ECON 1201 FINAL REVIEW - UConn PROF JOHNSON!!!!
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Law of Diminishing Return
SHORT RUN ONLY
- as more and more of variable input saddled to an existing feed input eventually
the additional output that one gets from additional input is going to fall
-additional cost must increase
- adding labor = output goes up
** explains why marginal cost eventually increases as output expands
Inelastic in demand
when people buy about the same amount whether price doors or rises.
less/no substitutions
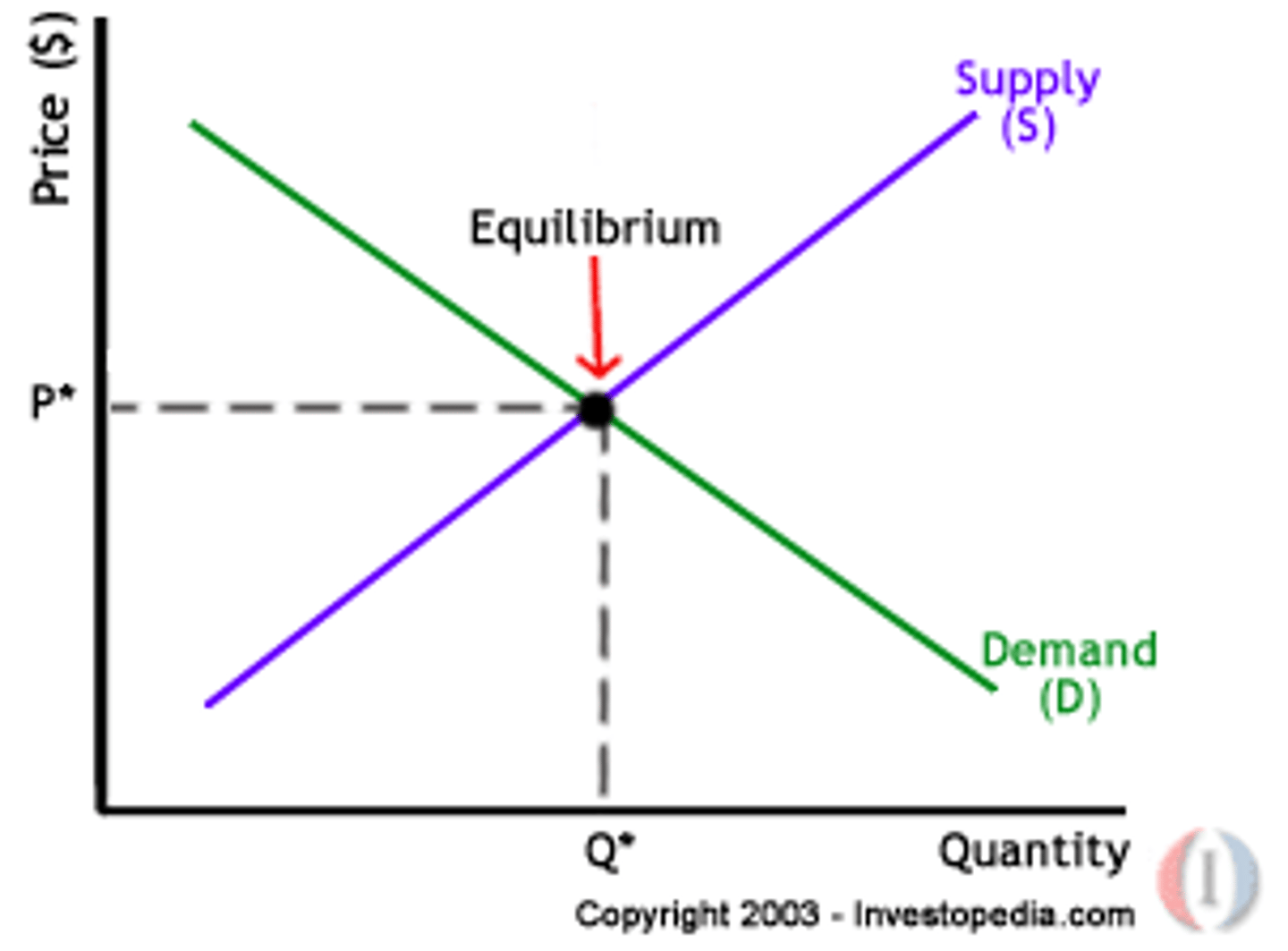
Equilibrium price
the price where demand for a product or a service is equal to the supply of the product or service
Short Run
that period of time during which at least one of the company's inputs or factors of production (labor, capital, and land) is constant or fixed
- **some inputs is fixed; others can vary or are variables
- labor is a variable; physical capital are fixed
Long Run
period of time which all of the company's inputs or factors of production can be varied or changed when new technologies are adopted. No fixed factor of production
**NO FIXED COST
Scarcity
unlimited wants exceed limited resources available
Decision Rules
MB > MC = do more
MC > MB = do less
MC = MB = optimal (can not do better by doing a little more/little less)
Markets
Bring buyers and sellers together to exchange goods and services
Choices are predicted on
1. costs of decision
2. benefits of a decision
3. feasible alternatives
4. available info
Individual choice
decisions by an individual make about what not to do
Principles of individual choice
1. people must make choices because resources are scarce
2. opportunity cost of an item - what u must give up
3. "how much" decision requires making TRADE OFFS @ margin comparing COSTS AND BENEFITS of doing a little bit more of an activity vs. doing less
4. people usually respond to incentives by exploring opportunities to make themselves better off
Resource
anything that can be used to produce something else
Principles of Interaction of Individual Choice
1. there are gains from trade
2. because people respond to incentives, markets move towards
equilibrium
3. resources should be used as efficiently as possible to achieve society's goals
4. because people usually exploit gains from trade, markets usually lead to efficiency
5. when markets don't achieve efficiency, gov't intervention can improve society's welfare
Trade
people divide tasks among themselves and each person provides a good or service that other people want in return for different goods and services
Gains from trade
by dividing tasks and trading, two people can each get more of what they want than they could by being self-sufficient
specialization
a situation in which different people each engage in different tasks, specializing in those task they are good at
Equilibrium
an economic situation when NO individual would be better off doing something else
Market Economy
ensure that resources are usually put to good use and that opporutnities to make people better off are not wasted
Market Failure
a situation in which a market left on its own fails to allocate resources efficiently
Sunk cost
a cost that has already been committed and cannot be recovered
Economic problems every society must solve
1. what goods and services are produced
2. who will receive goods and services produced
Do market discriminate?
Yes.
factors:
1. ability and willingness to pay
2. market and prices are just ways we ration scarce goods and services
3. markets are good way to organize economic activity
Prices signals...
the value that we place on a good or service (demand) and/or the costs to produce that good or service (supply)
Simple Model:
1, we look at the production possibility frontier, a model that helps economists think about the trade offs every economy faces
2. turn to comparative advantage, model that clarifies the principles of gains from trade -- trade both b/w individual and counties
3. examine the circular flow diagram, a schematic representation that helps us understand how flows of money, goods, and services are channeled through the economy
Production Possibilities Frontier
idea is to improve our understanding of trade offs by considering a simplified economy that produces only two goals
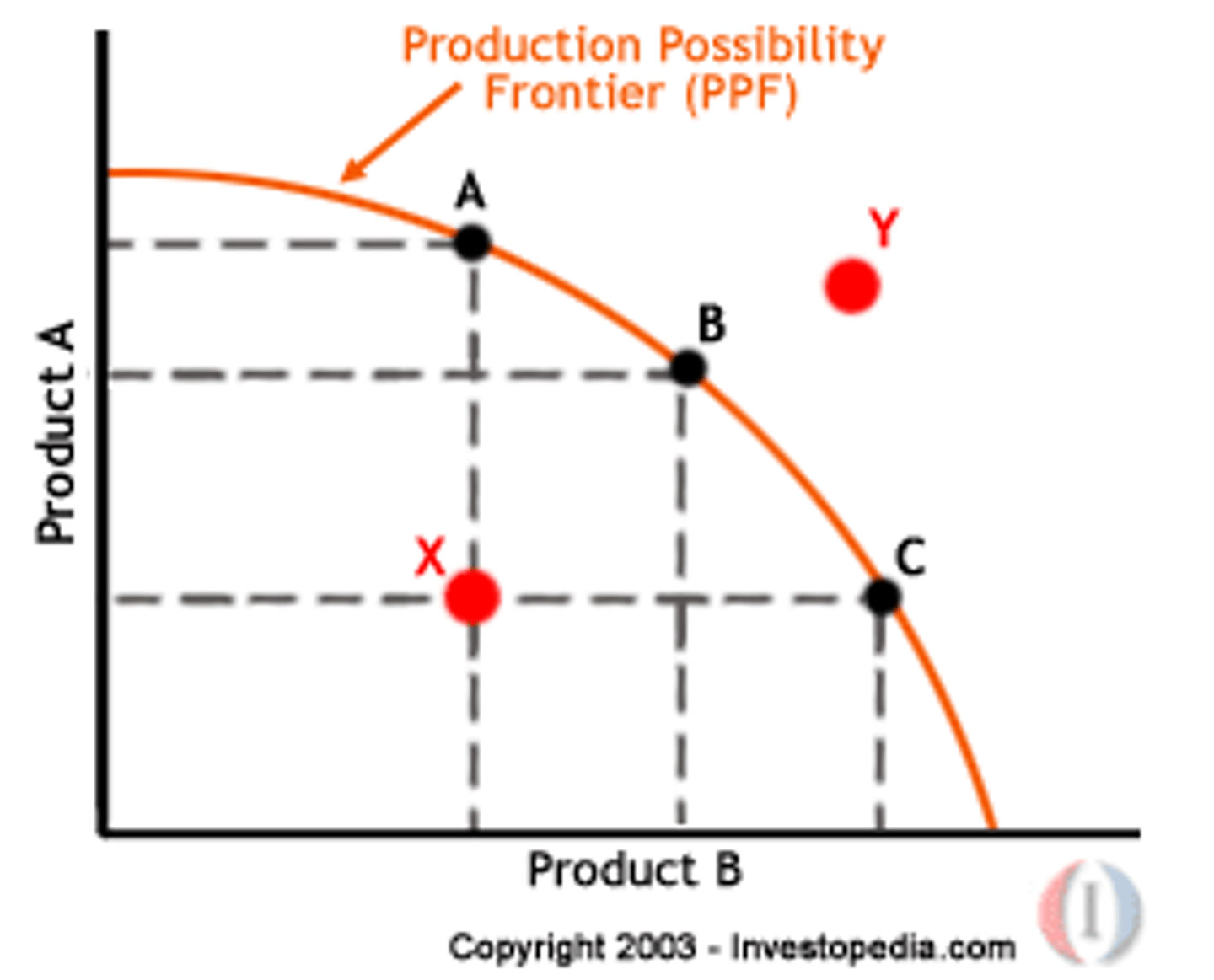
Efficiency
economy efficient if there are no missed opportunities. no way of producing more of one good without producing less of other goods. if the economy as a whole couldn't produce more of any one good without producing less of something else it is EFFICIENT IN PRODUCTION
inefficient in production
Situation in which the economy is using the same quantities of factors of production but is operating inside its production possibilities curve.
efficient in allocation
economy allocates its resources so that consumers are as well off as possible
allocate
to set apart or designate for a special purpose; to distribute
"natural" values
relatively unique attributes, resources, skills ,abilities that arise without artificial
"relative" values
legal rules and government imposed limitation making a good or service relatively scarce
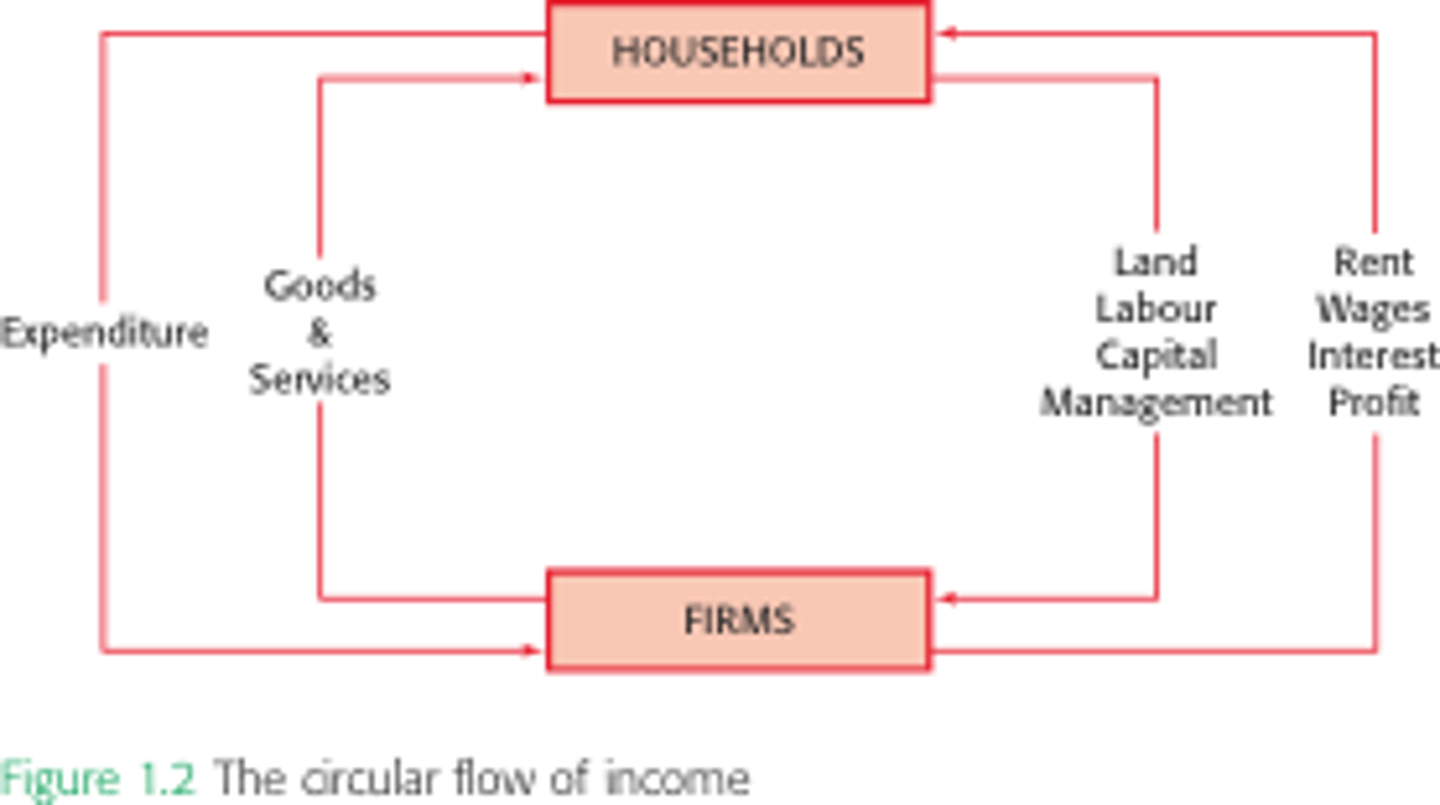
Two sector circular flow
IMAGE:
Boundary regulations
defining the market and rules of entry. do not allow to compete
Conduct regulations
defining permissible business conflict
Attribute regulation
defining the minimum or requisite quality requirements or dimension of a good
Government vs. Market
market can't exist without gov.
private property rights must be clear.
Supply and demand principles
- prices determined by the interactions of demand and supply
- prices reflect and are signals relating to consumers valuation and supplier's cost structure (relative scarcity)
Demand Schedule
a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
Right shift in demand curve
increase in demand
Left shift in demand curve
because a lower quantity demanded for a given price corresponds to a leftward movement on the horizontal axis. An example would be a lower quantity demanded for a given price of oil.
Right shift of supply curve
= decrease in marginal cost & increase in supply
Left shift of supply curve
= increase in marginal cost , decrease in supply
Economic Growth
an expansion of the economy's production possibilities; economy can produce more of everything
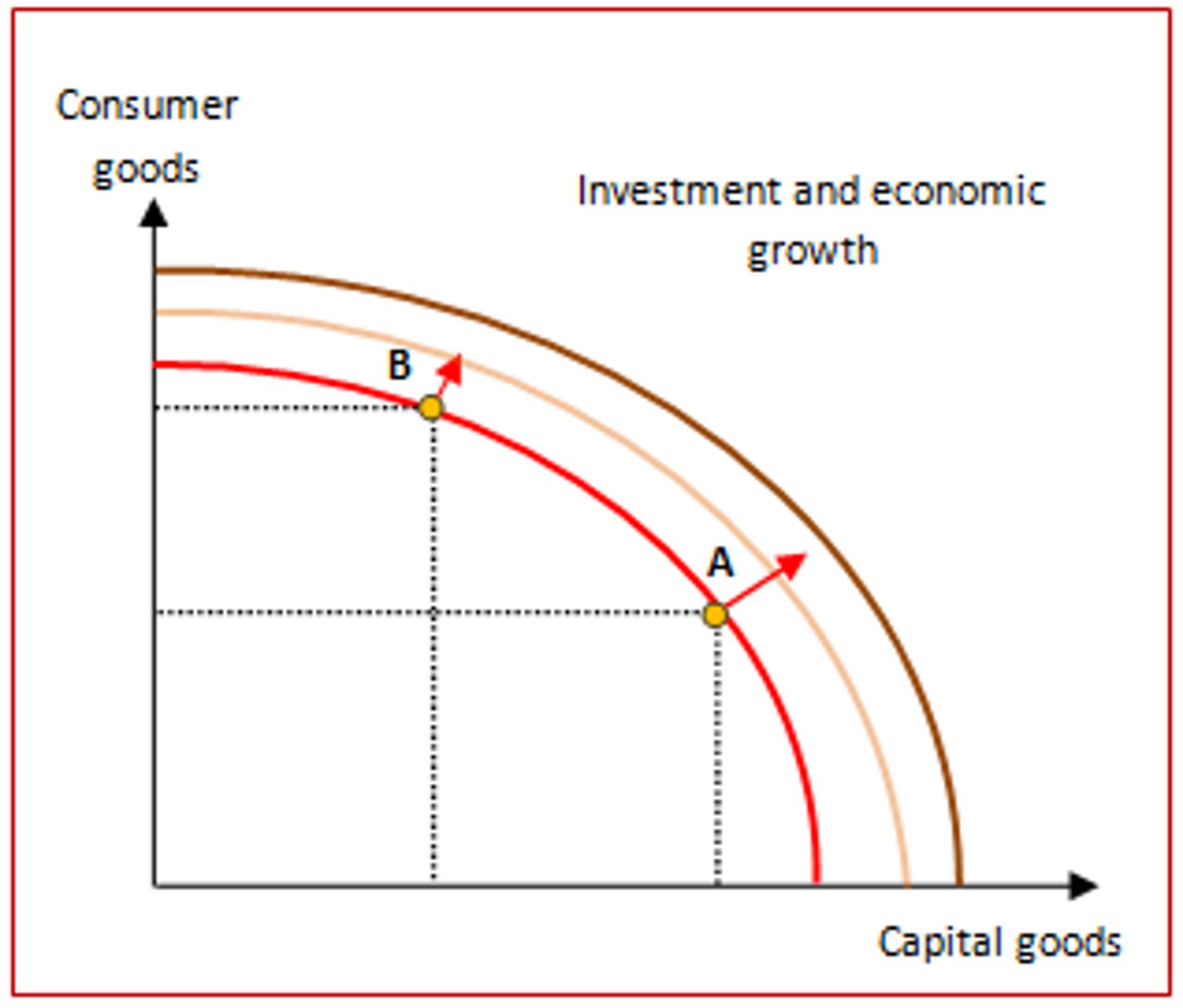
2 Source of Economic Growth
1. increase in economy's factors of production, resources used to produce goods and servcies
2. progress in technology, the technical means for the production of goods and services
Gains from trade graph
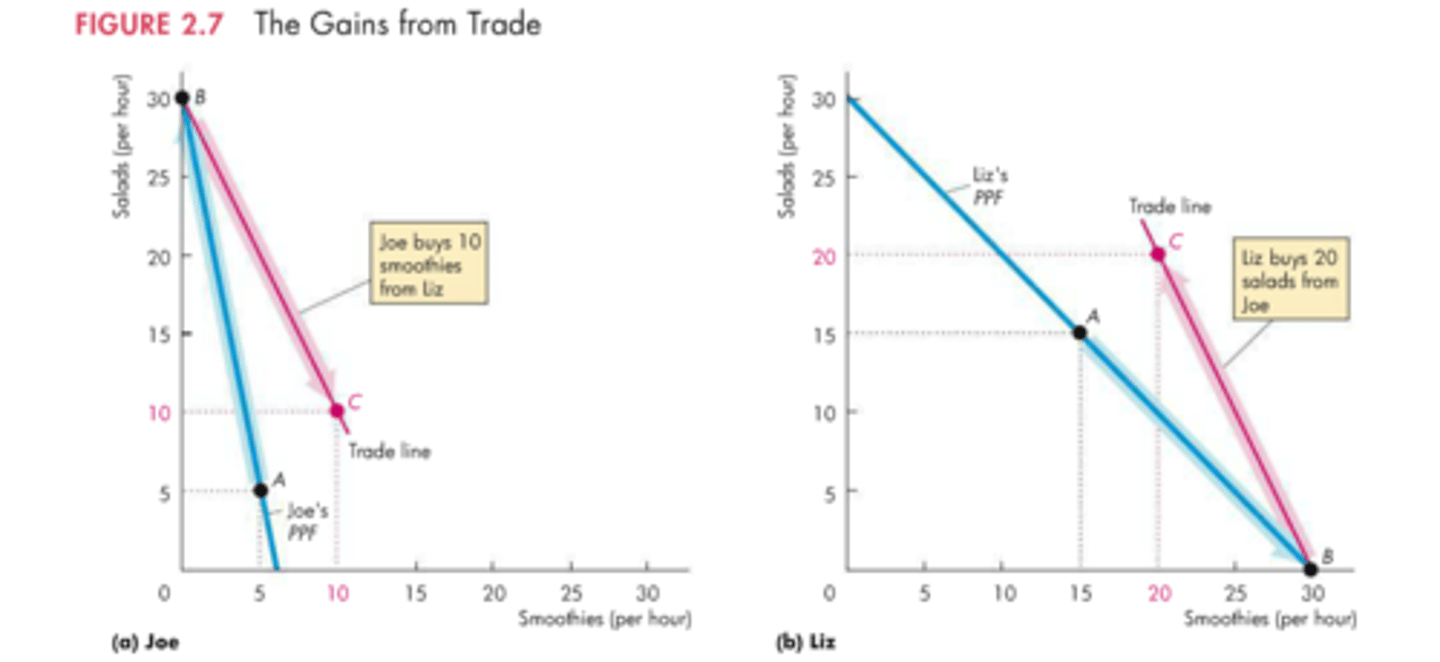
Comparative advantage
producing something if the opportunity cost of that production is lower in that country than in other country
absolute advantage
the ability to produce a good using fewer inputs than another producer
Barter
one party directly trades a good or service for another good or service without using money
Circular flow diagram
represents transactions that take place in an economy by two kinds of flow around the circle: google, labor, raw materials in one direction. money that pay for physical things in opposite direction
- household: consists of either individual or people that share income
- firm: produce goods and services for sale (employs members of household)
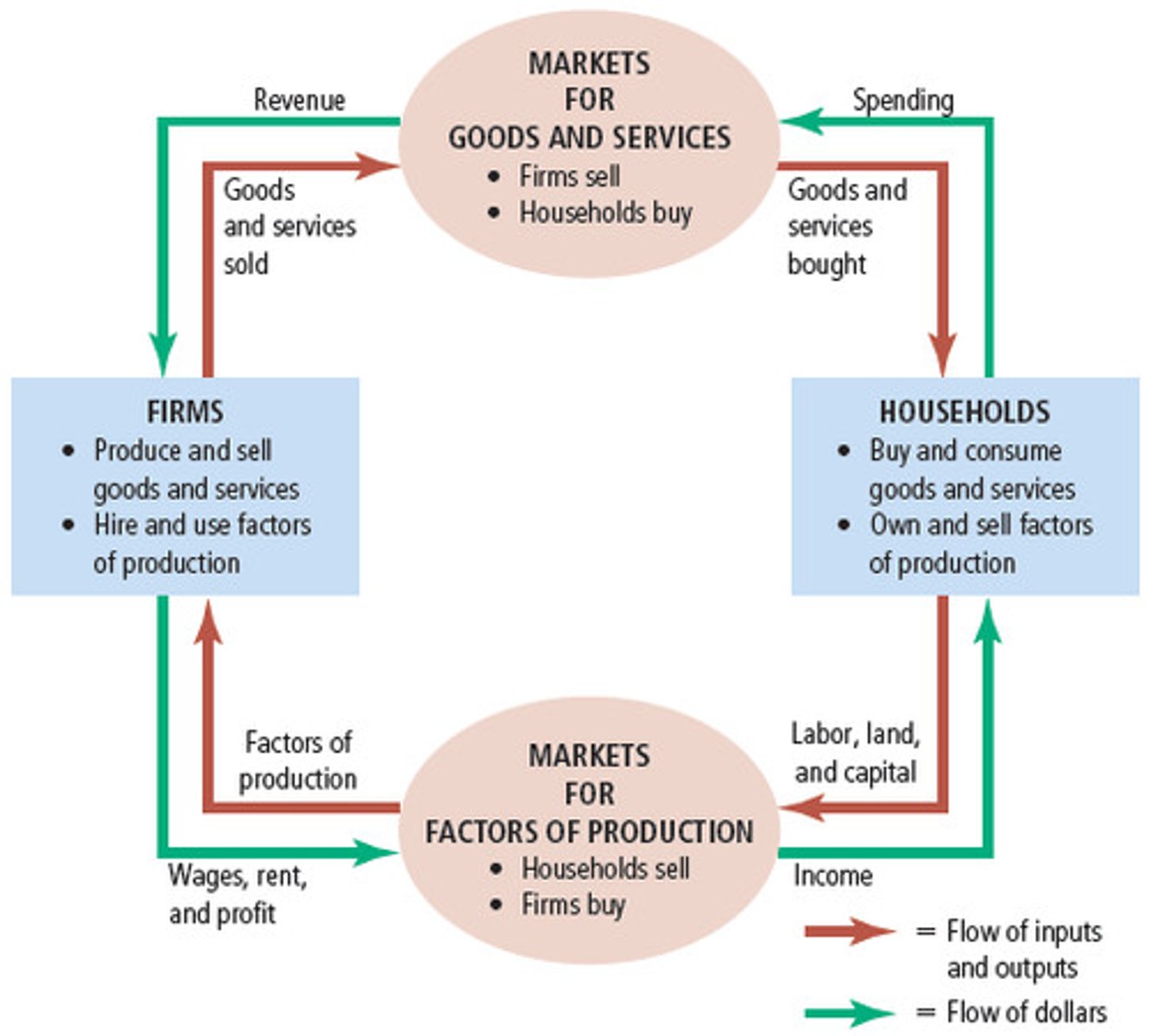
Markets for goods and services
household buy goods and services they want from firms
** goods => home
** money => firms
factor market
firm buy the resources they need to produce goods and services
income distribution
how the total income created in an economy is allocated between less skilled workers, highly skilled workers, and owners of capital and land
positive economics
analysis that tries to answer questions about the way world works (descriptive)
normative economics
analysis that involves saying how the world SHOULD work (prescription)
forecast
ask about future revenue
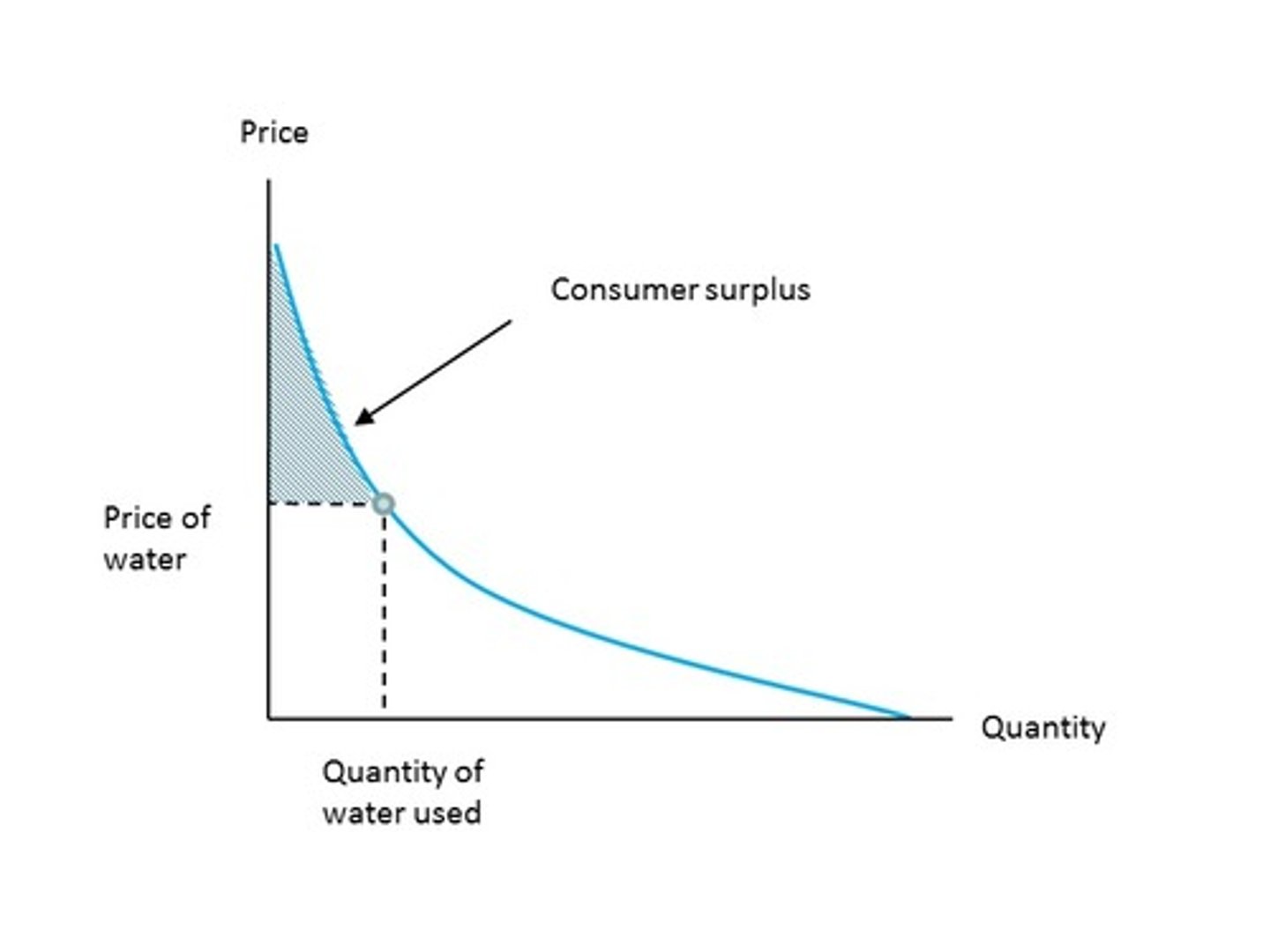
Demand curve
a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
supply curve
a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
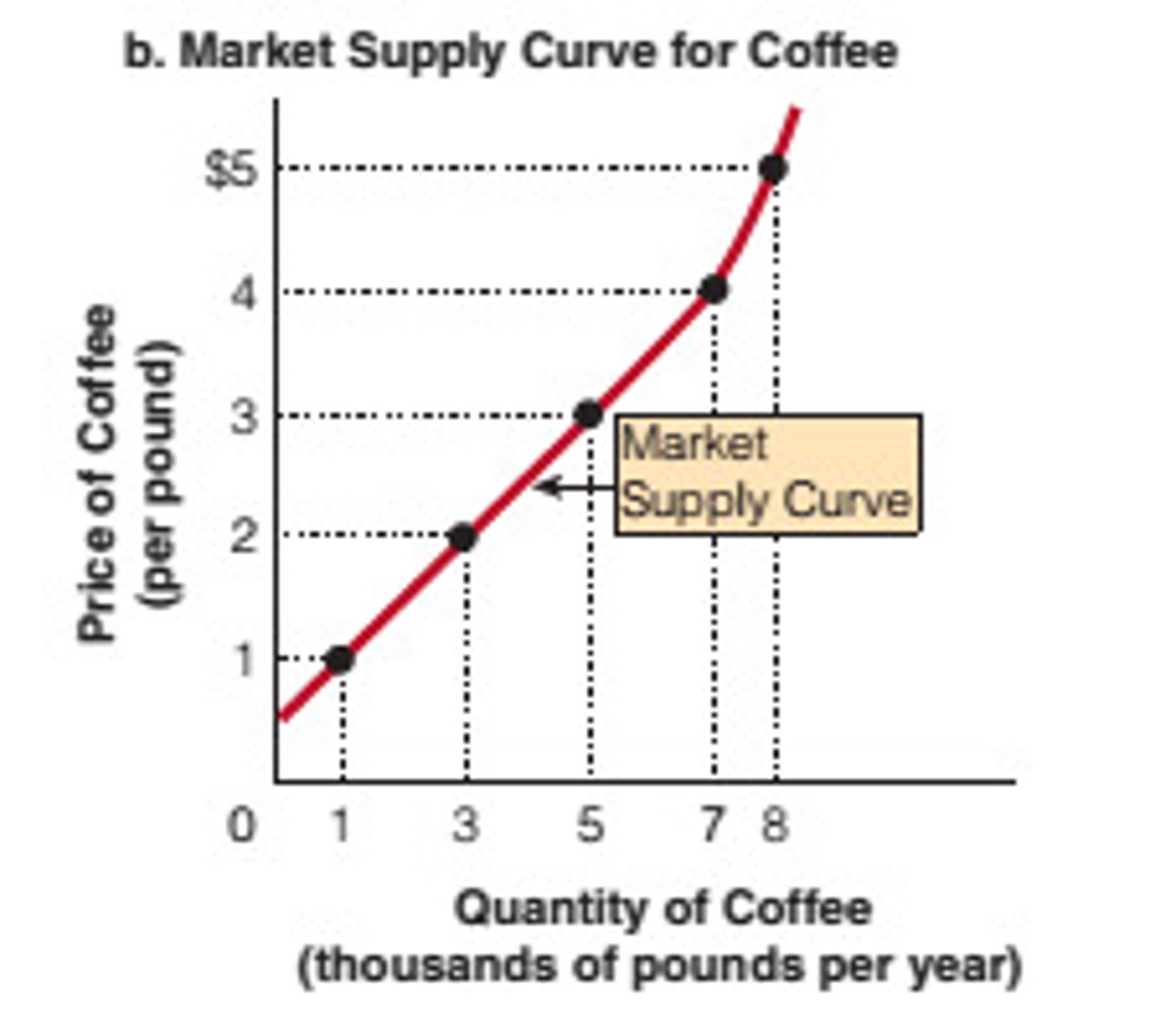
Quantity supplied
amount of a good or service that a seller is willing and able to sell at particular price
1st law of demand
there is a negative or inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
- lower the price, greater the quantity demanded (vise versa), holding everything else that may impact demand constant
Substitution effect
relatively more expensive
Real income effect
what we are holding constant (income) as price falls, our income rises and for most goods, we buy more as our income rises. as prices go up given fixed income, our real income is falling
- as income falls, we buy less
Factors that improve demand
1. expectations: income
2. substitutes and compliments
3. role of income
4. change in quantity demand = price
normal good
increase in income, increase in demand (decrease in income, decrease in demand)
inferior goods
goods whose demand decreases when income rises
factors impacting supply
1. expectations
2. increase/decrease in # of producers
3. changes in opportunity cost
4. technological progress and innovations
5. changes in the overall structure of inputs pirces
Increase in supply
a rightward shift of the supply curve
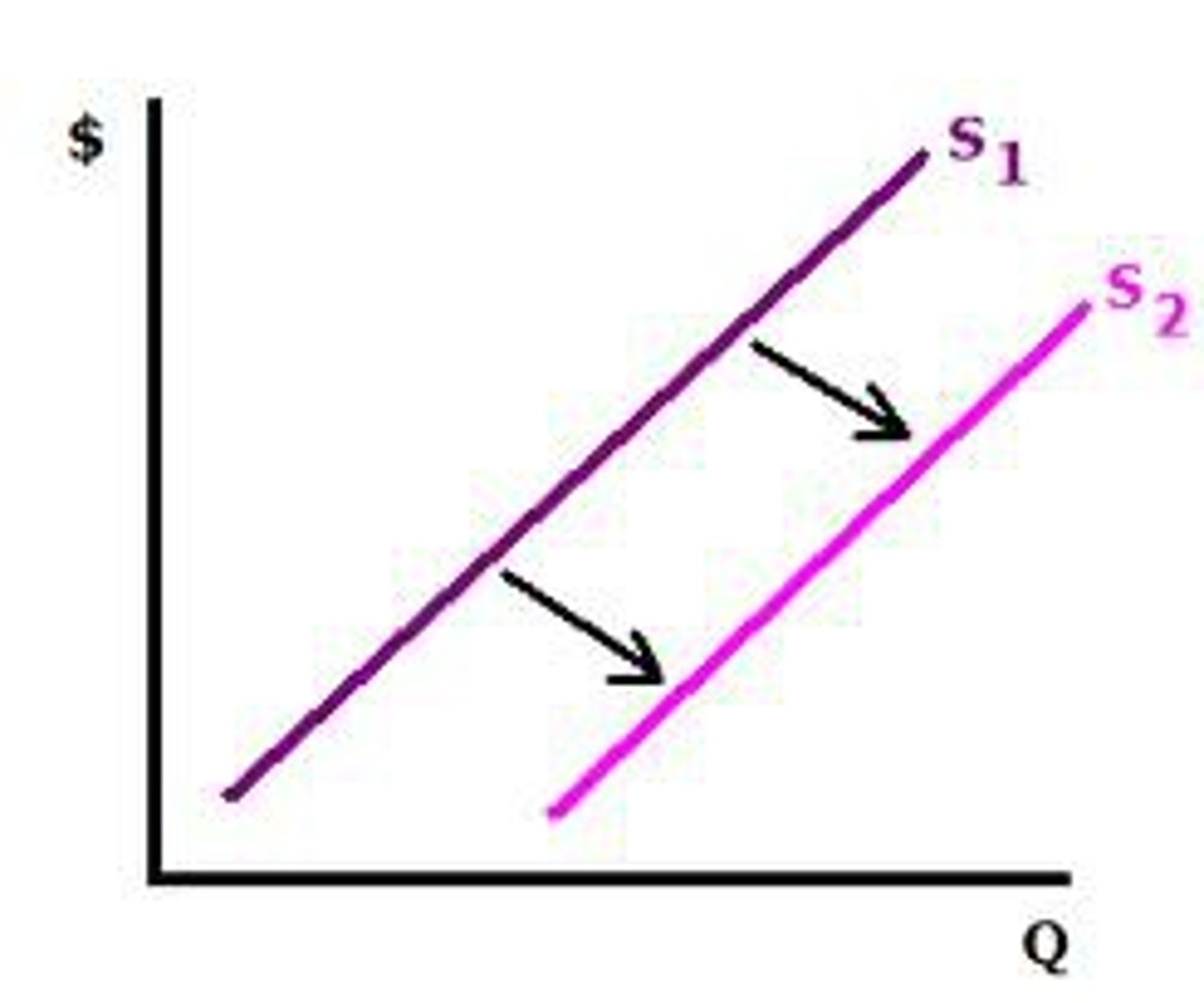
decrease in supply
a leftward shift of the supply curve
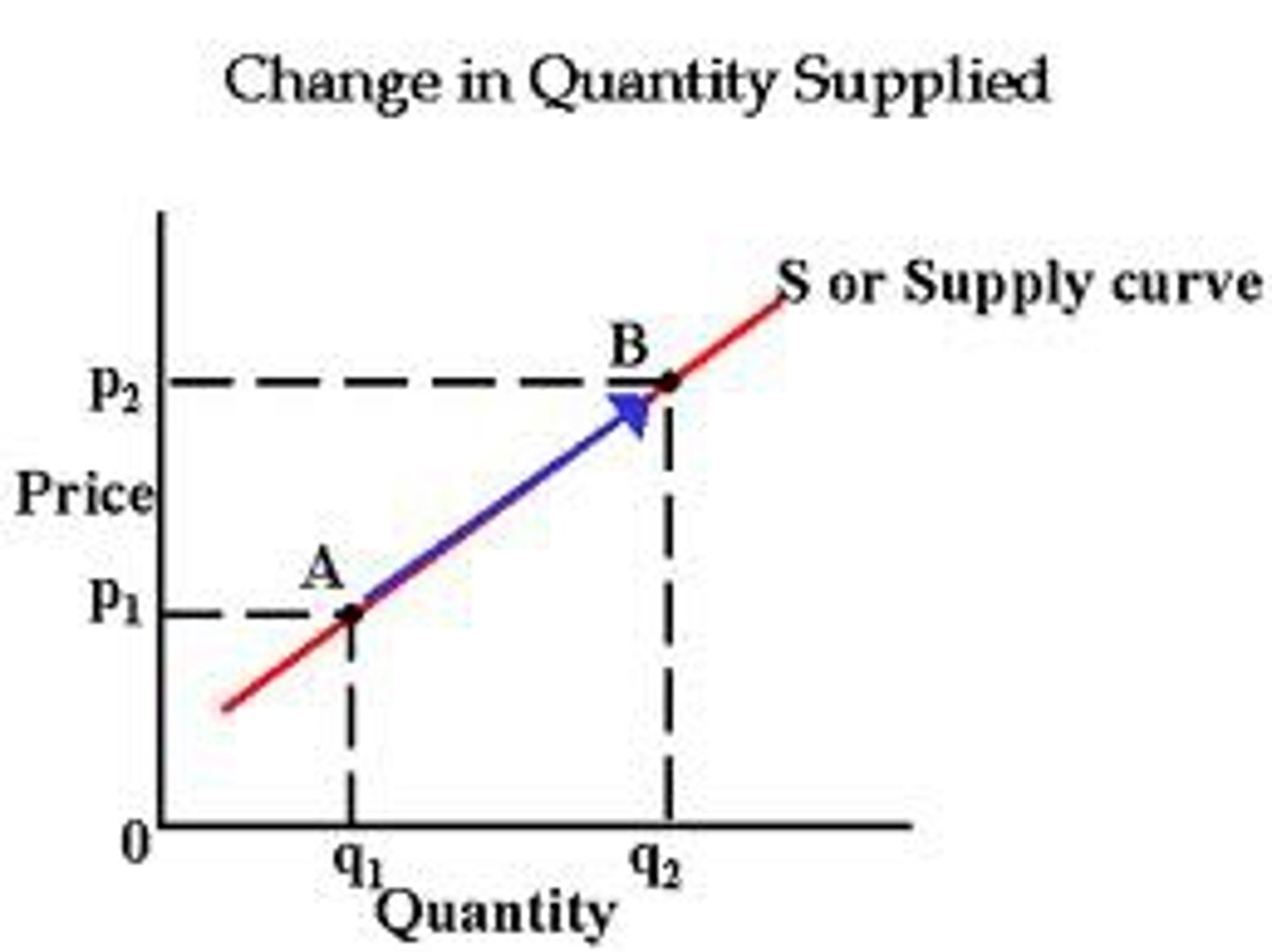
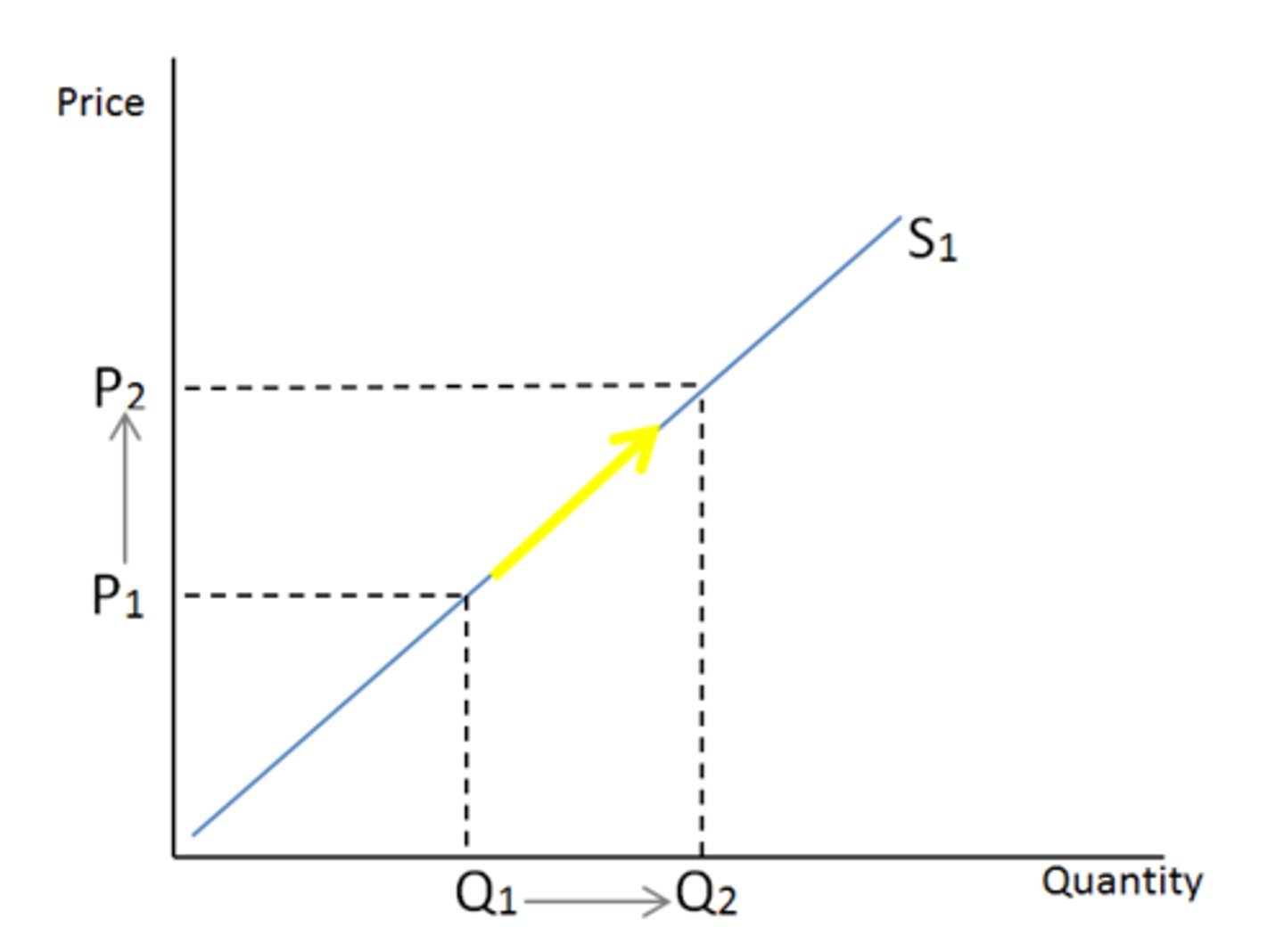
Change in quantity supplied
the change in amount offered for sale in response to a change in price
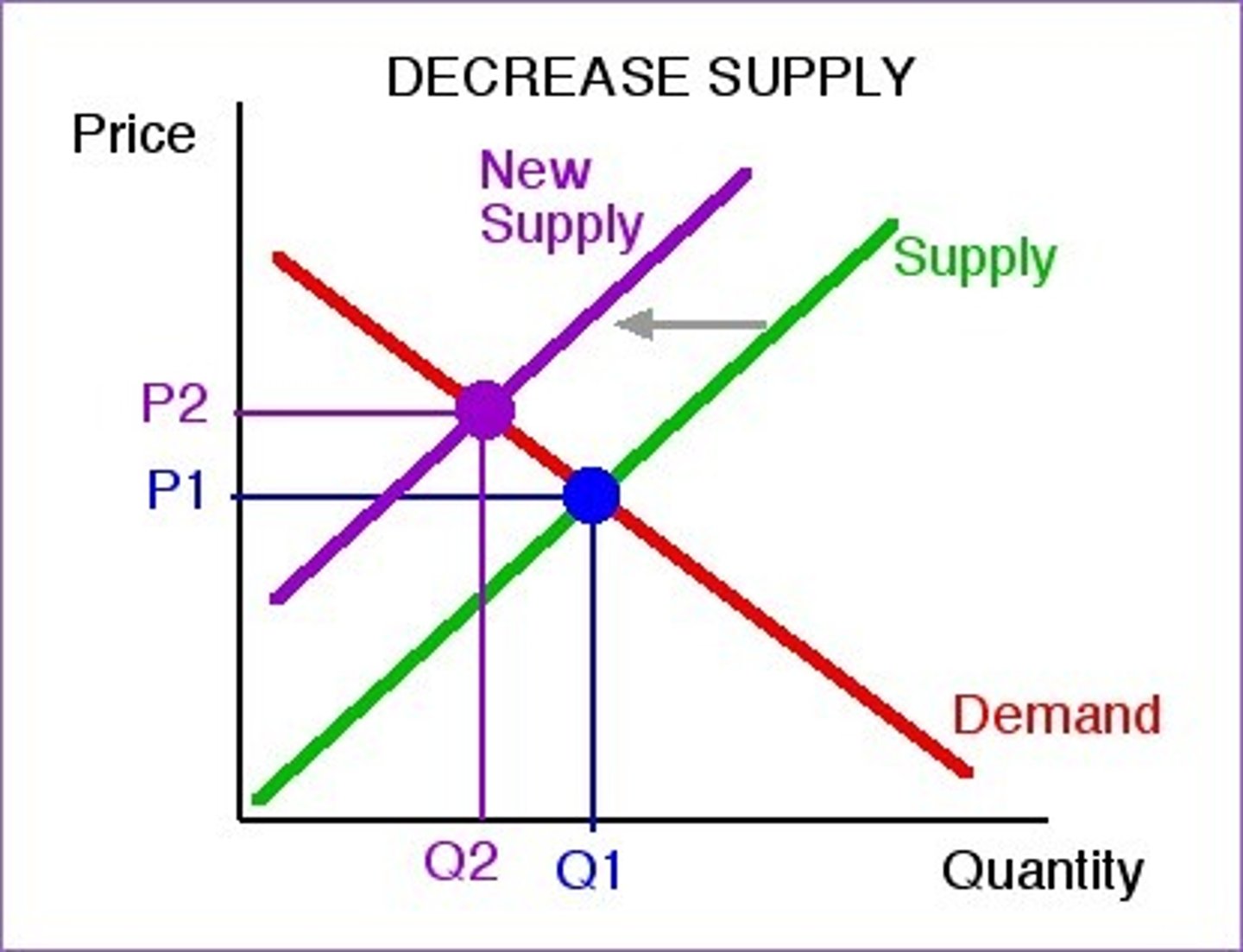
Supply decreases
at any given price suppliers are willing to supply less because at any given output it costs more to produce
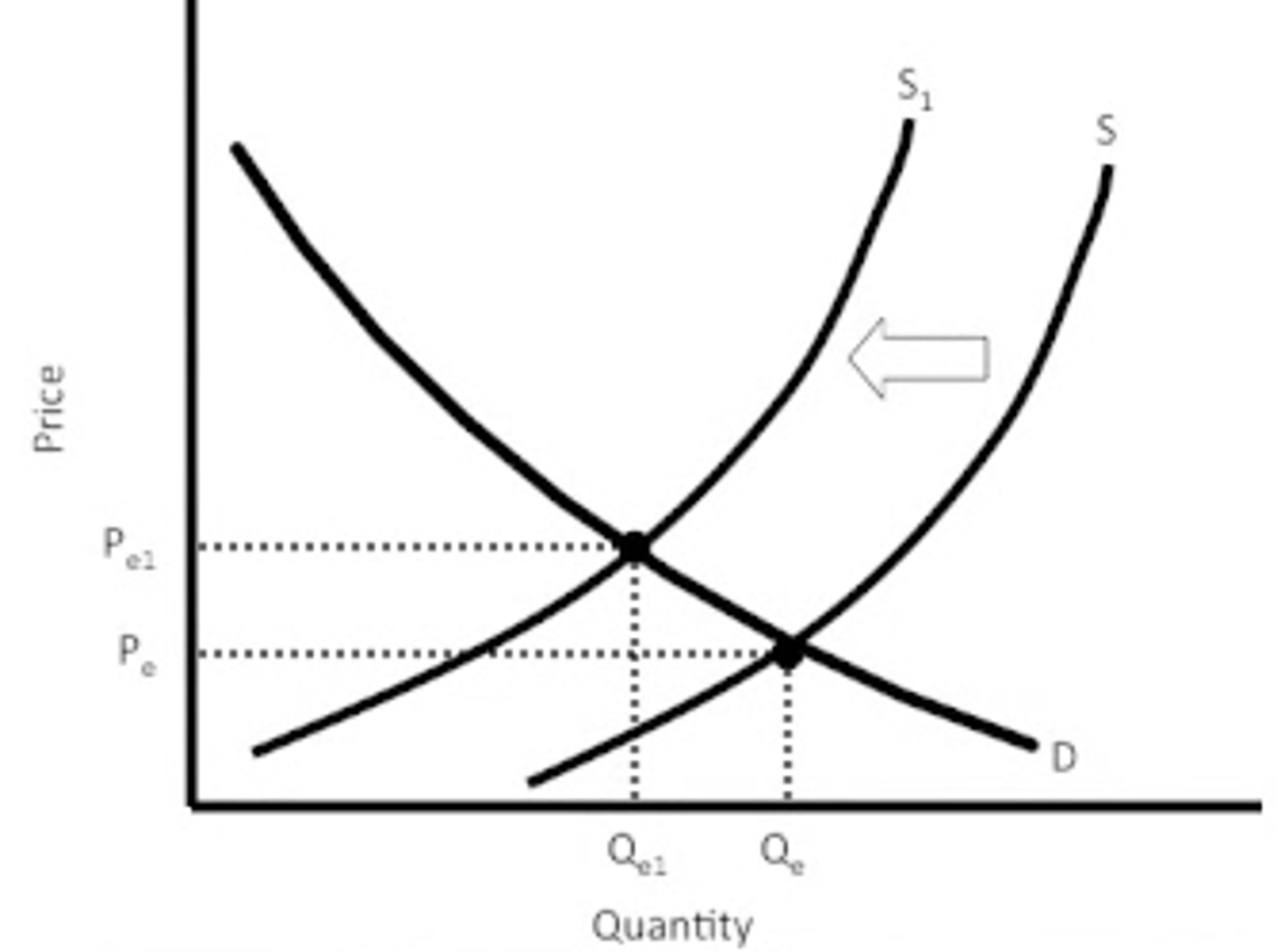
Decline in input prices
(cost of production) is graphically reflected as "shift down and to the right"
Complementary Good
a good you consume together
Substitutes Good
one or the other
increase in demand
shift to the right , increase in value, at only given price people want to buy more
decrease in demand
shift to left
How prices are rationed
as prices increase, it creates incentives for seller to expand production
economy of scale
a proportionate saving in costs gained by an increased level of production.