Year 9 - Geography Revision
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A mixture of all notes in the winter assessment revision page compiled into revision cards. There's many notes but study the ones that are most relevant to you. Again, these notes cover everything from, long shore drift to the food chain. I recommend reading quickly over the note document before attempting these revision cards. GLL!
Last updated 8:34 PM on 12/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
Decomposers
consume living /dead plants and animals and break them down into nutrients that are released into the soil.
2
New cards
Omnivores
get their energy by eating both /only plants and meat.
3
New cards
Corrosion
salts and acids in seawater dissolve the rock gradually over thousands of years.
4
New cards
Producers
produce or make their own soil /food.
5
New cards
Headlands
are usually formed of more resistant rock types than bays.If there are different bands of rock along a coastline, the weaker or softer rock, such as clay, is eroded fastest.
6
New cards
Landforms
created by erosion include headlands and bays, caves, arches, stacks and stumps.
7
New cards
mode
The mode is the number that occurs the most in a set of numbers.
8
New cards
coast
The is the area where land meets the sea.
9
New cards
Hydraulic action
puts pressure on the crack /fault in the headland, forcing the crack to widen into a cave.
10
New cards
Use of coastal areas
Tourism, Trade, Fishing, Settlement, Leisure/recreation, educational research/study
11
New cards
Abrasion
waves transport material which hit the cliff and gradually wear it away
12
New cards
Hydraulic action
as waves approach the coast they trap air and force it into gaps in the cliff
13
New cards
Attrition
waves cause the rocks to crash against each other, breaking them down into smaller and rounder pieces
14
New cards
Corrosion (also known as solution)
salts and acids in seawater dissolve the rock gradually over thousands of years
15
New cards
There are three main types of living things in an ecosystem
producers, consumers, and decomposers
16
New cards
How to solve a median
List all your numbers from smallest to largest
17
New cards
How to solve a mode
The mode is the number that occurs the most in a set of numbers
18
New cards
How to solve a mean
The mean (average) of a data set is found by adding all numbers in the data set and then dividing by the number of values in the set
19
New cards
Examples of Hard engineering strategies :
Groynes, Sea wall, Rock Armour
20
New cards
Examples of soft engineering strategies :
Salt marsh, Beach nourishment , Do nothing
21
New cards
benefits of groynes
builds up the by trapping sediment
acts as a natural barrier to erosion and attracts tourists
relatively cheap as most of them are made up of wood
relatively long lasting
Cheaper to repair than other hand engineering strategies.
acts as a natural barrier to erosion and attracts tourists
relatively cheap as most of them are made up of wood
relatively long lasting
Cheaper to repair than other hand engineering strategies.
22
New cards
benefits of sea walls
sea walls often have a promenade on top of them which are popular with tourists
sea walls tend to have a long life - span and provide excellent defence where wave energy is large
Sea walls do not impede the movement of sediment along the coast by longshore drift.
sea walls tend to have a long life - span and provide excellent defence where wave energy is large
Sea walls do not impede the movement of sediment along the coast by longshore drift.
23
New cards
What is long shore drift?
Long shore drift is the movement of material/sediment a long the beach by waves
24
New cards
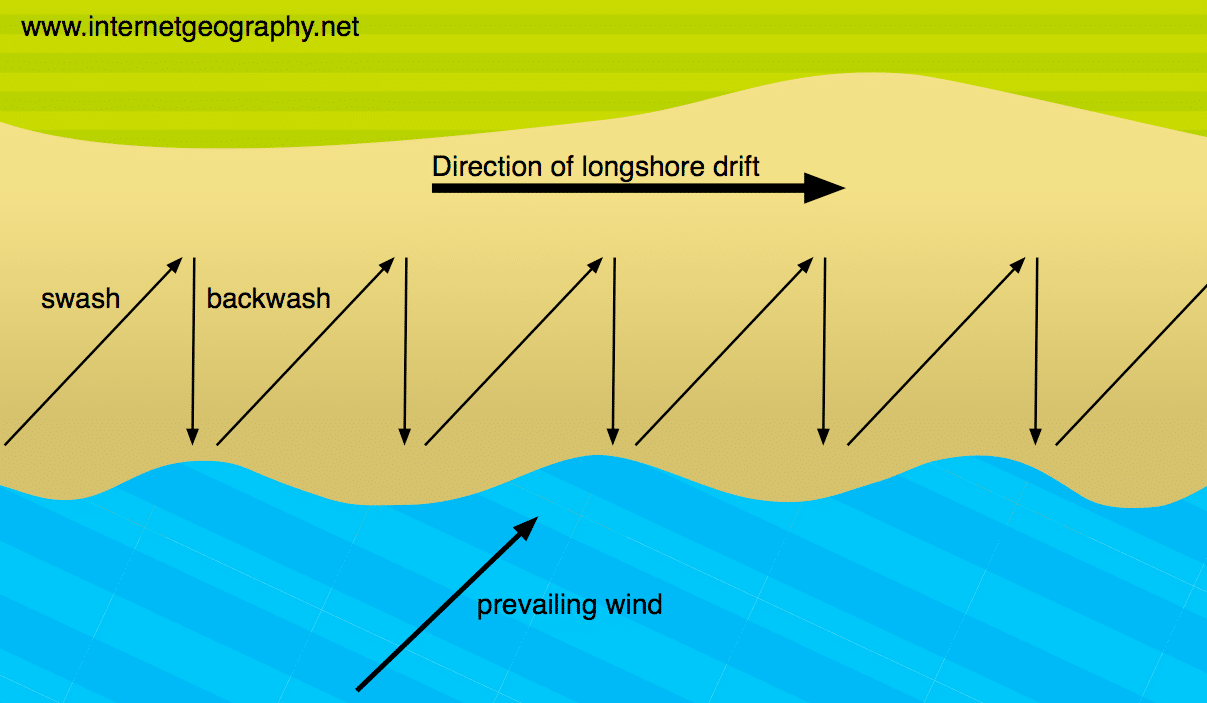
How does longshore drift happen?
The process of Long shore drift occurs in a zig zag pattern.
1.Waves hit the beach at an angle
2.The SWASH carries the material up at an angle
3.The BACKWASH returns the material back to the sea at a 90 degree angle
4.This process repeats itself and transports the material a long the beach in a zig zag pattern
1.Waves hit the beach at an angle
2.The SWASH carries the material up at an angle
3.The BACKWASH returns the material back to the sea at a 90 degree angle
4.This process repeats itself and transports the material a long the beach in a zig zag pattern
25
New cards
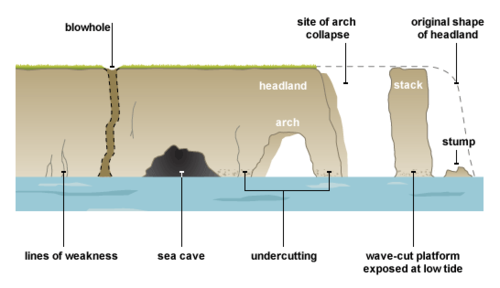
How are erosional coastal landforms created?
Waves attack the base of the cliff. Hydraulic action puts pressure on the crack/fault in the headland, forcing the crack to widen into a cave.
Waves continue to attack the base of the cliff. Abrasion causes waves to throw large amounts of sediment at the cave, creating a sand-blasting effect, which causes large amounts of the cave to be eroded. This leads to the cave widening and breaking through to the other side of the headland, forming an arch.
Continued abrasion at the base and weathering at the top of the arch cause it to weaken, eventually leading to the top collapsing.
This leaves the headland on one side and an isolated pillar of rock known as a stack on the other.
Waves continue to attack the base of the cliff. Abrasion causes waves to throw large amounts of sediment at the cave, creating a sand-blasting effect, which causes large amounts of the cave to be eroded. This leads to the cave widening and breaking through to the other side of the headland, forming an arch.
Continued abrasion at the base and weathering at the top of the arch cause it to weaken, eventually leading to the top collapsing.
This leaves the headland on one side and an isolated pillar of rock known as a stack on the other.
26
New cards
What is the role of producers, consumers and decomposers in a food chain?
Producers - Producers produce or make their own food. Usually, they make their food from sunlight through photosynthesis. Without producers, no animals would be able to survive.
Consumers - all animals are consumers and need to consume or eat their food. Some animals, called herbivores, get their energy from eating plants. Other animals, called carnivores, get their energy from eating other animals. The third group of animals are called omnivores. Omnivores get their energy by eating both plants and meat.
Decomposers - Decomposers consume dead plants and animals and break them down into nutrients that are released into the soil. These nutrients are used by producers like plants to help them grow, and the cycle begins all over again.
Consumers - all animals are consumers and need to consume or eat their food. Some animals, called herbivores, get their energy from eating plants. Other animals, called carnivores, get their energy from eating other animals. The third group of animals are called omnivores. Omnivores get their energy by eating both plants and meat.
Decomposers - Decomposers consume dead plants and animals and break them down into nutrients that are released into the soil. These nutrients are used by producers like plants to help them grow, and the cycle begins all over again.
27
New cards
Examples of producers
trees, flower, grass
28
New cards
Examples of consumers
Tiger, sheep, bear
29
New cards
Examples of decomposers
Fungi, worms, Snail
30
New cards
adaptations of the camel
Thin fur across body to maximise heat loss and keep them cool.
Can drink up to 46L in one session and can last very long periods without drinking water.
Camels don’t sweat very often nor urine
They have large, wide, flat and webbed feet to keep stable on sand and stop sinking
Thick fur on the top of their bodies to provide shade during the day as it is extremely hot during the day
Large body size to have more space where heat can leave, and they can tolerate temperatures up to 42 degrees Celsius .
Large nostrils and long eyelashes to protect from sandstorms
Can drink up to 46L in one session and can last very long periods without drinking water.
Camels don’t sweat very often nor urine
They have large, wide, flat and webbed feet to keep stable on sand and stop sinking
Thick fur on the top of their bodies to provide shade during the day as it is extremely hot during the day
Large body size to have more space where heat can leave, and they can tolerate temperatures up to 42 degrees Celsius .
Large nostrils and long eyelashes to protect from sandstorms
31
New cards
adaptations of the cactus
Large trunk to store water during the long periods of droughts
Spikes to stop animals or predators from attacking or stealing it’s supply
Have long, shallow root system that sucks up the rain as rainstorms are infrequent
Pleats on trunk that expand to store more water. Some cacti can store up to 5 tonnes of water
Spikes to stop animals or predators from attacking or stealing it’s supply
Have long, shallow root system that sucks up the rain as rainstorms are infrequent
Pleats on trunk that expand to store more water. Some cacti can store up to 5 tonnes of water