Lecture 18: Nuclear Physics
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Outline the structure and properties of the nucleus
Nucleus: densely packed centre of atom composed of (protons and neutrons)
neutrons and protons are collectively called nucleons
number of protons are called atomic number
total number of nucleons (neutrons + protons) is called the atomic mass number

What is nuclear mass?
Measured using mass spectrometer and expressed with reference to the mass of carbon-12 atom, which is assigned a mass of exactly 12u, where u is unified atomic mass unit
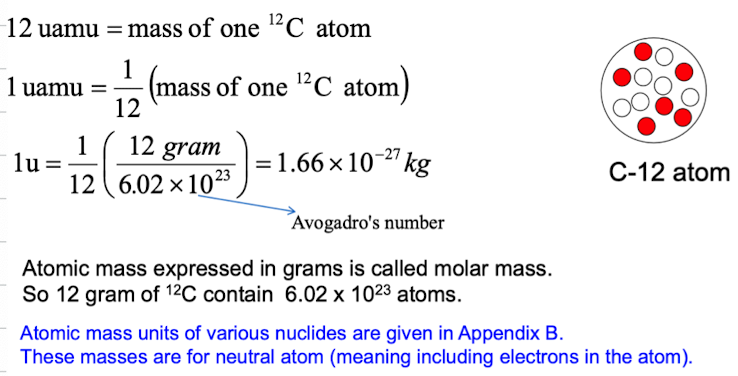
What is the energy equivalence of mass?
Masses can also be expressed in terms of their energy equivalent
E = mc²
What is binding energy?
the total mass of a nucleus is always less than the mass of protons and neutrons in it
this mass difference is a measure of the BE that holds the nucleus together
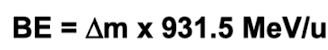
What holds the nucleons together?
Two opposing forces act between nucleons: Nuclear and Coulomb
For a nucleus to be stable, attractive force between nucleons must overcome the repulsive force between protons
What is nuclear force?
A force that binds nucleons together
attractive (between p-p, p-n, n-n)
short range (only attracts nearest neighbours appx = 10^-15
What is coulomb force?
A force that breaks protons apart
repulsive (p-p)
long range (acts across the nucleus)
outline radioactivity
late 19th century minerals were found that would darken a photographic plate even in the absence of light
these minerals emit radiation
this phenomenon is called radioactivity
what 2 highly radioactive elements did marie and pierre curie isolate
polonium and radium
Describe radiation
radioactivity is the result of the disintegration or decay of an unstable nucleus
certain isotopes aren’t stable and decay with emission of radiation
they found rays could be classified into 3 distinct types according to their penetrating power (alpha, beta and gamma)
alpha rays are positively charged
beta rays are negatively charged
gamma rays are neutral
What is radioactivity?
Radioactivity: the spontaneous emission of radiation from unstable nuclei
alpha, beta and gamma emission
alpha = nuclei of helium atoms
beta = electrons
gamma = high energy photons
outline how a smoke detector works
it contains about 0.2mg of the radioactive americium isotope Am-241 in the form of AmO2 (1.0 µCi)
alpha particles from Am-241 continually ionizes the air molecules in the air space between the two oppositely charged plates
the positive and negative ions are attracted by the charged plates which results in a current flow through the circuit
when smoke enters between the plates, the ions become attached to the smoke particles, thus resulting in a drop of current
the current drop is detected by the electronic circuitry and sets off the alarm
outline alpha decay
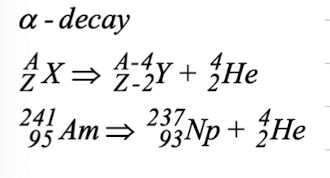
outline beta decay
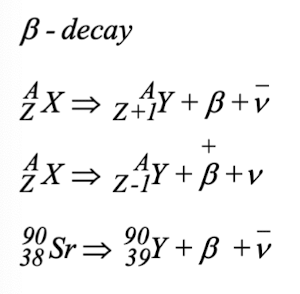
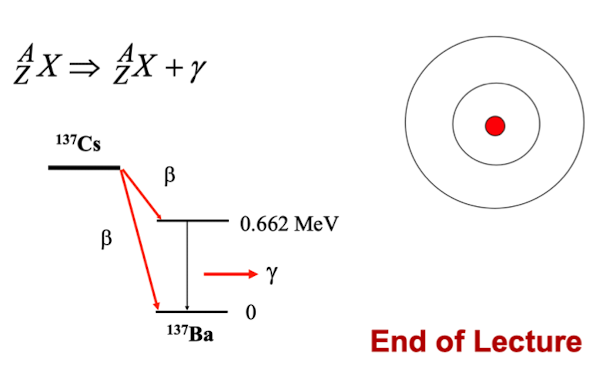
outline gamma decay
photon is emitted from an excited nucleus