Ch. 9: Molecular structure of DNA and RNA
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
the central dogma
the flow of biological information
DNA —→ RNA —→ Protein
eukaryotic DNA
linear and organized into chromosomes
tertiary structure
the complex packaging of DNA (chromatin)
nucleosome
DNA wrapped around histone proteins
primary structure
string of nucleotides joined together by phosphodiester linages
order of nucleotides
secondary structure
DNA’s stable 3-D structure
DNA structure
two complimentary and antiparallel strands that from a double helix
nucleic acids
linear molecules made up of repeating subunits
nucleotide
contains a phosphate, a nitrogenous base, and a ribose or deoxyribose
phosphodiester bonds
what covalently links nucleotides together
deoxyribonucleic acid
lacks O on the pentose sugar (only has H)
ribonucleic acid
has O on pentose sugar (has OH)
purines
double ringed
adenine and guanine
pyrimidines
single ringed
thymine, uracil, cytosine
3
number of bonds between G and C
2
number of bonds between A and T
hydrogen bonds
type of bonding that occurs between base pairs
low energy bonds
they stabilize the molecule but can be disrupted by enzymes or with the input of energy
3’ to 5’
since strands run in anti parallel directions, if one side runs 5’ to 3’3 the other side must run
secondary structures
how RNA stabilizes itself
folds on itself by finding complimentary base pairing
bulge loop
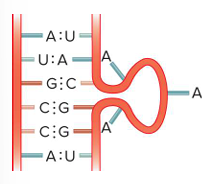
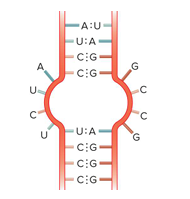
internal loop
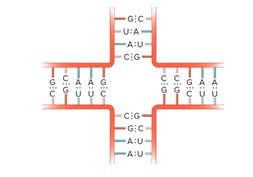
multibranched loop
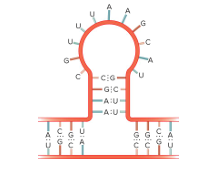
stem loop
factors contributing to tertiary structure of RNA
base paring and base stacking within the RNA itself
interactions with ions, small molecules and large proteins
criteria genetic material must meet to fulfill its role
information: it must contain the information necessary to make an entire organism
transmission: it must be passed from parent to offspring
replication: it must be copied in order to be passed from parent to offspring
variation: it must be capable of changes to account for the known phenotype variation in each species
principle of transformation
discovered by Griffith in 1928
he isolated two strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae
One strain was virulent (disease-causing) and had polysaccharide coat that made the colonies appear smooth (IIIS)
Virulent forms occasionally mutated into non-virulent forms and lost the polysaccharide coat and appeared to be rough (IIR)
he injected live mice with Streptococcus pneumoniae
Smooth (type IIIS): mouse dies
virulent bacteria recovered
Rough (type IIR): mouse lives
no bacteria recovered
Heat killed smooth (type IIIS): mouse lives
no bacteria recovered
Heat killed Smooth (type IIIS) mixed with Rough (type IIR): mouse dies
virulent bacteria recovered
transforming principle
Avery, McCloud, and McCarthy 1944
only DNA had the ability to transform
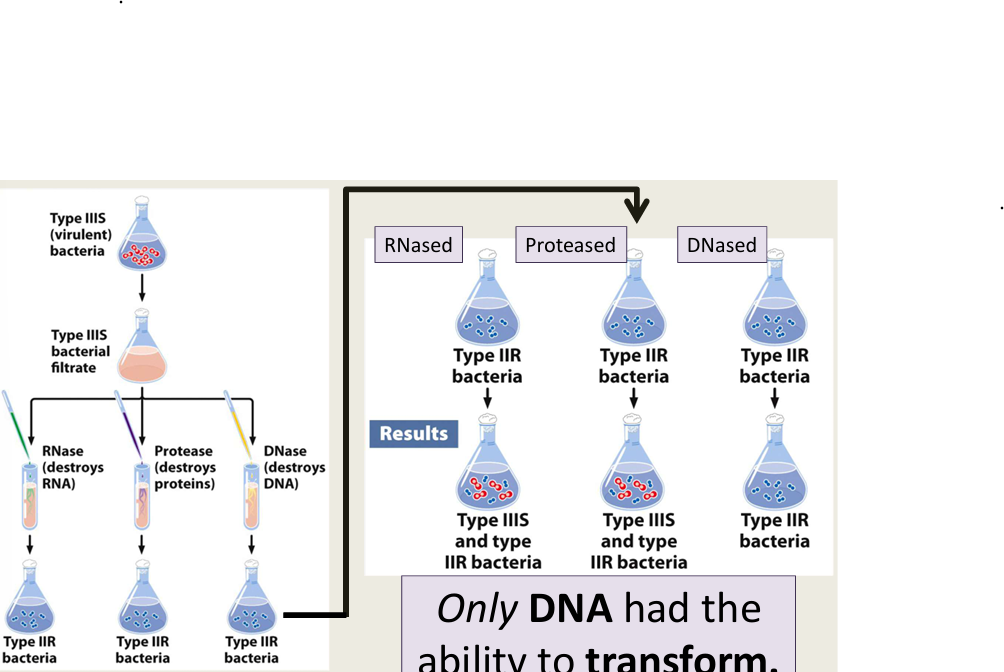
confirmation the DNA is the genetic material
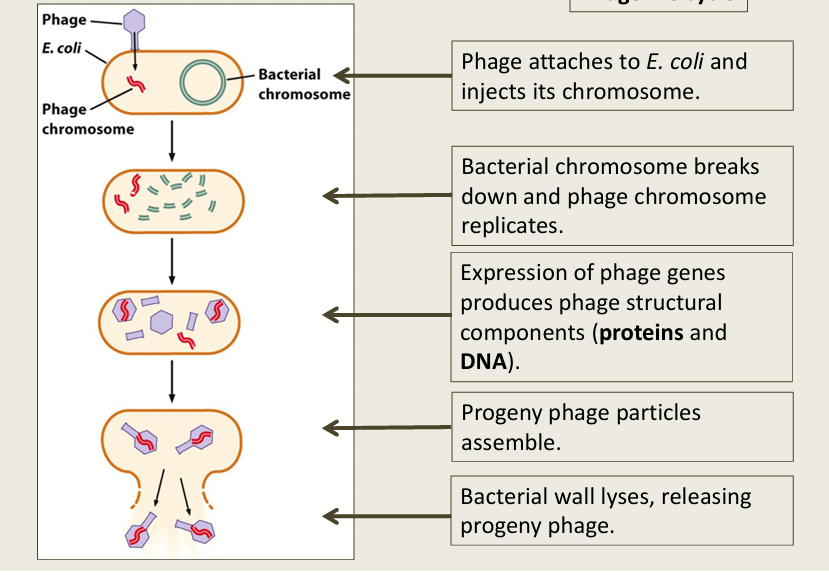
Hershey and Chase
Used Bacteriophage T2 (infects E. coli)
radioactively labeling molecules us a common technique to track molecule of interest
Hershey-Chase incorporates:
Radioactive P in DNA
Radioactive S in proteins
Chargaff’s rule
found that amounts of the four bases varied between species but their ratios did not
adenine = thymine
guanine = cytosine
X-ray diffraction of DNA fibers
Rosalind Franklin
studies wet fibers of DNA
a diffraction pattern is interpreted to provide information concerning the structure of molecule
three-dimensional structure of DNA
James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953
used existing data (including Rosalind Franklin’s) molecule models and knowledge of structural chemistry
Watson recognized and adenine could bond with a thymine and a guanine could bond with a cytosine