BIOL.122 Lecture 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
complete
Last updated 9:23 AM on 5/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
Name 5 types of connective tissue
Loose CT. Dense CT. Cartilage. Bone. Blood
2
New cards
What is the role of most CT
To provide strength and support
3
New cards
Adipose tissue role
Energy storage
4
New cards
Examples of loose CT
areola, adipose, reticular
5
New cards
Examples of dense CT
Regular, irregular, elastic
6
New cards
Three cartilage types
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
7
New cards
structure of reticular connective protein fibres
thin and branched collagen with other proteins
8
New cards
Qualities of collagen protein fibres
non elastic, strong, flexible
9
New cards
Qualities of elastic protein fibres
‘rubbery’, fibrillin and elastin
10
New cards
Qualities of reticular protein fibres
thin and branched collagen. much looser, associated with internal organs
11
New cards
where is areola CT found
surrounding blood vessels and nerves
12
New cards
what is the role of areolar CT
protects nerves and vessels from mechanical stressors, the fibroblasts also secrete collagen
13
New cards
name the three types of protein fibres
collagen, elastic, reticular
14
New cards
what role is adipose tissue adapted to
storage of triglycerides for energy, shock absorption, thermal insulation
15
New cards
Structure of Regular Dense CT
Closely packed parallel collagen fibres
16
New cards
where is regular dense CT found
areas where tension is exerted along axis of fibres. eg tendons, ligamentsm cornea, and sclera
17
New cards
Why is regular dense CT used
for protection
18
New cards
structure of dense irregular CT
thick and irregular collagen fibres
19
New cards
where is dense irregular CT found
where tension is exerted in different planes eg the skin dermis.
20
New cards
role of elastic CT
combines strength with elasticity
21
New cards
where is elastic CT found
artery walls
22
New cards
what is a molecule with many hydrophobic regions
elastin
23
New cards
what is the most widely distributed cartilage
hyaline
24
New cards
what is the role of hyaline cartilage
firm support with flexibility, shock absorption
25
New cards
what is articular cartilage
cartilage at the ends of long bones to help reduce joint friction
26
New cards
where is elastic cartilage found
places where strength and flexibility is found
27
New cards
structure of fibrocartilage
parallel collagen fibres with chondrocytes
28
New cards
qualities of fibrocartilage
strong and rigid
29
New cards
where is fibrocartilage found
where strong support is needed, eg intervertebral discs.
30
New cards
structure of bone
collagen fibres with matrix of inorganic calcium salts
31
New cards
role of bone
\-supports and protects soft tissues
\-fat storage
\-synthesis of blood cells
\-storage of stem cells
\-fat storage
\-synthesis of blood cells
\-storage of stem cells
32
New cards
exocrine secretion types
unicellular, multicellular
33
New cards
glandular epithelium secretion types
endocrine and exocrine
34
New cards
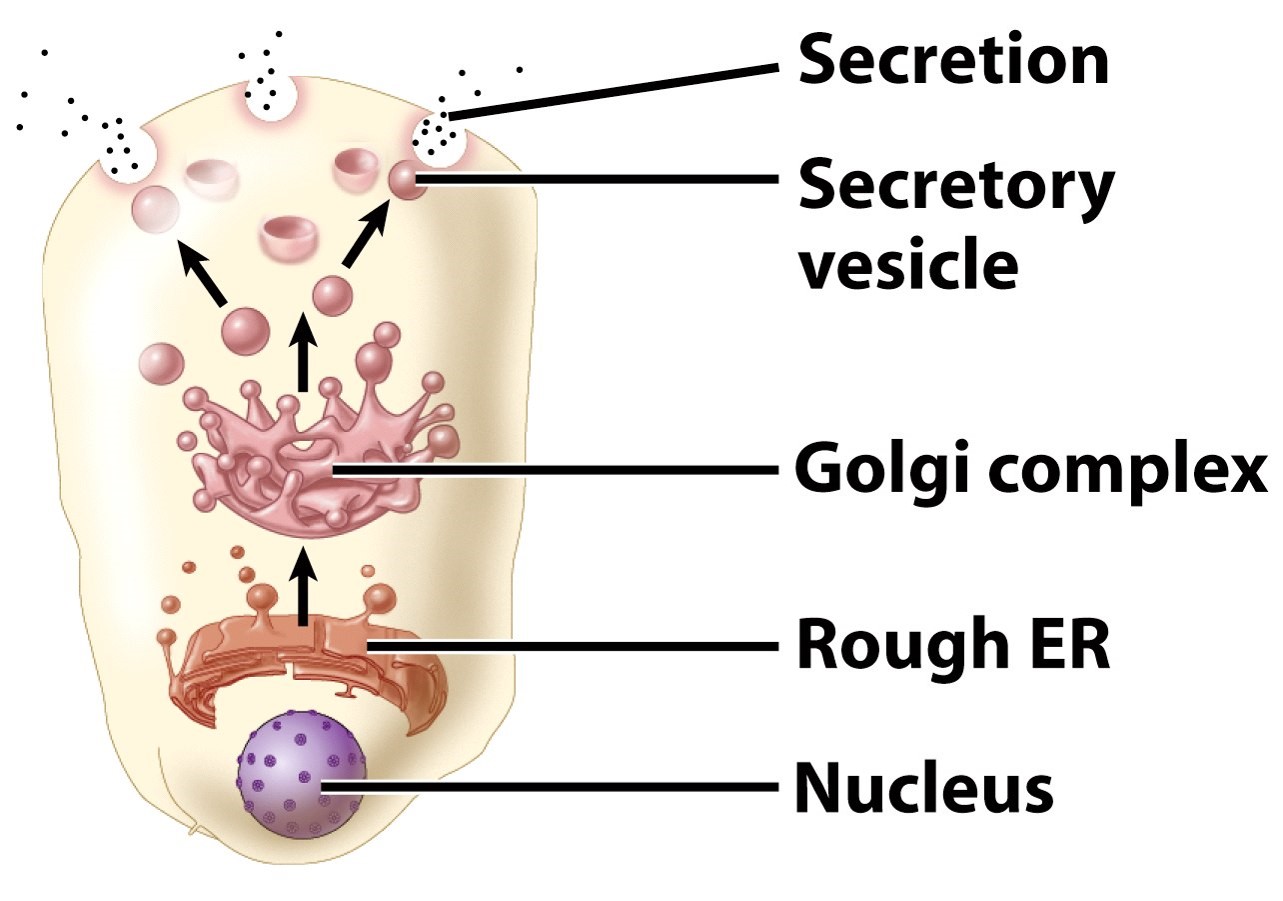
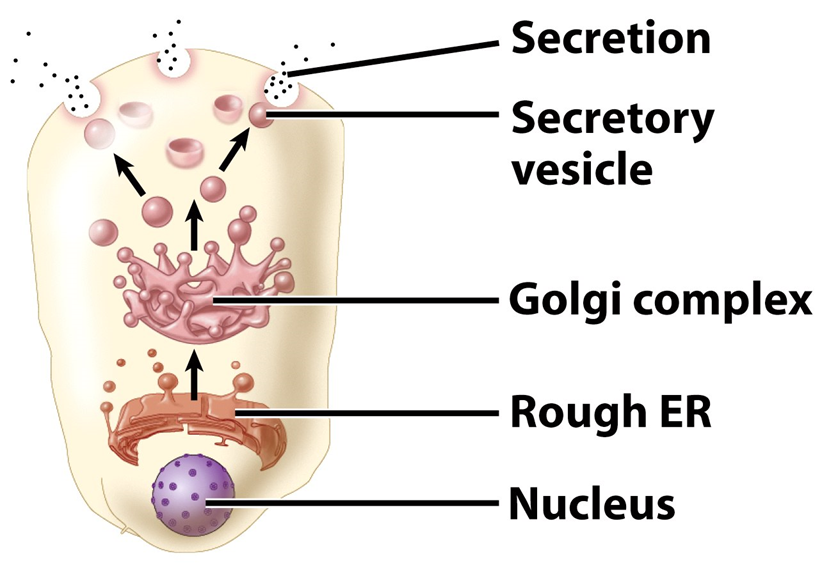
merocrine secretion
very common, often by goblet cells
35
New cards
types of secretion from common to rare
merocrine, apocrine, holocrine
36
New cards
what is the difference between simple and compound glands
simple have no branching, compound does branch
37
New cards
what type of CT is blood
Atypical, liquid
38
New cards
What are red and white blood cells surrounded by
fluid plasma matrix
39
New cards
What is seen in both types of gland
tubular, tubular coiled, acinar