AP physics EM finals T3
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits to solutions go to ejtahid.com
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Transformer Turns Ratio Formula
NP: Number of turns in the primary coil
NS: Number of turns in the secondary coil
VP: Voltage in the primary coil
VS: Voltage in the secondary coil
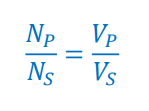
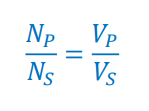
Given this formula, how do we find the power dissipated in the resistor?
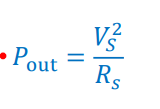
What is the unit of power?
W (watt)
What is the unit of resistance?
Ω (ohm)
How would increasing the number of turns of wire on the secondary coil of a transformer impact the currents and voltages in the primary and secondary circuits?
Overall, the whole thing will behave as a step-up transformer
There would be no effect on the primary components
Vs would increase
Is (secondary current) would decrease
Describe the impact on the currents and voltages in the primary and secondary circuits of a transformer of increasing the number of turns of wire on the primary coil of a transformer.
Overall, the whole thing will behave as a step-down transformer
Ip (primary current) will decrease
Vs will decrease
Is will increase
What is the general behavior of a stepdown transformer?
Stepdown: Np > Ns (Voltage goes DOWN)
Vs < Vp
Is > Ip
What is the general behavior of a step-up transformer?
Step-up: Ns > Np (Voltage goes UP)
Vs > Vp
Is < Ip
For an ideal step-down transformer, which of the following is/are the same in the primary coil and in the secondary coil?
Frequency
Maximum voltage
Maximum current
Average Power
Frequency and Average power
Describe the relationship between current and voltage when XL>XC?
XL>XC
ELI
E = VOLTAGE leads current
L = More INDUCTIVE than capacitive
I = phase angle ϕ is POSITIVE
Describe the relationship between current and voltage when XL< XC?
XL< XC
ICE
I = CURRENT leads voltage
C = more CAPACITIVE than inductive
E = phase angle ϕ is NEGATIVE
Describe the relationship between current and voltage when XL= XC?
voltage and current are IN PHASE
purely resistive (resonance)
phase angle ϕ is 0
When does resonance occur?
When XL= XC (inductive reactance is equal o inductive capacitance)
What is the SI unit of capacitive reactance AND inductive reactance?
ohm (Ω)
What is the formula of angular frequency?
ω = angular frequency in rad/s
f = frequency in Hz
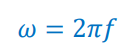
Instantaneous Voltage in AC Circuit
v = instantaneous voltage
Vmax = peak (maximum) voltage
ω = angular frequency
t = time
sin(ωt) = describes how the voltage varies sinusoidally with time
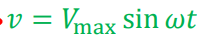
How do we find Vmax from the RMS value?
(multiply root(2) with the RMS)

How do we find the RMS value from Vmax?
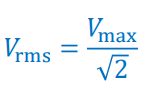
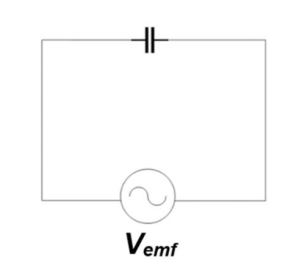
Q9a) A circuit containing a capacitor has a source of time-varying EMF that provides a voltage given by V = VCsinωt. What is the current in the circuit when the potential difference across the capacitor is largest?
IC = 0

Q9b) A circuit containing a capacitor has a source of time-varying EMF that provides a voltage given by V = VCsinωt. What is the potential difference across the capacitor when the current in the circuit is the largest?
VC = 0
What is formula of XL?
XL = ωL
What is formula of XC?
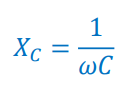
What is the impedance formula?
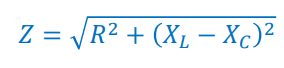
How do we find Imax from impedance (Z) and Vmax?
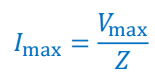
How do we find the phase constant?
(according to Q12 of the structure?)
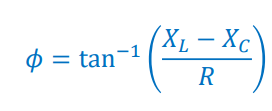
Intensity of unpolarized light after passing through the first polarizer
I0 = Initial intensity
I1 = New (first) intensity
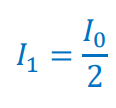
Intensity of polarized light after passing through the second polarizer
I2 = New (second) intensity
θ = angle
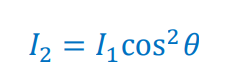
What’s the unit of light intensity?
W/m2
Q14) Unpolarized light is passed through a Polaroid filter. What happens to the vibration directions and the intensity of the transmitted light?
Vibration direction: in one direction only (in a single plane along the filter's axis)
Intensity: half the original intensity (halved)
Q15) How do we find the frequency of a radio wave?
f = Frequency of the wave
c = speed of light 3×108
λ = wavelength in meters
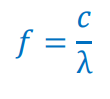
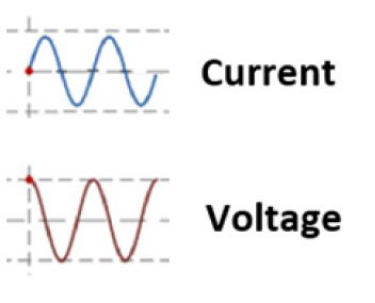
Who is leading who?
What is the electrical component doing this?
(hint: look at the beginning of the graph and which one is higher on the Y axis)
Voltage is leading current
this is the INDUCTOR
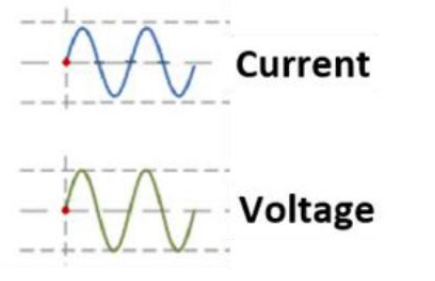
Who is leading who?
What is the electrical component doing this?
(hint: look at the beginning of the graph and which one is higher on the Y axis)
Voltage and current are in phase
This is the RESISTOR
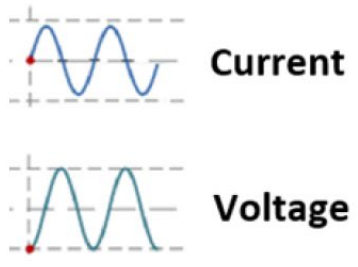
Who is leading who?
What is the electrical component doing this?
(hint: look at the beginning of the graph and which one is higher on the Y axis)
Voltage lags current (or) Current leads voltage
This is the CAPACITOR
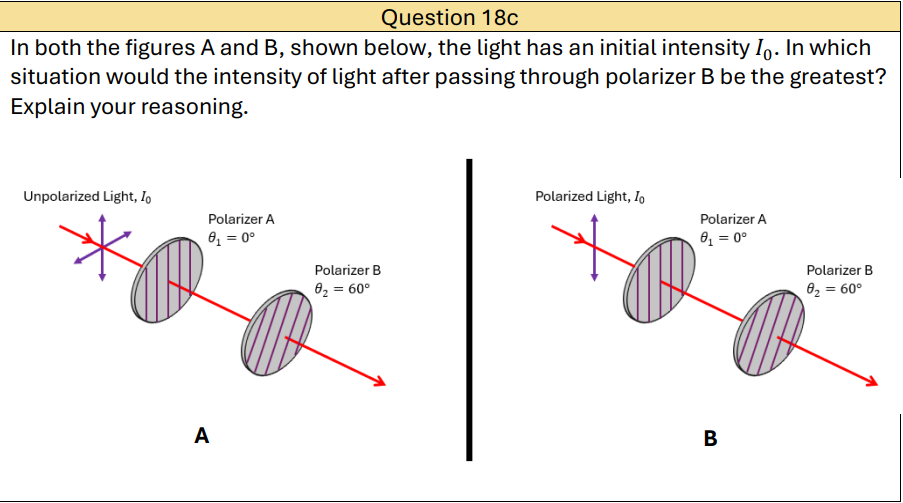
Why does polarized light end up having greater intensity?
because it starts with a higher intensity before reaching Polarizer B
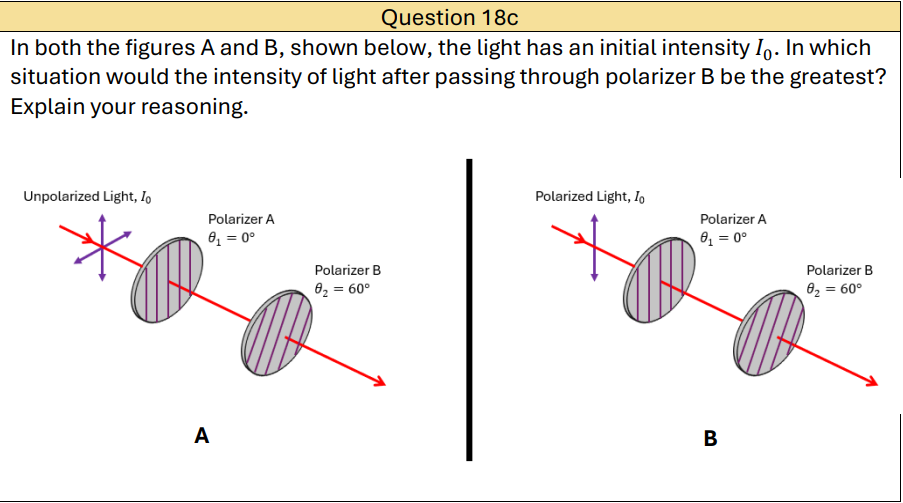
Why doesn’t the polarized light lose its intensity after passing through polarizer A?
its polarization direction is parallel to the polarizer’s axis.
Q19c) What would be the effect of increasing the resistance of the resistor on the resonant frequency and maximum current in a series RLC circuit?
As the resistance increases, the maximum current decreases.
Resonant frequency remains constant
The graph will be smaller and broader
Q19d) What would be the effect of decreasing the resistance of the resistor on the resonant frequency and maximum current in a series RLC circuit?
As the resistance decreases, the maximum current increases.
Resonant frequency remains constant
The graph will be larger and sharper
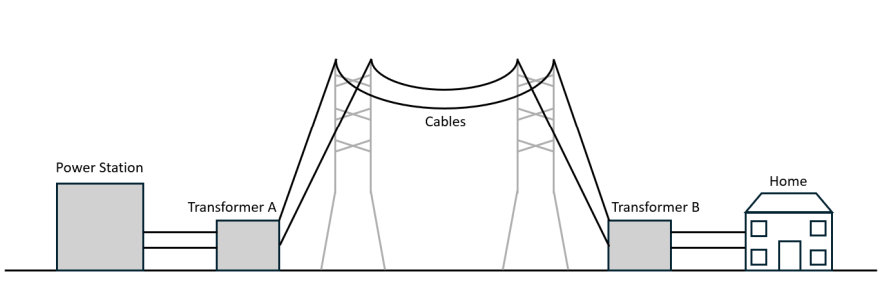
Q17) What type of transformer is ‘transformer A’ and what does it do?
A: Step-up transformer increases the voltage to reduce power loss.
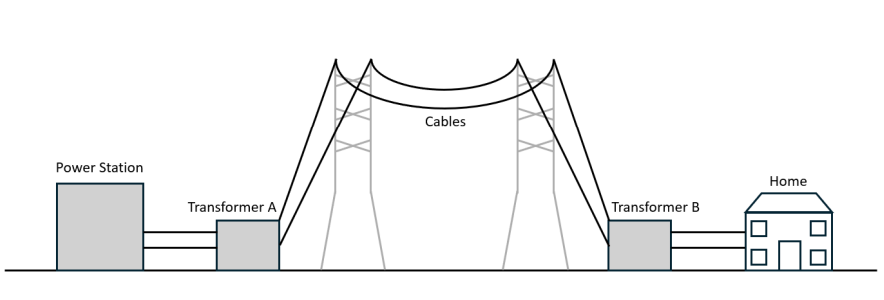
Q17a) What type of transformer is ‘transformer B’ and what does it do?
B: Step-down transformer decreases the voltage for home applications.
Q17d) Why do we use high alternating voltage to transmit electrical power over large distances?

How does a step-up transformer look like?
REMEMBER: more secondary turns
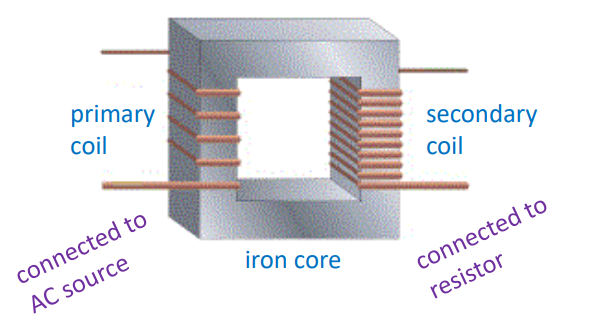
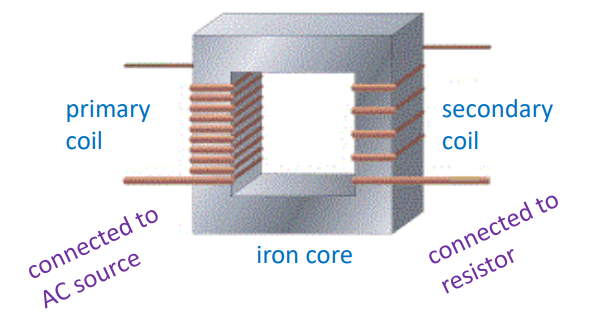
How does a step-down transformer look like?
REMEMBER: more primary turns
Q13) How do we find the angle between 2 polarizers?
IMPORTANT: PLEASE SET YOUR CALCULATOR IN DEGREES!!!
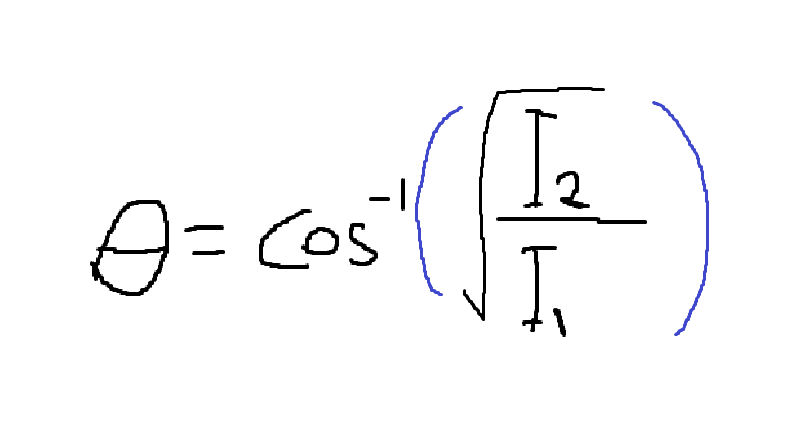
Speed of light
3×10^8