Biology chapter 5 and 6
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:00 AM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
1
New cards
Protein
Function: building blocks of life, defense transport, cellular communication, structural support
Monomer: amino acids
Polymer: polypeptides
Examples: enzymes, signaling, proteins, and receptor proteins
Monomer: amino acids
Polymer: polypeptides
Examples: enzymes, signaling, proteins, and receptor proteins
2
New cards
Lipids
Function: long term energy storage
Monomer: fatty acids and glycerol
Polymer: no true polymer
Examples: oil, phospholipid bilayer, and steroids
Monomer: fatty acids and glycerol
Polymer: no true polymer
Examples: oil, phospholipid bilayer, and steroids
3
New cards
Nucleic acid
Function: storage and transport of genetic info
Monomer: nucleotides
Polymer: polynucleotides
Examples: DNA and RNA
Monomer: nucleotides
Polymer: polynucleotides
Examples: DNA and RNA
4
New cards
Carbohydrate
Function: short term energy storage and building material
Monomer: monosaccaride
Polymer: polysaccharides
Examples: cellulose (beta linkages), starch and glycogen (alpha linkages)
carbohydrates are connected through glycosidic linkages, which form through dehydration synthesis
Monomer: monosaccaride
Polymer: polysaccharides
Examples: cellulose (beta linkages), starch and glycogen (alpha linkages)
carbohydrates are connected through glycosidic linkages, which form through dehydration synthesis
5
New cards
Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different positions of bonds between atoms.
True
6
New cards
Non polar molecules are hydrophilic, while polar molecules are hydrophobic.
False
7
New cards
Carboxyl groups act as acids, while amino groups act as bases.
True
8
New cards
Dehydration reactions remove a water molecules to form a bond, while hydrolysis adds a water molecule to break a bond.
True (lysis=cut, cutting bond with H2O)
9
New cards
Lipids and important components:
\-hydrophobic, made mostly of hydrocarbon regions
\-does not include true polymers
-function for long-term energy storage
-ester linkages formed through dehydration reactions
-fats, phospholipids, and steroids
\-does not include true polymers
-function for long-term energy storage
-ester linkages formed through dehydration reactions
-fats, phospholipids, and steroids
10
New cards
Saturated fatty acids
\-"saturated with hydrogens" (max number of hydrogens)
-no double bonds
-solid at room temperature
-mostly animal fats
-no double bonds
-solid at room temperature
-mostly animal fats
11
New cards
\
Phospholipids
Phospholipids
\-two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to glycerol -fatty acid tails are hydrophobic, while phosphate heads are hydrophilic
-this allows for a formation of bilayers, as the phospholipids will self assemble in water to orient themselves to have their tails face the interior
-this allows for a formation of bilayers, as the phospholipids will self assemble in water to orient themselves to have their tails face the interior
12
New cards
Steroids and example of them:
\-lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton with four fused rings
-ex. cholesterol; component of animal cell membranes and a precursor to other steroids
-ex. cholesterol; component of animal cell membranes and a precursor to other steroids
13
New cards
Monosaccarides
\-simple sugar, monomer of carbohydrate, usually multiples of CH2O
14
New cards
Disaccharides
\-two monosaccarides linked together
15
New cards
Polysaccharides
\-multiple monosaccharides bonded together
-polymer, complex carbohydrates/complex sugars
-polymer, complex carbohydrates/complex sugars
16
New cards
Cellulose
\-structural polysaccharide in plants-give plans cell walls rigidity
-contains beta linkages
-contains beta linkages
17
New cards
Starch
\-storage polysaccharide in plants
-contains alpha linkages
-contains alpha linkages
18
New cards
Glycogen
\-storage polysaccharides in animals
\-stored in liver and muscle cells
\-stored in liver and muscle cells
19
New cards
Enzymes
\-enzymes break down and digest carbs
-enzymes that digest starch can hydrolyze alpha linkages, but NOT the beta linkages in cellulose, so cellulose passes through as insoluble fiber in animals
-some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose, such as those found in symbolic relationships in herbivores
-enzymes that digest starch can hydrolyze alpha linkages, but NOT the beta linkages in cellulose, so cellulose passes through as insoluble fiber in animals
-some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose, such as those found in symbolic relationships in herbivores
20
New cards
What bond is formed in the formation of polysaccharides?
Glycosidic linkages
\*One OH is removed and one H is removed causing dehydration/removal of the water causing the O that is still standing to go over to the middle of the glycosidic linkage \*Glucose; most common monomer
\*One OH is removed and one H is removed causing dehydration/removal of the water causing the O that is still standing to go over to the middle of the glycosidic linkage \*Glucose; most common monomer
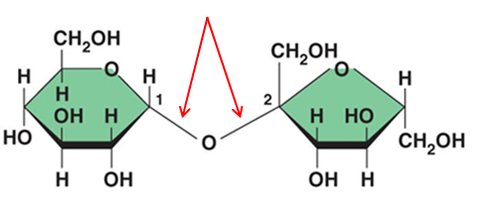
21
New cards
Identify and describe some examples of proteins
\-Enzymes: accelerate chemical reactions, helps break down carbohydrates and foods
-Transport proteins: transport substances, ex: hemoglobin transports oxygen
-Receptor proteins: response of cell to chemical stimuli, ex: nerve cells
Hormonal proteins: coordinate organism activities, ex: insulin regulating blood sugar
Contractile and motor proteins: ex: cilia and flagella, actin and myosin cause muscle contractions
Storage: ex: ovalbumin in egg white providing amino acids for developing embryo
-Transport proteins: transport substances, ex: hemoglobin transports oxygen
-Receptor proteins: response of cell to chemical stimuli, ex: nerve cells
Hormonal proteins: coordinate organism activities, ex: insulin regulating blood sugar
Contractile and motor proteins: ex: cilia and flagella, actin and myosin cause muscle contractions
Storage: ex: ovalbumin in egg white providing amino acids for developing embryo
22
New cards
Draw and label the structure of an amino acid. Which part determines its properties? Why are amino acids so important?
R group: determines its properties. Amino acids are so important because the order of amino acids determines a protein of 3D structure, which then determines protein function.
Amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds (why we cal the polymer of amino acids polypeptide)
Amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds (why we cal the polymer of amino acids polypeptide)
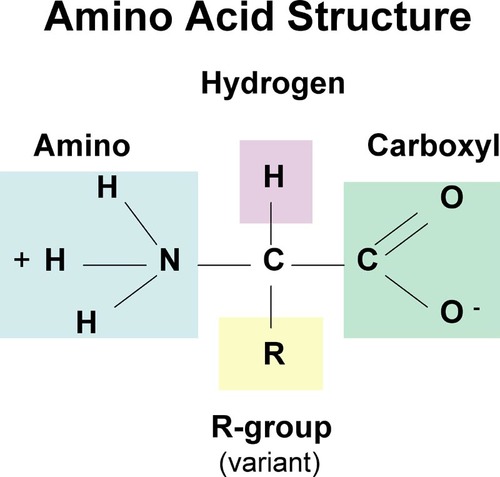
23
New cards
Explain the levels of protein structure
Primary: amino acid sequence, determined by genetic information (DNA sequence)-
Secondary: coils and folds, called alpha helixes and beta pleated sheets, result of hydrogen bonds between common components of the backbone (NOT R GROUPS)
Tertiary: interactions among side chains (R groups), include hydrogen bonds, ionic bond, hydrophobic interactions, and Van Der Waals interactions (weak), ex: disulfide bridges between Cysteines \\n Quaternary: multiple polypeptide chains
Secondary: coils and folds, called alpha helixes and beta pleated sheets, result of hydrogen bonds between common components of the backbone (NOT R GROUPS)
Tertiary: interactions among side chains (R groups), include hydrogen bonds, ionic bond, hydrophobic interactions, and Van Der Waals interactions (weak), ex: disulfide bridges between Cysteines \\n Quaternary: multiple polypeptide chains
24
New cards
How can a proton become denatured?
\-Temperature
-Sal concentration: hypertonic/hypotonic solution
-pH
-Sal concentration: hypertonic/hypotonic solution
-pH
25
New cards
What are our "units of inheritance"? What are they mad of?
\-Genes are our units of inheritance
-Consists of DNA, a nucleus acid made of nucleotides
-Consists of DNA, a nucleus acid made of nucleotides
26
New cards
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
\-Nucleotides
-Composed of a nitrogenous
\* a nucleotide is only the nitrogenous base and sugar
-Composed of a nitrogenous
\* a nucleotide is only the nitrogenous base and sugar
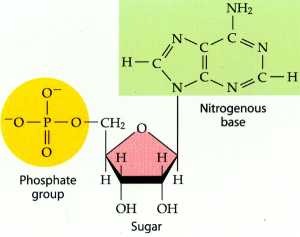
27
New cards
What are the two major examples of nucleic acids/ How do they differ?
DNA:
\-double stranded
-codes for mRNA
-ATCG
-deoxyribose sugar which is missing at 2' OH
-antiparallel and complementary strands run in opposite directions (5' to 3')
RNA
-single stranded (but complementary pairing may still occur within a strand or between two strands)
-different functions, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
\-AUCG
-ribose sugar which contains a 2' OH
\-double stranded
-codes for mRNA
-ATCG
-deoxyribose sugar which is missing at 2' OH
-antiparallel and complementary strands run in opposite directions (5' to 3')
RNA
-single stranded (but complementary pairing may still occur within a strand or between two strands)
-different functions, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
\-AUCG
-ribose sugar which contains a 2' OH
28
New cards
Purines
\-six membered ring fused to a five-membered ring (2 rings)
\-A and G
\-AG, big about the rings, HUGE school
\-A and G
\-AG, big about the rings, HUGE school
29
New cards
Pyrimidines
\-single six-membered ring
\-T,C,U (3 bases)
\-T,C,U (3 bases)
30
New cards
Which of the following links together the monomers of nucleic acid?
phosphodiester linkage
31
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a significant function of proteins?
Energy storage
32
New cards
Which of the following is true of unsaturated fatty acids?
They contain double bonds
33
New cards
Which of the following is the most common monosaccharide?
Glucose
34
New cards
In DNA, there are two hydrogen bonds between A and T nucleotides, and three hydrogen bonds between C and G
True
35
New cards
Side chains (R groups) are involved in the secondary structure of protein folding
False; involved in the Tertiary
36
New cards
Starch is a storage carbohydrates
True
37
New cards
Saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature because they contain double bonds
False; they do not contain double bonds
38
New cards
A nucleotide contains of a nitrogenous base, a peons sugar, and a phosphate group
False, nucleotides lack a phosphate
39
New cards
What organisms are found in prokaryotic cells?
\-bacteria
\-archaea
\-archaea
40
New cards
What organisms are found in eukaryotic cells?
\-protists
\-fungi
\-animals
\-plants
\-fungi
\-animals
\-plants
41
New cards
What are the basic features of all cells? Define their function/role:
Plasma membrane; indicates cell from environment but allows specific substances to be exchanged
42
New cards
Cytosol
matrix for everything to float inside
43
New cards
Chromosomes
carry genes-genetic information
44
New cards
Ribosomes
translate information from mRNA to make proteins
45
New cards
Prokaryotic cells:
\-no nucleus
\-DNA in unbound nucleic region
\-no membrane-bound organelles
\-cytoplasm bound by plasma
\-ribosomes
\-DNA in unbound nucleic region
\-no membrane-bound organelles
\-cytoplasm bound by plasma
\-ribosomes
46
New cards
Eukaryotic cells:
\-DNA contained in a nucleus
\-cytoplasm contained in region between plasma membrane and nucleus
\-contains membrane-bound organelles
\-cytoplasm contained in region between plasma membrane and nucleus
\-contains membrane-bound organelles
47
New cards
Describe the plasma membrane. Why is it so important?
\-selective barrier that allows passage of oxygen, nutrients, waste
\-made of phospholipids (hydrophilic heads face out) (hydrophobic tails face in)
\-necessary for metabolism-resources in and waste out
\-made of phospholipids (hydrophilic heads face out) (hydrophobic tails face in)
\-necessary for metabolism-resources in and waste out
48
New cards
Describe the function and components of the nucleus:
\-Nucleus: contains most of the cell’s DNA
\-Nuclear envelop contains the double membrane and is surrounded with pores lined with pore complexes that regulate entry and exit of molecules
\-DNA is organized into chromosomes containing condensed chromatin = DNA + histone proteins
nucleus: sit of rRNA synthesis within nucleus
\-Nuclear envelop contains the double membrane and is surrounded with pores lined with pore complexes that regulate entry and exit of molecules
\-DNA is organized into chromosomes containing condensed chromatin = DNA + histone proteins
nucleus: sit of rRNA synthesis within nucleus
49
New cards
Explain the function and list the components of the endomembrane system
Function: regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions
Components:
\-nuclear membrane
\-endoplasmic reticulum
\-golgi apparatus
\-lysosomes
\-vacuoles
\-plasma membrane
Components:
\-nuclear membrane
\-endoplasmic reticulum
\-golgi apparatus
\-lysosomes
\-vacuoles
\-plasma membrane
50
New cards
Endoplasmic reticulum:
\*Biosynthetic factory, continuous with nuclear envelope
Smooth ER
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Rough ER
51
New cards
Smooth ER
\*lacks ribosomes
\-synthesizes lipids
\-detoxifies drugs and poisons -adds OH
\-stores calcium ions
\-synthesizes lipids
\-detoxifies drugs and poisons -adds OH
\-stores calcium ions
52
New cards
Rough ER
\*studded with ribosomes
\-bound ribosomes secrete glycoproteins, (protein+sugars)
\-distributes transport vesicles
\-is a membrane factory for the cell
\-bound ribosomes secrete glycoproteins, (protein+sugars)
\-distributes transport vesicles
\-is a membrane factory for the cell
53
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
\*Shipping & receiving center
\-consists of cistern: flattened membranous sace
\-modifies products of ER
\-sorts and packages materials into vesicles
\-consists of cistern: flattened membranous sace
\-modifies products of ER
\-sorts and packages materials into vesicles
54
New cards
Lysosomes
\*Digestive compartments
\-membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that work best in acidic environment
\-phagocytosis forms food vacuoles that fuse with lysosomes to digest contents
\-autophagy: recycling cell’s own organelles and macromolecule
\-membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that work best in acidic environment
\-phagocytosis forms food vacuoles that fuse with lysosomes to digest contents
\-autophagy: recycling cell’s own organelles and macromolecule
55
New cards
Vacuoles
\*Diverse maintenance compartments
\-food vacuoles
\-contractile vacuoles; found in freshwater protests, pump excess water out of cells
\-central vacuoles-plant cells, contain sap, serve as plant cells main respiratory of inorganic ions (K+/CL-)
\-food vacuoles
\-contractile vacuoles; found in freshwater protests, pump excess water out of cells
\-central vacuoles-plant cells, contain sap, serve as plant cells main respiratory of inorganic ions (K+/CL-)
56
New cards
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
\*Change energy from one form to another
Mitochondria:
\-cellular resiration
use oxygen to generate ATP
\-foldings called cristae
\-intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix
Chloroplasts:
\-plants and algae
\-sites of photosynthesis
\-contain chlorophyll and enzymes
\-thylakoids stocked to form granum
\-stomainternal fluid
Mitochondria:
\-cellular resiration
use oxygen to generate ATP
\-foldings called cristae
\-intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix
Chloroplasts:
\-plants and algae
\-sites of photosynthesis
\-contain chlorophyll and enzymes
\-thylakoids stocked to form granum
\-stomainternal fluid
57
New cards
Ribosomes
\*rRNA and protein build protein
\-free ribosomes-in the cytosol
\-bound ribosomes- on the outside of the R or nuclear envelope
\-free ribosomes-in the cytosol
\-bound ribosomes- on the outside of the R or nuclear envelope
58
New cards
Peroxisomes
\*Oxidation
\-enzymes remove hydration atoms and transfer them to oxygen to form hydrogen peroxide
\-reaction functions:
\-using oxygen to break fatty acids for fuel for respiration
\-in liver, they detoxify alcohol and other compounds
\-enzymes remove hydration atoms and transfer them to oxygen to form hydrogen peroxide
\-reaction functions:
\-using oxygen to break fatty acids for fuel for respiration
\-in liver, they detoxify alcohol and other compounds
59
New cards
What is the cytoskeleton? What is its role?
\-network of protein filaments that support the cell and maintain its shape
\-interacts with morrow proteins to produce motility
\-provides the ‘tracks’ for vesicles and organelles to walk on using motor protein feet
\-interacts with morrow proteins to produce motility
\-provides the ‘tracks’ for vesicles and organelles to walk on using motor protein feet
60
New cards
What three fibers make up the cytoskeleton? What are they made of and what are their roles?
Microtubules:
\-tubulin dimers
\-chromosome movement in cell division
\-movement of organelles
\-shaping the cell
\-cellular reconstruction, separate chromosomes and cell division
\-animal cells-grow out a centrosome near the nucleus
\-centrosome has a pair of centrioles-each with a triplets of microtubules in a ring
\-tubulin dimers
\-chromosome movement in cell division
\-movement of organelles
\-shaping the cell
\-cellular reconstruction, separate chromosomes and cell division
\-animal cells-grow out a centrosome near the nucleus
\-centrosome has a pair of centrioles-each with a triplets of microtubules in a ring
61
New cards
Microfilaments
\-actin subunits in twisted double chain
\-muscle contraction
\-myosin
\*actin is powered by ATP to assemble its filamentous form; serves as a track for the movement of a motor protein called myosin
\-muscle contraction
\-myosin
\*actin is powered by ATP to assemble its filamentous form; serves as a track for the movement of a motor protein called myosin
62
New cards
Intermediate filaments
\-keratins
\-anchorage of nucleus
\-anchorage of nucleus
63
New cards
Cell wall
\-extracellular structure that distinguishes plant from animal cells
\-prokaryotes, fungi, protists also have cell walls
\-protects plant cell, maintains shape, prevents excessive water uptake
\-made of cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and proteins’-may have multiple layers
\-prokaryotes, fungi, protists also have cell walls
\-protects plant cell, maintains shape, prevents excessive water uptake
\-made of cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and proteins’-may have multiple layers
64
New cards
Tell me about the extracellular matrix:
\-in animal cells
\-made of glycoproteins: collagen, proteoglycans, and fibronectin
\-regulate cell behavior by communicating with a cell through integrins
\-made of glycoproteins: collagen, proteoglycans, and fibronectin
\-regulate cell behavior by communicating with a cell through integrins
65
New cards
Which structure is directly responsible for the formation of proteins within the cell
ribosomes
66
New cards
Which of the following is NOT true of Eukaryotic cells
DNA is located in a nucleic region
67
New cards
cell membrane
cholesterol is very important in cell membrane because it functions to keep the fluidity of the membrane
68
New cards
Hydroxyl
\-polar covalent (react with water) or other polar molecules
69
New cards
Carboxyl
\-acts as an acid
\-can increase {H+"} I solution
\-importat element of amino acids
\-can increase {H+"} I solution
\-importat element of amino acids
70
New cards
Carbonyl
\-looks like an eel
\-double bond between C and O
\-found in ketones and aldehydes
\-double bond between C and O
\-found in ketones and aldehydes
71
New cards
Phosphate
\-high electronegativity of oxygens gives negative charge-can react wit H2O
\-polar
\-found in ATP
\-polar
\-found in ATP
72
New cards
Methyl
\-regulates gene expression by transcription
\-affects shape and function of sex hormones
\-nonpolar
\-affects shape and function of sex hormones
\-nonpolar
73
New cards
Sulfhydryl
\-fond in amino acid cysteine
\-involved in formation of secondary structures of protein
\-involved in formation of secondary structures of protein
74
New cards
Amino
\-acts as a base
\-can lower {H+} by trapping it in solution
\-important element element in amino acids
\-can lower {H+} by trapping it in solution
\-important element element in amino acids
75
New cards
Denaturation
\-breaking of many weak linkages or bonds
\*hydrogen bonds
\-the process of denaturation occurs with proteins, in which these molecules are being deactivated
\*affecting shape of structure which will overall affect the function
\*hydrogen bonds
\-the process of denaturation occurs with proteins, in which these molecules are being deactivated
\*affecting shape of structure which will overall affect the function
76
New cards
Bonds
Lipids: ester linkages
Carbohydrates; glycosidic linkage
Amino Acids: peptide bonds
Nucelic acid: phosphodiester
Carbohydrates; glycosidic linkage
Amino Acids: peptide bonds
Nucelic acid: phosphodiester