b1 | thermal energy transfers
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
the kinetic theory of matter is a model that…
attempts to explain the properties of the three states of matter
in the kinetic theory of matter, particles are assumed to be…
small spheres
the difference between solid ice, liquid water and gaseous steam is…
the arrangement of the particles
particles in a solid are … packed
closely
particles in a solid are arranged in a fixed … structure
lattice pattern
particles in a solid can only … about their fixed positions
vibrate
particles in a solid have … energies compared to particles in liquids and gases
low
particles in a solid do/do not have enough energy to overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction holding them together because of …
do not | low energies compared to liquids and gases
solids have a fixed … and …
shape | volume
solids are very … to compress
difficult
solids have lower/higher densities that liquids and gases
higher
particles in a liquid are … packed
closely
particles in a liquid are … arranged
randomly
particles in a liquid can/cannot flow past each other
can
liquids have higher energy than … but less than …
particles in solids | gas particles
liquids have enough energy to …. overcome the intermolecular forces of attraction
partially
liquids do/do not have a fixed shape
do not
liquids have a … volume
fixed
liquids are easy/difficult to compress
difficult
particles in a gas are close to each other/far apart
far apart
particles in a gas are … arranged
randomly
gases move around …. at a … of speeds
in all directions | variety
gases occasionally collide with …. and ….
each other | walls of the container
gases have high/low density
low
gases have higher energies than …
solids and liquids
gases can/cannot overcome the intermolecular forces
can
density is the …. of an object
mass per unit volume
if two objects occupy the same volume the object with a lower density will have a …
lower mass
formula for density?
density = mass/volume of container
absolute zero refers to…
the lowest possible temperature, at which the molecules ina substance have zero kinetic energy
absolute zero is equal to …K or …C
0 | -273
it is not possible to … from a system at 0K
remove any more energy
the melting point of ice is …K and …C
273 | 0
because particle in gases usually have a range of speeds, the average kinetic enegry can be calculated using…
E k = 3/ 2 k B T
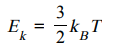
explain this formula: E k = 3/ 2 k B T
3/2: comes from the number of translational degrees of freedom for a particle in three-dimensional space (x, y, z). Per degree, the energy contribution is 1/2kBT.
KB: converts between temp(K) and energy(joules).
KB: 1.38 × 10-23J/K
T: absolute temperature of the gas(K)
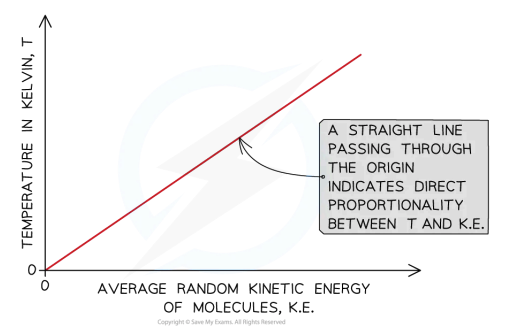
this graph shows that…
the absolute temperature of a body is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the molecules within the body
in the average kinetic energy of molecules EK at the start of the formula can be equated with…
1/2mv2
when a substance gains or loses thermal energy what increases or decreases?
thermal energy
the internal energy of a substance is the sum of…
total kinetic energy and total intermolecular potential energy
an increase in potential energy occurs when..
particles move further away from each other, because work is being done to overcome the attractive forces
an increase in average kinetic enegry occurs when… OR/AND …
molecules vibrate | move at higher speeds
an increase in temperature is brought about by an increase which of the below?
average kinetic energy | potential energy
average kinetic energy
due to thermal expansion what increases with the temperature of a substance…
the potential energy of the molecules
does potential energy change cause temperature change?
nono extent
to what extent does temperature change occur with state change?
no extent
does a change in internal energy correspond with a change in temperature? why or why not?
no, because change in potential energy doesn’t change temperature
thermal energy is a fancy word for?
heat
thermal energy is transferred from … to …
hotter region | lower region ther
thermal energy transfer stops when…
both regions are the same temperature
thermal equillibirum is when…
two substances in contact with each other no longer exchange any heat energy and both reach an equal temperature
during a phase change what is transferred to or from the substance?
thermal energy
what doesn’t change during phase change?
temperature
the thermal energy provided or removed does not affect… but it does affect …
kinetic energy | potential energy(spacing between atoms)
condensation is …. and … thermal energy
gas to liquid | releasing
melting and boiling occurs when thermal energy is…
absorbed
melting and freezing happen only at…
the melting/freezing point
vaporisation and condensation happen only at…
the boiling point of a substance
every substance has a unique/the same boiling/freezing point?
unique
the amount of thermal energy to change the temp of an object depends on what three things?
the mass of the object
the greater the mass the more energy is needed
the specific heat capacity
the higher the more energy is needed
change in temperature wanted
the larger the change the more energy required
thermal energy is the amount of energy required to…
cause a temperature change, depending on the substance's mass and specific heat capacity
the formula for thermal energy transferred is
Q = mc change in temp

the specific heat capacity is the energy required to change the temperature of …. of a substance by ….
1kg |1K or 1C
the higher the specific heat capacity…
the longer it takes for the substance to warm up or cool down
during a phase change, the temp of the substance changes/does not change
does not change
when temperature of a substance does not change thermal energy can be calculated by

how can thermal energy increase without a temperature change?
because during a state change the energy goes into changing the state of the substance not increasing kinetic energy
the energy used to overcome intermolecular forces is…
latent heat
what is latent heat stored as?
potential energy
even though thermal energy is added temp remains constant because
all the energy is used for phase transition
latent heat is defined as the amount of energy required to…
change the state of 1kg of a substance without changing the temperature
the higher the specific latent heat…
the greater the energy required to change its state
is the specific latent heat for melting and freezing the same?
no
specific latent heat of fusion is the energy released/absorbed when
1kg of solid/liquid freezes/melts to become solid/liquid at constant temp
fusion applies to…
melting
freezing
specific latent heat of vaporisation is the energy released/absorbed when..
1kg of gas/liquid condenses/evaporated to become liquid/gas at constant temp
vaporisation applies to…
evaporation
condensation
latent heat of vaporisation > specific latent heat of fusion because…
intermolecular forces must be completely overcome to transfer from liquid to gas but not for solid to liquid
vaporisation = more energy
what can thermal energy be substituted for in equations?
P = E/t
E = Pt
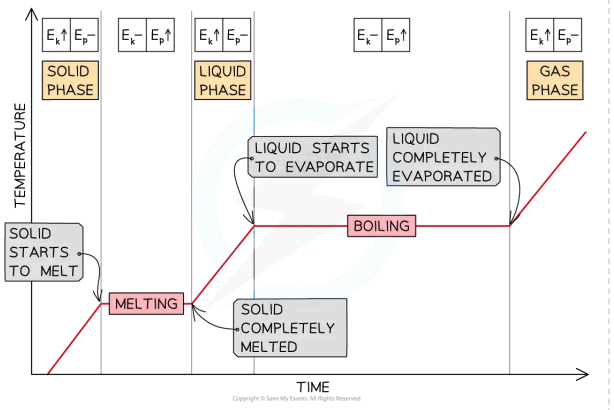
explain this graph in terms of flat sections, non-flat section
state what type of curve it is
heating curve
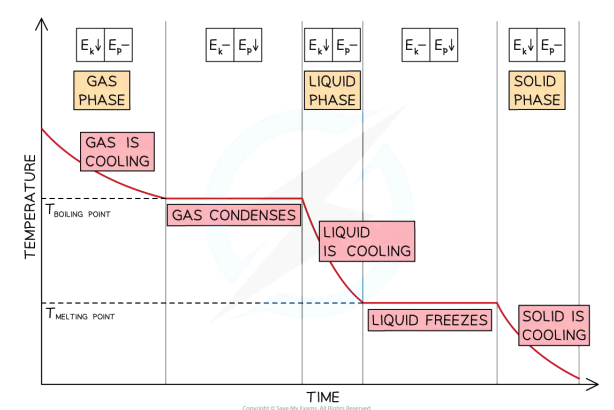
explain this graph in terms of flat sections, non-flat section
state what type of curve it is
cooling curve
what are the three mechanisms of thermal energy transfer
radiation
convection
conduction
objects will always lose heat until…
they are at thermal equilibrium with their surroundings
conduction occurs when thermal energy is transferred between two objects…
in contact with one another
metals are the best thermal conductors because…
they have a high number of delocalised electrons
faster rate of transfer of vibrations
liquids and gases are poor thermal conductors because…
the atoms are further apart
what two mechanisms can conduction occur through?
atomic vibrations
free electron collisions
explain the process of atomic vibrations and free electron collisions in conduction?
the hotter atoms vibrate more so when they collide with the cooler ones they transfer energy until thermal equilibrium is reached
what is a free electron?
an electron that is not bound within the atom and is free to move
thermal conductivity is the ability of a substance to…
transfer heat via conduction
good thermal conductors have what three things?
high values of thermal conductivity
fast rate of thermal energy transfer
large number of delocalised electrons
a temperature gradient is when…
in the presence of a temperature difference, thermal energy flows from the region of higher temp to the region of lower temp
the formula for the rate of heat transfer is
k = thermal conductivity of the material (W m K )
A = cross-sectional area (m )
ΔT = temperature difference (K or °C)
Δx = thickness of the material (m)
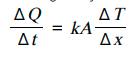
is the flow of thermal energy per second across a temperature gradient uniform or non-uniform?
uniform
convection occurs when a fluid…
is heated causing the movement of groups of atoms/molecules due to density variations
convection cannot occur in… because..
solids | particles cannot travel relative to one another
what happens when a fluid is heated from below, so in a convection current?
the increase in EK causes the molecules to push each other apart so the fluid expands
as the hot fluid is less dense it rises
the cool fluid moves in to take its place
eventually the hot fluid cools, contracts and sinks back down
a perfect black body is an object that…
absorbs all of the radiation incident on it, and does not reflect or transmit any
a good absorber is also a…
good emitter
an object which completely absorbs all radiation will be black because…
the colour black is what is seen when all colours from the visible light spectrum are absorbed
black body radiation is…
the thermal radiation emitted by all bodies