Topic 1/2 - Motion & Forces
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
What is a scalar?
A quantity with magnitude/size only - no specific direction.
What is a vector?
A quantity with magnitude/size and direction.
Give examples of scalar quantities
Speed
Distance
Mass
Energy
Temperature
Give examples of vector quantities
Velocity
Displacement
Weight
Force
Acceleration
Momentum
Is speed a vector or scalar?
Scalar
Is velocity a vector or scalar?
Vector
Is distance a vector or scalar?
Scalar
Is displacement a vector or scalar?
Vector
Is mass a vector or scalar?
Scalar
Is weight a vector or scalar?
Vector
Is energy a vector or scalar?
Scalar
Is momentum a vector or scalar?
Vector
Is temperature a vector or scalar?
Scalar
Is force a vector or scalar?
Vector
Is acceleration a vector or scalar?
Vector
Define: Distance
How far apart 2 objects are.
Define: Displacement
How far apart 2 objects are in a straight line.
Define: Speed
How quickly an object travels in a given time.
Define: Velocity
How quickly an objects travels in a particular direction.
Define: Instantaneous speed
Speed at a particular point in time.
Define: Acceleration
Change in velocity within a given time.
What is uniform acceleration?
Constant acceleration
Which 3 calculations link speed, distance and time?
Speed = Distance / Time
Distance = Speed x Time
Time = Distance / Speed
Calculate: Speed
Speed = Distance / Time
Calculate: Distance
Distance = Speed x Time
State the symbols for speed, distance and time.
Speed = s
Distance = x
Time = t
State the units for speed, distance and time.
Speed = m/s
Distance = metres
Time = seconds
Which 3 calculations can we use for acceleration?
Final - Initial / Time
(final velocity)2 – (initial velocity)2 = 2 × acceleration × distance
Resultant Force = Mass x Acceleration
State the units for acceleration, velocity, time and distance.
Acceleration = m/s²
Velocity = m/s
Time = seconds
Distance = metres
State the symbols for acceleration, velocity, time and distance
Acceleration = a
Velocity = v
Time = t
Distance = x
State the symbols for final and initial velocity
Final - v
Initial - u
How can you find the speed from a distance / time graph?
Change in vertical / change in horizontal.
On a distance / time graph, what does the gradient of the line show?
Speed/Velocity
On a distance / time graph, what does the flat line show?
Object has stopped/is stationary
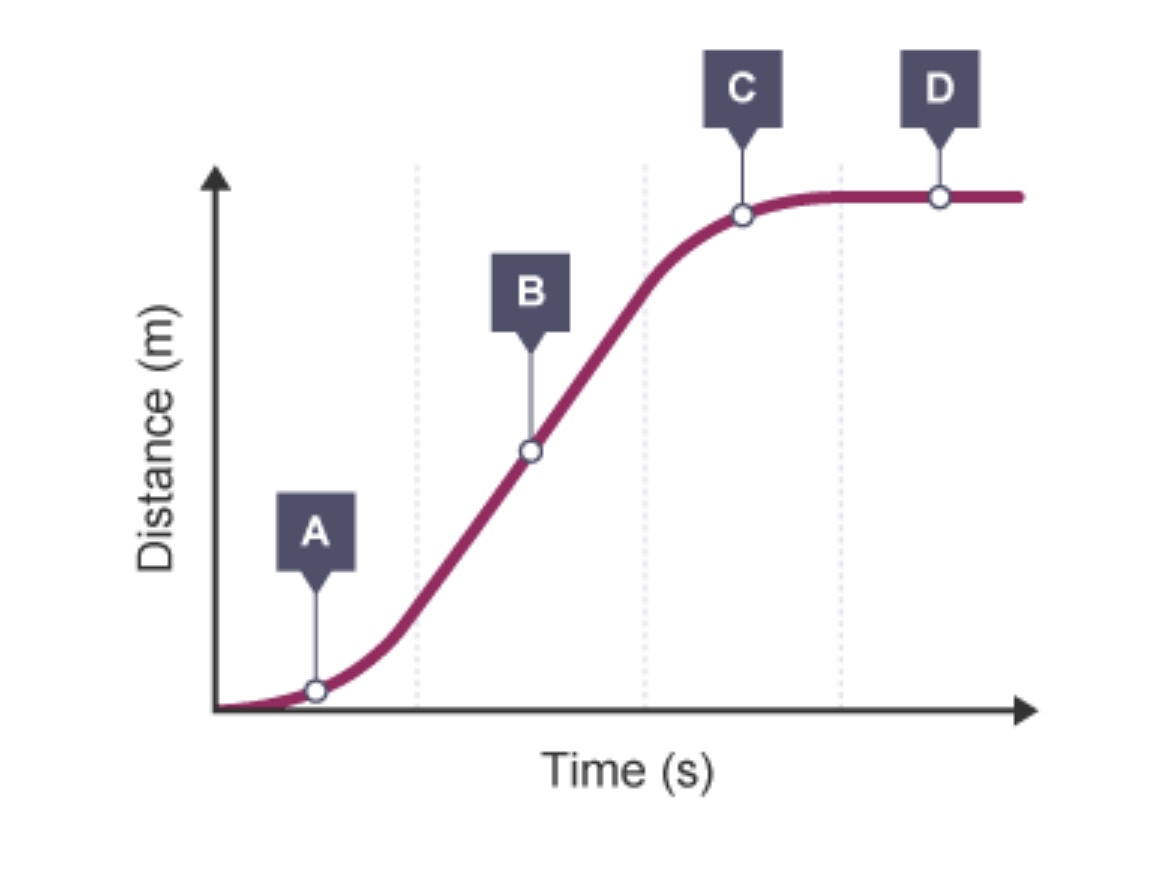
Describe what is happening at A, B, C and D
A - Increasing speed; it’s accelerating
B - Constant speed
C - Decreasing speed; decelerating
D - Stationary
On a velocity / time graph, what does the gradient of the line show?
Acceleration
On a velocity / time graph, how do you calculate acceleration?
Change in velocity / change in time
On a velocity / time graph, what does a steeper line mean?
Greater acceleration
On a velocity / time graph, how do you calculate distance?
Area under graph
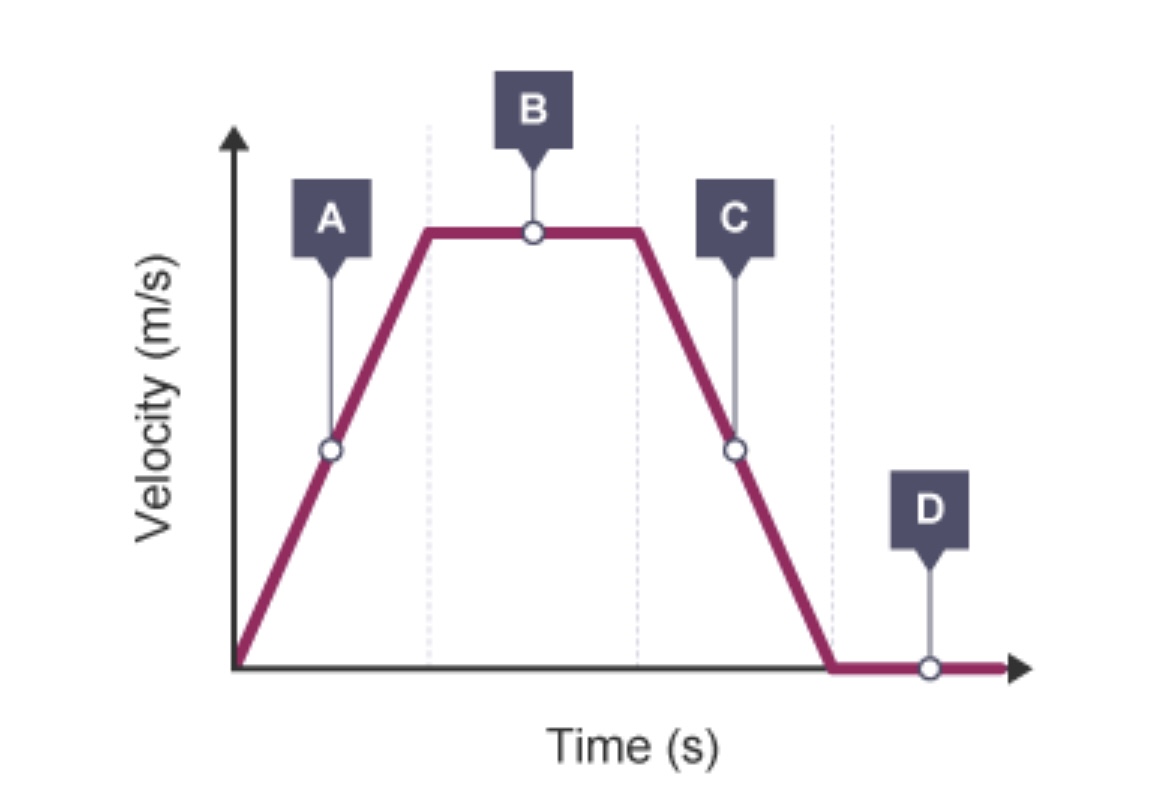
Describe what is happening at A, B, C and D
A - Constant acceleration + Increasing velocity
B - Constant velocity
C - Constant deceleration + Decreasing velocity
Define: Mass
The quantity of matter in an object.
Define: Weight
The force an object exerts due to gravity.
Is mass the same everywhere?
Yes; it never changes.
Is weight the same everywhere?
No; it changes depending on gravity.
Calculate: Mass
Weight / Gravitational field strength
Calculate: Weight
Mass x Gravitational field strength
Which 3 calculations link mass, weight and gravitational field strength?
Weight = mass x gravitational strength
Mass = Weight / Gravitational strength
Gravitational strength = Weight / Mass
State the units for weight, mass and gravitational field strength
Weight = N
Mass = Kg
Gravitational field strength = N/kg
State the symbol for weight, mass and gravitational field strength
Weight = w
Mass = m
Gravitational field strength = g
What is the typical walking speed?
1.5 m/s
What is the typical running speed?
3 m/s
What is the typical cycling speed?
5.5 - 6 m/s
What is the typical car speed?
13 - 30 m/s
What is the typical aeroplane speed?
250 m/s
What is the typical train speed?
50 - 55 m/s
What is a force?
A push, pull or twist.
How does a force being exerted change an object?
Changes an objects speed, direction or shape.
Complete: Forces always appear in ___
Pairs
Name the 2 force pairs
Action and reaction force.
What is the resultant force?
Single overall force used to represent ALL the forces acting on an object.
Which type of diagram can be used to represent the forces acting on an object?
Free body diagram
What does the length of an arrow in a free body diagram show?
Magnitude/Size of the force.
What does the direction of an arrow in a free body diagram show?
Direction of force.
If the backwards force is greater than the forwards force, what is happening to the object?
Objects is decelerating.
If the forwards force is greater than the backwards force, what is happening to the object?
Object is accelerating.
If the forcing acting on an object are equal/balanced, what is happening to the object?
Object is stationary or moving at a constant speed/velocity.
If the force is acting in the opposite direction of the force, what happens to the object?
Object will decelerate.
If the force is acting in the same direction of the force, what happens to the object?
Object will accelerate.
When forces occur, what is transferred?
Energy
What happens when all the forces on an object balance out?
Equilibrium
Define: Contact forces
Forces that occur when 2 objects are are in direct physical contact with eachother.
What is a force called when it occurs between objects physically touching?
Contact force
Define: Non contact forces
Forces that occur when objects are not physically touching.
What is a force called when it occurs between objects not physically touching?
Non contact forces
Give examples of contact forces
Reaction force
Tension
Friction
Air resistance
Upthrust
Give examples of non contact forces
Magnetism
Gravity
Electrostatic force
Which force is acts on objects at rest on a surface?
Reaction force
Which force is acts on objects being stretched?
Tension
Which force is acts on two objects sliding past each other?
Friction
Which force is acts on objects flying through the air?
Air resistance
Which force is acts on objects partially or completely submerged in water?
Upthrust
Which force causes objects to move?
Thrust
Which force is acts on any magnetic material in a magnetic field?
Magnetism
Which force is acts on any charged particle in an electric field?
Electrostatic force
Which force is acts on any mass in a gravitational field?
Gravity
Are forces balanced when the resultant force is equal to or more than 0N?
Equal to 0 Newtons.
Are forces unbalanced when the resultant force is equal to or more than 0N?
More than 0 Newtons.
When resultant force is equal to 0 Newtons, are forced balanced or unbalanced?
Balanced
When resultant force is more than 0 Newtons, are forced balanced or unbalanced?
Unbalanced
What is the resultant force if all forces are balanced?
0 Newtons.
What is Newton’s 1st law?
A resultant force is required to change the motion of an object. If there is no resultant force acting on an object and forces are balanced, motion will remain constant.
If an object is already at rest, the object will remain stationary. If the object is already moving, it will continue to move in the same direction at the same speed.
Which of Newton’s Laws states that a resultant force is required to change the motion of an object?
Newton’s 1st Law.
What happens to an object if all the forces are balanced?
If the object is already stationary, then it will remain stationary
If the object is already moving, it will continue to move in the same direct at the same speed
What is Newton’s 2nd law?
Non zero resultant forces acting on an object cause the object to accelerate. Acceleration depends on:
Size of the force
Mass of the object
Which of Newton’s Laws states that a non zero resultant force acting on an object cause the object to accelerate; acceleration depends on size of the force and mass of the object?
Newton’ 2nd Law.
What does the acceleration of an object depend on?
Size of force + Mass of object
What equation is linked to Newton’s 2nd law?
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Calculate: Resultant Force
Mass x Acceleration
Which 3 equation links resultant force, mass and acceleration?
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Mass = Force / Acceleration
Acceleration = Force / Mass
State the symbols for resultant force, acceleration and mass
Resultant force = f
Mass = m
Acceleration = a