Cytomegalovirus
5.0(1)Studied by 9 people
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:00 PM on 3/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
Herpes
==Cytomegalovirus:==
* Belongs to the _______ virus family
* Exposure increases with age
* Belongs to the _______ virus family
* Exposure increases with age
2
New cards
Saliva Urine Cervical secretions
==Transmission of CMV occurs when coming into contact with the virus through:==
* _______
* Blood
* _______
* Breast milk
* _______ _______
* Semen
* _______
* Blood
* _______
* Breast milk
* _______ _______
* Semen
3
New cards
36
91
91
In the US \~ ___% of children 6-11 years old are CMV+
By 80 years old seropositivity increases to ___%
By 80 years old seropositivity increases to ___%
4
New cards
no
mild
mild
Most healthy children and adults infected with CMV will have ___ symptoms or might develop only a ______ mononucleosis-like illness
5
New cards
reactivate
mother
mother
==Once infected with CMV:==
* Virus can _________, but healthy immune system prevents this in most cases
* A _________ carrier can transmit virus to fetus which causes developmental issues in infant.
* Acute symptoms at birth
* Permanent disabilities
* Both
\
* Virus can _________, but healthy immune system prevents this in most cases
* A _________ carrier can transmit virus to fetus which causes developmental issues in infant.
* Acute symptoms at birth
* Permanent disabilities
* Both
\
6
New cards
In-utero
prenatal
prenatal
==Diagnosis of Congenital CMV:==
either _________ through amniocenteses OR in the _________ period for from direct assessment of the infant in the postnatal period.
either _________ through amniocenteses OR in the _________ period for from direct assessment of the infant in the postnatal period.
7
New cards
21
Testing for congenital CMV must be completed in ____ days from birth otherwise it is IMPOSSIBLE to distinguish congenital from acquired.
8
New cards
amniocenteses
* A test offered during pregnancy to check if a baby has a genetic or chromosomal condition.
* It involves removing and testing a small sample of cells from amnioticfluid (the fluid that surrounds the baby in the womb)
* It involves removing and testing a small sample of cells from amnioticfluid (the fluid that surrounds the baby in the womb)
9
New cards
CMV
21
21
___ is the most common intrauterine infection in the US with \~ __% of pregnant women being symptomatic (like mononucleosis)
10
New cards
universal
US
US
_________ = 0.64-.70% of live births
_________ = 0.2 to 2.2% (congenital) with estimated 0.5 to 1.0 newborns infected in the prenatal period
_________ = 0.2 to 2.2% (congenital) with estimated 0.5 to 1.0 newborns infected in the prenatal period
11
New cards
Symptoms
* Generalized petechiae
* Hyperbilirubinemia
* Hepatosplenomegaly
* Purpuric rash (3-10mm)
* Microcephaly
* Seizures
* Focal or general neurologic deficits
* Retinitis
* Intracranial calcifications
* Hyperbilirubinemia
* Hepatosplenomegaly
* Purpuric rash (3-10mm)
* Microcephaly
* Seizures
* Focal or general neurologic deficits
* Retinitis
* Intracranial calcifications
12
New cards
**F**ocal/general neurologic deficits
**H**yperbilirubinemia
**G**eneralized petechiae
**S**eizures
**H**epatosplenomegaly
**R**etinitis
**I**ntracranial calficiations
**M**icrocephaly
**P**urpuric rash
**H**yperbilirubinemia
**G**eneralized petechiae
**S**eizures
**H**epatosplenomegaly
**R**etinitis
**I**ntracranial calficiations
**M**icrocephaly
**P**urpuric rash
CMV Symptoms:
Fat Hairless Gumbo SHRIMP
(FHGSHRIMP)
Fat Hairless Gumbo SHRIMP
(FHGSHRIMP)
13
New cards
90 to 95
Most aka ___ to ____% of infants w/ congenital CMV will **NOT** have any clinically significants apparent symptoms at birth.
14
New cards
No
Are newborns screened from CMV in the US?
15
New cards
blood spot
It is possible to ID children with CMV by obtaining a newborn _________ _________ for analysis
16
New cards
urine or saliva
Typically diagnosed through detection within _________ or _________ within the first 3 weeks of life (21 days)
17
New cards
mother exposure during pregnancy
What would lead to testing at birth?
18
New cards
referred NBHS
Utah, Illinois, Connecticut, Iowa, New York, and Virginia participates in a screening for cCMV following a _________ _________
19
New cards
Sequela
Any abnormal condition that follows and is the result of a disease, treatment, or injury, such as paralysis after poliomyelitis, deafness after treatment with an ototoxic drug, or scar formation after a laceration
20
New cards
Sequela
Both symptomatic and asymptomatic infants may later develop _________.
* More severe and frequent in the symptomatic infants.
* More severe and frequent in the symptomatic infants.
21
New cards
CMV Sequela
* SNHL
* Retinitis
* Mental Retardation
* Microcephaly
* Seizure
* Cerebral palsy
* Retinitis
* Mental Retardation
* Microcephaly
* Seizure
* Cerebral palsy
22
New cards
10 to 15
SNHL is most common sequela of cCMV
__% to __%
__% to __%
23
New cards
30 to 50
HL occurs in __% to __% of children with **symptoms** at birth
24
New cards
8 to 12
HL occurs in in __% to __% of children who are **asymptomatic** at birth
25
New cards
Mild to profound
Unilateral or bilateral
fluctuating progressive
Unilateral or bilateral
fluctuating progressive
* No predictable audiometric configuration
* _________ to _________
* Laterality: Unilateral or bilateral
* Some involve 4-8k Hz only - others all frequencies are involved
* HL may be _________ and/or _________
* Develop within the first years for some
* _________ to _________
* Laterality: Unilateral or bilateral
* Some involve 4-8k Hz only - others all frequencies are involved
* HL may be _________ and/or _________
* Develop within the first years for some
26
New cards
50
\~ __% of the cases of CMV related HL are late-onset/and/or progressive.
__(Not always detected at birth…. ~7% of cCMV cases were detected)__
__(Not always detected at birth…. ~7% of cCMV cases were detected)__
27
New cards
21
25
25
Recent estimates:
* __% of Hl at birth is cCMV related
* Late onset HL = __% of HL in children by age 4 likely CMV related.
(Suggest that CMV is the leading non genetic cause of HL in Peds for the US)
* __% of Hl at birth is cCMV related
* Late onset HL = __% of HL in children by age 4 likely CMV related.
(Suggest that CMV is the leading non genetic cause of HL in Peds for the US)
28
New cards
Pathogenesis
==Animal and human studies on temporal bone suggest:==
* CMV may be present in the **epithelium** and **neural cells of the inner ear.**
* Cause U__amage by virus-mediated damage to neural cells and/or cause inflammatory responses resulting in damage__ to the auditory apparatus therefore causing HL
* Doesn’t explain late onset or progressive loss!!!
* CMV may be present in the **epithelium** and **neural cells of the inner ear.**
* Cause U__amage by virus-mediated damage to neural cells and/or cause inflammatory responses resulting in damage__ to the auditory apparatus therefore causing HL
* Doesn’t explain late onset or progressive loss!!!
29
New cards
audiologic evaluations
changes
changes
JCIH treatment:
* Babies ID’s early need impediment and more frequent _________ _________ to allow close monitoring
* _________ in hearing should be considered in treating the HL
* May program HAs more often.
* Communication methods/needs to accommodate a changing HL
* Babies ID’s early need impediment and more frequent _________ _________ to allow close monitoring
* _________ in hearing should be considered in treating the HL
* May program HAs more often.
* Communication methods/needs to accommodate a changing HL
30
New cards
regular
vision
vision
CDC recommendations:
* _________ hearing checks
* routine _________ screening
* Developmental milestone checks
* _________ hearing checks
* routine _________ screening
* Developmental milestone checks
31
New cards
Multi-disciplinary team
* Infectious disease specialists
* Otolaryngology
* Neurology
* Primary care/Pediatrician
* Audiology
* Opthamology
* Otolaryngology
* Neurology
* Primary care/Pediatrician
* Audiology
* Opthamology
32
New cards
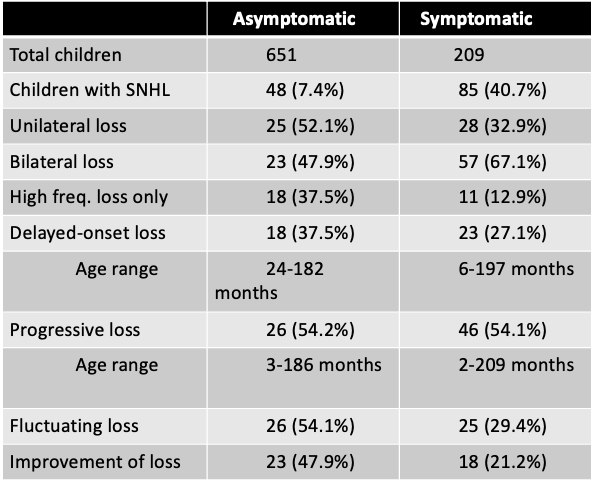
\
(Dahle et al., 2000)
Longitudinal study (24 years)
860 children with CMV were studied (651 asymptomatic, 209 symptomatic)
Test battery:
* ABR (chloral hydrate)
* Air and bone conduction if AC>25 dBnHL
* Tympanometry
* VRA (from 9 months to 3 years old)
Longitudinal study (24 years)
860 children with CMV were studied (651 asymptomatic, 209 symptomatic)
Test battery:
* ABR (chloral hydrate)
* Air and bone conduction if AC>25 dBnHL
* Tympanometry
* VRA (from 9 months to 3 years old)
33
New cards
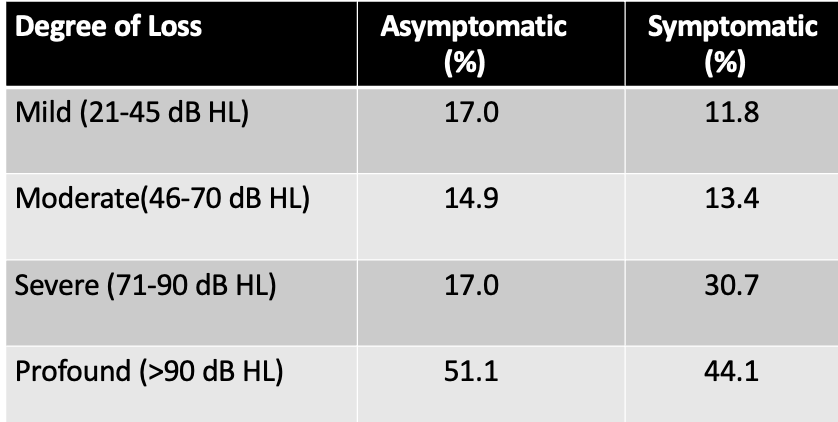
Longitudinal study outcomes:
* Bilateral moderate to severe SNHL (equally severe in asymptomatic patients)
* Delay onset of hearing loss (wide age range: 6 months to 16.4 years)
* Gradually progressive (sometimes sudden decreases reaversed w/ steroids)
* Threshold fluctuations without progression of their loss (may experience improvement)
* Low frequencies (250 and 500 Hz) less stable than higher frequencies
* Bilateral moderate to severe SNHL (equally severe in asymptomatic patients)
* Delay onset of hearing loss (wide age range: 6 months to 16.4 years)
* Gradually progressive (sometimes sudden decreases reaversed w/ steroids)
* Threshold fluctuations without progression of their loss (may experience improvement)
* Low frequencies (250 and 500 Hz) less stable than higher frequencies
34
New cards
flat
high
high
Audiometric pattern:
* _________ hearing loss was the predominant threshold configuration
* Initially by a sloping _________-frequency loss may gradually progress to include the lower frequencies
* Upward sloping (symptomatic)
* Downward sloping (asymptomatic)
* _________ hearing loss was the predominant threshold configuration
* Initially by a sloping _________-frequency loss may gradually progress to include the lower frequencies
* Upward sloping (symptomatic)
* Downward sloping (asymptomatic)
35
New cards
Symptomatic audio
upward sloping
36
New cards
Asymptomatic audio
downward sloping
37
New cards
laboratory
CNS
growth and development
CNS
growth and development
==Medical management/evaluation:==
* A general medical examination
* _________ procedures to document the diagnosis of CMV
* An examination to determine damage to the _________ (EEG)
* Assessment of the child’s _________ and _________.
* A general medical examination
* _________ procedures to document the diagnosis of CMV
* An examination to determine damage to the _________ (EEG)
* Assessment of the child’s _________ and _________.
38
New cards
antiviral treatment
==Medical management==
Prolonged _________ _________ for cCMV with SNHL showed improvement (58-79%) in hearing status and no deterioration in unaffected ears at baseline.
Prolonged _________ _________ for cCMV with SNHL showed improvement (58-79%) in hearing status and no deterioration in unaffected ears at baseline.
39
New cards
==Pharmacological Treatment:==
==Ganciclovir==
(inhibitor of viral DNA synthesis) **antiviral drug may have a beneficial effect in newborns affected** by severe congenital CMV infection such as preventing hearing deterioration
* Maintained normal hearing or stops the progression of hearing loss in 76% of infants when baseline compared to tests 6 months later
* Significant side effects including __**bone marrow suppression**__, therefore if severe-profound hearing loss is present at birth, the doctors will likely not administer Ganciclovir due to physical risk and limited benefit in terms of hearing restoration.
(inhibitor of viral DNA synthesis) **antiviral drug may have a beneficial effect in newborns affected** by severe congenital CMV infection such as preventing hearing deterioration
* Maintained normal hearing or stops the progression of hearing loss in 76% of infants when baseline compared to tests 6 months later
* Significant side effects including __**bone marrow suppression**__, therefore if severe-profound hearing loss is present at birth, the doctors will likely not administer Ganciclovir due to physical risk and limited benefit in terms of hearing restoration.
40
New cards
6 to 12
Hearing eval:
* Audiogram
* ABR
* OAR
* Tympanometry
If suspected a child should be routinely monitored:
* Child should be assessed every __ to __ months
Speech and language therapy
* Must be tailored to needs
Appropriate counseling for the parents!
* Audiogram
* ABR
* OAR
* Tympanometry
If suspected a child should be routinely monitored:
* Child should be assessed every __ to __ months
Speech and language therapy
* Must be tailored to needs
Appropriate counseling for the parents!
41
New cards
vaccine
No approved _________ for prevention of CMV
42
New cards
Hand washing
_________ _________ is the #1 preventer
(esp when pregnant or trying to get pregnant)
(esp when pregnant or trying to get pregnant)
43
New cards
day care
mothers
toddlers
mothers
toddlers
_________ _________ providers and _________ of _________ are at the highest risk of contraction
44
New cards
Young children
This population tend to secrete the virus in their saliva and urine for many months following the first infection.
\[typically asymptomatic\]
\[typically asymptomatic\]