Lecture 1.1 and 1.2
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Evolution
inherited changes in the properties of groups of organisms over time
descent with modification
Darwin’s phrase for evolution: species share common ancestry and change across generations.
Gradualism
Evolutionary change occurs in small steps over long time.
Differences between even radically different organisms had evolved by small steps (Darwin)
population change
Evolution occurs at the population level, not the individual.
Evolution occurs by changes in frequencies of different variant within a population (Darwin)
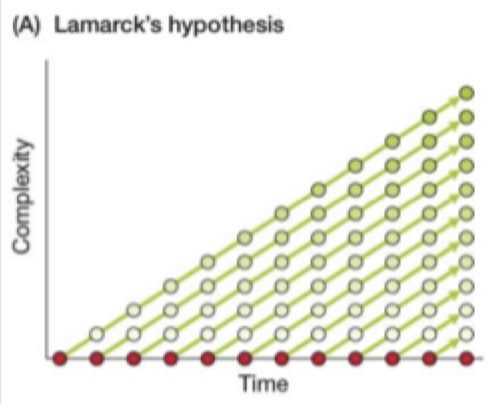
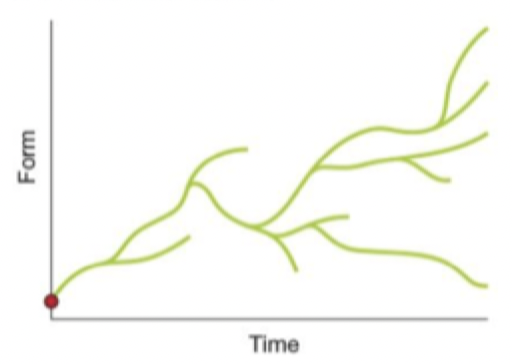
Lamarck
Life has many origins (spontaneous generation); each lineage becomes more complex over time, result resembles chain of being. Extinction does not occur
Who????
Lamarck
Whose hypothesis is this?
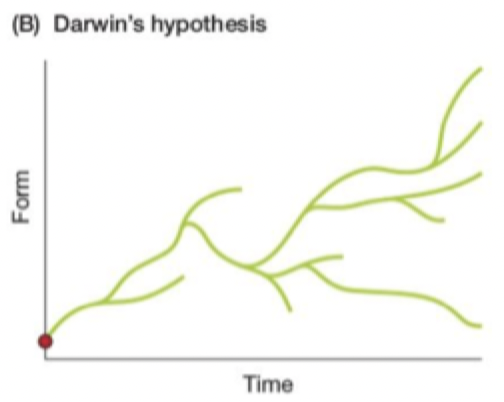
Darwin
Life represented as a tree with one origin; different lineages arise by speciating (splitting); lineages diverge, but do not necessarily become more complex. lineages can go extinct
Who????
Darwin
Whose hypothesis is this?
Variation
Differences among individuals in a population.
inheritance
Passing of traits from parents to offspring (genetic).
adaptation
A trait that increases an organism’s fitness (survival and reproduction)
natural selection
Process where individuals with advantageous traits leave more offspring.
genetic drift
Random changes in allele frequencies, often in small populations.
gene flow
Movement of alleles between populations.
mutation
Random change in DNA sequence; source of new variation.
common descent
All species trace back to shared ancestors.
scala naturae
“Great Chain of Being,” pre-Darwinian view of life arranged in a hierarchy.
lamarckism
Hypothesis that acquired traits (e.g., long giraffe neck from stretching) are inherited.
orthogenesis
Theory that evolution follows a predetermined straight-line path.
mutationism
Early idea that new species arise directly from mutations, without selection.
modern synthesis
Integration of Darwin’s natural selection with Mendelian genetics (1930s–40s).
genetic
“inherited changes” means that the changes are —
voyage of the beagle
a pivotal scientific expedition aboard HMS Beagle that profoundly shaped Charles Darwin’s ideas about evolution.
Charted coastlines (especially South America) and collect natural history observations
inductive
Darwin collected a huge body of empirical data (plants, animals, fossils, geological notes) during the Voyage of the Beagle and later studies.
From these particular observations, he built a general theory of evolution by natural selection.
This is using — reasoning
inductive reasoning
Patterns we see in nature leads us to general principles
slowly
Darwin believed that change happened (fast/slowly)
Alfred Russel Wallace
independently came up with the idea of evolution by natural selection and catalyzed darwin to publish
unchanging
The great chain of being thought of species as —
imperfection
The great chain of being described variation as —
essentialism
Every entity has an “essence” (set of unchanging characteristics) that defines what it is.
means that each species has a fixed, perfect “type”
industrial melanism
the evolutionary process where darker-colored individuals in a species become more common than lighter ones because of industrial pollution.
blending inheritance
an early (but incorrect) idea about heredity
The idea that offspring are a “blend” or average of their parents’ traits.
Example: A tall parent × a short parent → medium-height child.
neolamarckism
modified version of lamarc’s theory of evolution
use and disuse, but also adds heredity ideas
orthogenesis
Organisms evolve in a fixed direction, often toward increasing complexity. (incorrect)
raw material
Mutation is the — for natural selection
microevolution
Small-scale evolutionary changes within a population or species over a short period of time.
microevolution
(micro/macro evolution) focuses on changes in allele frequencies due to factors like natural selection, mutation, gene flow, and genetic drift
macroevolution
Large-scale evolutionary changes that occur above the species level, often leading to the formation of new species, genera, or higher taxa.
microevolution
— is observed in real time
macroevolution
— is observed in fossil record or long-term studies
No
Does natural selection always act for the good of the species?
differential reproductive success
Natural selection operates solely by —
Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA)
the most recent population of organisms from which all life on Earth today descends. It’s not the very first life form, but rather the common ancestor of bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes.
no
Are viruses living?
grow, reproduce, evolve
Viruses —, —, and —
metabolic processes
Viruses dont carry out —
systematics
the study of patterns of diversity of organisms and the relationships among them
classification
allocation of things to groups, according to shared characteristics or perceived or deduced affinities
taxonomy
theory and practice of classification, particularly of organisms
taxonomy, nomenclature, classification
systematics includes —, — and —
nomenclature
a system of names and the rules for their formation and use
phylogeny
the history of descent of a group of taxa from their common ancestors
monera, protista, fungi, plantae, animalia
the 5 kingdom system included which 5 kingdoms?
bacteria, archaea, eukarya
the 3 domain system includes
root
the common ancestor of all taxa in a tree
internal node
branchpoint in a tree
terminal node
endpoint in a tree
clade
a group of 2 or more taxa that includes both their common ancestor and all their descendants
lineage
A temporal series connected by ancestor-descendant relationships
2n - 1
for a phlogeny with n terminal nodes:
taxa =
n-1
for a phlogeny with n terminal nodes:
clades =
n
for a phlogeny with n terminal nodes:
lineages =
monophyletic
Clades are — groups
monophyletic
A — group contains a common ancestor and ALL of its descendants
paraphyletic
a group that contains a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants
polyphyletic
a group that consists of members of more than one lineage, but does not include the most recent common ancestor of those lineages and all of its descendants
monophyletic
this is a — group
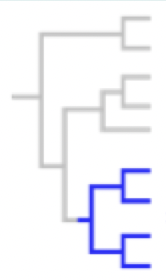
paraphyletic
this is a — group
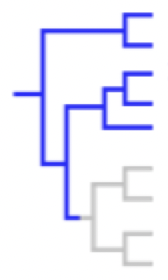
polyphyletic
this is a — group