Physics Chp 2 Matter, Atoms, and Atomic Structures
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Element is a ____ substance
simple; cannot be broken down into any smaller substances
atom is an
element
Atom is the basic building ____ of all substances
block
What is a compound?
2 or more elements chemically combined
Compound is a ____ substance
complex
What is the smallest particle of a compound?
molecule
Define molecule
two or more atoms chemically united
Radiation is a term applied to many forms of ____
energy
What is the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation?
Ionizing radiation has the energy/power to remove electron from a bond. This can cause serious disruption of the metabolic relationships in the body(dangerous). Non-ionizing is not a dangerous form of radiation
Fundamental particles of an atom
neutron, proton, elecron
What two sub particles are at the center of the nucleus
neutron and proton
What sub particle is outside the nucleus?
electron
amu of a neutron
1.008 amu
amu of a proton
1.007 amu
amu of electron
5.48 x 10^-4
An electron is extremely ______ compared to a proton and neutron
small
What part of the atom distinguishes one element from another?
proton
A neutral atom has the same number of
protons and electrons
What are the names of the electron shells innermost to outermost
K-shell, L-shell, M-shell, N-shell, O-shell, P-shell, Q-shell
The nucleus has a __________ charge
positive
Most of the space in an atom is _____ because of the distance from the nucleus to orbital shells
empty
What is the closest shell to the nucleus?
K shell
How many electrons can the K shell hold?
2 electrons max
What is the equation to determine the max number of electrons each shell can hold?
max # = 2n^2
(n= shell number) (shells are numbered 1-7 starting with the K shell as 1)
What is the octet rule?
The outermost shell (valence shell) of a stable atom cannot hold more than 8 electrons
Valence shell is ____ when there is 8 electrons in the valence shell
inert
T or F: The octet rule trumps the max # electron shell rule
True
Define the electron binding energy
How tightly the electron is held in its shell
How is the electron binding energy determined?
By the distance of electron shell from the nucleus
What shell has the highest binding energy?
K shell (binding energy decreases the further the shell)
eV
electron volt
Ionization
Adding or removing an electron from its shell
What type of charge will an atom have if an electron is added
it is a negative ion
What type of charge will an atom have if an electron is removed
it is a positive ion
When is non-ionizing radiation released
When an electron moves from an inner shell to an outer shell
T or F: An electron gets excited if given extra energy
True
How is atomic mass calculated?
protons + neutrons in an atom
How is the atomic number determined?
# of protons
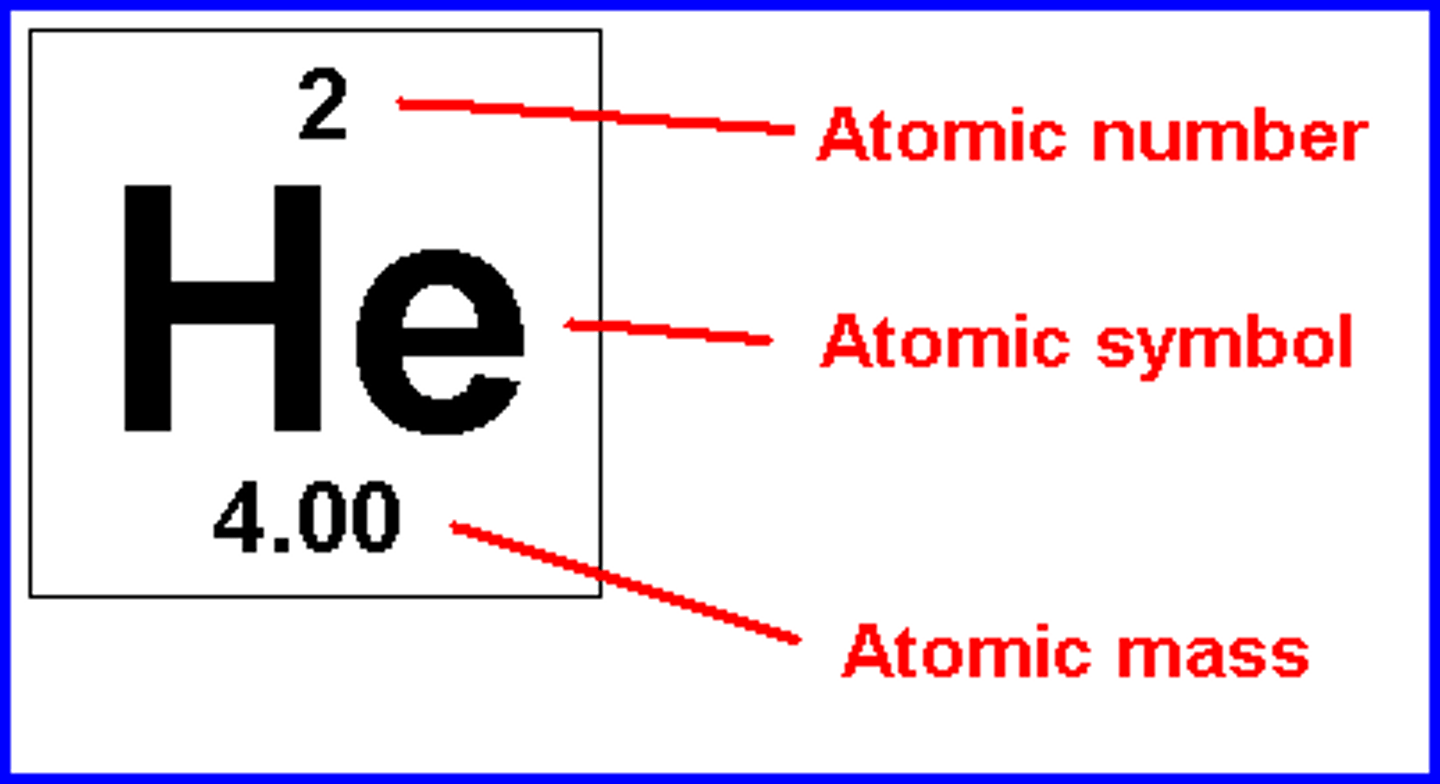
What happens if you change the number of protons?
change the element
On the periodic table a row (horizontal) is known as?
period
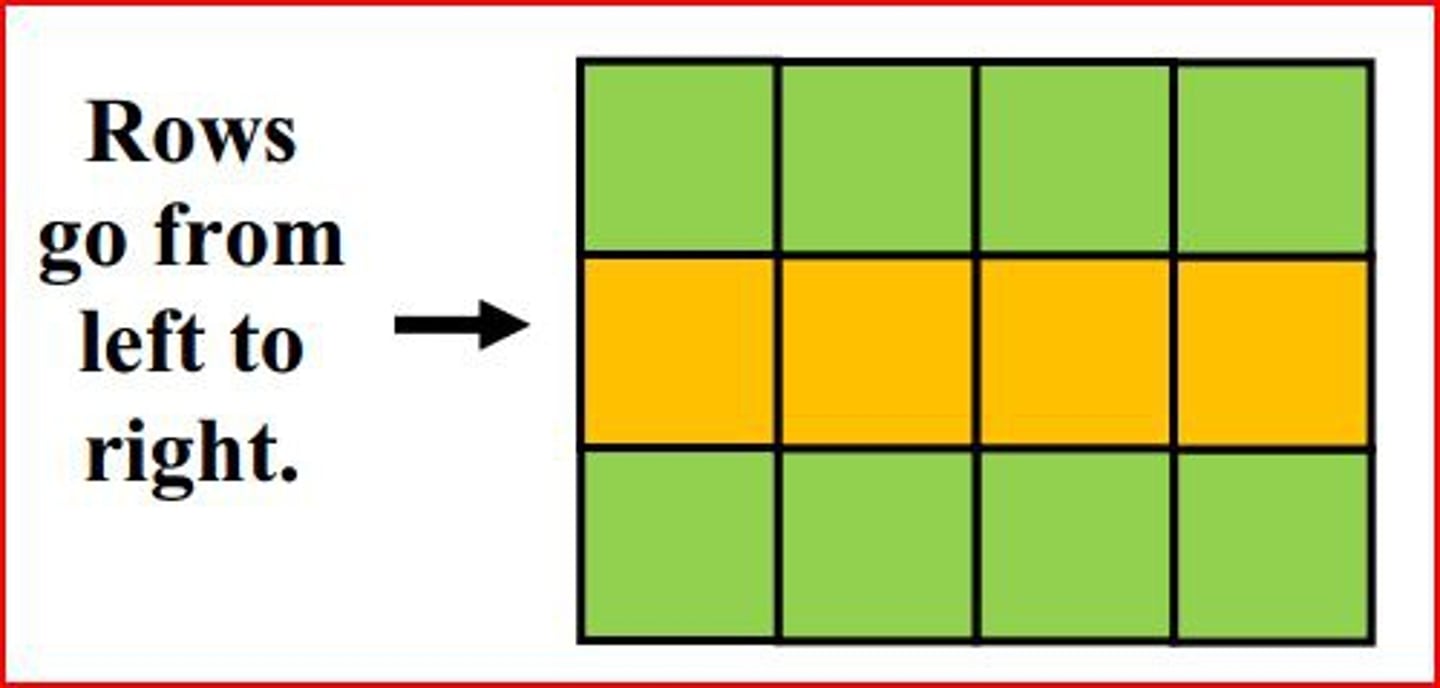
A column (vertical) on the period table is a?
group
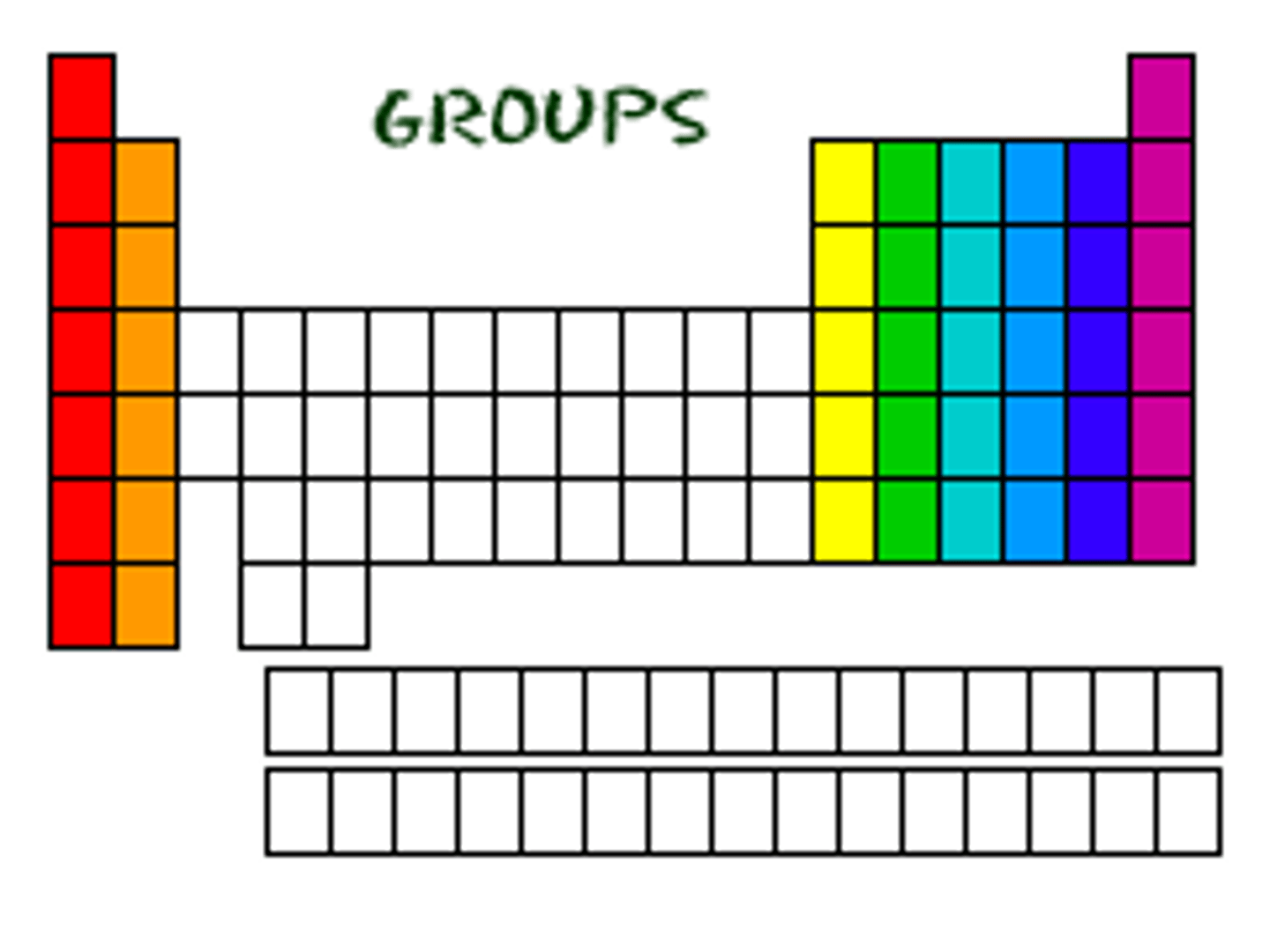
What do elements in the same GROUP have in common on the periodic table?
elements have the same # of electrons in outermost shell (valence shell)
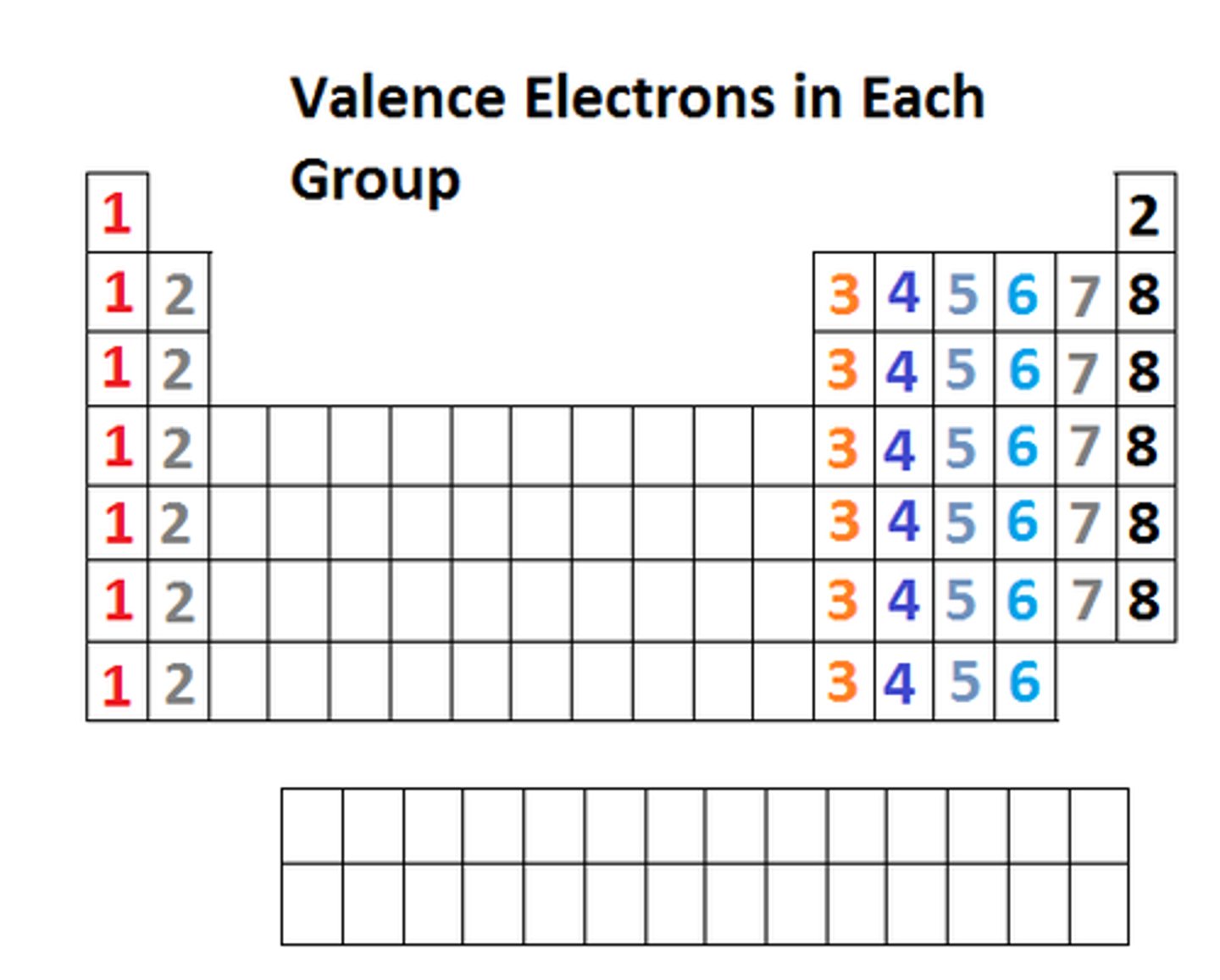
What do elements in the same PERIOD have in common?
elements have the same amount of electron shells "n"
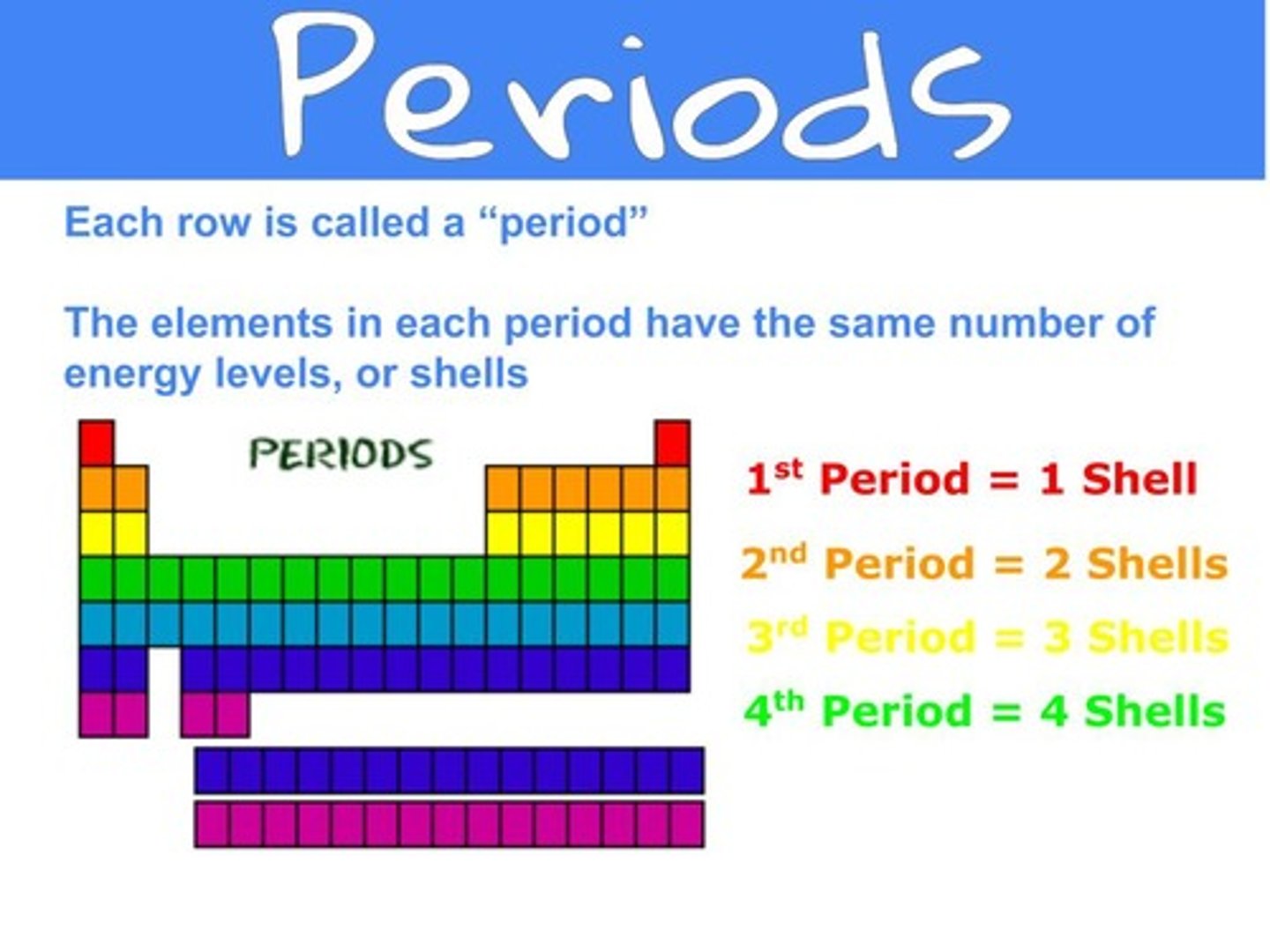
Atoms are arranged by their ____ on the periodic table
atomic number
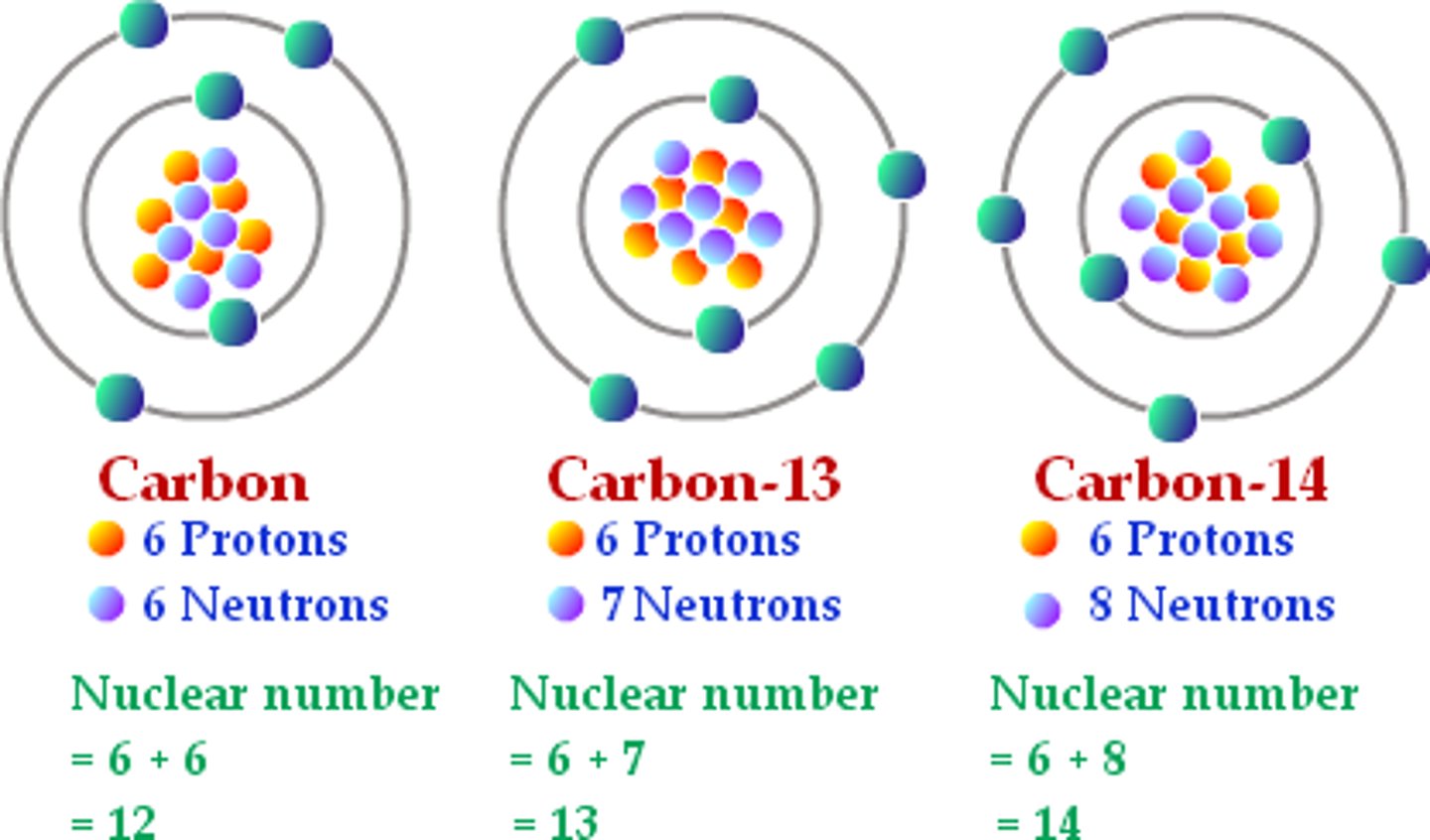
Isotope
Atoms have the same element who's nuclei contain the same number of protons but different number of neutrons (have DIFFERENT MASS NUMBERS)
Isobar
Have the same atomic mass but different atomic numbers (different # of protons = different elements)
Isomer
Atoms have the same atomic number and same atomic mass but they are formed different
A carbon isotope has 18 mass. What is the neutron #?
18-6 (carbon has 6 protons) = 12 neutrons
Mass - protons = neutrons
Define weight
force that an object exerts under the influence of gravity
Define mass
quantity of matter contained in an object
Unit of mass is 1 kilogram = ____ grams
1,000
Define substance
material that has a definite and constant composition
Two or more substances are called
mixture
Simple substance is an
element
Complex substances is a
compound
What is an atom?
Smallest particle of an element
Two or more atoms that are chemically united is a
molecule
Unit of energy
joule (j)
Define radiation
when energy is emitted and transferred through matter
Can electrons be divided into smaller parts?
No
In a neutral atom the number of _______
protons and electrons are equal
If an atom gains or loses NEUTRONS the result is
an isotope
If an atom gains or loses an ELECTRON the result is
an ion
Mass of an atom is almost entirely concentrated in the _____
nucleus
Atomic mass unit (amu)
mass of the particles of an atom
Mass of an atom is described by
atomic mass number
What determines the energy level or shell the electron occupies?
the distance from nucleus
Define electron binding energy
amount of energy needed to remove the electron from the atom
What is the principal quantum number?
The number of each shell (n)
K shell : n= 1
L shell: n= 2
M shell: n=3
And so on
How many electrons can the L shell hold?
2n^2
2(2)^2 = 8
How many electrons can the M shell hold?
2n^2
2(3)^2 = 18
As the number of electrons and protons increases, what happens to the binding energy?
binding energy increases
When does the binding energy of an electron decrease?
as the distance from the nucleus increases
electron volt (eV)
binding energy of an electron
Electron volt is the energy one electron will have when...
it is accelerated by an electrical potential of one volt
1 keV = ________ electron volts
1,000
What is an ionic bond?
An element will freely give up an electron to bind with another element
What is a covalent bond?
an element will share electrons to bond with another element
What was John Dalton's main idea
solid sphere model: atom was a sphere made up of smaller spheres
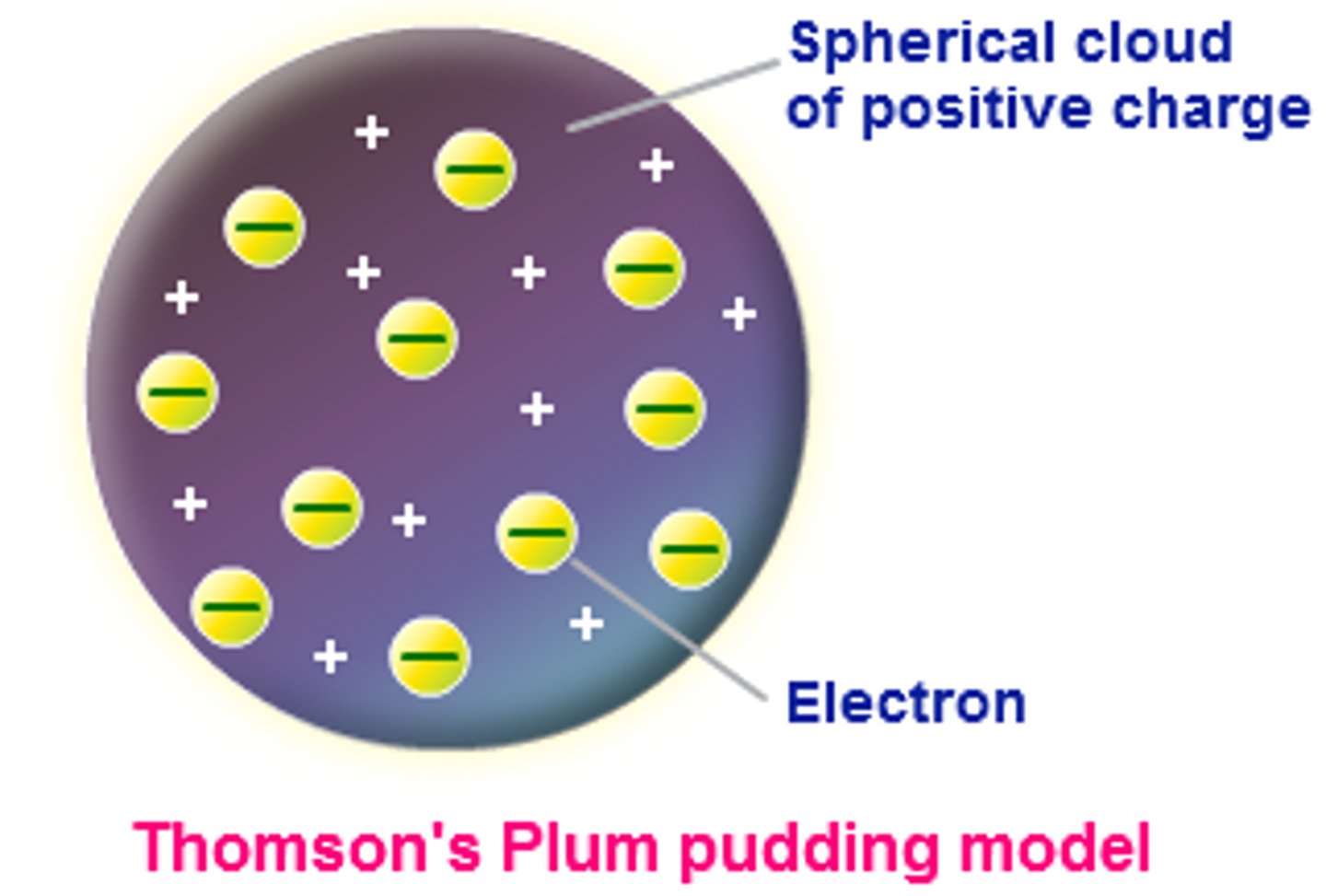
What is the plum pudding model
JJ Thompson's theory that the atom is composed of positive and negative particles but they were inside the atom with no actual structure
What was Ernest Rutherford's main idea and model?
Nuclear model: most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in a tiny positively charged nucleus at the center with negatively charged electrons orbiting it
Who is the father of the periodic table?
Dimitri Mendeleev
Who first recognized that there are 4 different types of matter?
Greeks
Mass
Kilograms
Length
meter
time
seconds
define mass
quantity of matter in a body (measured in kilogram)
Energy is the ability to do____
work
Bohr model
central positive nucleus surrounded by electrons moving around the nucleus in orbital shells
How many naturally occurring elements are there?
92
How many elements have been artificially produced
26
Radioisotopes
unstable isotopes that spontaneously transform into different elements
The time for an atom to decay is called
half-life