Bone Tumors, Arthritis & Connective Tissue Diseases: Degenerative Disc Disease, Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is degenerative disc disease?
it is herniated discs that pinch the nerves that emerge through the intervertebral foramen
What are the common sites of degenerative disc disease?
L4-5
L5-S1
C5-6
C6-7
What are the signs and symptoms of degenerative disc disease?
radiculopathy and radiating pain down spine
numbness and tingling in spine
decreased strength in spine
limited range of motion in spine
What are the lab and diagnostic tests for degenerative disc disease?
x-rays
myelogram
MRI
CT
Epidural venogram or discogram
EMG
What is osteoporosis?
it is weak and brittle bones, increasing risk of fracture
What are the signs and symptoms of osteoporosis?
asymptomatic
several fractures within a short time frame
What are the labs and diagnostic tests for osteoporosis?
Hx & physical assessment
x-rays
bone mineral density tests (BMD)
What are some teachings for patients with osteoporosis?
tell pt. to take calcium carbonate with food
tell pt. to take calcium citrate on an empty stomach
tell pt. to take bisphosphonates with water, sit up for 30 minutes, take for at least 5 years, and wait at least 30 minutes before eating
tell female pt. to take 1000 mg/day calcium (19 to 50 years)
tell female pt. to take 1200 mg/day calcium (51 years and older)
tell male pt. to take 1000 mg/day calcium (19 to 70 years)
tell male pt. to take 1200 mg/day calcium (71 years and older)
tell pt. to take 800 units of vitamin D daily
What is osteoarthritis?
it is a degenerative joint disease caused by wear and tear of articular cartilage
What joints are affected by osteoarthritis?
hips
knees
metatarsophalangeal (MTP)
cervical vertebrae
lumbar vertebrae
distal interphalangeal (DIP)
proximal interphalangeal (PIP)
metacarpophalangeal (MCP)
What are the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis?
joint pain with movement or weight bearing
stiff joints
crepitus
pain relief with rest
enlargement of joints
herberden’s nodes in distal joints
bouchard’s nodes in hip joints
What are the labs and diagnostic tests for osteoarthritis?
bone scans
x-rays
CT
MRI
What are some surgical interventions for osteoarthritis?
hip replacement
knee replacement
What are some teachings for patients with osteoarthritis?
tell pt. they can take 200mg ibuprofen up to 4 times a day for pain
tell pt. they can take isopropyl to decrease GI side effects
tell pt. they can get intraarticular corticosteroid injections every 3 months
tell pt. they can do alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, or Tai Chi
tell pt. to take fish oil or ginger for inflammation
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
it is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease caused by antibodies from the bloodstream moving into the synovial lining of joints, causing joint swelling
What joints are affected by rheumatoid arthritis?
wrists
hands
knees
feet
What are some signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
morning stiffness in joints due to inflammation
movement helps with joint stiffness
fever
weight loss
limited range of motion due to inflammation and pain
What are the labs and diagnostic tests for rheumatoid arthritis?
antinuclear antibody (ANA)
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ERS)
Gamma globulins
x-rays
Synovial fluid analysis
Tissue biopsy
bone scans
What are some surgical interventions for rheumatoid arthritis?
Synovectomy
Total joint replacement (arthroplasty)
What are some teachings for patients with rheumatoid arthritis?
tell pt. that Methotrexate is used for early treatment
tell pt. that Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) & hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) is used for mild to moderate rheumatoid arthritis
tell pt. if they are taking Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) & hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), they need to have regular eye exams every 6-12 months
tell pt. Leflunomide (Arava) blocks immune cell overproduction
tell pt. they cannot have live vaccines of they are taking Biological Response Modifiers
What is gout?
it is a buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints
What can cause gout?
metabolic syndrome
increased intake of high purine foods
prolonged fasting
excessive alcohol
What are some signs and symptoms of gout?
acute onset of excruciating in joint
redness around joint
nephrolithiasis (kidney stones)
What are the labs and diagnostic tests for gout?
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
C-reactive protein (CRP)
serum uric acid
urinary uric acid
Arthrocentesis
What are some nursing actions and interventions for gout?
give oral colchicine when ordered
administer NSAIDs when ordered
administer corticosteroids when ordered
if pt. is taking Allopurinol, monitor liver levels
What are some teachings for patients with gout?
tell pt. side effect of oral colchicine is diarrhea
tell pt. oral colchicine helps with inflammation
tell pt. NSAIDs help with joint pain
tell pt. to not take colchicine or steroids when on NSAIDs
tell pt. that aspirin does not work for pain due to gout
tell pt. to limit alcohol and food high in purine (beans, beer, red meats, fried foods, etc.)
What is systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
it is a multisystemic inflammatory autoimmune disease that leads to necrosis & inflammation in blood vessel, lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract and pleura
What are some signs and symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
butterfly rash across nose and cheeks
heart dysrhythmias
dry, scaly skin
joint pain
light sensitivity
What are the labs and diagnostic tests for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
antinuclear antibody (ANA)
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ERS)
C-reactive protein (CRP)
What are some nursing actions and interventions for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
administer NSAIDs for joint pain when ordered
administer antimalarial drugs for fatigue and skin & joint problems
administer corticosteroids for inflammation when ordered
taper off and give at lowest effective dose of corticosteroids
administer immunosuppressive drugs when ordered
assess ADLs
monitor neurological function
What are some teachings for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
tell pt. there is not cure for SLE
tell pt. to avoid crowded areas if taking immunosuppressive drugs
tell pt. they can apply topical immunomodulators for butterfly rash on face and discoid lesions
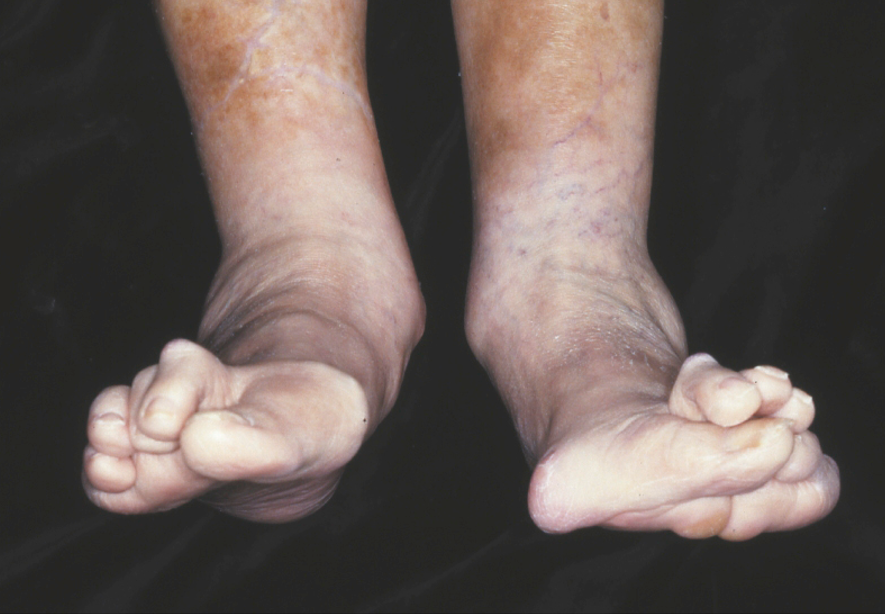
What picture depicts osteoarthritis?
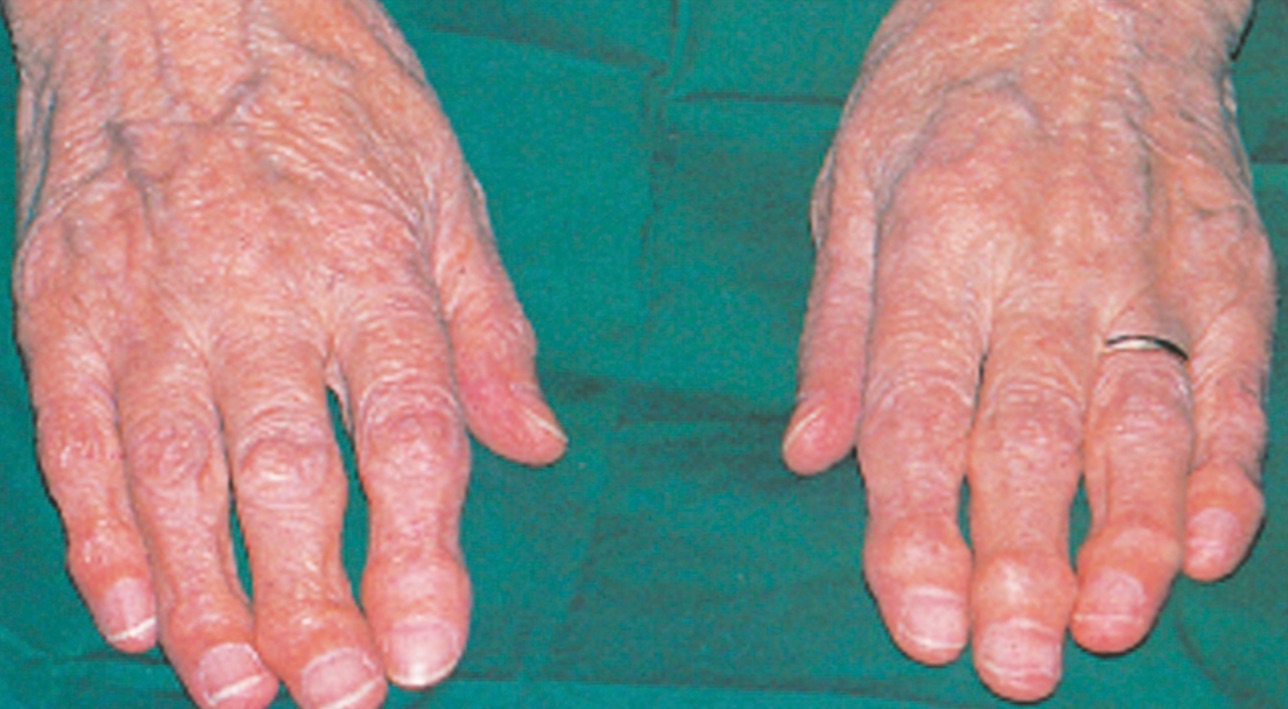
What picture depicts rheumatoid arthritis?
What type of medications does the provider need to order for patients with rheumatoid arthritis?
disease modifying antirheumatic drugs