Chapter 2: Earth's physical systems
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Matter
Material that occupies space
Element
type of matter W/ properties that can’t be broken down
Atom
Smallest unit that matian it’s cehmical element, form molecules via bonds
Proton
Positive, pair iwth nuetrons in nucleaus (add up to make atomic #)
Nuetrons
nuetral, pair iwht protons in nucleus (add up to make atomic #)
Electron
Negative, on ring outside of nucleus
Isotope
Atoms W/ the same element with different numbers of neutrons
Ex: Carbon-14 has 8 nuetrons and 6 protons (should have 6 and 6)
compound
A molucule with 2+ elements (H20)
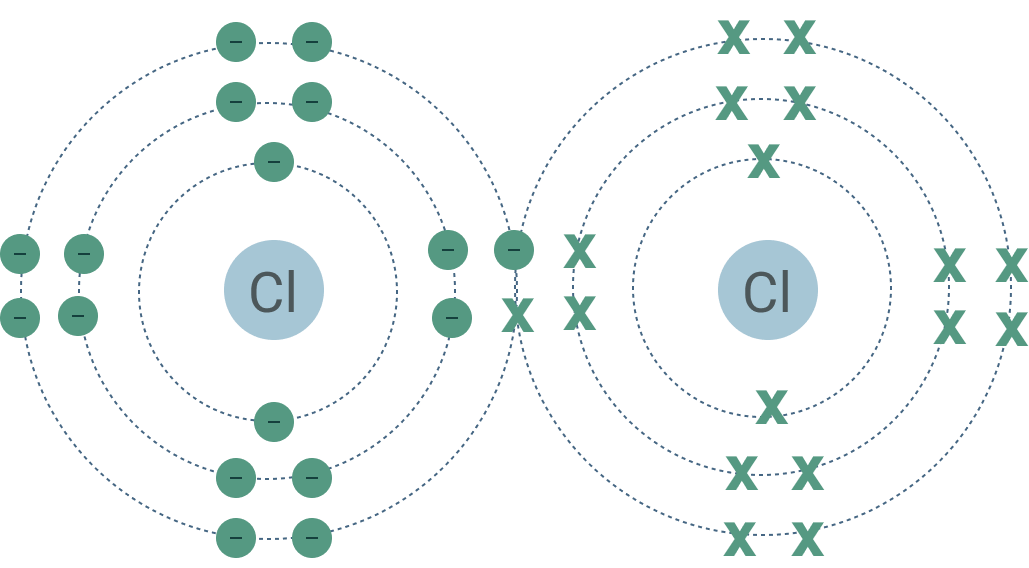
covelant bonds
share electrons
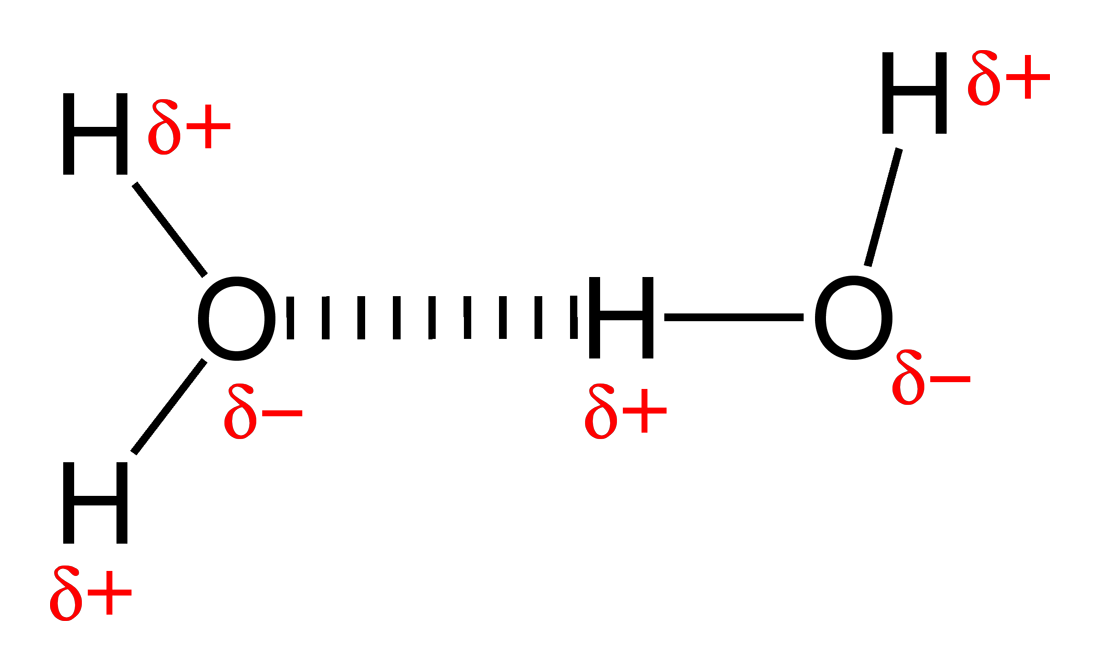
Hydrogen bond
Bonded through a neg/pos charge and a hydrogen atom
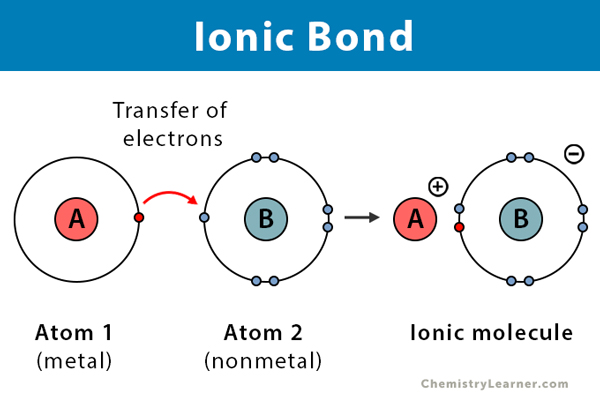
Ionic bond
When one molecule directly gives an electron to another molecule
Organic compounds
Carbon atoms that are joined by covalent bonds and may include other elements
Polymers
Longs chains made up of repeated molecules (consist of organic compounds)
Protiens
made of amino chains, different tpyes=different functiond
Nucleaic acids Carb
Made up of RNA and DNA, direct protien produciton
Carbs
simple sugars, prvide fuel
Lipids
fats and oils, do a variety of things depending on the type (I’ll straight up die of its on the test)
fine. steroids=hormone production
phospholipids=cell membrane
waxes=structure
Energy
capacity to change position, pysical composition,, or temp of matter (a force that can accomplish work)
potential energy
energy of position/ compositon (Ex. bonds)
kinetic energy
energy of movement
1st law of hermodynamics
energy can niether be created not destoryed
2nd law of thermodynamics
systems naturally mvoes towards a state of disorder (entropy)
Photosythesis
carbon, oxogyn and sunlight are broken down to create carbs (energy) and carbon
6CO2+6H20+sun energy=C6H12O6+6O2
Cellular respiration
Cells use oxygen to convert glucose back into water and carbon
C6H12O6+6O2=6CO2+6H20+energy
Chemosythesis
geothermal heating trat uses Hydrogen Sulfatte transofrms carbon into organic carbon compounds (sulfieric acid and sugars)
6C02+6H2O+3H2S=C6H12O6+3H2SO4
Geology
Study of earths physical history, features, and processes
Crust layout
Crust=10 miles (outer layer 30-40km) (inner (5-7km))
Mantle: Ultra Mafic rocks
Core: Outer=liquid iron& nickel (p=11) Inner=solid iron+nickel
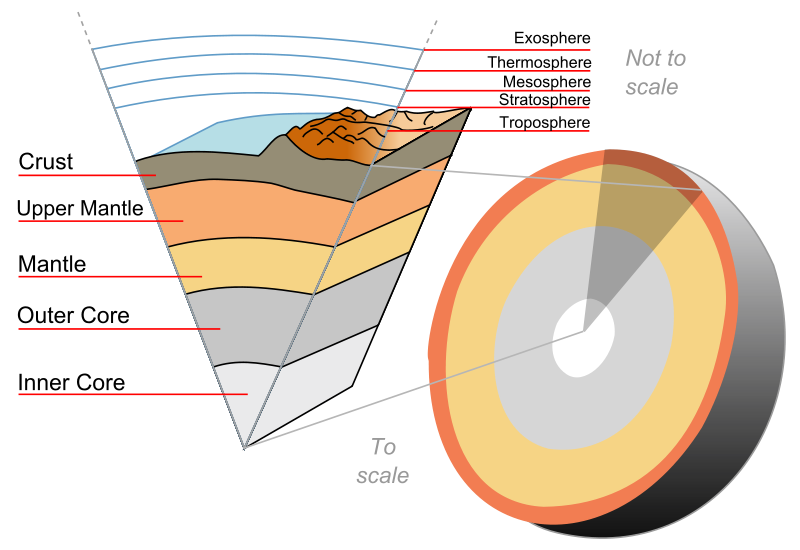
Plate tectonics
Movement of mantle material produced by heat convection (15 major plates, shapes topography)
(2 types, continental and ocean)
Divergent palte boudries
Magma rises, pushes plates apart
Transform plate boundries
Plates slip and grind agiasnt one another (can create earthquake)
Convergent plate boundry
2 plates come togehter directly
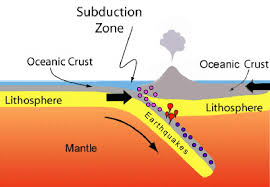
Sundiction
lithosphere slips under plate, OR, contienetal colision cuases moutnais to form
Rock
Solid Aggregation of minerals
Mineral
Natural solid ement w crytal structure, special chemical property
Ingenous orck
Formed when lava/magma cools (Intrusive=inside/slow, extrusive=outside/fast)
(Ex. Granite, Basalt, Andestite)
Sedimentary rock
Sediments (rock particles) are physically packed together
(Ex. Sandstone, shale, limestone, haltic)
Metamorphic
Rock subjected to great heat+pressure (creates new rock)
Ex. Shale becomes slate
Ex. Limestone becomes marble
Ex. Sandstone becomes quartz
Density
Wieght of matter
Density= Mass/Volume
Density scale
Water=1
Salt=2.2
Quartx=2.6
Iron=8
Falsic rock
p average is 2.8 (high in aslumminum potassium soium)
Mafic rock
p average=3 (high in iron, calcium, magnesium
Ultramafic rocks
average p=3.3-8 High in iron and magnesium
Subduction
lithosphere slips udner plate, mountaisn or islands form
Separation of plates
often occurs on ocean floor, creates mid ocean ridges
Sliding plates
Form fault lines