Biology : SACE : Stage 2 : DNA and Proteins
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
DNA profiling
A procedure that analyzes DNA fragments to determine whether they come from a specific individual.
DNA analysis
A scientific technique capable of;
- Identifying people through their distinctive gene patterns
- Determining genetic and evolutionary relationships between Organisms
- Identification of gene mutations, which lead to the development of genetic diseases
DNA profile
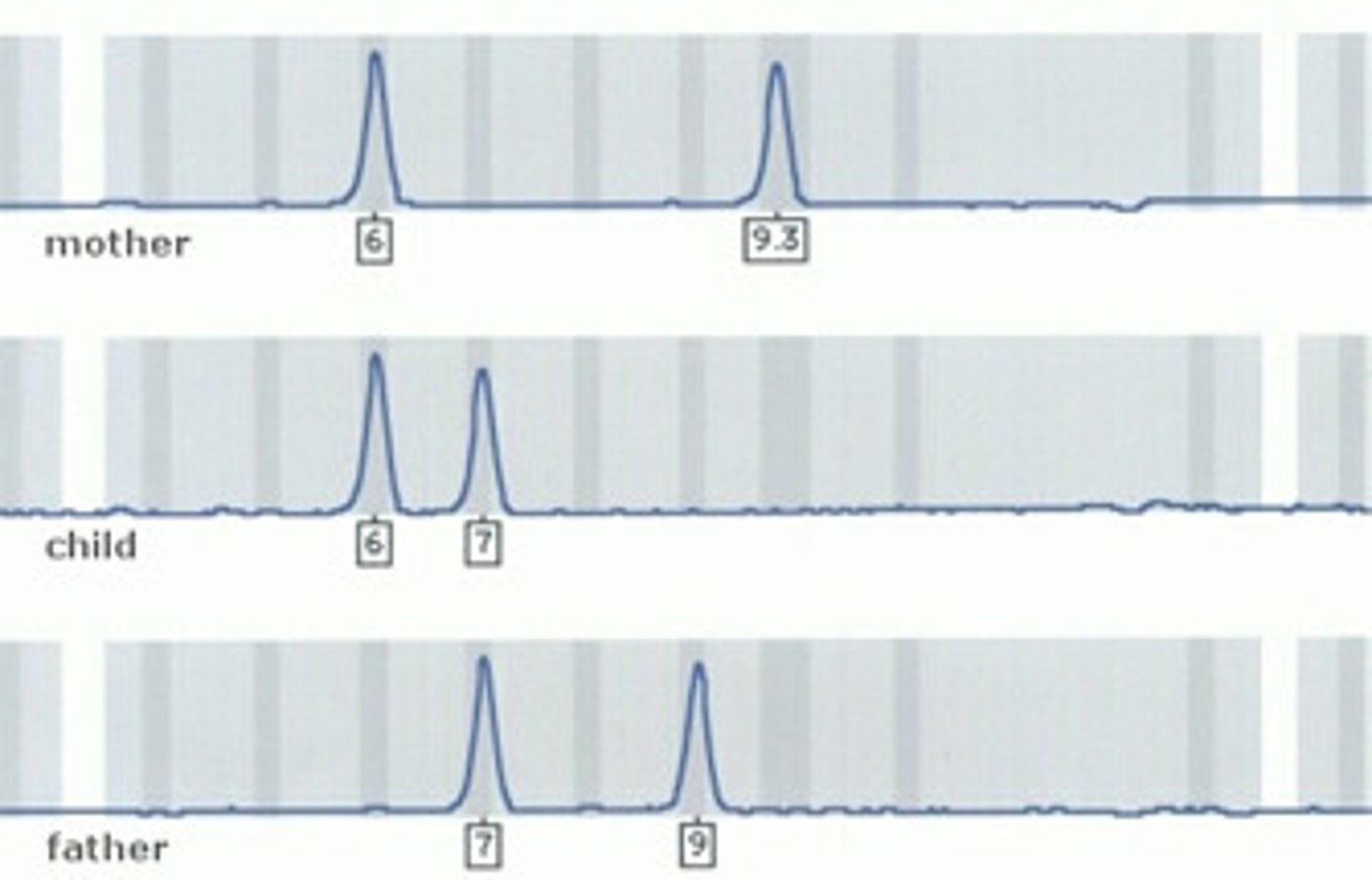
A distinctive pattern of DNA fragments that can be used to match a sample of biological matter to an individual (The bands are equally inherited from the Father and Mother)
DNA extraction
The process of separating DNA from an isolated cell;
1. The cell and the nucleus are broken open to release the DNA inside (mechanically or chemically)
2. DNA is separated from the cellular debris, through the use of sodium and alcohol
3. The separated DNA is then purified through further exposure to alcohol
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
A technique for amplifying DNA in vitro;
1. Heating DNA to 90˚C (Separating hydrogen bonds)
2. Introduction of DNA primers (Heat resistant) at 40-65˚C
3. Introduction of DNA polymerase (Bacterial) at 72˚C
4. Free floating DNA nucleotides bond to the DNA fragments
5. Repeated several times afterwards
Target DNA
Specific sequence of DNA that will be copied
Primers in PCR
RNA segments that specify a segment of DNA to be amplified.
Gel electrophoresis
Procedure used to separate and assist with analysis of DNA fragments;
1. Placing a mixture of DNA fragments at one end of a porous gel
2. Apply an electrical current to the substance, separating the fragments dependent on the size
STR analysis
A method of DNA profiling that involves the comparison of the lengths of short tandem repeat (STR) sequences selected from specific sites within the genome
Genetic engineering
The direct manipulation of gene sequences for practical purposes.
Restriction enzymes
An enzyme produced by certain bacteria, capable of separating DNA molecules at specific sequences of nucleotides on either strand
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
Nucleic acids
A type of organic macromolecule. Most common examples are DNA and RNA
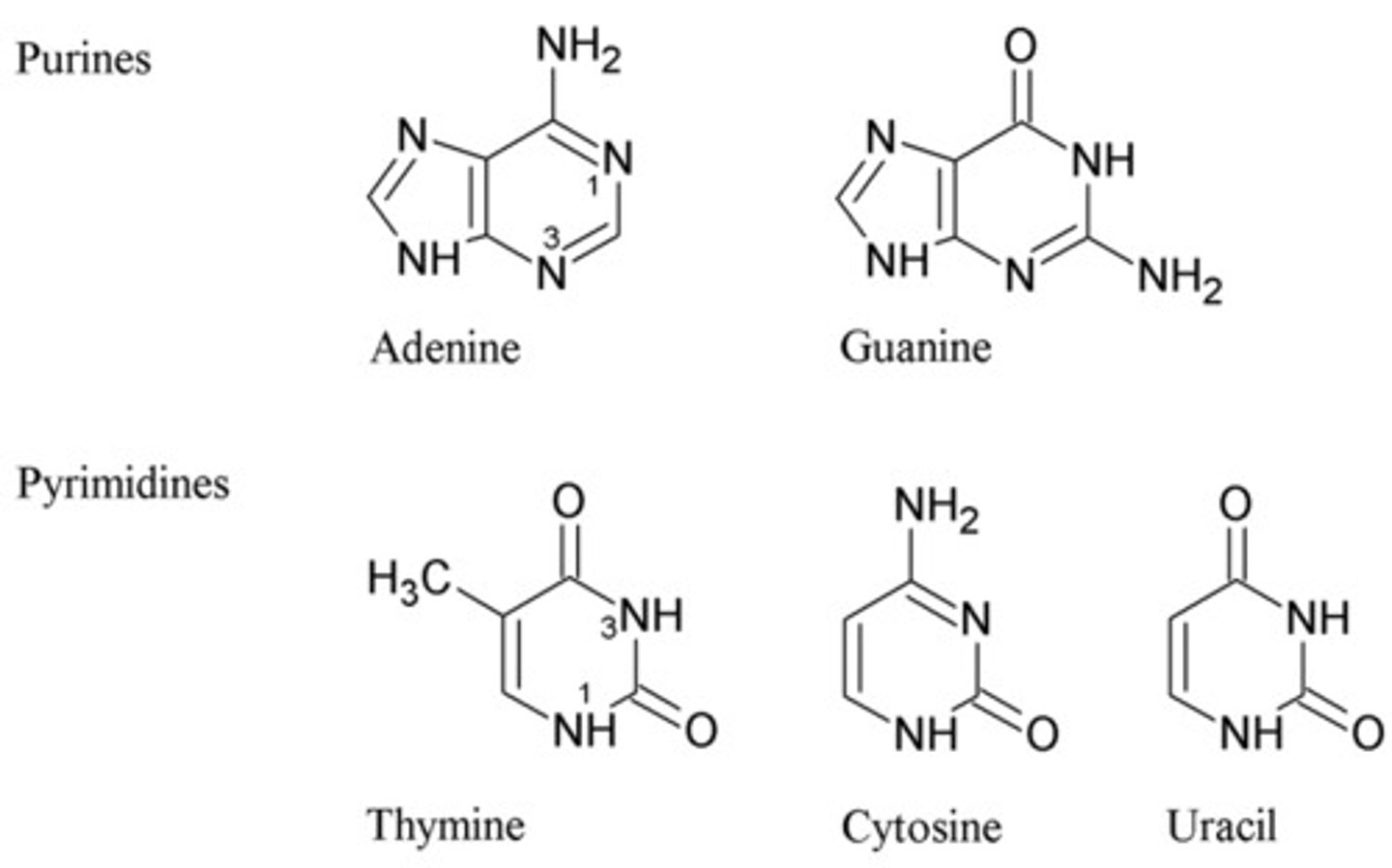
Nitrogenous base
A molecule found in DNA and RNA that encodes genetic information in cells.
5 Nitrogenous bases located in DNA and RNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil
Sugar-phosphate backbone
The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate to which the DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases are attached
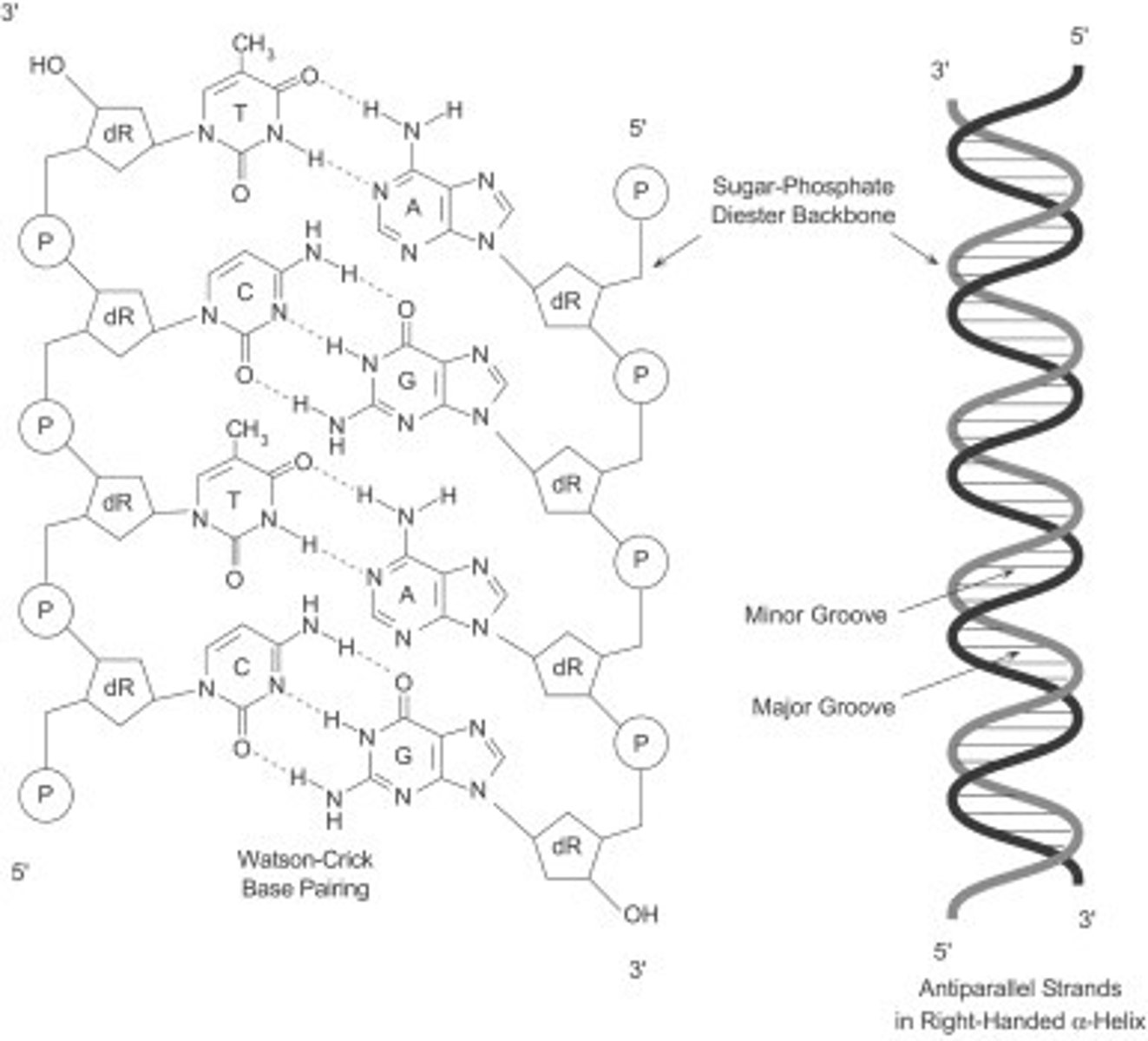
Hydrogen bonds in DNA
Bonds that form between the nitrogenous bases that form the "rungs" of the DNA ladder
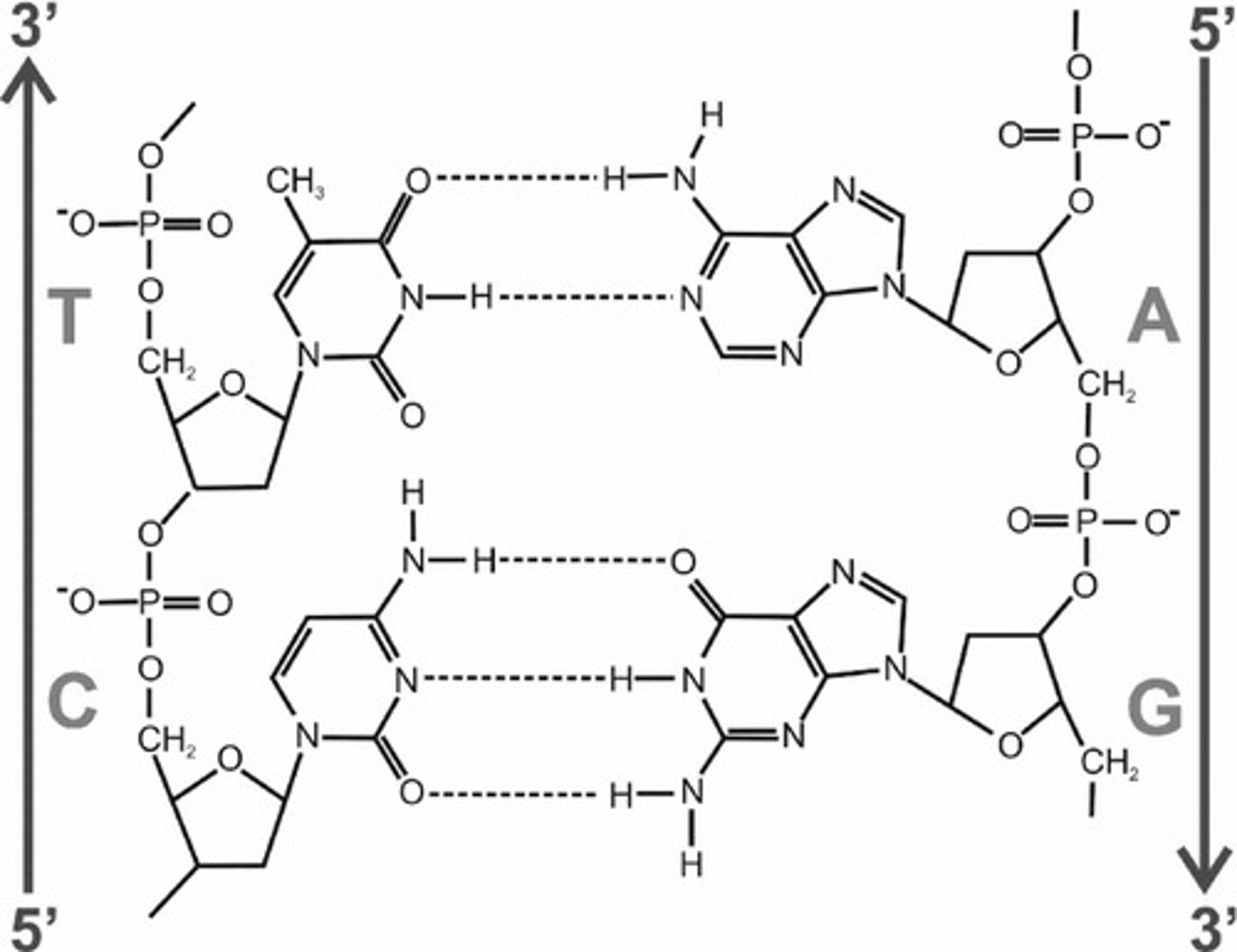
DNA in eukaryotic cells
- Linear
- associated with proteins called histones forming chromatin
- multiple chromosomes
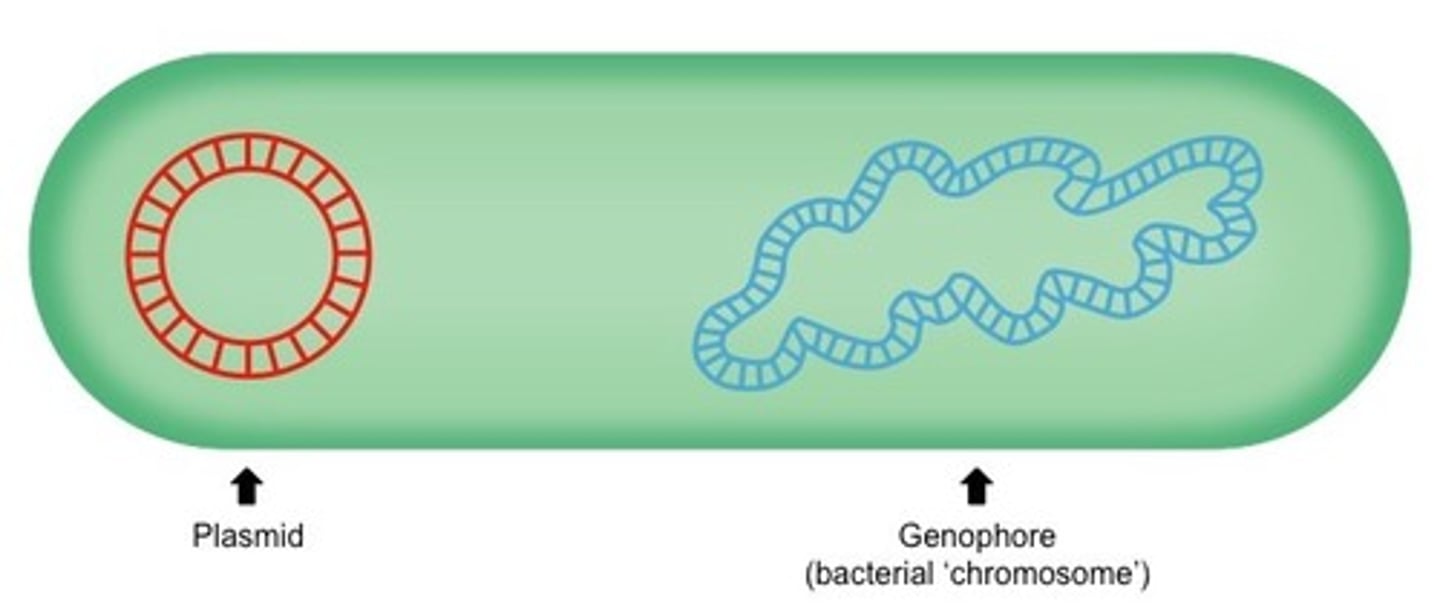
DNA in prokaryotic cells
- Coiled into a region called the nucleoid
- no membrane surrounds the DNA
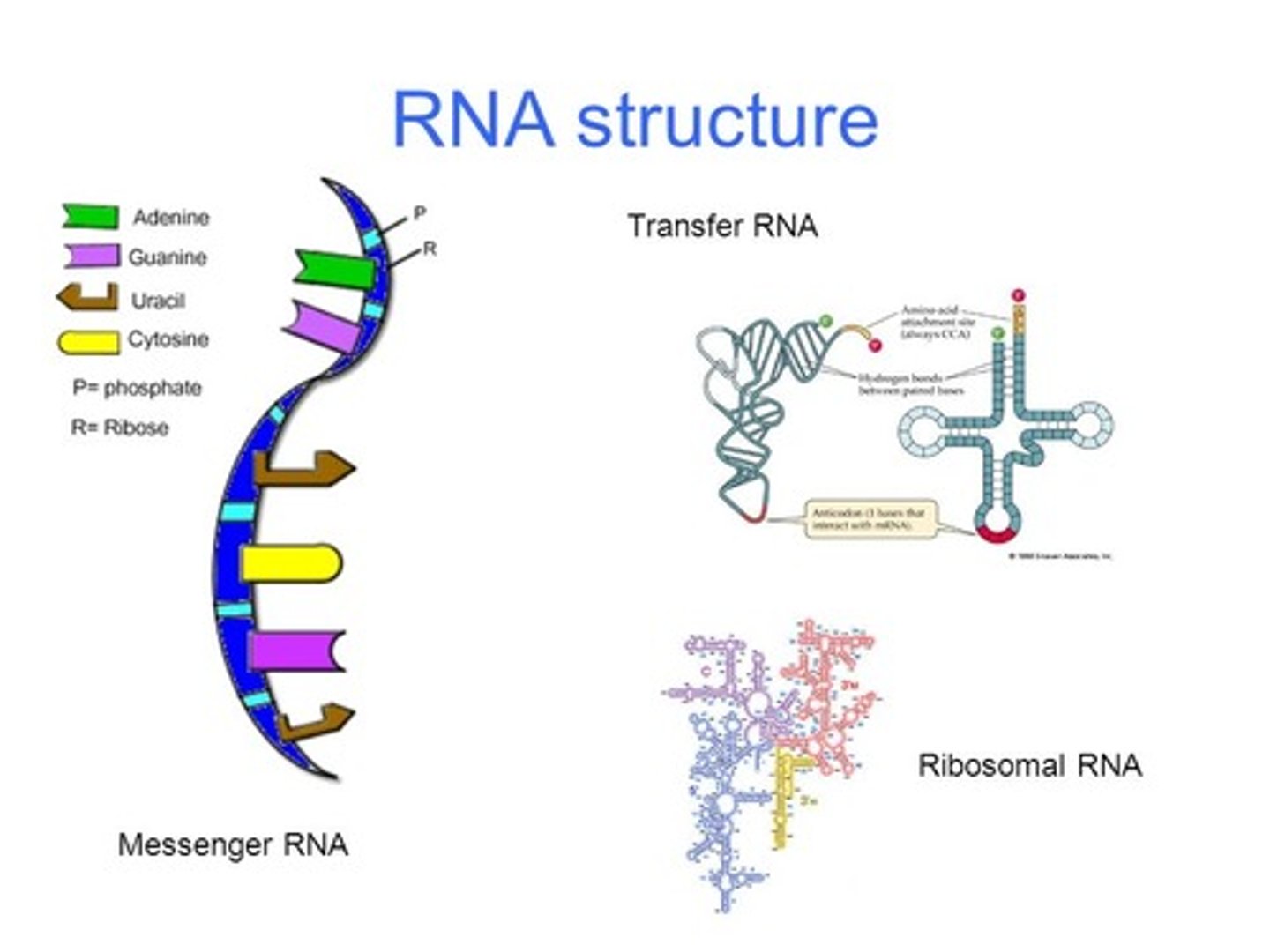
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along and transcribes genetic messages. It also contains the nitrogenous bases Uracil, Adenine, Guanine, and Cytosine
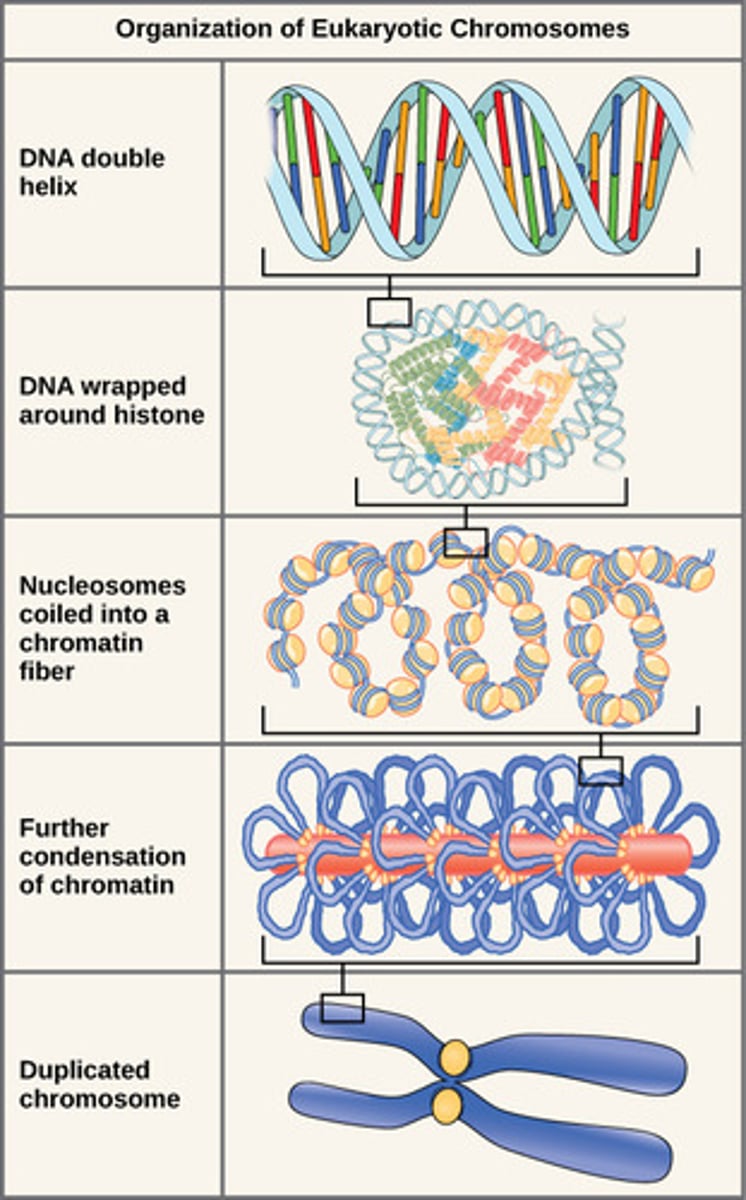
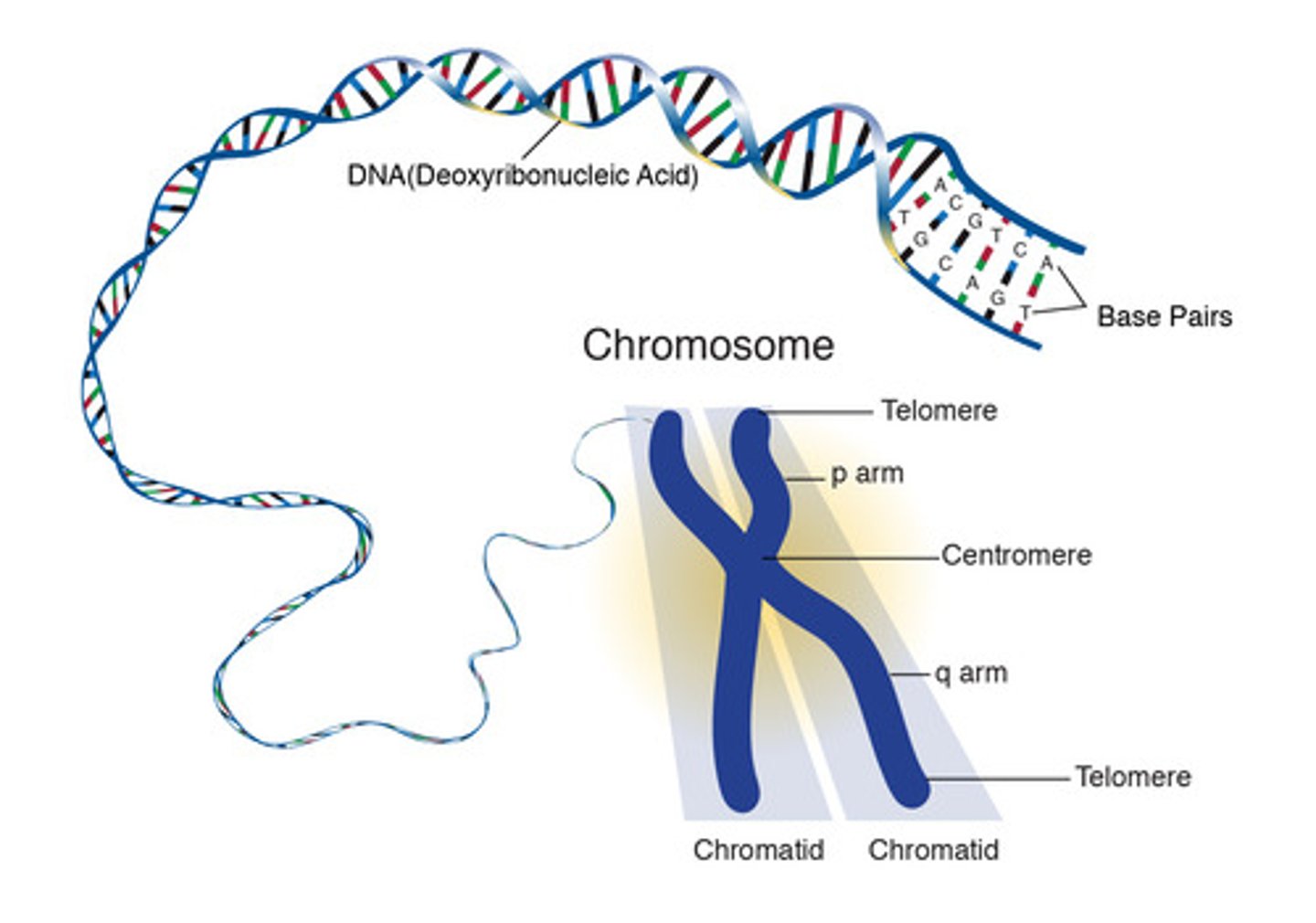
Chromosomes
A compacted threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself, through a semi conservative process
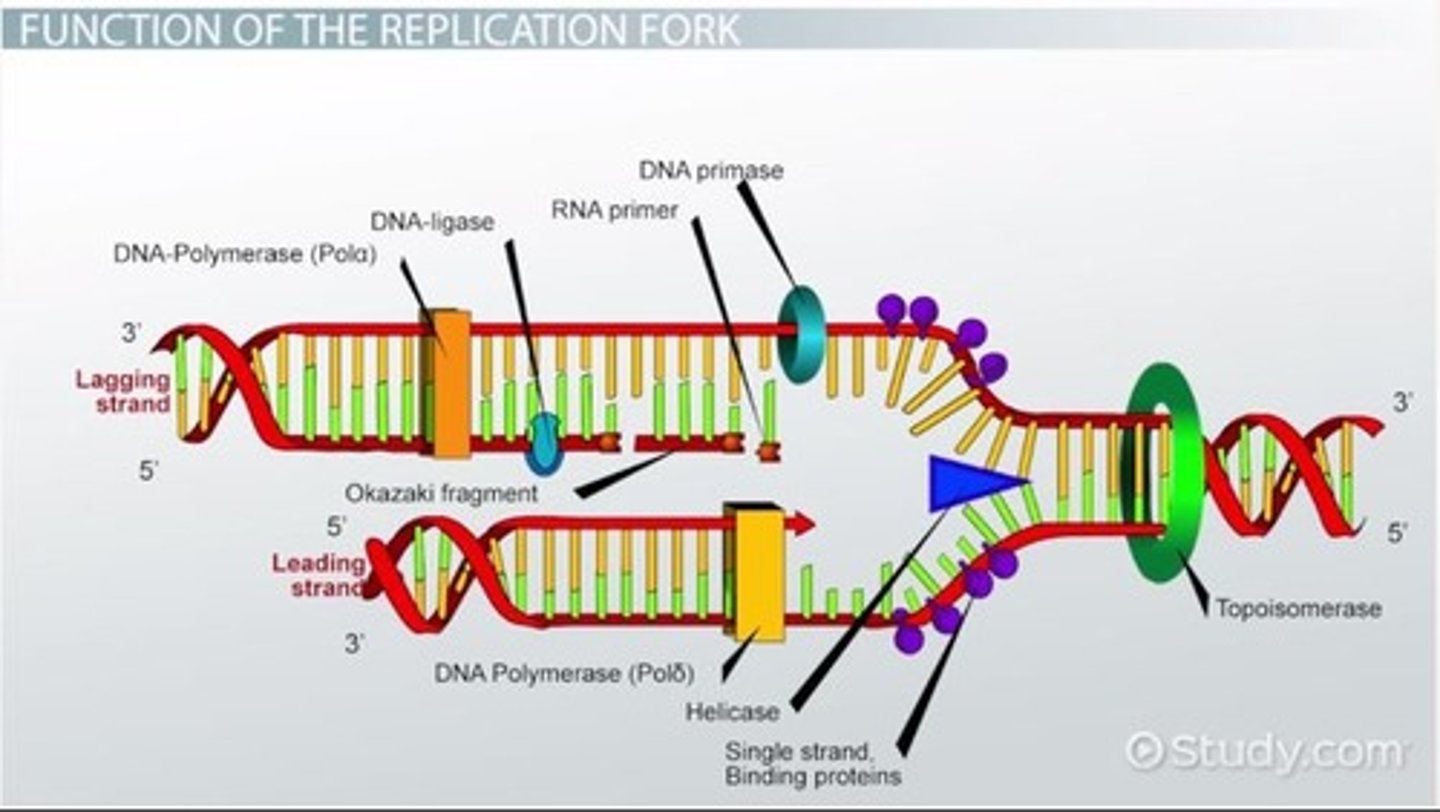
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks.
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait or protein
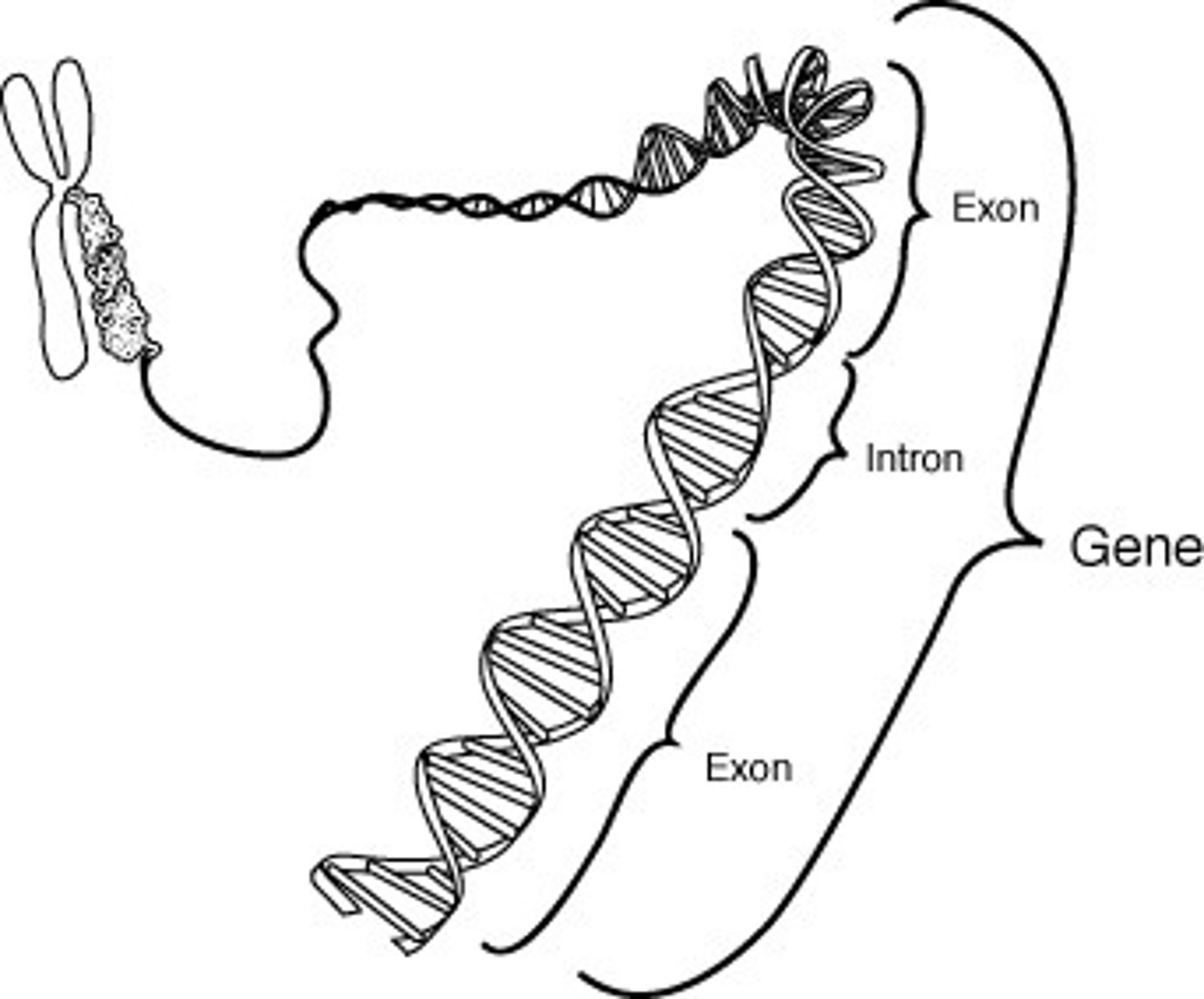
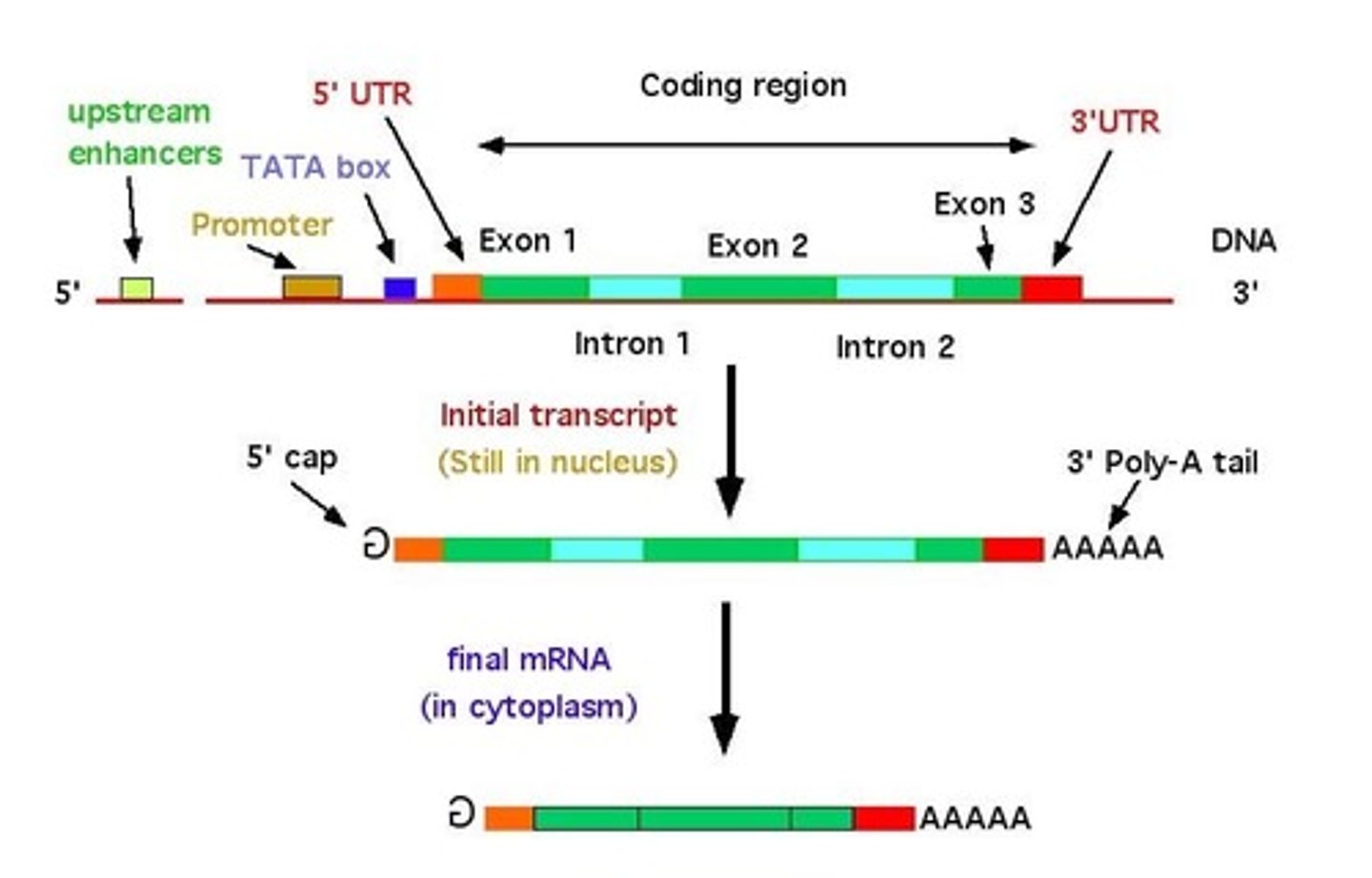
Exons
Coding segments of eukaryotic DNA.
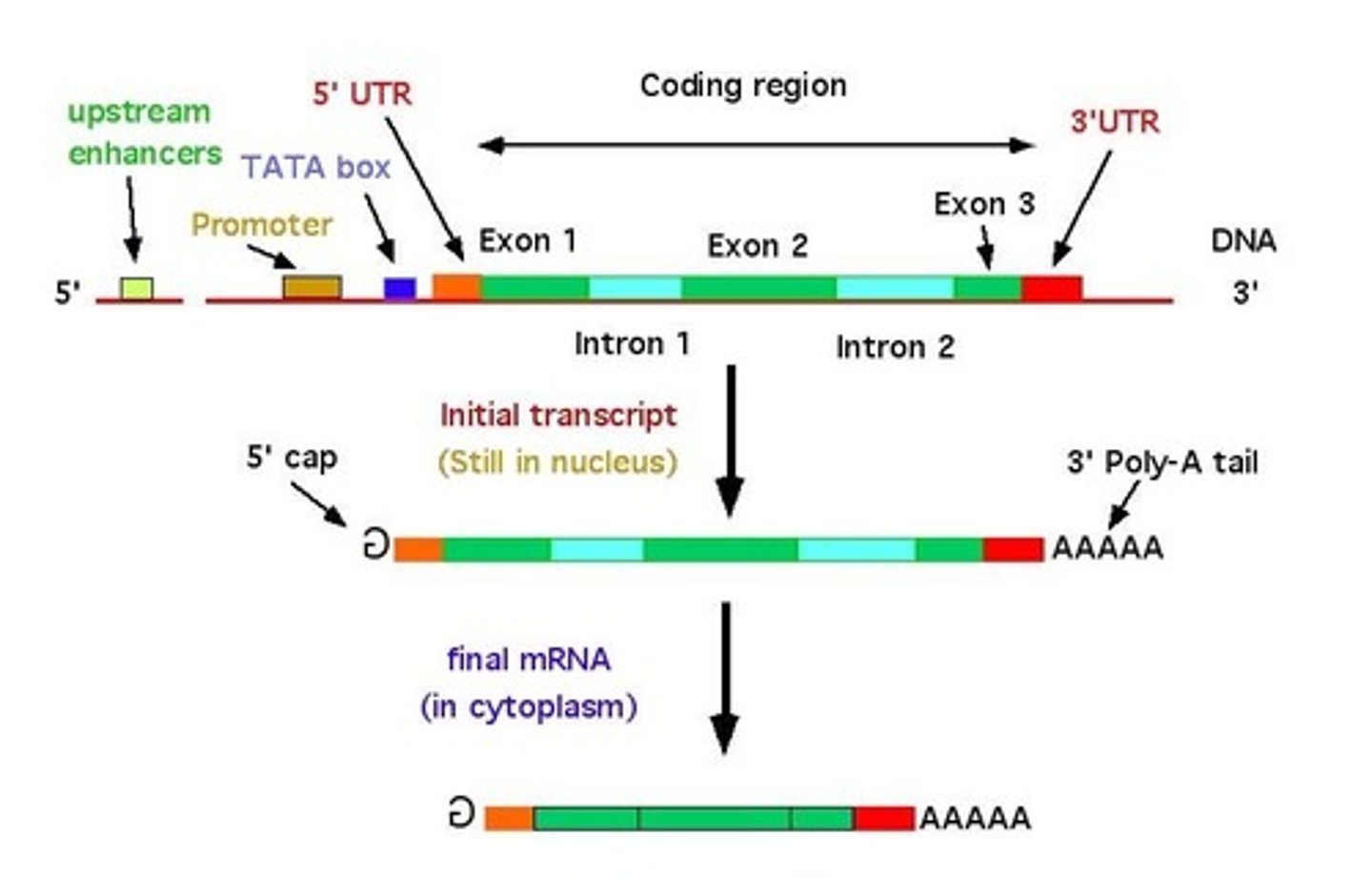
Introns
A noncoding, intervening sequence within a eukaryotic gene.
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
protein synthesis
Forming proteins based on information in DNA and carried out by RNA molecules
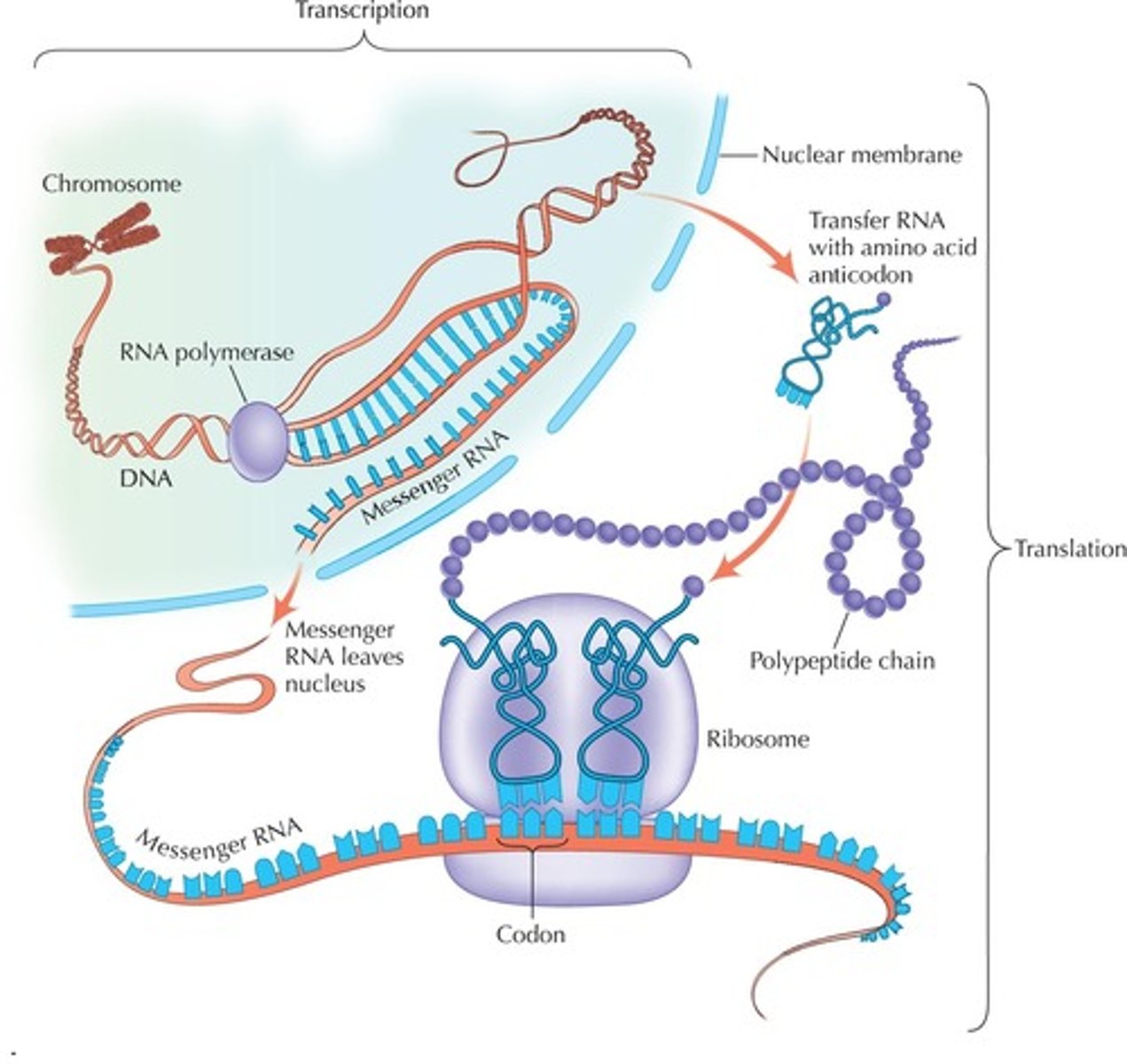
Transcription
Synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template;
1. DNA strand is separated at specific region
2. Free floating nucleotides attach to the desired Gene, forming a pre-mRNA strand
3. Once passing through the Nucleus into the cytoplasm, introns are removed, therefore becoming a mature mRNA Strand.
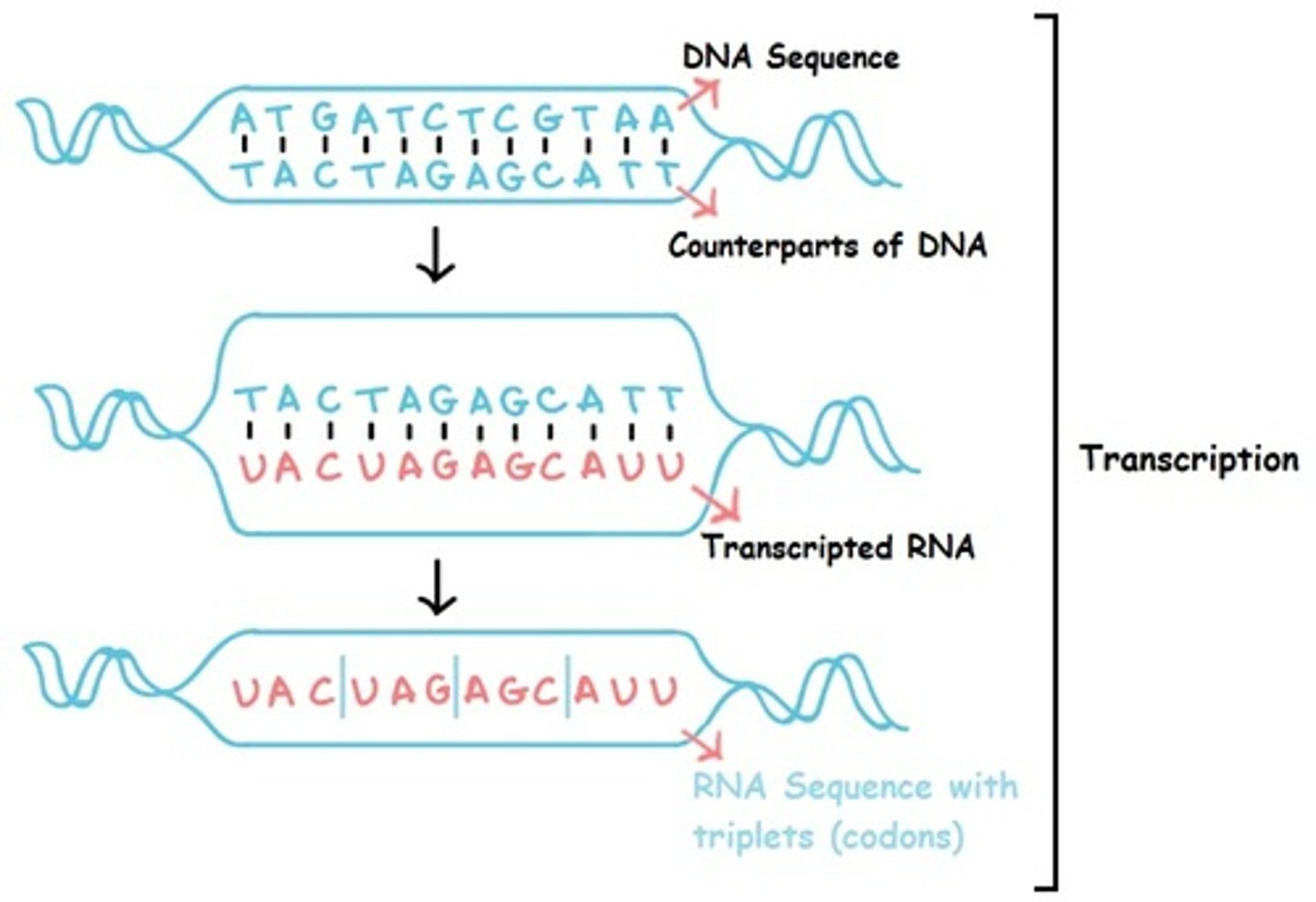
Codons
A three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code.
Translation
the process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome in the cytoplasm;
1. mRNA template attaches to the Ribosomal unit
2. Codons on the mRNA strand attract complimentary anti-codons on the tRNA molecule
3. Once bonded, the tRNA molecule transfers the corresponding amino acid to the proceeding tRNA
4. This transferring of the amino acid chain continues until the ribosome reaches a termination codon on the mRNA
5. After the termination of the mRNA template, a specific polypeptide chain is synthesised from the sequence of amnio acids
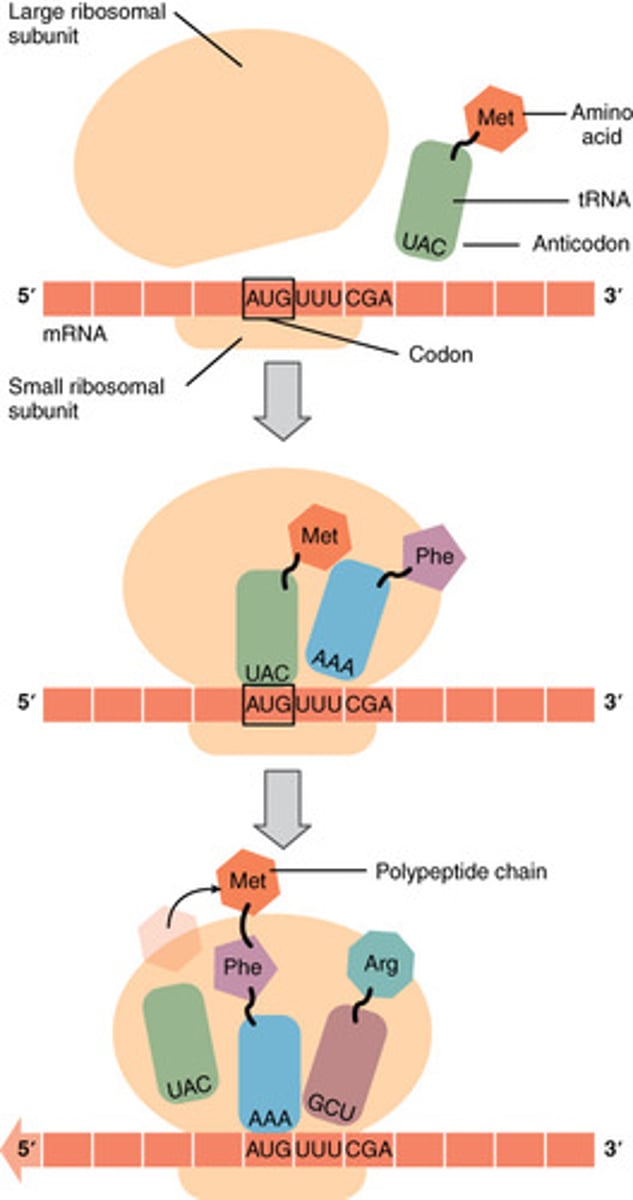
Anticodon
Group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to a mRNA codon
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
Type of RNA that makes up the major part of ribosomes
tRNA (transfer RNA)
Type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis
mRNA (messenger RNA)
A single-stranded RNA molecule that is a template of a Gene, which encodes the genetic information to make a protein
Amino acids
An organic compound which when repeated in specific sequences constitutes the basic structure of proteins
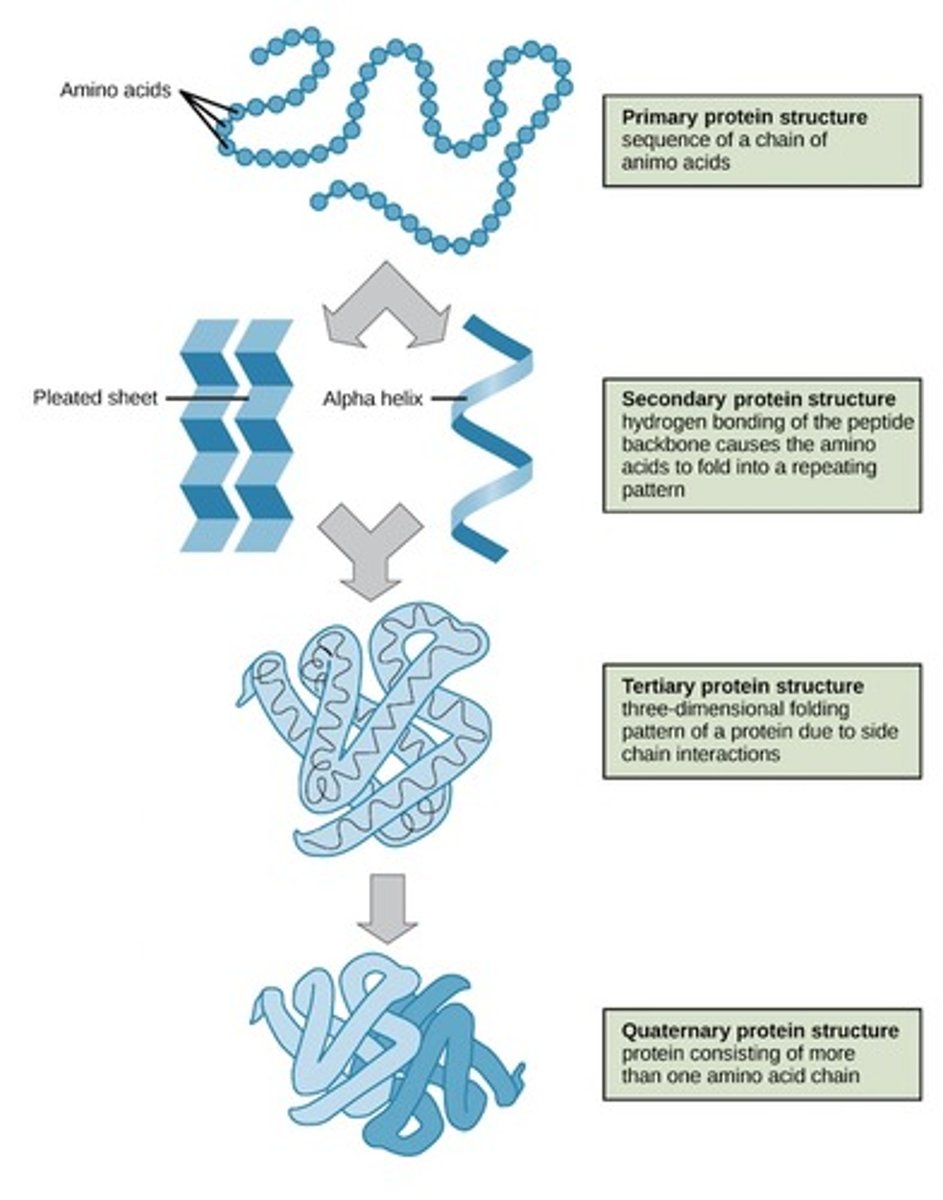
Primary structure (Protein)
The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain
Secondary structure (Protein)
Protein structure is formed by folding and twisting of amino acid chain (hydrogen bonding between peptide groups) - a-helix, b-sheet
Tertiary structure (Protein)
Defined by the Unique interactions between R groups of amino acid chains (Active sites are created); Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic, Covalent bonding, Hydrogen Bonding
Quaternary structure (Protein)
Results when a protein consists of multiple polypeptide chains
Enzymes
Biological Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things
Intracelluar enzymes
Enzymes that catalyse reaction inside cell
Extracellular enzymes
Enzymes that act outside of the cell in which they are produced
Induced fit model
Change in the shape of an enzyme's active site that enhances the fit between the active site and its substrate(s)
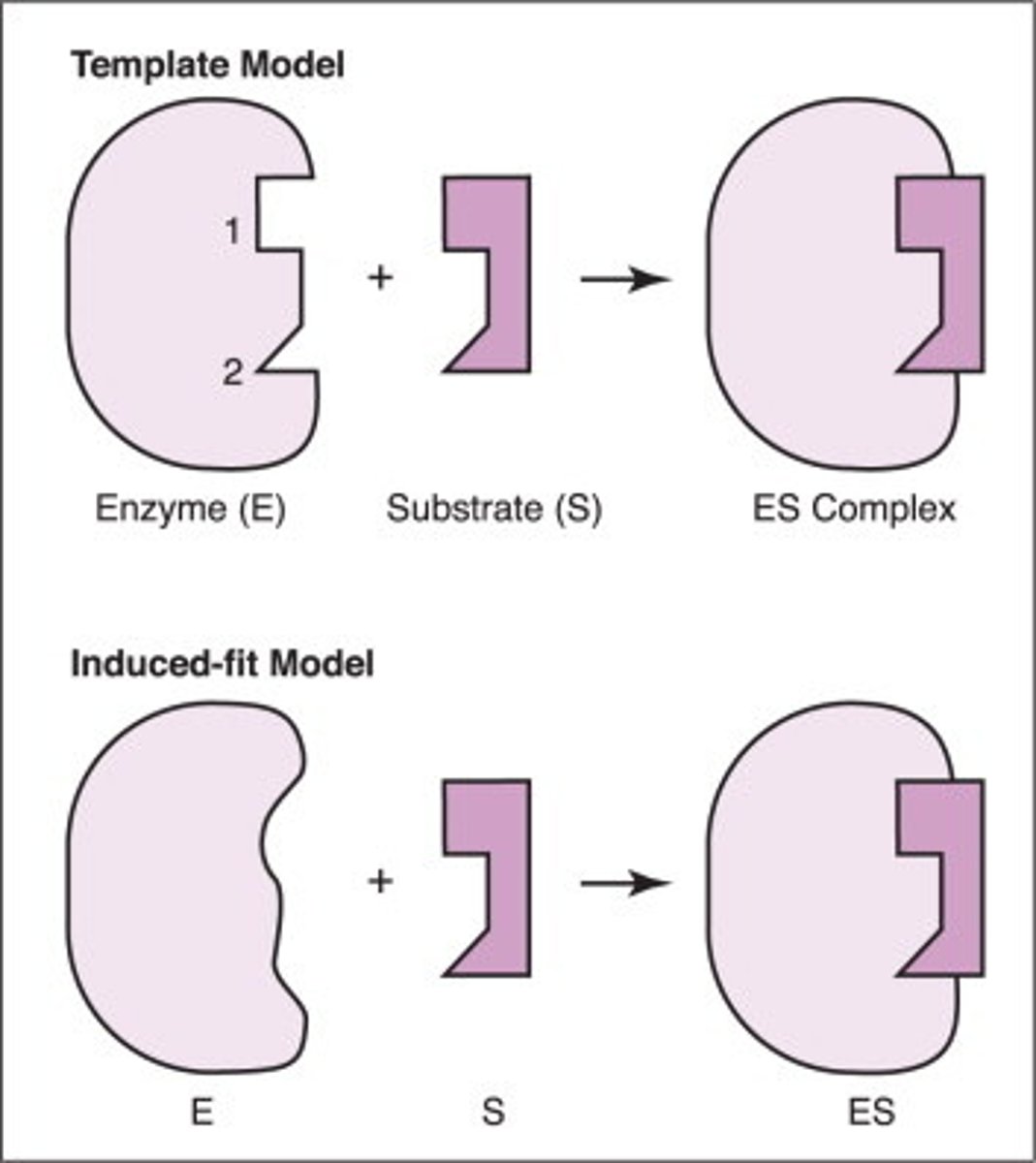
Chemical inhibitors
Binds to enzymes and slows reaction rates
Non-competitive inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate.
Competitive inhibitor
A substance, other than the substrate, which binds to the active site of an enzyme
Exergonic reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy.
Endergonic reaction
A non-spontaneous chemical reaction in which free energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
Activation energy
The minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
Enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction
1. Correct orientation of reactants
2. Placing strain on the chemical bonds
3. Breaks down the reaction into multiple stages
Gene expression
A process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out a specific function
Promotor region
A portion of a gene which signals for RNA polymerase to begin transcription
Regulators of Transcription (Transcription factor)
Bind to DNA in the vicinity of a promoter and affect transcription of one or more nearby genes
Activators and Repressors
A protein which binds close to the promoter on a DNA Strand and either activates or represses the activity of RNA polymerase (transcription)
Phenotype
An organism's physical expression of it's gene or visible traits.
Cell differentiation
The process by which a stem cell becomes specialized for a specific structure or function.
Stem cells
Unspecialized cells that are able to renew themselves for long periods of time by cell division
Pluripotent stem cells
Stem cells that can become almost all types of tissues and cells in the body.
Multipotent stem cells
Stem cells that can become a limited number of types of tissues and cells in the body
Methylation of DNA
The process by which the methyl groups are added to certain nucleotides in genomic DNA, blocks the function of RNA polymerase (cytosine)
Cancer
Any malignant growth or tumor caused by abnormal and uncontrolled cell division
Tumour suppressor genes
These keep the activity of proto-oncogenes in check in normal healthy cells.
Protooncogenes
Normal cellular genes that regulate cell proliferation and differentiation that can become oncogenes.
Epigenetics
The study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a specific change in DNA sequence
Promotor region
Portion of a gene that signals for RNA polymerase to start transcription
CCDIAL
Communication and Collaboration
Development
Influence
Application and Limitation
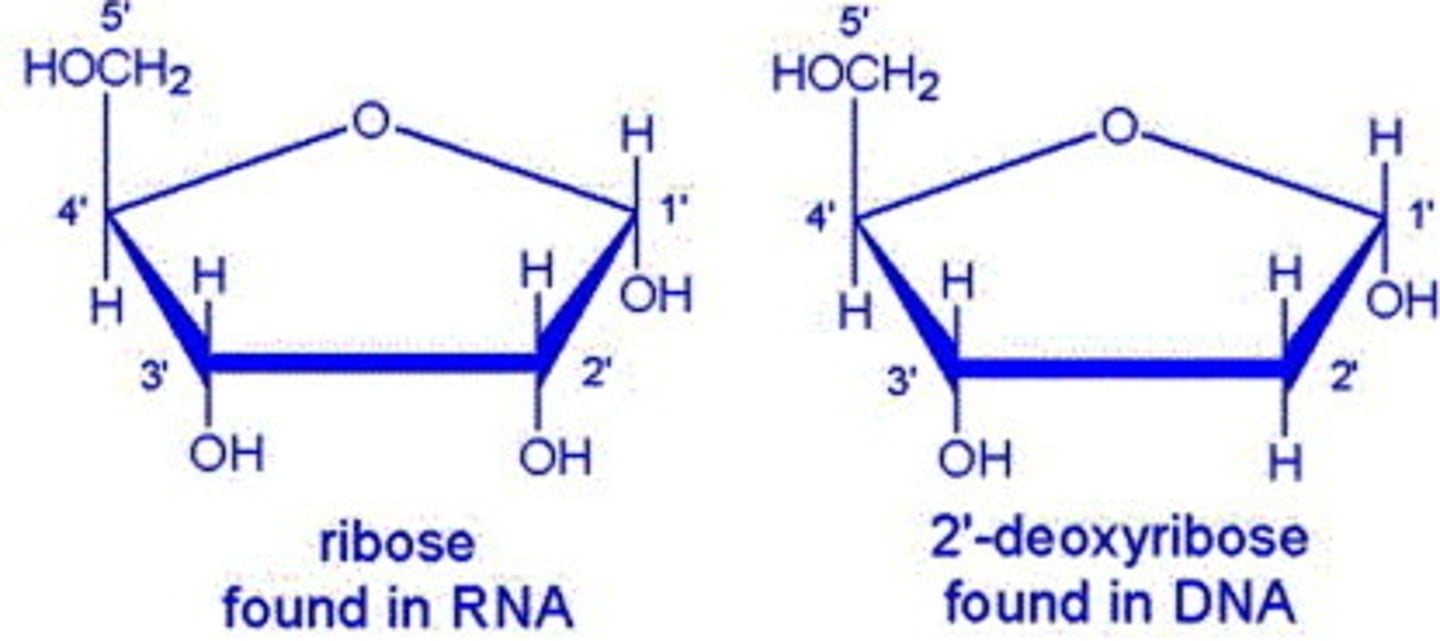
Nucleotide
A monomer of nucleic acids consisting of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis in the cell (Facilitate translation)
Factors affecting enzyme activity
- Temperature
- pH levels
- Enzyme concentration
- Substrate concentration
- Presence of Chemical Inhibitors
Mutation
Change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information
Point mutation
A mutation affecting only one or very few nucleotides in a gene sequence.
Substitution (mutation)
A type of point mutation in which a single nucleotide is substituted with (or exchanged for) a different nucleotide that may result in an altered sequence of amino acid during translation, which may render the newly synthesized protein ineffective.
Inversion (mutation)
A genetic mutation in which the order of a segment of genetic material is reversed. This type of mutation can involve a small number of nucleotides as well as larger sections of a chromosome containing more than one gene
Deletion (mutation)
A change in the base sequence of a gene that results from the loss of one or more nucleotide base pairs in the DNA
Insertion (mutation)
The addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence
Mutagen
Chemical or physical agents in the environment that interact with DNA and may cause a mutation
Ionising radiation
Type of radiation such as UV, X ray or gamma rays that can cause mutations in DNA, by breaking the bonds between DNA molecules
Non-ionising radiation
Radiation with photons that do not have enough energy to ionise molecules, and can cause chemical bonds to form between adjacent thymine bases
Mutagenic chemicals
Substances which interact with the structure of a DNA molecule and facilitate the occurrence of a point mutation
Virus (mutation)
Certain Viruses can initiate un-controlled cell division, through inserting oncogenes into the genome
Aneuploidy
The presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, e.g. a human cell having 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46
Polyploidy
A condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes
(Mutations) Spontaneous
Occurs Naturally - a sudden random change in the DNA structure
(Mutations) Induced
Caused by mutagenic factors in the external environment
Somatic cells
Any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells.
Germ cells
Reproductive cells that give rise to sperm and ovum
Somatic mutation
A mutation that occurs in cells of the body other than gametes
Germ-line mutation
A mutation occurring in gametes; passed on to offspring
DNA/RNA probes
A stretched single strand of DNA/RNA, used to detect the presence of a complimentary nucleotide sequence (target sequences)
CRISPR
Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats; A collection of DNA fragments which tell Cas9 where to cut
Antibody Method (Gene location)
1. A protein, generated by the specific gene of interest, is injected into an multicellular organism.
2. The organism then creates antibodies which bind to the protein
3. The antibodies are collated and labelled (Radioactively or Chemically)
4. All DNA from the cell is separated into fragments, and incorporated into a large of number of bacteria, through recombinant DNA technology
5. Each bacterial cell absorbs 1-2 of the fragments
6. Each bacterial cell is incubated into colonies, which will use the new DNA fragment to produce proteins
7. All colonies are exposed to the labelled antibodies, but will only bind to the colony producing the original protein
Gene Cloning (Bacterial Plasmids)
A process through which a specified segment of DNA is inserted into a bacterial cell through the use of plasmids, which allows for the gene to be copied during binary fission
Transgenesis
The process during which foreign DNA is incorporated into higher order multicellular organisms
Ti plasmid
A plasmid of a tumor-inducing bacterium (Agrobacterium) which integrates a segment of its DNA into the host chromosome of a plant; frequently used as a carrier for genetic engineering in plants.
Viral vectors
Use of a virus as a delivery system (called a vector) to carry a gene into the nuclei of target cells to alter protein synthesis.
Microinjection
The introduction of DNA into the nucleus of an embryo or other cell by injection through a very fine needle.
Factors of gene expression
- Methylation or the addition of methyl groups to DNA (cytosine)
- Coiling of DNA around the Histones
- Transcription Factors
- The "Switching on/off" of specific genes during cellular differentiation