Systems Path Section 5 - The heart pg 76-100
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
progressive heart failure, secondary to ischemic damage due to past MI or long-term CAD
chronic ischemic heart disease
sudden sustained arrhythmia leading to pump failure and death
sudden cardiac death (SCD)
MC cause of SCD
ischemic injury (CAD)
how does someone get SCD?
interruption of normal heart rhythm leading to systole or v-fib
who/why does someone get SCD?
Hx. of MI leading to fibrosis of heart, cardiomyopathies
chest wall trauma induced arrhythmia which causes SCD and is 50% lethal
commotion cordis
who does commotio cords occur in?
younger male athletes with underdeveloped chest
valvular heart diseases
stenosis, insufficiency, murmur
narrowing of heart valve, failure to open (calcification or fibrosis)
stenosis
failure of heart valve to close
insufficiency (aka regurgitation or incompetence)
turbulent flow through diseased valve
murmur
turbulence causing palpable vibration in heart
thrill
Mc cause of aortic valve stenosis
calcific aortic stenosis
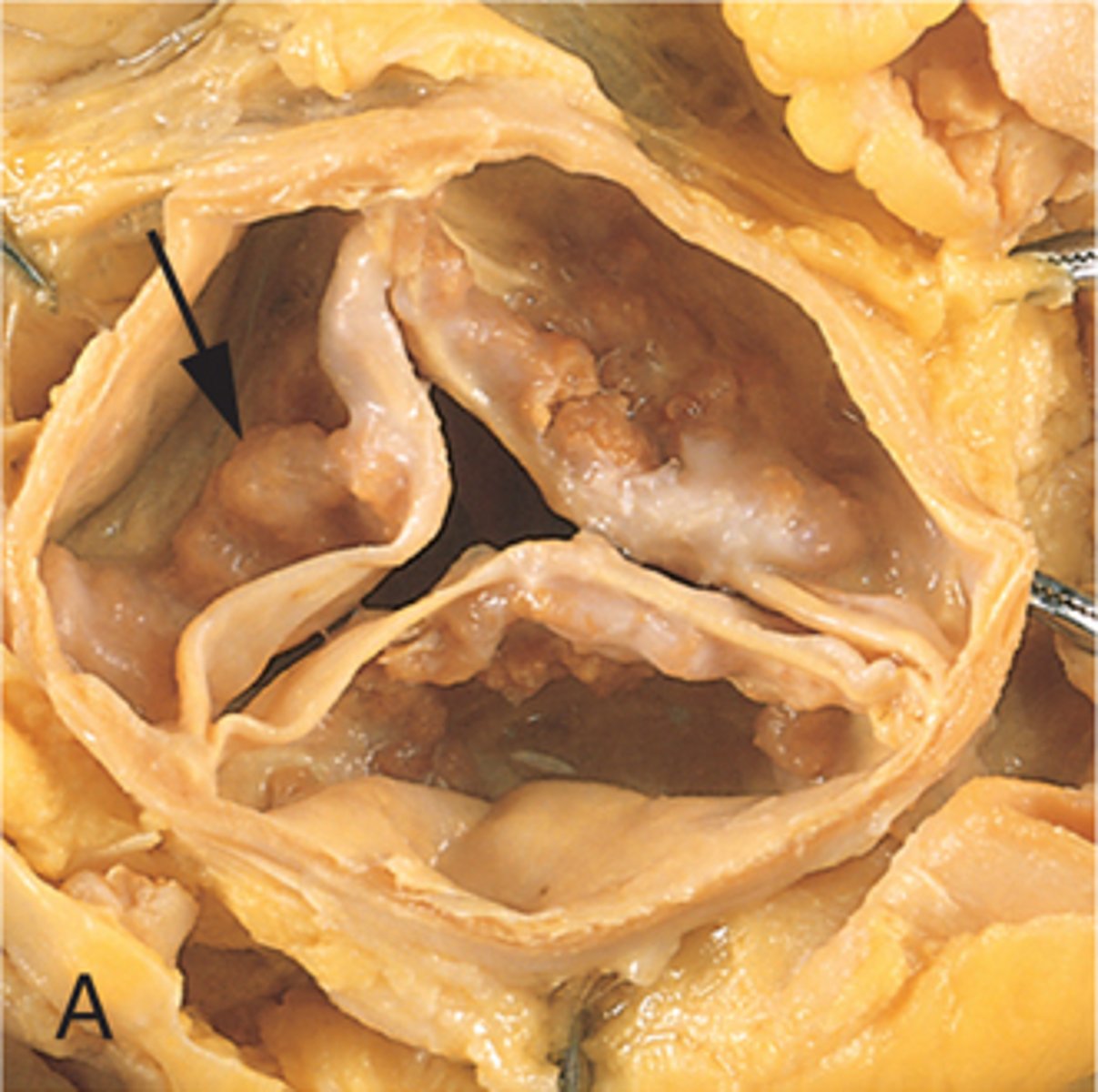
symptoms of the early stages of calcific aortic stenosis
asymptomatic, murmur, decreased cardiac output
symptoms of late stages of calcific aortic stenosis
left ventricular hypertrophy, Ca+-> severe stenosis
who is most likely to get calcific aortic stenosis ?
70-80 or younger with bicuspid aortic valve
risks associated with calcific aortic stenosis
HTN, infection/inflammation, increased cholesterol, bicuspid aortic valve
inflammatory valve disease 2-3 weeks after group A beta hemolytic strep infection NOT active bacterial infection
rheumatic valve disease
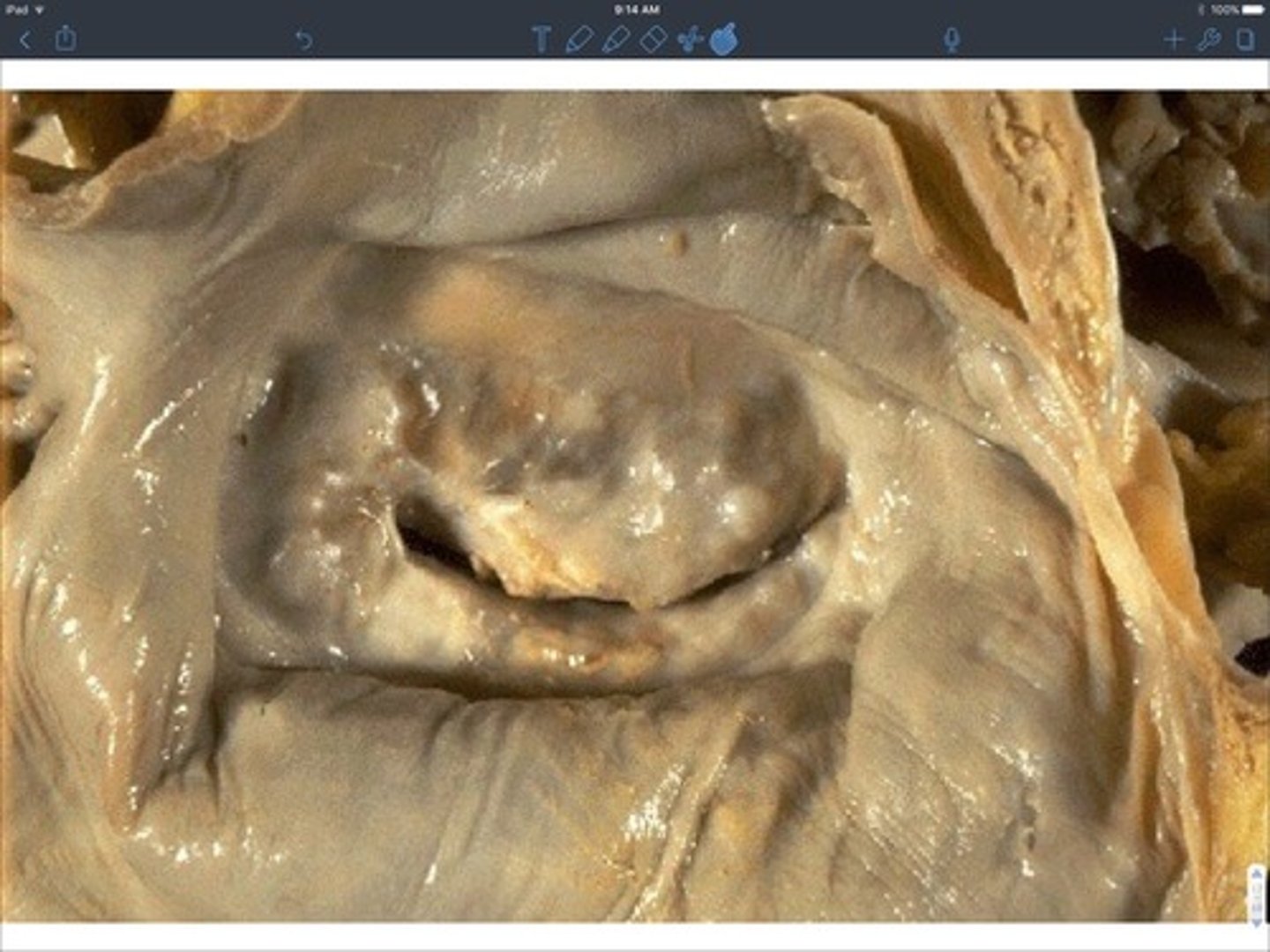
how does rheumatic valve disease occur?
immune cross reactivity due to molecular mimicry causing left side valve damage (mitral) and potential valve fusion
who is most likely to get rheumatic valve disease?
5-15 + untreated strep throat
why would someone get rheumatic valve disease?
untreated group A beta hemolytic strep
symptoms of rheumatic valve disease
fever, carditis (children), migratory polyarthritis (adults), Sydenham's chorea, skin rash
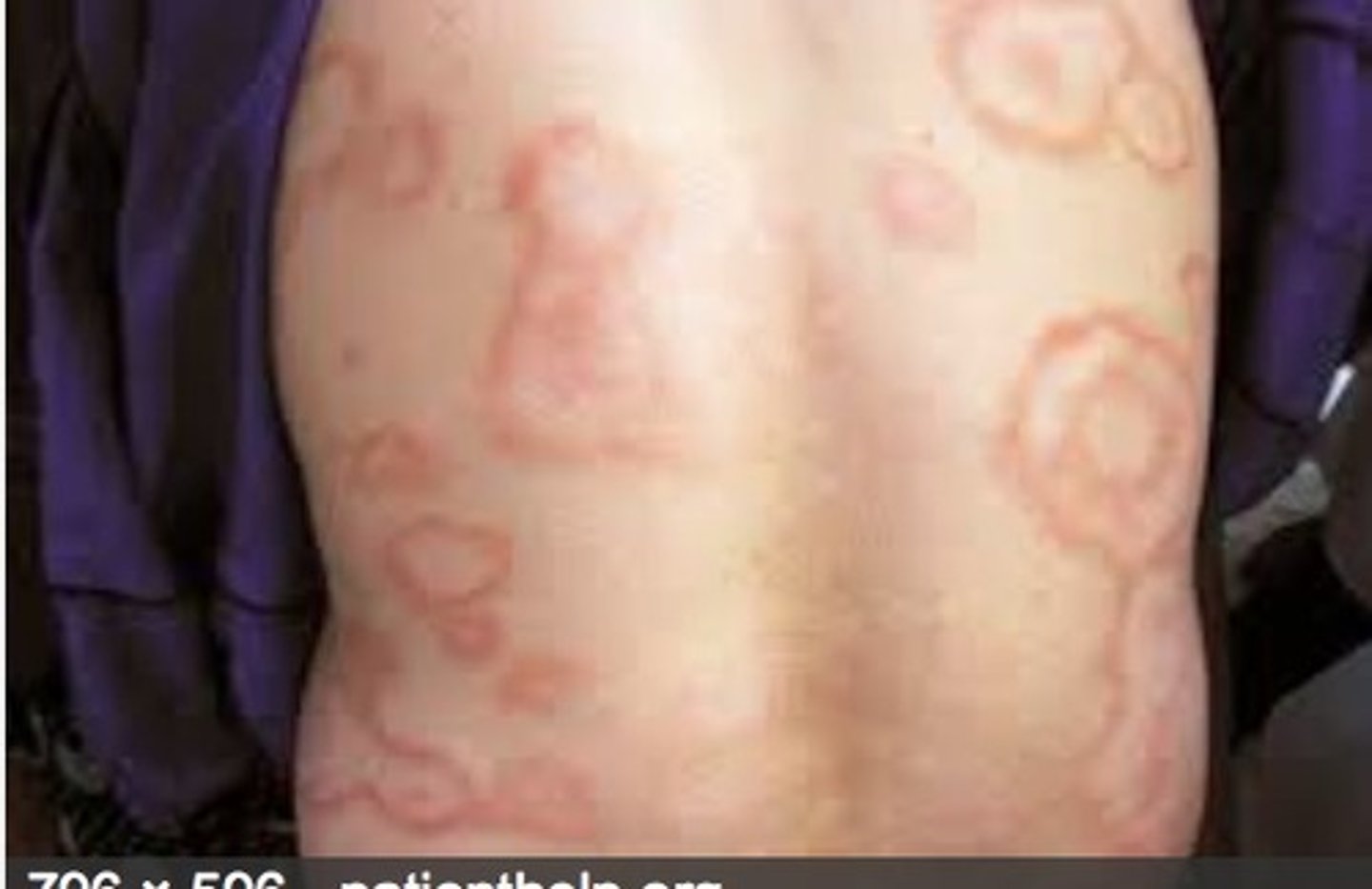
skin rash associated with rheumatic fever
erythema marginatum
what is found in 1/3 of all cases of acute rheumatic fever because of damage to corpus striatum and basal ganglia?
sydenham's chorea
70% of rheumatic valvular disease involves which valve?
mitral
rheumatic heart disease symptoms/signs
pancarditis, possible arrhythmia, valvular damage, Aschoff bodies, fibrosis