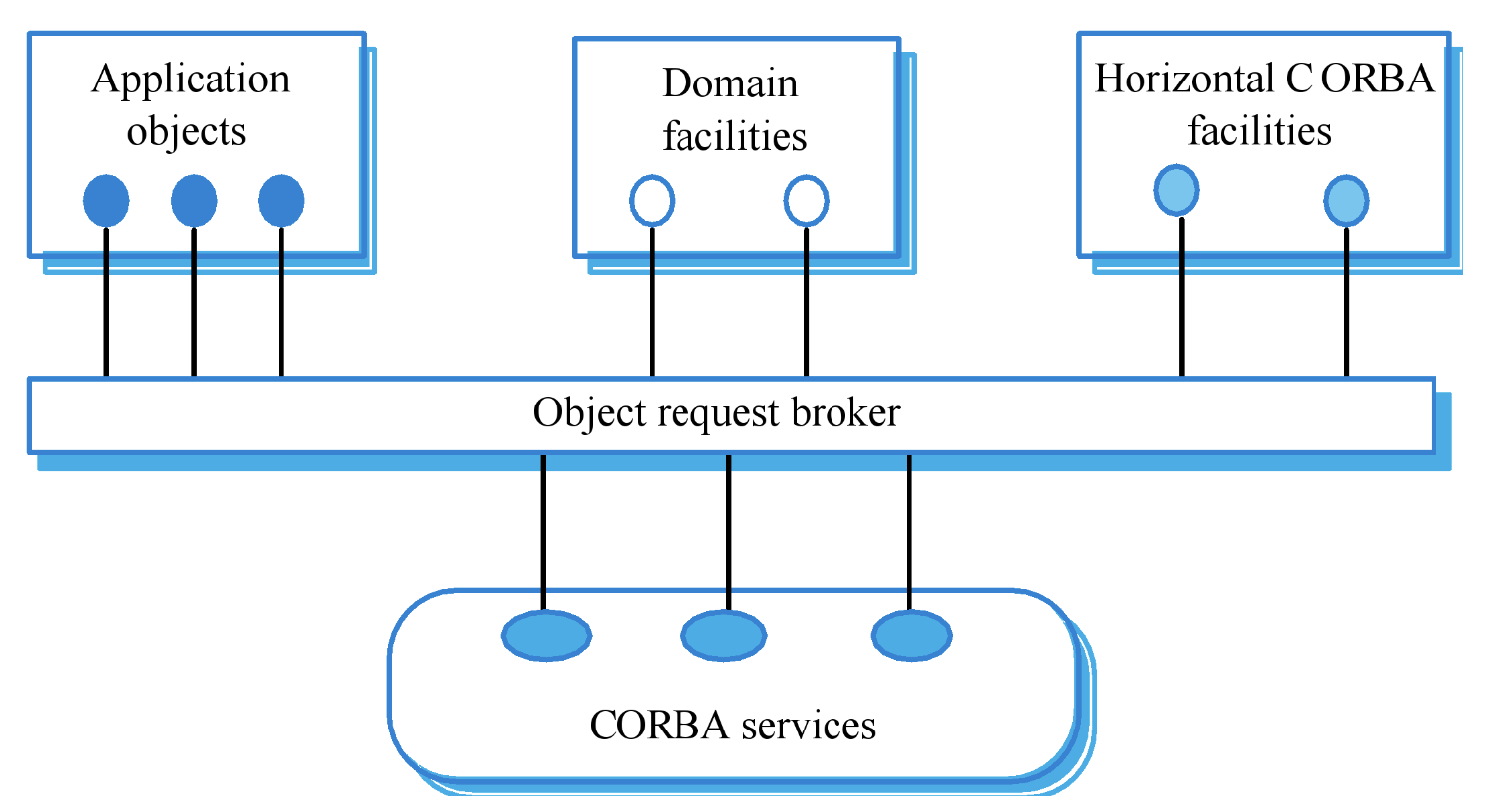
CORBA services
naming and trading services
notification services
transaction services
Peer-toPeer architectures
decentralised systems where computations may be carried out by any node in network
designed to take advantage of coputational power and storage of large number or networked computers
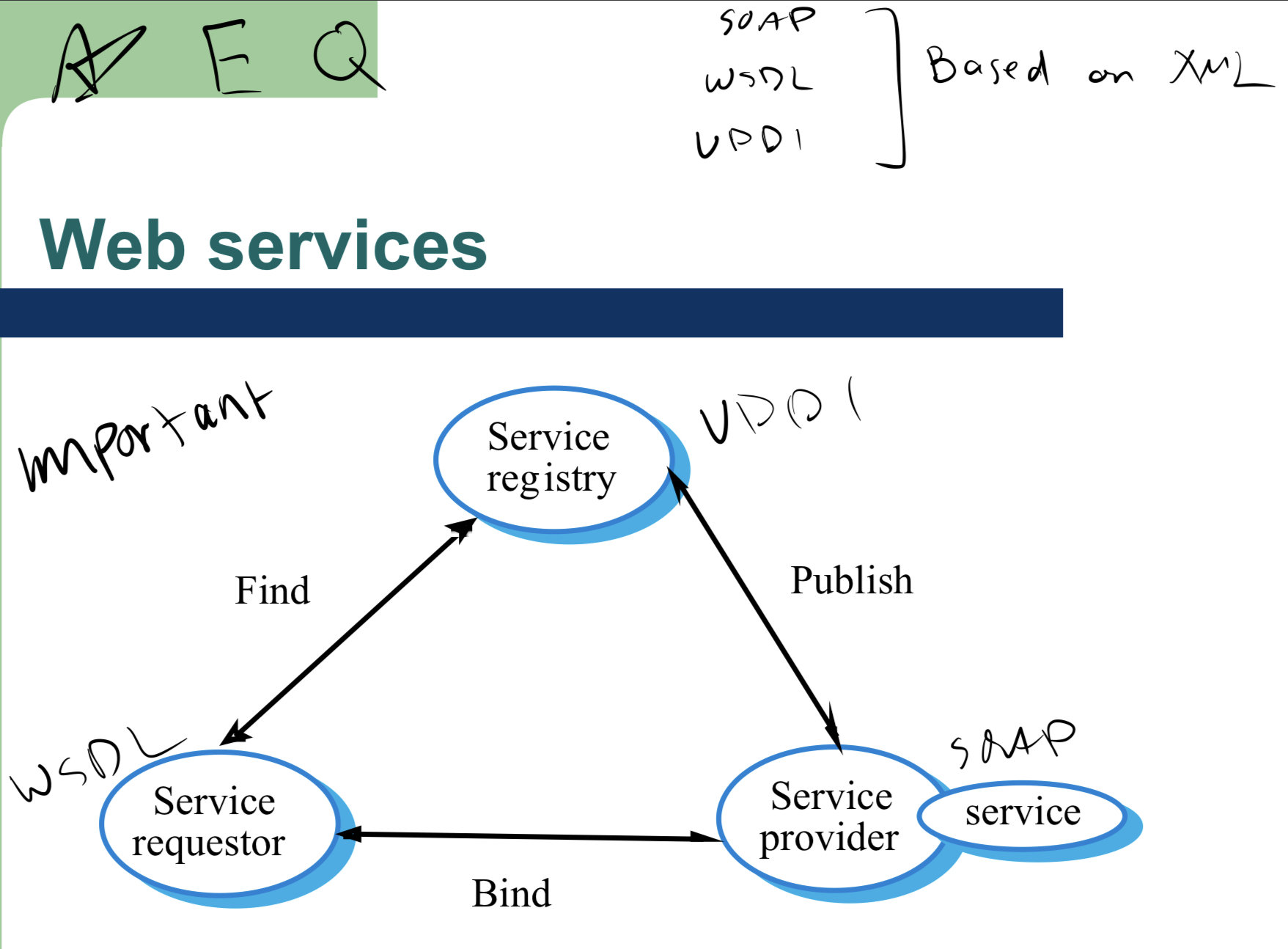
Service-oriented architectures
based around notion of externally provided services
web service is standard approach to making reusable component available and accessible across the web
Web Services chart: (EXAM)
exam question
Services and distributed objects:
provider independence
public advertising
service binding
opportunistic construction of new services
pay for use of services
smaller applications
reactive and adaptive apps
services standards (EXAM)
SOAP - simple object access protocol
WSDL - web services description language
UDDI - universal description, discovery and integration
Agile methods
focus on code over design
based on iterative approach to software dev
intended to deliver working software fast
reduce overheads in software process (limiting documentation)
Agile manifesto (EXAM)
while (value in items on the right), value items on the left more
individuals/interactions > processes and tools
working software > documentation
customer collab > contract neogtiation
responding to change > following a plan
Principles of agile methods:
customer involvement
incremental delivery
people not process
embrace change
maintain simplicity
Plan-driven development
heavy weight approach
based around separate development stages with outputs produced at each stage planned in advance
example: waterfall
agile development
light weight approach
spec, design, implementation, testing are interleaved
outputs are decided through process of negotiation during development process
Extreme programming
extreme approach to iterative dev.
new versions built several times a day
increments delivered every 2 weeks
tests must be run for every build and build only accepted if tests run successfully
Refactoring:
programming team look for possible improvements and make these improvements
improves understandability of software
changes are easier to make b/c code is well structured and clear
some changes require architecture refatoring which is COSTLY
Test-First development:
writing tests b4 code clarifies requirements
tests written as programs rather than data so they can be executed automatically
prev and new tests run auto when new functionality is added to check for new errors
customer helps write tests as dev proceeds.
Test automation:
tests are written as executable components b4 task is implemented
Pair-Programming
work in pairs
helps dev common ownership of code and spreads knowledge across the team
serves as informal review process
encourages refactoring
Scrum: (most popular agile methodology) (EXAM)
most popular form of agile development
deliverables every 2-4 weeks
3 phases
outline planning
sprint cycles
project closure phase
Scaling agile methods
successful for small and medium sized projects
improved communications
scaling up agile methods involves changing these to cope with larger, longer projects
scaling up vs scaling out
scaling up = using agile methods for large software that cannot be developed by small team
scaling out = how agile methods can be introduced to large orgs with many years of software experience (convincing people to use agile)
Software Cost Estimation (EXAM)
predicting resources required for software dev process
Software cost components (EXAM)
hardware and software costs
travel and training costs
effort costs (DOMINANT)
Productivity Measures
size related measures
function-related measures
Measurement Problems
estimating size of measure
estimation total # of programmer months which have elapsed
estimating contractor productivity
Factors affecting productivity:
application domain experience
process quality
project size
technology support
working environment
Estimation Techniques (EXAM)
alogrithmic cost modelling
cost estimation is code size
expert judgement
1+ experts use experience to predict software costs
Pros: relatively cheap estimation, can be accurate
Cons: inaccurate if there are no experts
estimation by analogy
cost computed by comoparing project to similar projects
accurate if project data is available
Impossible if no project found
pricing to win
costs whatever customer has to spend on it
pro: you get contract
con: probability customer gets system they want is small.
Managing people:
managing people working as individuals and in groups
people = orgs most important asset
Motivation:
complex issue but appears there are different types of motivation based on
basic needs
personal needs
social needs
Human Needs Hierarchy:
Top to bottom
self-realization needs
> esteem needs
> social needs
> safety needs
> physiological needs
Personality types
task oriented
motivation for doing the work is the work itself
self oriented
work is a means to an end which is the achievementof individual goals
interaction oriented
presence and actions of co-workers. people go to work b/c they like to go
Group Working:
key determinant of group performance
Group Composition:
an effective group has balance of all types
can be difficult to ahcieve because most are task-oriented
need for all members to be involved In decisions which affect the group
Group leadership
depends on respect, not title or status
technical and managerial leader
career path based on technical competence should be supported
Group cohesiveness:
members consider the group to be more improtant than any individual in it
Pros:
group quality standards develop
inhibitions caused by ignorance reduced
memberes learn from each other
egoless programming can be practiced
Group communications:
essentail for effective group working
info must be exchanged on status of work
good communications strengthen group cohesion
Group organization: (EXAM)
grop sizes should be < 8 members
break big projects into small ones
Staff selection factors:
personality,
attitude,
adaptability ,
communicatoin ability,
educational background,
programming language experience,
platform experience,
application domain experience
People Capability matruity model:
5 stages
initial
repeatable
defined
managed
optimising
What does COCOMO stand for and when was it released?
Constructive Cost Model in 1981
SLOC stands for?
Source lines of code
5 scale drivers are:
precedence
development flexibility
architecture/risk resolution
team cohesion
process maturity
Effort Equation:
_________________
EAF = _____________
E = ______________
KSLOC = ______________
effort = 2.94 x EAF x (KSLOC)^E PERSON MONTHS
effort adjustment factor from cost drivers = all cost factors multiplied together
exponent derived from 5 scale drivers
Kilo source lines of code
Duration Equation: ___________
SE = ________
duration = 3.67(Effort)^SE
schedule equation exponent from 5 scale drivers
Average staffing = ?
average staffing = effort / duration = people
what is cloud computing?
INTERNET BASED COMPUTING where software and information are provided ON DEMAND. PAY-FOR-WHAT-YOU-USE.
Cloud Computing Service Models:
Infrastructure-as-a-service: storage, memory, networks
Pro: revenue less volatile, fast to setup
Con: fierce competition, privacy concerns
Platform-as-a-service: middleware, dev tools
Pro: revenue less volatile, software licenses cost avoidance
Con: customers are heavy users, security breach concerns
Software-as-a-service: netflix, google doc
Pro: increased profit, lower up-front costs
Con: difficult integration with legacy software, connectivity requirements
Hybrid Cloud Platforms are:
big data - large volume of data to by analyzed
machine learning - use of AI to auto learn
IoT - collect/transfer data over network
Fog - structure between cloud and devices that produce data