Immunology - ANA patterns/ENA antibodies
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Anti-SSA/Ro
positive in 10-50% SLE patients; 70% Sjogrens
Must use Hep2 cells (not present on mouse stomach/kidney)
Anti-SSB/La
positive in 10-20% SLE patients (must be pos for SSA); ~ 1/2 Sjogrens
Must use Hep2 cells!!!
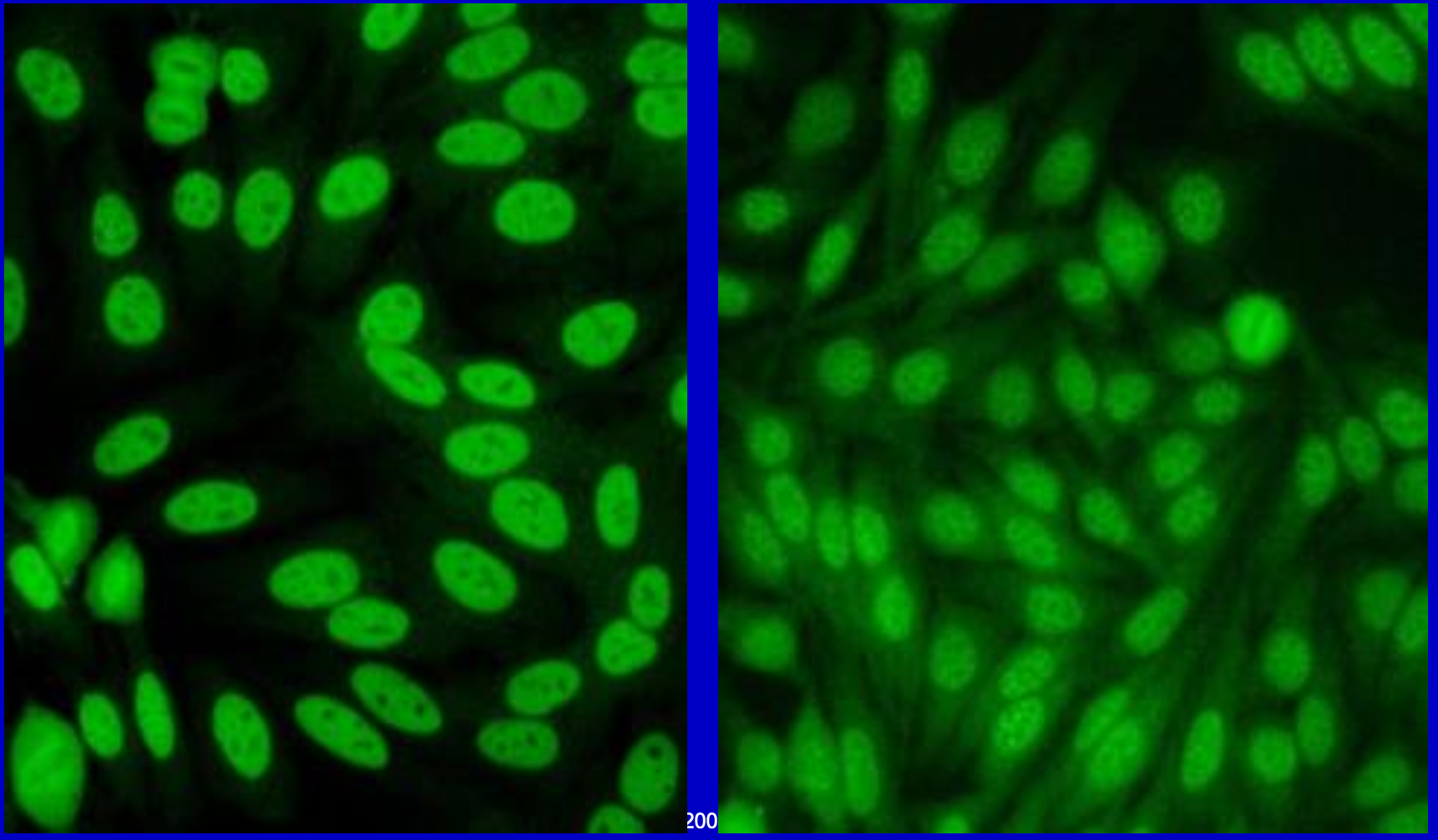
Finely Speckled
Anti-SSA/SSB
Anti-Sm (smith)
positive in 1/3 SLE; presence confirms SLE, but a negative cannot rule out SLE
Coarse speckled
Anti-nRNP
high titer —> indicative of mixed connective tissue disease, Sjogrens, systemic sclerosis.
low titer —> SLE
Coarsely speckled
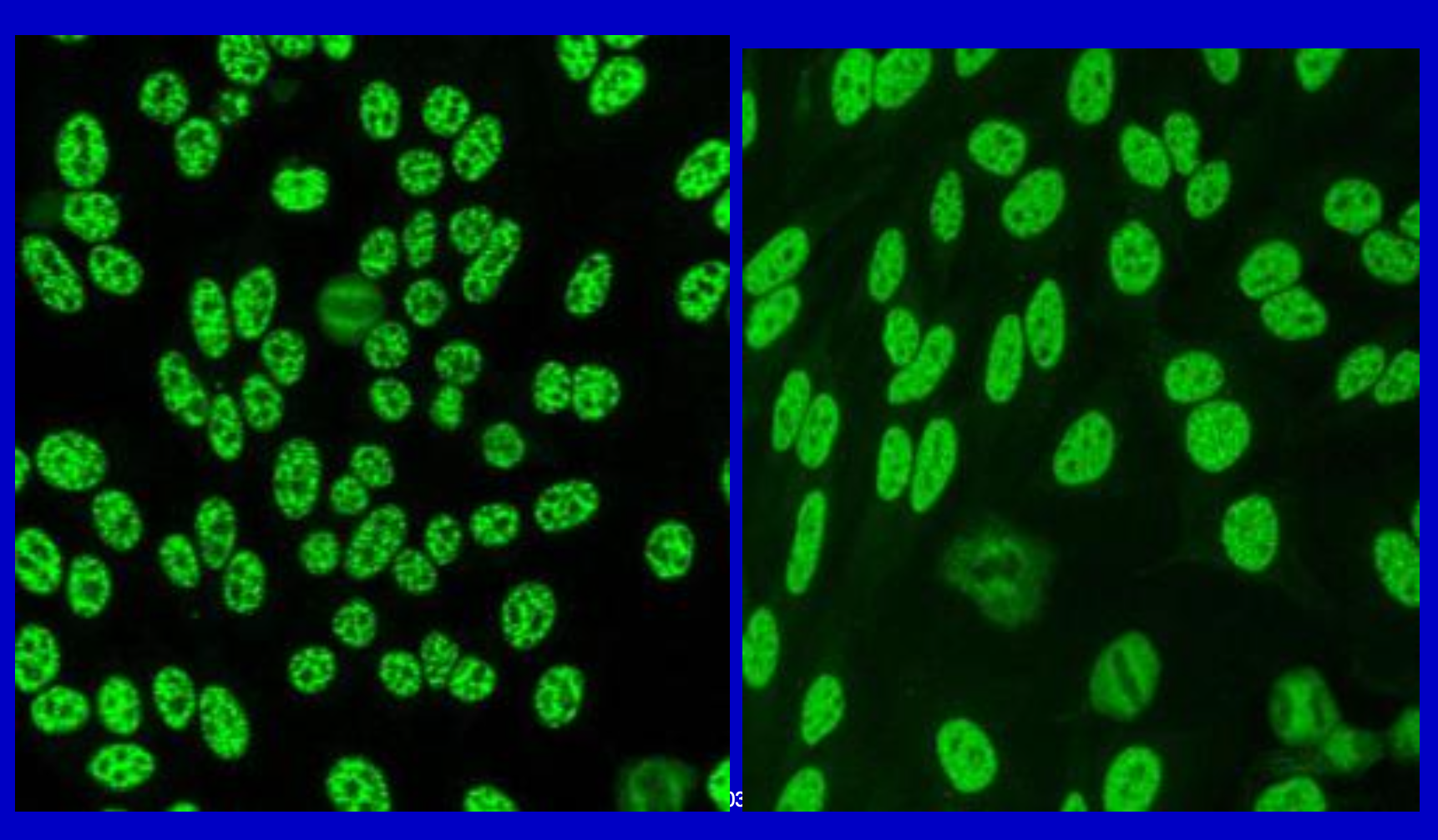
Coarsely Speckled
Anti-Sm, Anti-nRNP
Anti-Scl-70
Diagnostic of Scleroderma (SSc or systemic sclerosis) only seen in 1/5 patients though.
antibody to DNA topoisomerase I nuclear protein
Atypical specks/Nucleolar Pattern
Anti-Jo-1
Positive in 1/3 of patients with Polymyositis
antibody to histidyl-tRNA synthtase
atypical specks/Nucleolar pattern
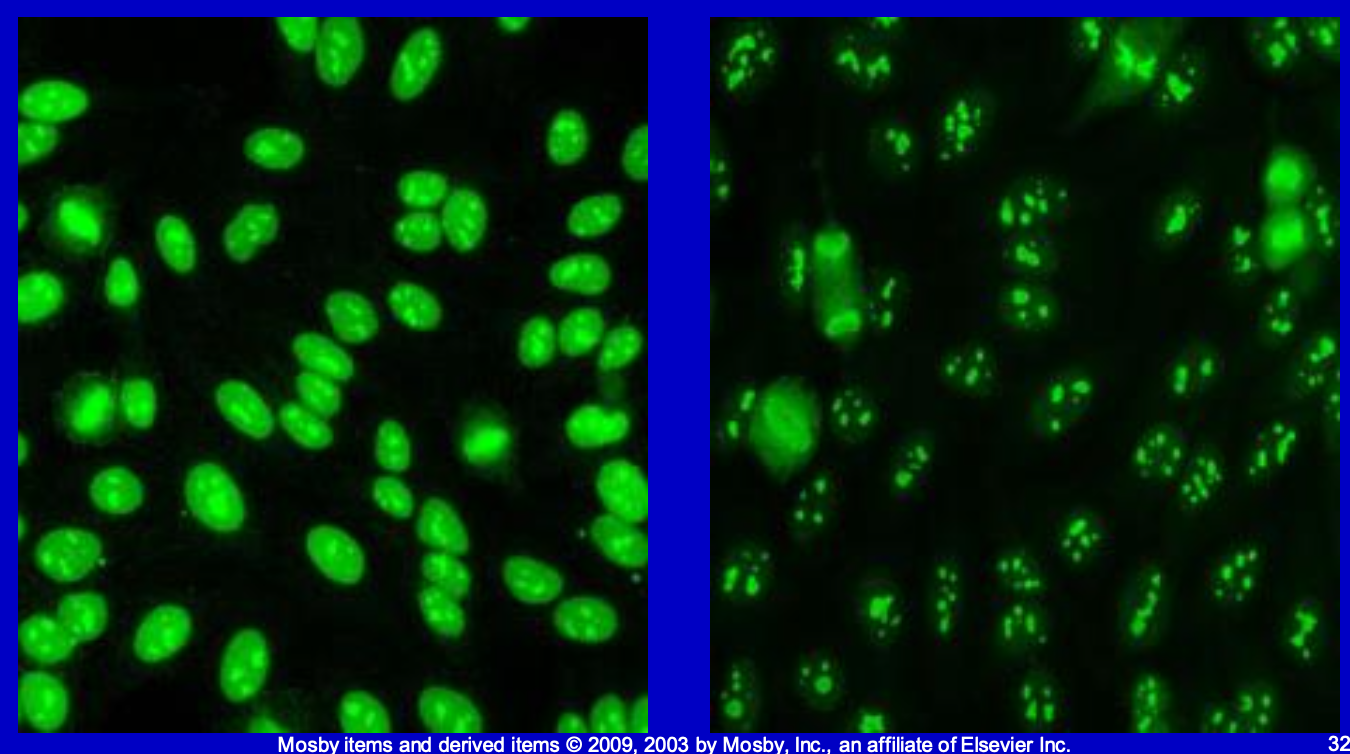
Nucleolar pattern; Anti-Scl-70, Anti-Jo-1
Anti-dsDNA
Used as criteria for diagnosis of SLE. High titers = high degree of specificity for SLE, BUT only ~ ¾ patients are positive.
Homogenous (Diffuse) pattern
Describe an immunofluorescent test for anti-dsDNA.
One type of assay for anti ds-DNA is an immunofluorescent test using Crithidia luciliae, a hemoflagellate, as the substrate. This organism has ds-DNA in the kinetoplast. This test has a high degree of specificity, because high titers help confirm the diagnosis of SLE, but about one-fourth of patients with SLE do not have this antibody.
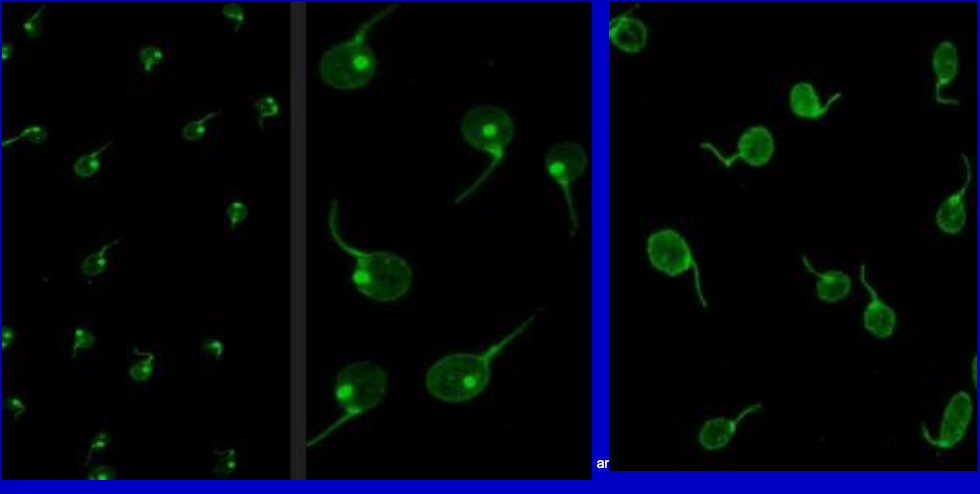
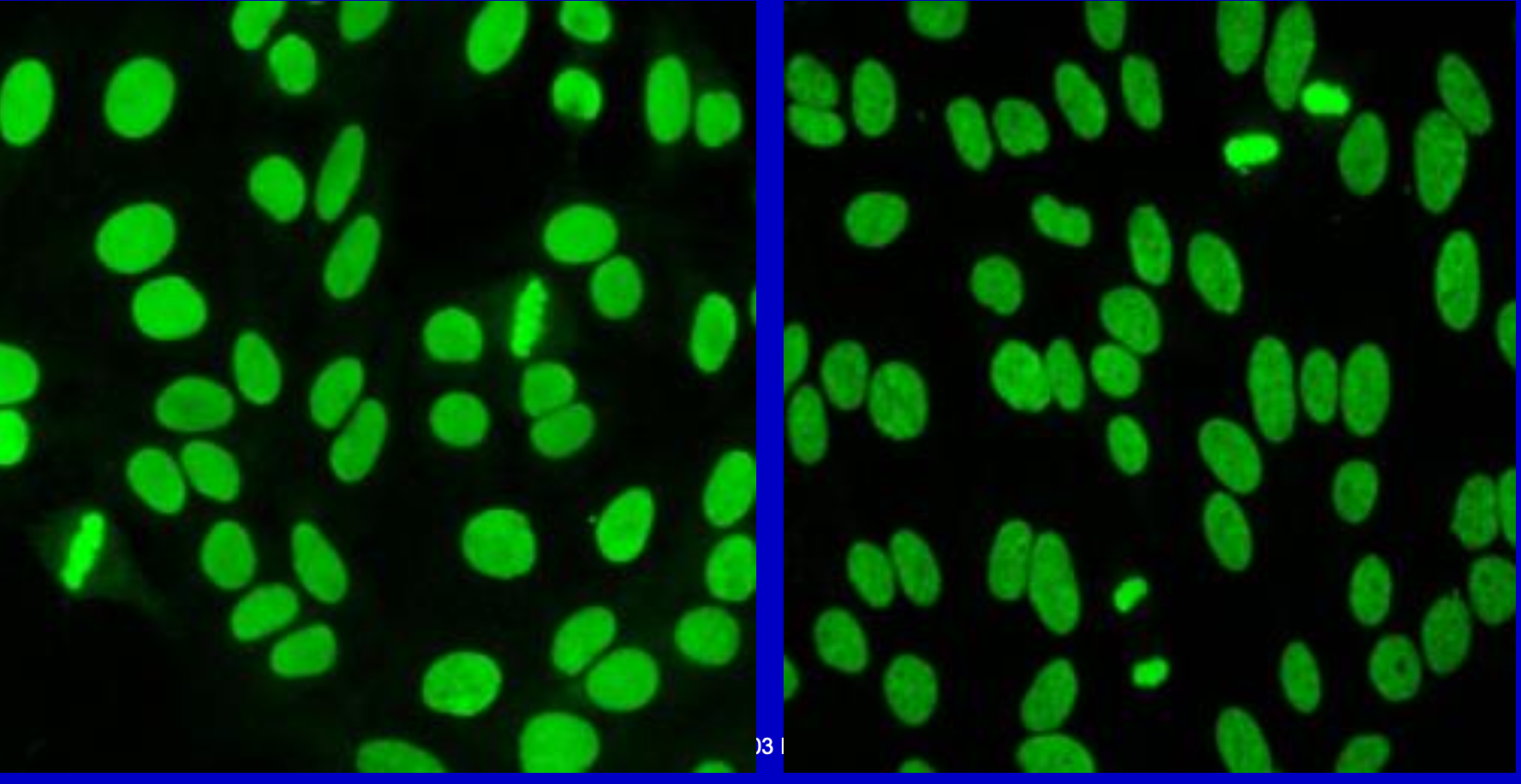
Homogenous Pattern; Anti-dsDNA
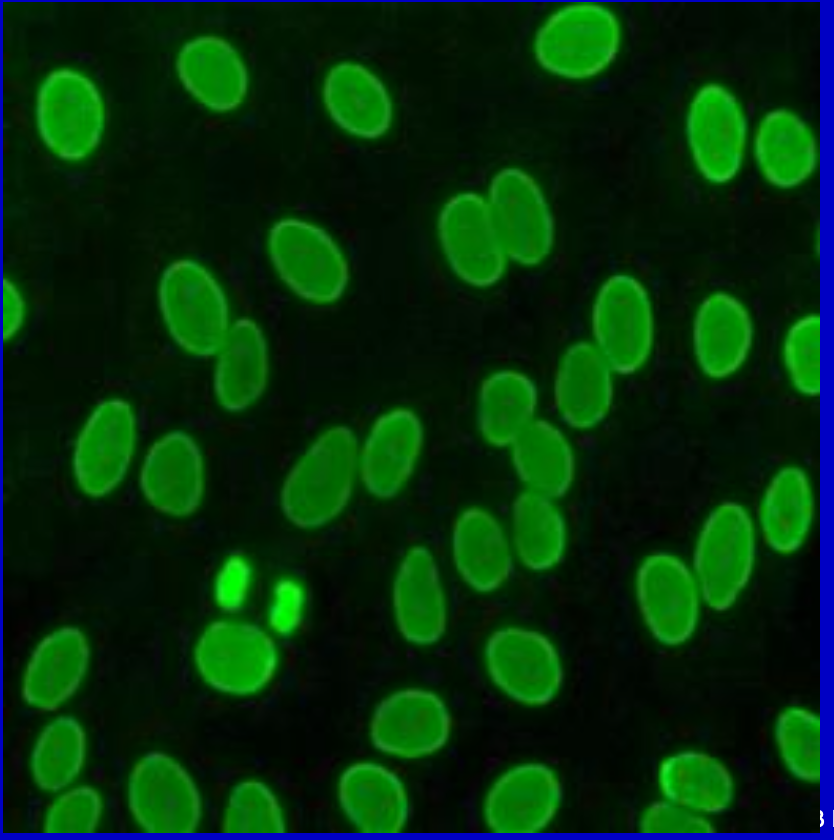
Homogenous Rim Pattern
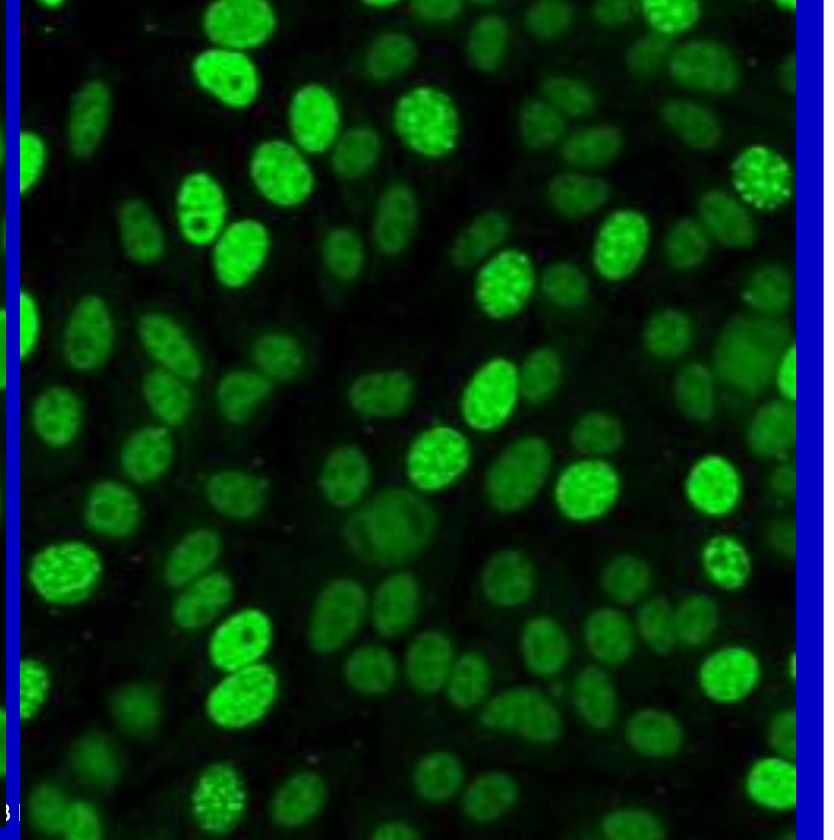
PCNA pattern
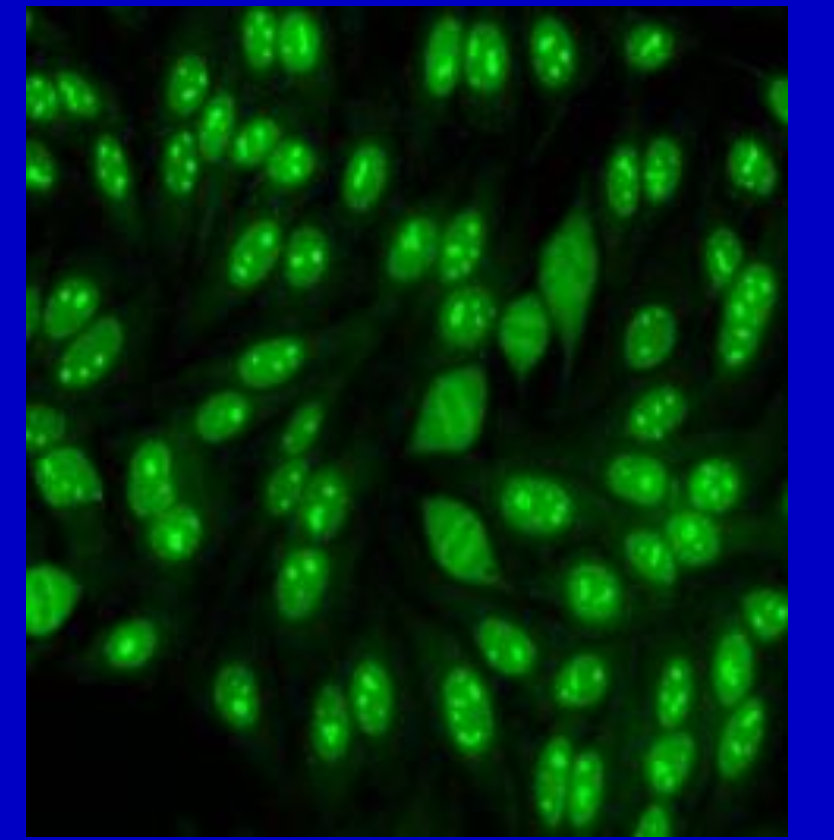
Speckled and Nucleolar mixed pattern
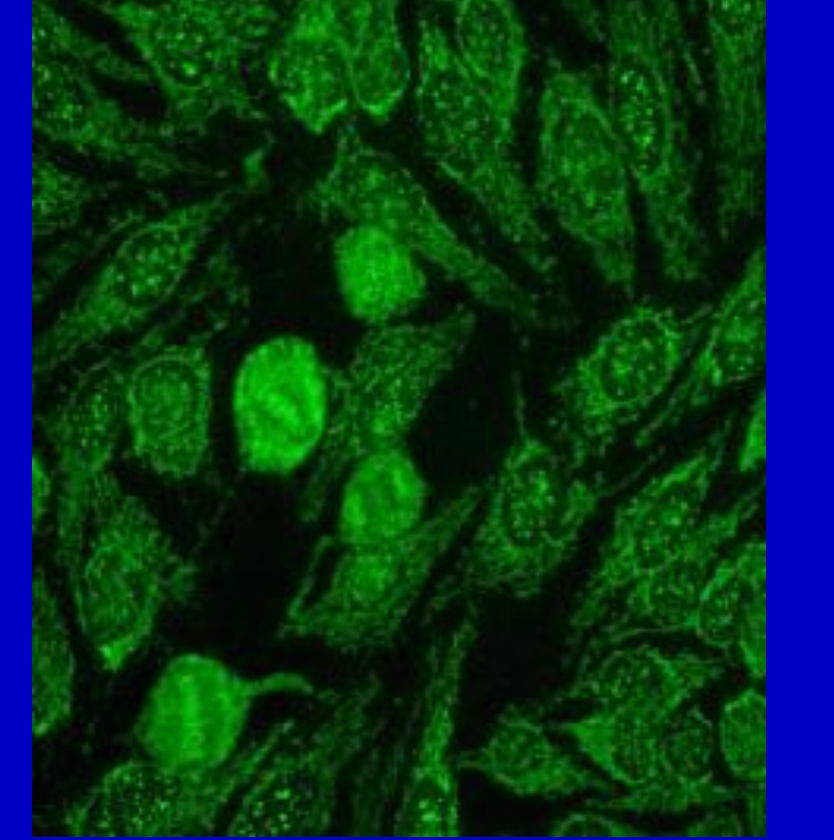
Centromere and Mitochondrial mixed pattern
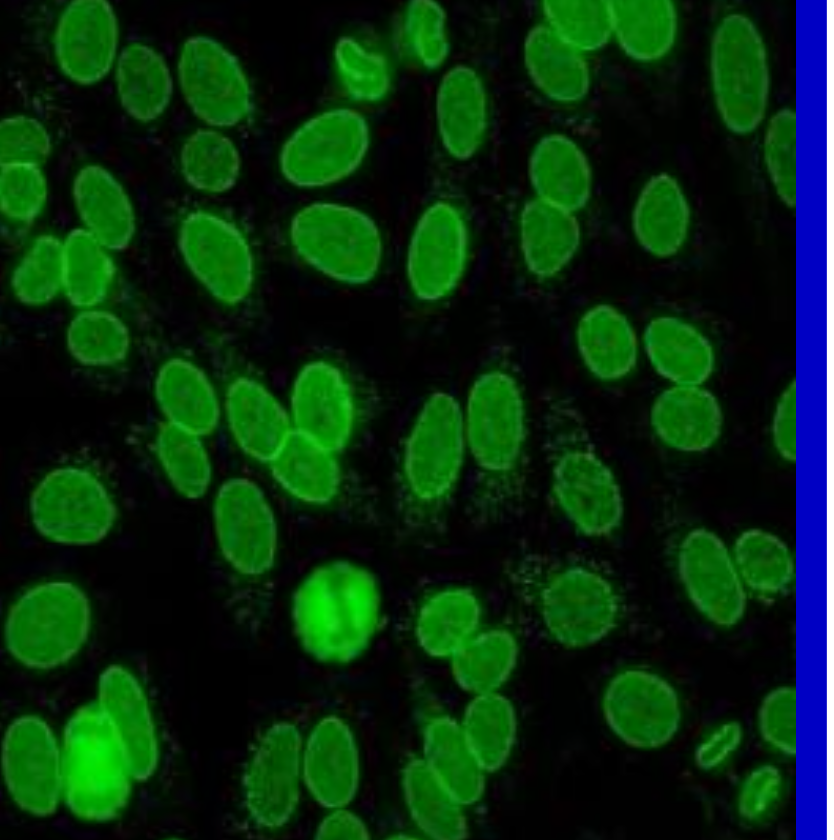
Anti-nuclear membrane pattern
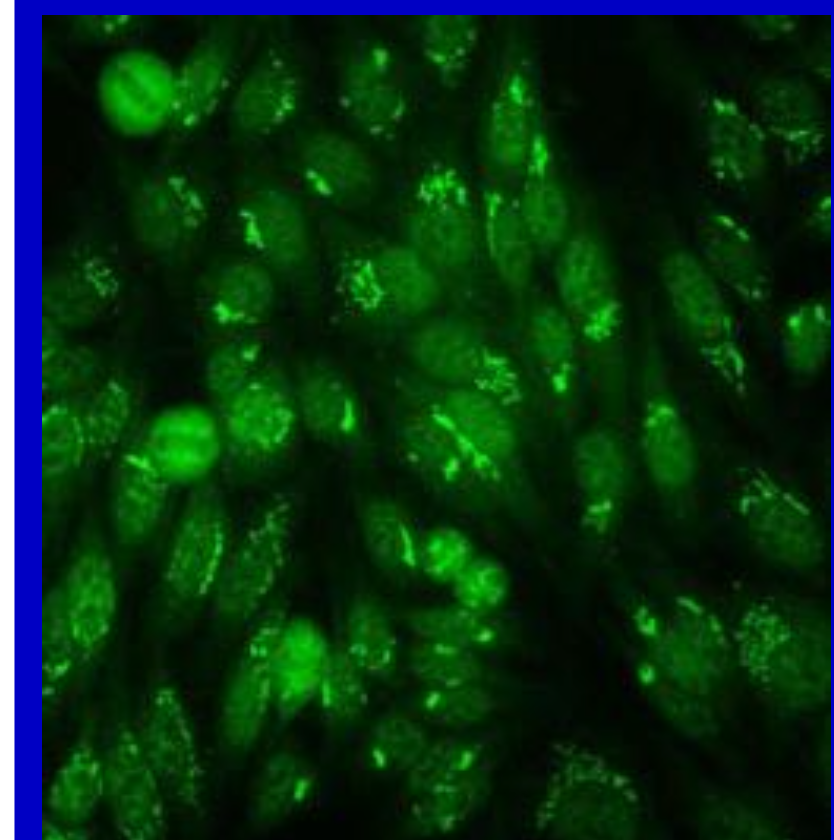
Anti-golgi pattern
Anti-cardiolipin
Positive in patients with SLE w/ thrombosis. Elevation may be predictive of risk of thrombosis or recurrent spontaneous abortions of early pregnancy. (with or without SLE) Also called lupus anticoagulants and phospholipid antibodies.
Anti-centromere
Antibodies to chromosomal centromeres. CREST syndrome!! 1/3 Raynaud’s disease and about 10% of patients with systemic sclerosis.
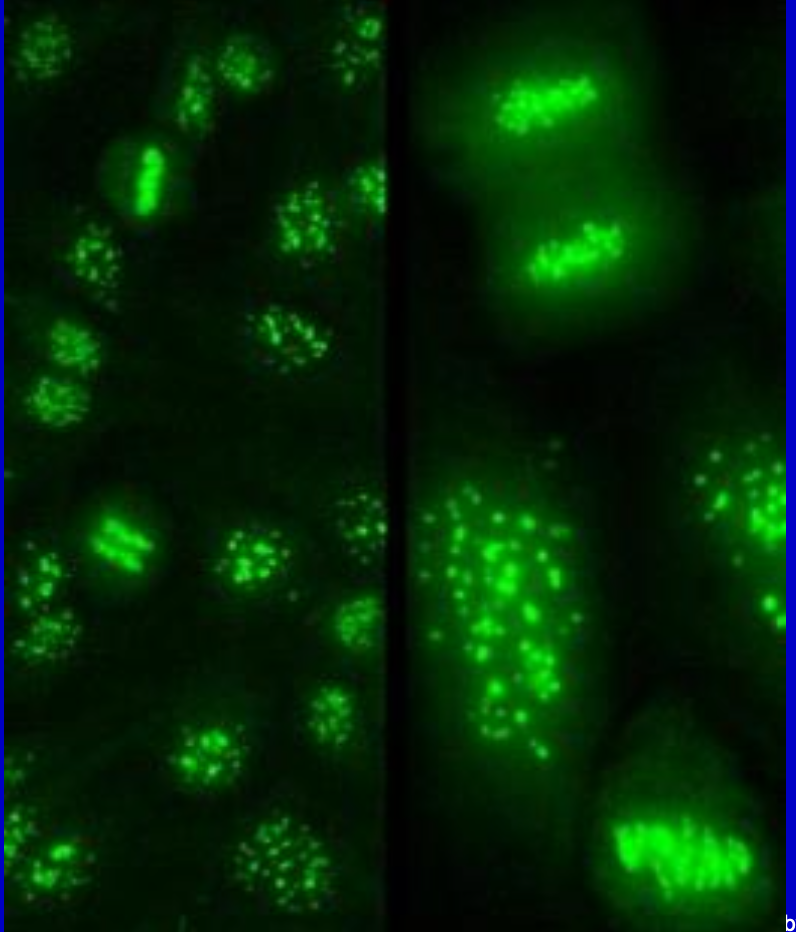
Anti-Centromere
Goodpasture’s Syndrome
the presence of autoantibody to glomerular, renal tubular, and alveolar basement membranes, resulting in injury to the glomerulus that can rapidly progress to renal failure.
Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody
High titers are suggestive of Goodpasture’s disease or anti-GBM nephritis. Negative results do not rule out Goodpasture’s disease.
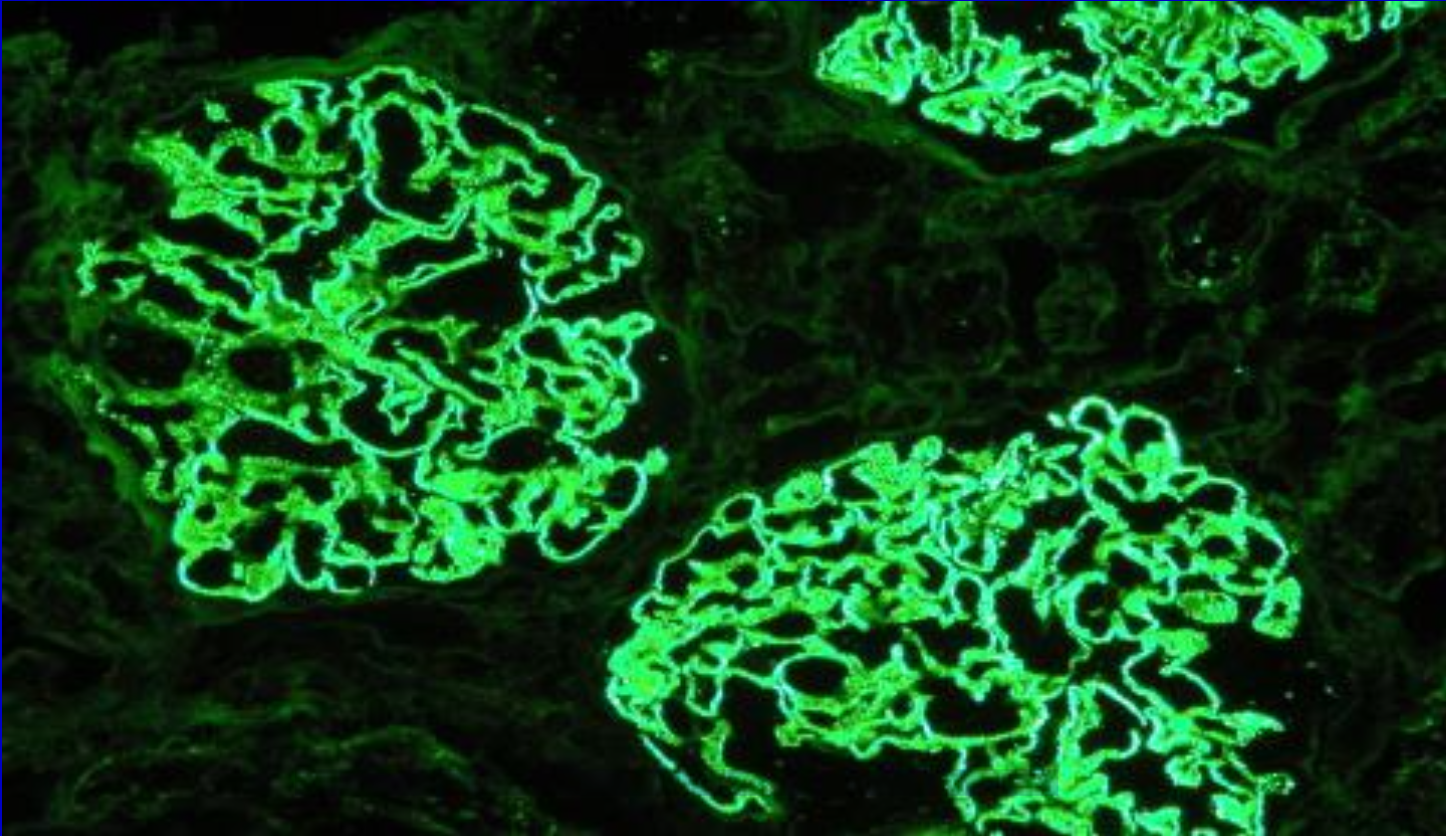
Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody
Anti-mitocondrial
A high titer strongly suggests primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC);
the absence is strong evidenceagainst PBC. Other forms of liver disease often show low mitochondrial antibody titers.
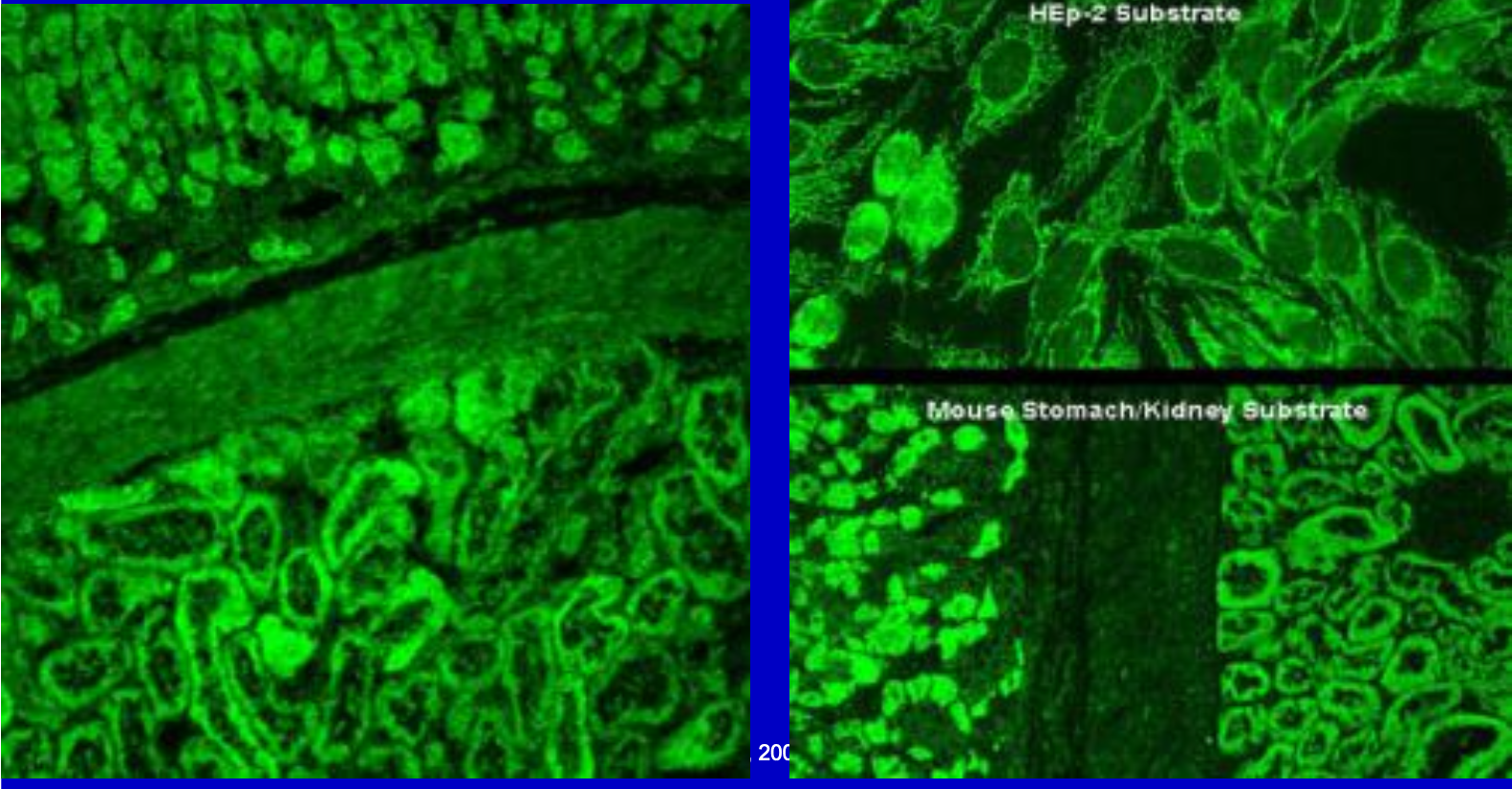
Anti-mitocondrial
Anti-Neutrophil
an autoantibody producing a characteristic granular cytoplasmic staining pattern (c-ANCA) to cytoplasmic constituents of neutrophilic granulocytes. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody has been described as a sensitive and specific marker for active Wegener’s granulomatosis, a systemic vasculitis. Antibody producing a perinuclear staining of neutrophils (p-ANCA) occurs in a wide range of diseases.
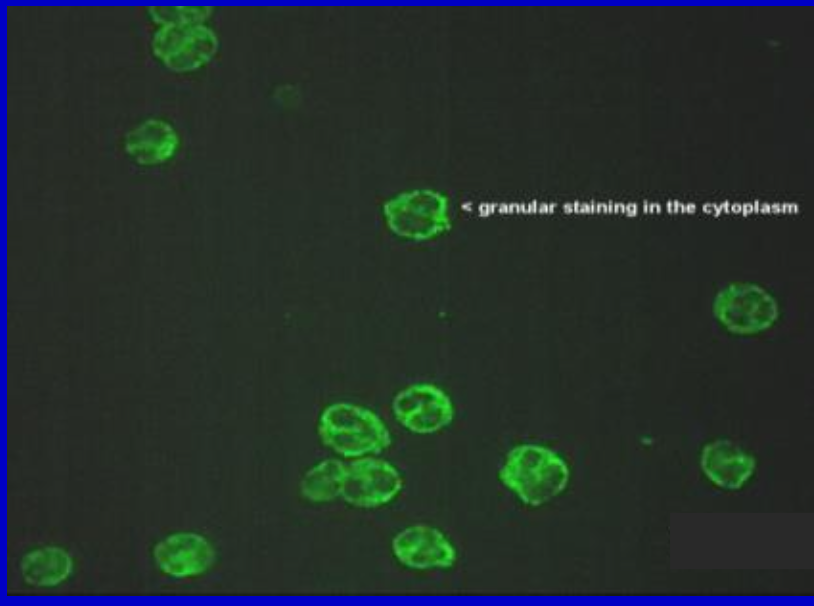
C-ANCA
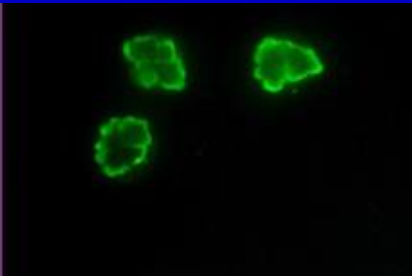
P-ANCA
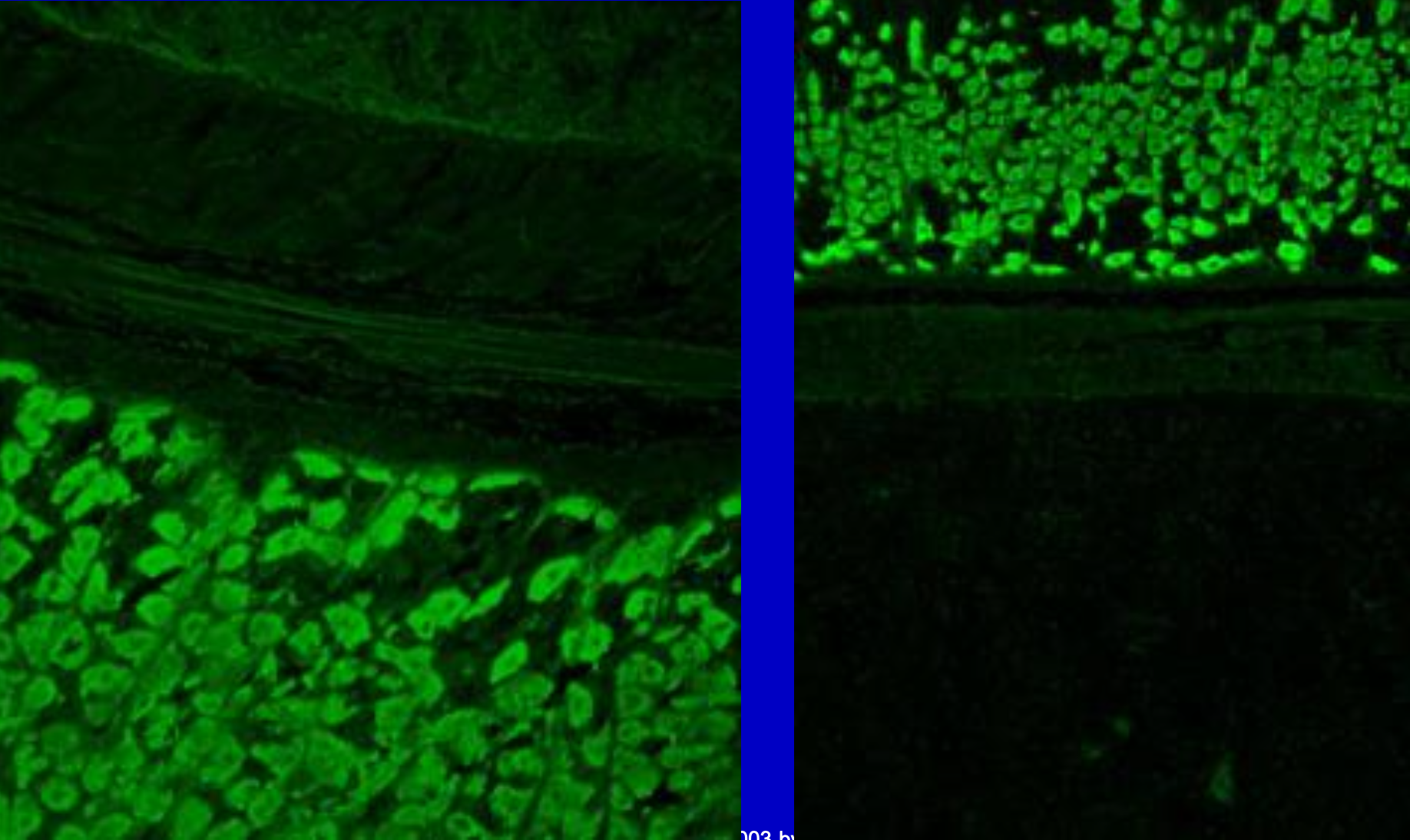
Anti-Parietal Cell
Pernicious Anemia patients
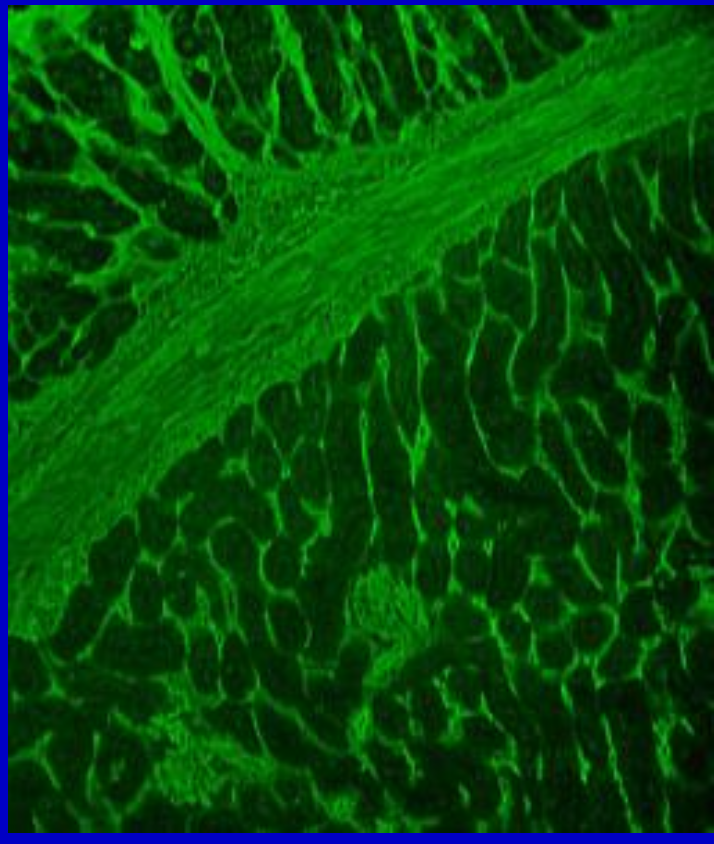
Anti-reticulin
childhood gluten sensitive enteropathy
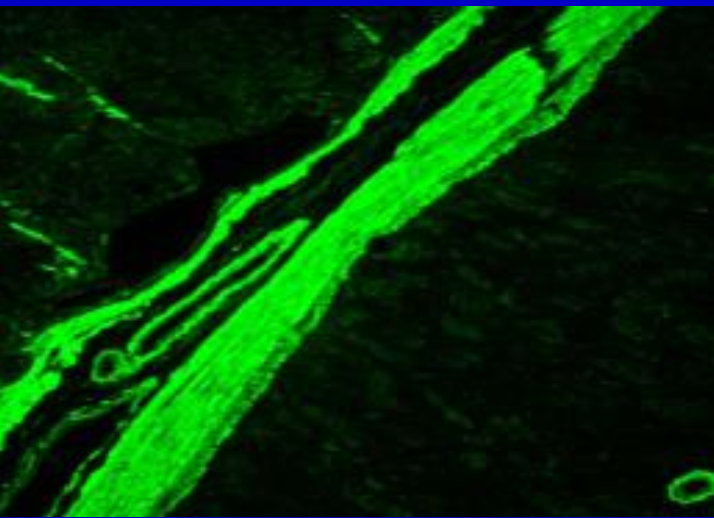
Anti-smooth muscle
hepatitis, infectious mono