Materials HW 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Match the material classification or sub-classification to its corresponding example.
Metals
Titanium
Match the material classification or sub-classification to its corresponding example.
Ceramics
NaCl
Match the material classification or sub-classification to its corresponding example.
Composites
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plate
Match the material classification or sub-classification to its corresponding example.
Bio-materials
Artificial Bone
Match the material classification or sub-classification to its corresponding example.
Polymers
PVC
Smart materials
Shape memory alloy
What is different about the angstrom when compared to other SI prefixes
SI prefixes can be used for any unit, but angstroms are specific to meters
Order the SI prefixes from smallest to largest
Pico
Micro
Milli
Mega
Giga
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
Fe-Ni
Metallic
Match the system with its type of bonding using electronegativities
H-F
Ionic
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
Si-C
Polar Covalent
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
K-Cl
Ionic
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
Na-Cl
Ionic
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
Mn-Co
Metallic
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
C-C
Covalent
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
Sn-S
Polar Covalent
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
Si-P
Covalent
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
Ni-Ni
Metallic
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
B-N
Polar Covalent
Match the system with it's type of bonding using electronegativities
Al-Mg
Metallic
Following periodic table trends, order the atomic radius from largest to smallest (you don't need to look up the actual values!)
(Mo S Ba Cu)
Largest
Ba
Mo
Cu
S
Smallest
Following periodic table trends, order the atomic radius from largest to smallest (you don't need to look up the actual values!)
(Co Cl Al Sr)
Largest
Sr
Co
Al
Cl
Smallest
What type of bond is both directional and dictated by the shapes of orbitals?
Covalent bonding
What type of bond is both non-directional and limited by like charge repulsion?
Ionic bonding
What type of bond is both non-directional and leads to highly dense packing?
Metallic Bonding
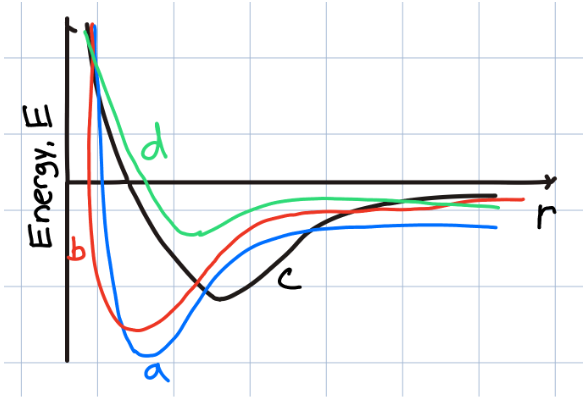
c
Which specific secondary bond is both the weakest, and is due to temporary electron cloud asymmetry in non-polar atoms and molecules?
Induced Dipole
Which specific type of secondary bonding occurs between to polar molecules, and is especially effective when hydrogen is involved?
Permanent Dipole Bonds
Which sample material has the shortest equilibrium bond length?
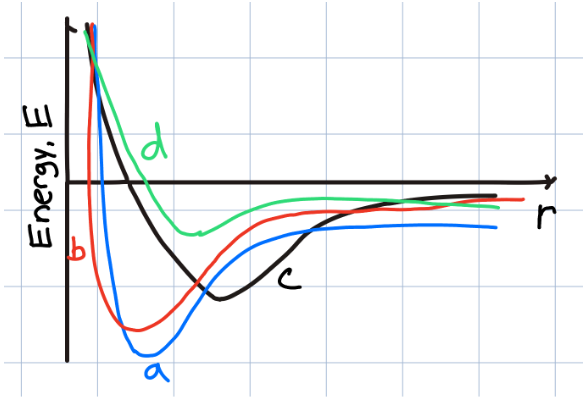
a
b
c
d
b
Which of the sample materials should have the lowest melting point?
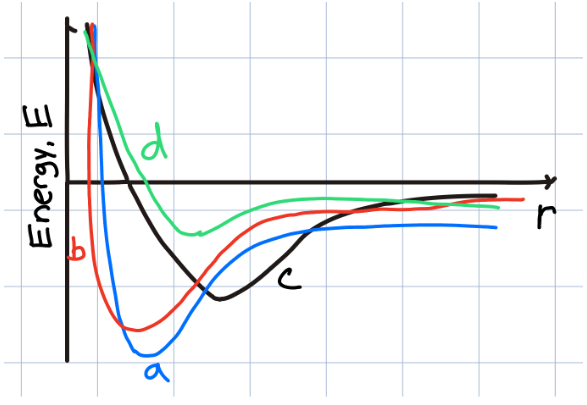
a
b
c
d
d
Which sample material should have the highest melting point?
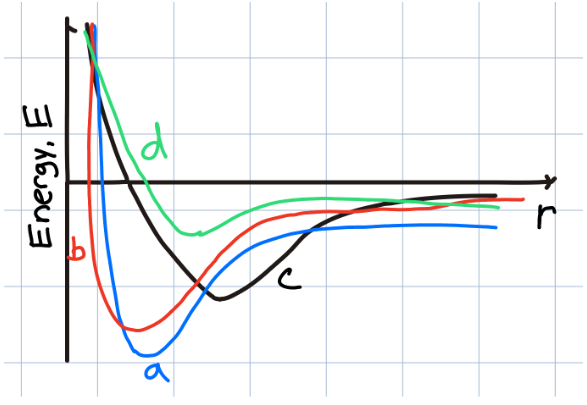
a
b
c
d
a
Which statement is true concerning Bravais lattices and crystal systems?
There are 7 crystal systems and 14 Bravais lattices
Which term correctly describes the following image of atomic packing?
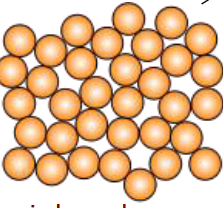
Amorphous
Which term correctly describes this following image of atomic packing?
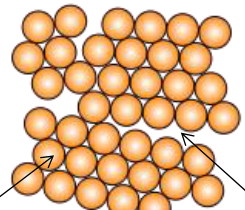
Polycrystalline
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the direction shown on the unit cell below? (Negatives are denoted by an underline instead of an overline due to Canvas limitations)
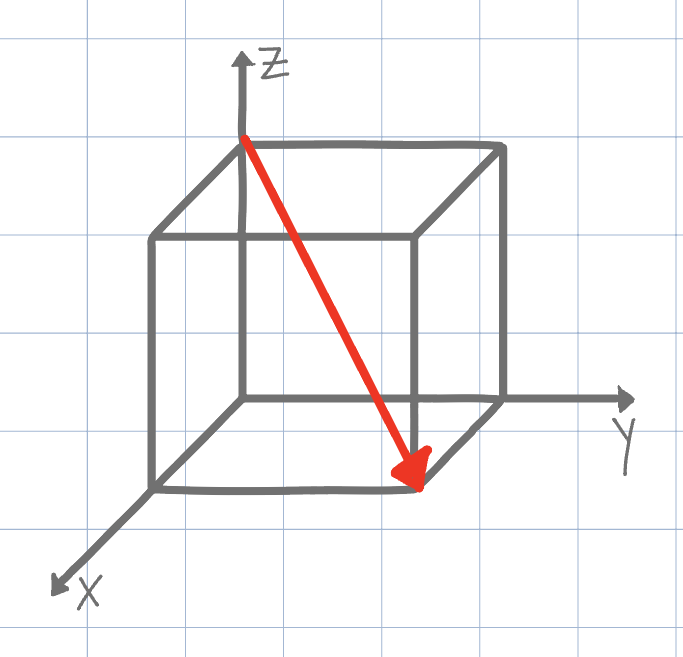
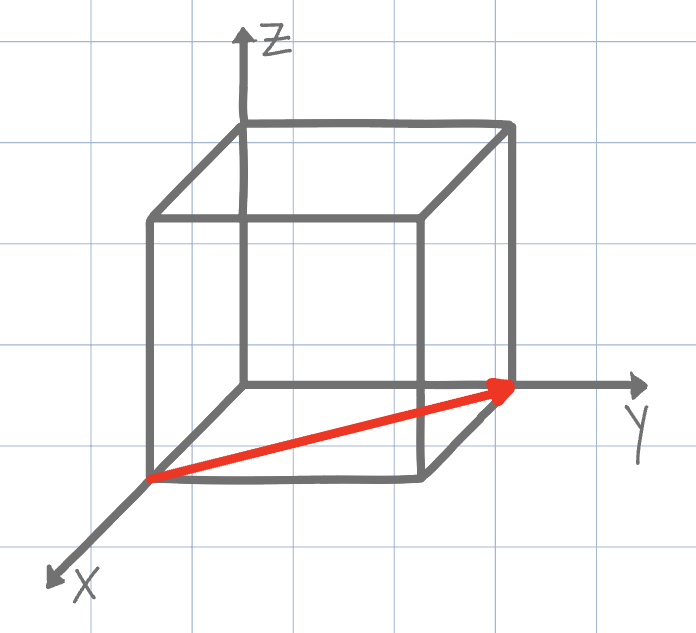
[111]
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the direction shown on the unit cell below? (Negatives are denoted by an underline instead of an overline due to Canvas limitations)
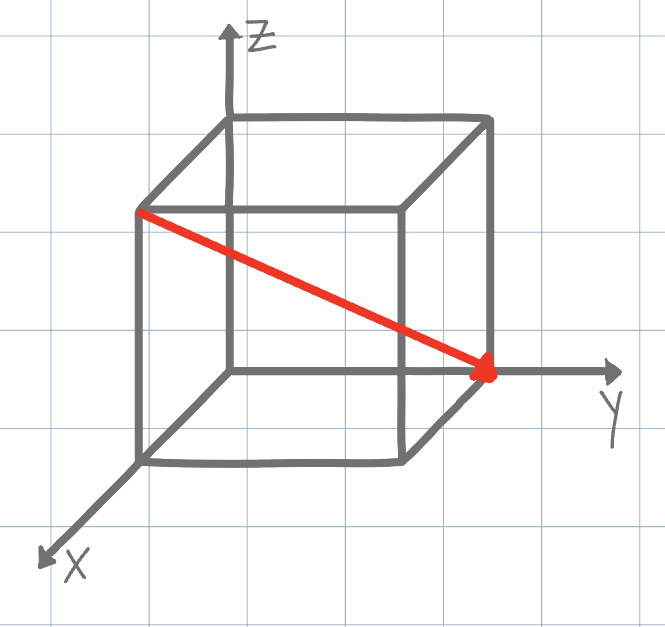
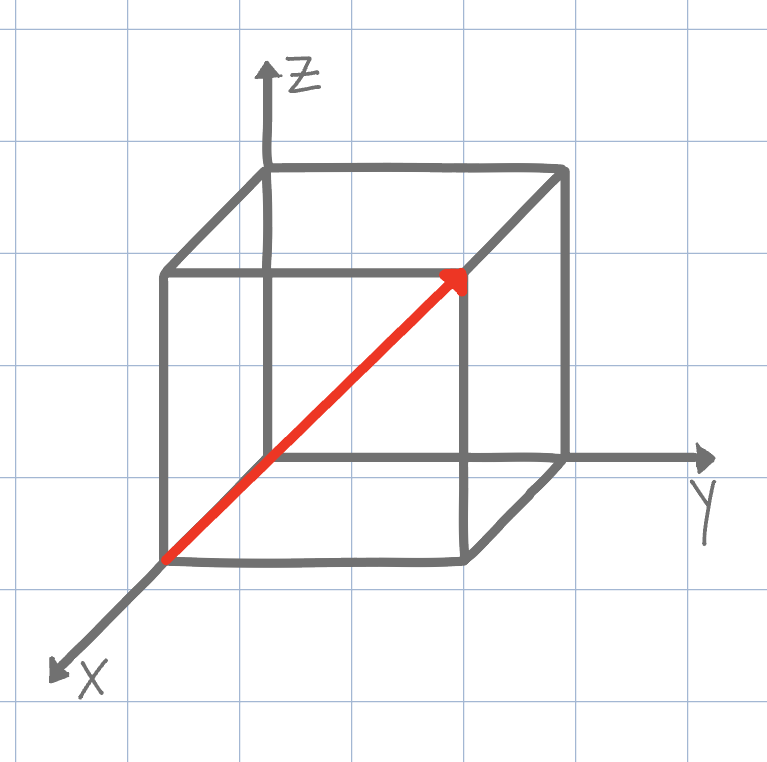
[111]
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the direction shown on the unit cell below? (Negatives are denoted by an underline instead of an overline due to Canvas limitations)
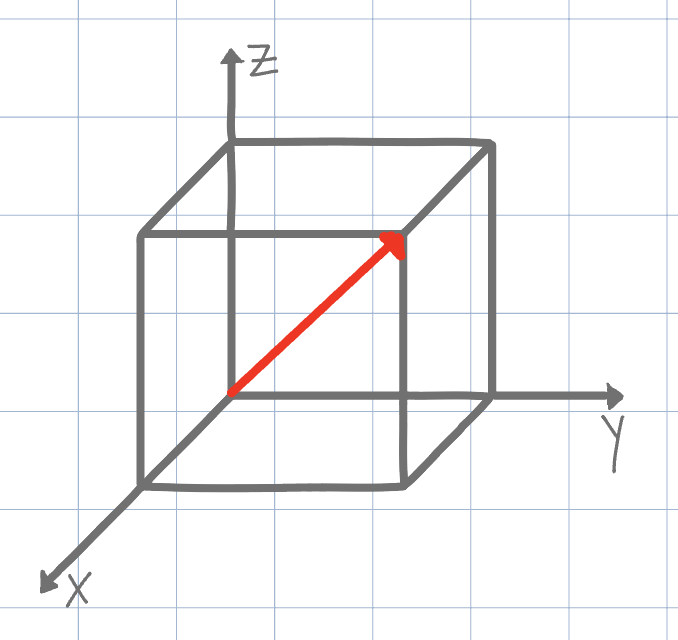
[111]
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the direction shown on the unit cell below? (Negatives are denoted by an underline instead of an overline due to Canvas limitations)
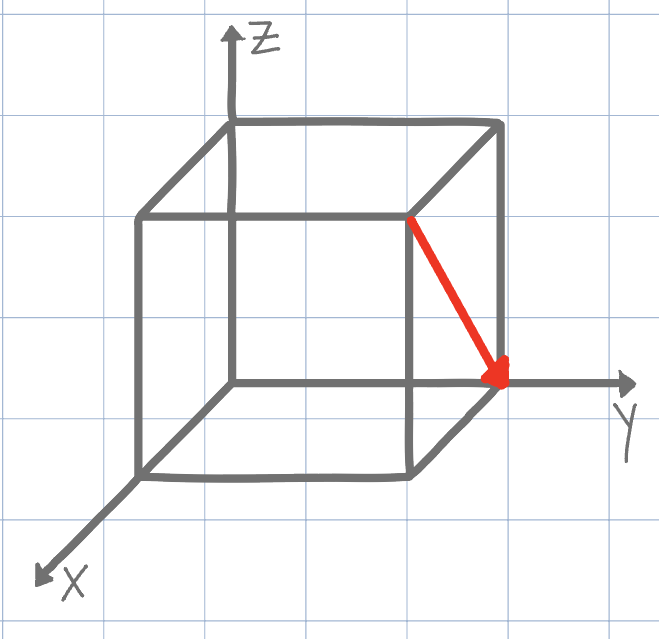
[101]
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the direction shown on the unit cell below? (Negatives are denoted by an underline instead of an overline due to Canvas limitations)
[011]
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the direction shown on the unit cell below? (Negatives are denoted by an underline instead of an overline due to Canvas limitations)
[110]
Now for something a little more challenging. This is a non-cubic lattice. Name the direction.
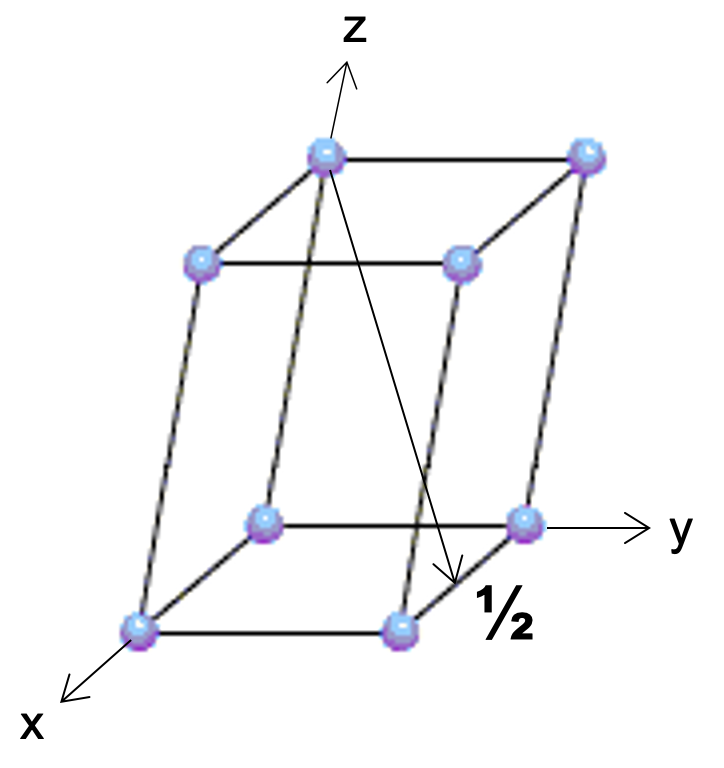
[122]
This last one is tricky. Notice I've given you the lattice parameters this time. Name the direction depicted in this non-cubic unit cell.
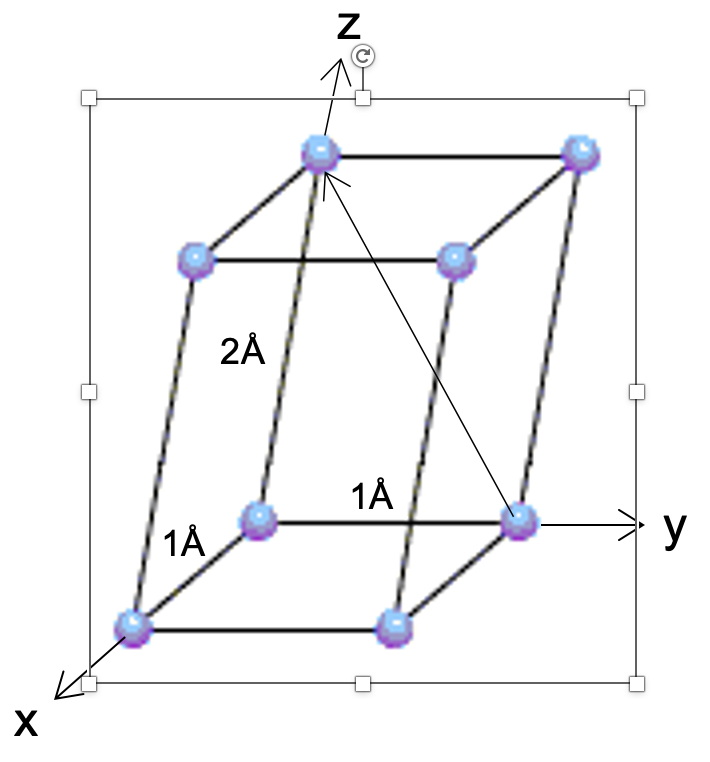
[011]
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the plane shown on the unit cell below? (Negatives are denoted by an underline instead of an overline due to Canvas limitations)
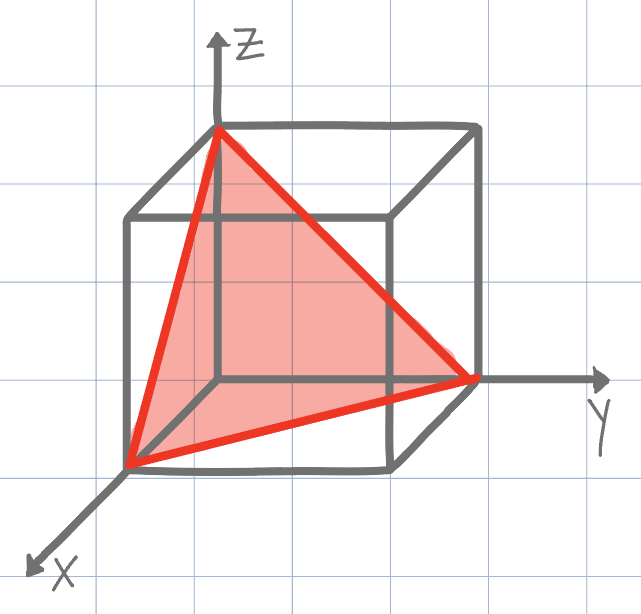
(111)
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the plane shown on the unit cell below?
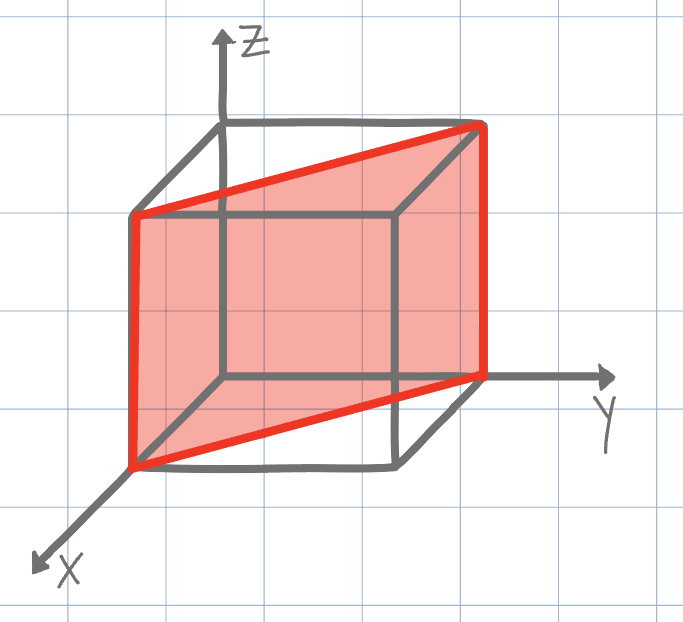
(110)
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the plane shown on the unit cell below?
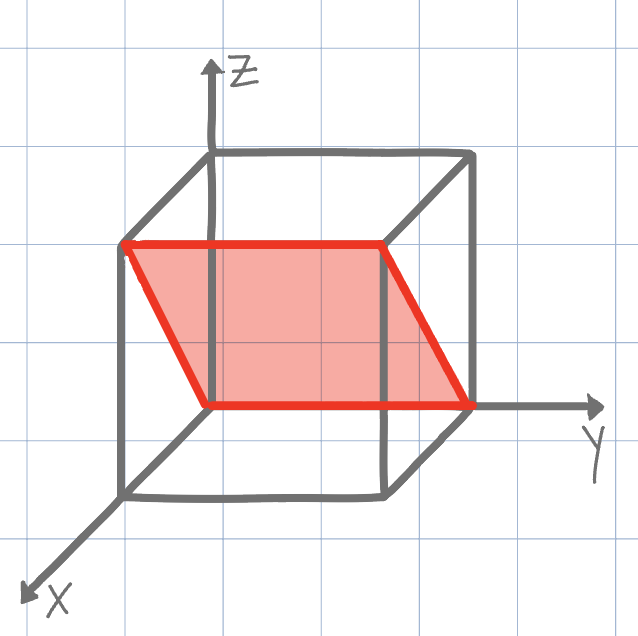
(101)
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the plane shown on the unit cell below?
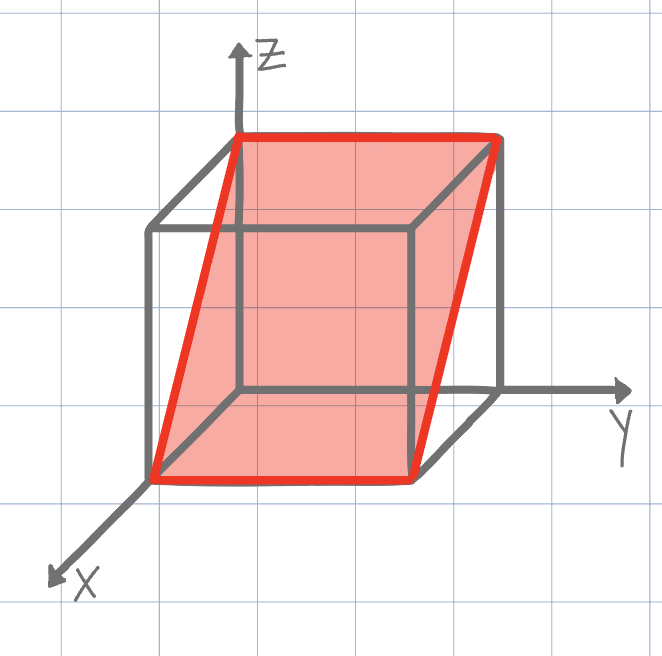
(101)
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the plane shown on the unit cell below?
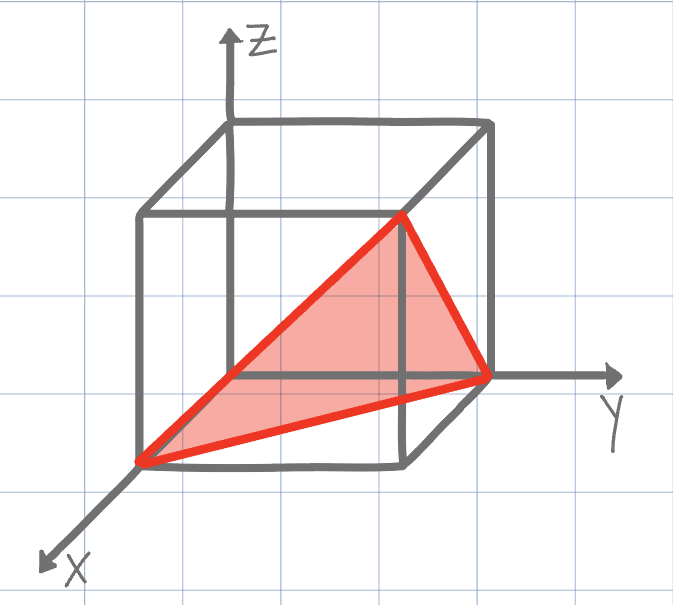
(111)
Using the conventional naming methods for Miller Indices, what is the plane shown on the unit cell below?
Plane on a cube
from top back left to top front right to bottom front left
(111)
Now let's try a harder one with planes. Again, this is a non-cubic lattice. Name that plane.
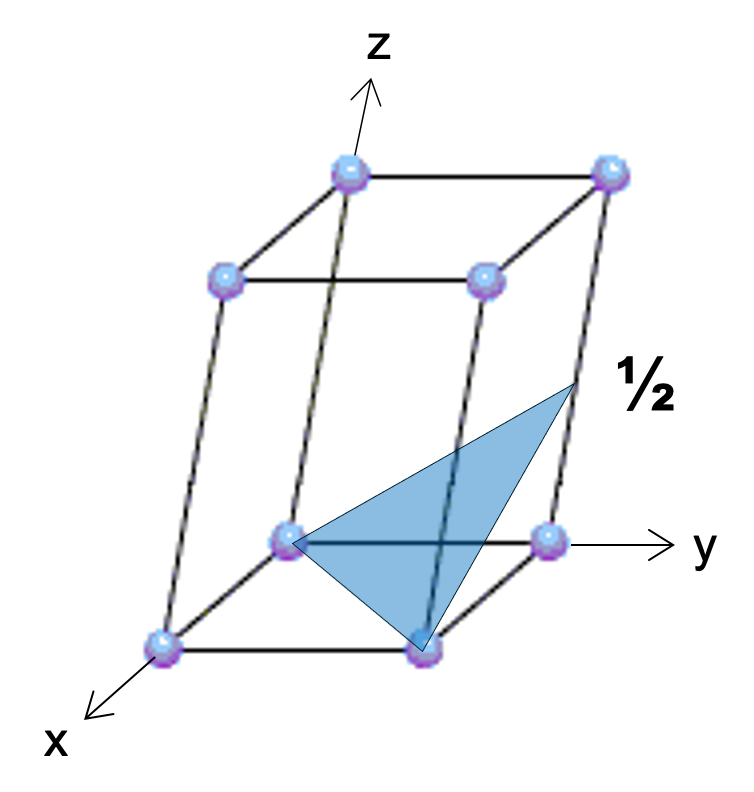
(112)
What family of planes in a metallic crystal structure is depicted in the image below?
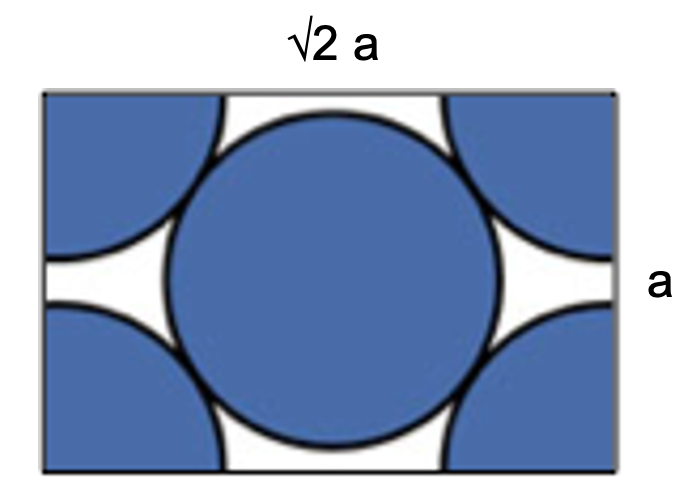
{110} BCC
How many atoms are there in the metallic BCC unit cell?
1
2
3
4
2
How many atoms are there in the metallic FCC unit cell?
1
2
3
4
4
How many atoms are there in the non-extended metallic HCP unit cell?
1
2
3
4
2
Which metallic crystal structure(s) have an atomic packing factor (APF) of 0.74, the theoretical maximum for same-size spheres filling 3-D space?
FCC and HCP
Calculate the linear packing factor of the [110] direction for an BCC unit cell (answer as a decimal, not a percentage).
0.612
Calculate the linear packing factor of the [100] direction for an BCC unit cell (answer as a decimal, not a percentage).
0.866
Calculate the linear packing factor of the [111] direction for an FCC unit cell (answer as a decimal, not a percentage).
0.408
Calculate the linear packing factor of the [100] direction for an FCC unit cell (answer as a decimal, not a percentage).
0.707
Calculate the planar packing factor for the BCC unit cell in the (110) plane (answer as a decimal, not a percentage).
0.833
Calculate the planar packing factor for the BCC unit cell in the (100) plane (answer as a decimal, not a percentage).
0.589
An unidentified metal has an atomic weight of 176.8 g/mol, an FCC structure, and an atomic radius 0.20 nm . Calculate the theoretical density
6.488 g/cm³