Prehistoric Time Periods and Cultural Developments in Human Evolution
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Important Time Period covered in class ___,___ BCE -> --,--- BCE
From 100,000 BCE -> 10,000 BCE
Pleistocene Era - other name, time period and climate
Ice age, 2 million years ago -> 10,000 BCE, major climate contrasts with the ice sheet advances and retreat
Lower Stone Age/Paleolithic Time Range
2.6 million -> 120,000 BCE
What is the Lower Palaeolithic period characterized by? (people and tool)
Earliest forms of mans kind, hand-axe industries
Middle Stone Age/Paleolithic Time Range
120,000 BCE -> 40,000-35,000 BCE
What type of people is the Middle Stone/Palaeolithic known for?
Neanderthal man
Upper Stone Age/Paleolithic Time Range
40-35,000 BCE -> 14,000/10,000BCE
What development is upper Palaeolithic known for?
the development of Homo Sapiens from c. 40,000 years ago
Mesolithic Time Range (also, what period is it known as/other name?)
the transition between the paleolithic and neolithic - from 14,000/12,000 BCE - 10,000/8,000 BCE.
Holocene - began when/came after? People argue it has ____ and we have entered the _____ era or the era of man.
Began 10,000 years ago after the Pleistocene when the ice began to reduce; some argue it has ended, we have entered the Anthropocene era/era of man.
Lower Palaolithic culture
Acheulian - handaxes by using cobble/large flake to turn it into an oval and slice it. First appeared 1.5 million years ago in Africa and unmodified until 150,000 yrs ago.
Middle Stone Age culture/other name
Mousterian
Lower Stone Age/Paleolithic Cultures and characterization CAGSBMD (Clever Apes Gather Sharp Blades, Making Dwellings)
Châtelperronian, Aurignacian, Gravettian, Solutrean, Badegoulian, Magdalenian and Azilian - flint blades, cave/portable art, using tools/weapons from hard animal materials, Homo sapiens expanded their territory
Mesolithic Characterization and replaced by what period/revolution?
micro-liths or smaller sharpened tools, expert carving and drilling in bone, ivory and stone replaced quickly by the neolithic period and the agrarian revolution which follows.
Why do we make art?
To represent important time periods in our lives!
BC, BCE, CE, AD
Before Christ, Before Common Era, Common Era, AD - Anno Domini which is the time after birth of christ
What current time period are we in?
It is said that we are currently in the Holocene Era (beginning in 10,000 BCE) but it is argued that we are now in Anthropocene or era of man.

What is this object? Used by who/time period? Made how? Used for what?
A stone chopper, typically used by early humans in Africa. Made by hammerstones and striking for shark edges, usually to get meat and bone marrow from large animals. It is from the Paleolithic era, specifically the Lower or Ice Age?
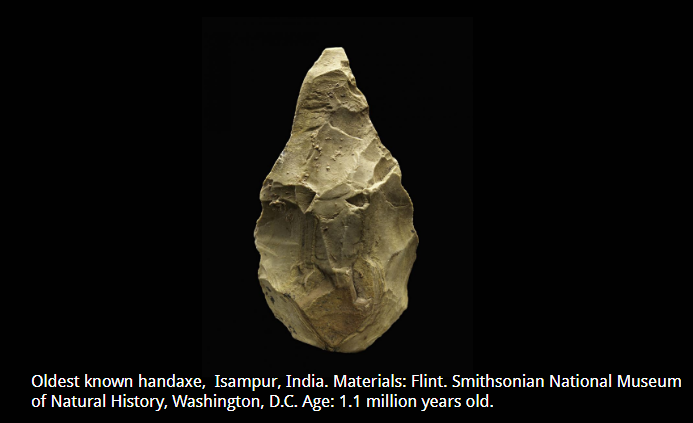

What object is this? Time period? Used for/by who?
It is the oldest knoown handaxe, and is 1.1 million years old, or from the Lower Paleolithic Period. It is used by early Hominids, and they used it for cutting through bone to make tools.
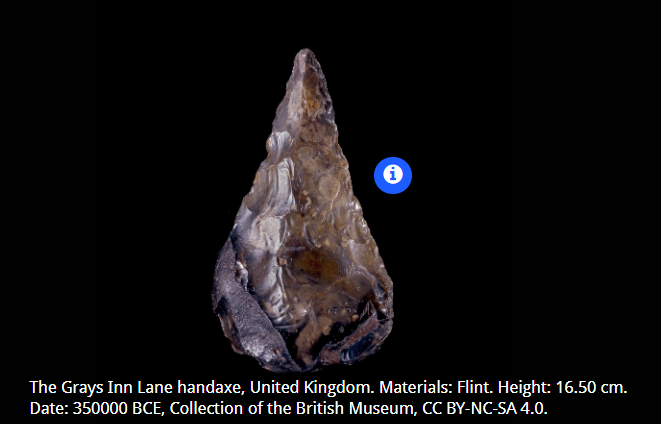

What tool is this? Describe it.
The Grays Inn Hand axe. Pointed and shaped on both sides but has a rounded tips. Some small chips on edge from use, part of it still has original stone surface and it has turned orange-brown from sitting in river gravel for a long time.
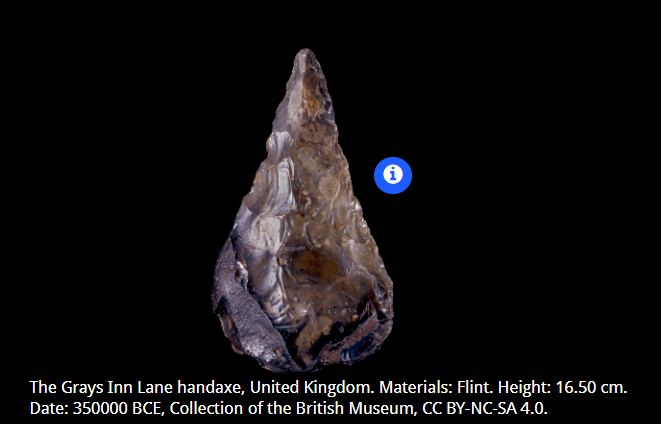

Why does this tool matter? (when was it found and where? helped people to realise what? What problems did it cause?)
It was found in 1763 in London, very deep in the ground. It was the first stone tool ever drawn & published, helping people to realise that people are much older than the bible says which caused issues as science doesnt match religious ideas.
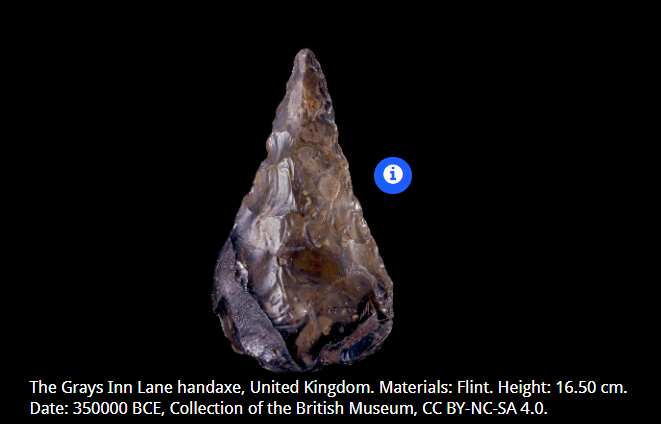

Importance of the Gray’s Inn Lane Handaxe?
It is a very old stone tool used to cut through bone, and the first ever found. It helped to prove that humans lived MUCH longer than written history recorded.

What tool is this? How old? Used for/by who? What did this prove about early Hominids?
The Katanda Harpoon Point. It is about 90,000-80,000 years old. It is used for piercing and fishing, and showed that early hominids were learning to adapt to their environment and expand their reach.
Who used the Katanda Harpoon point, handaxes, stone chopper and bone awl?
Early hominids and homo sapien sapiens
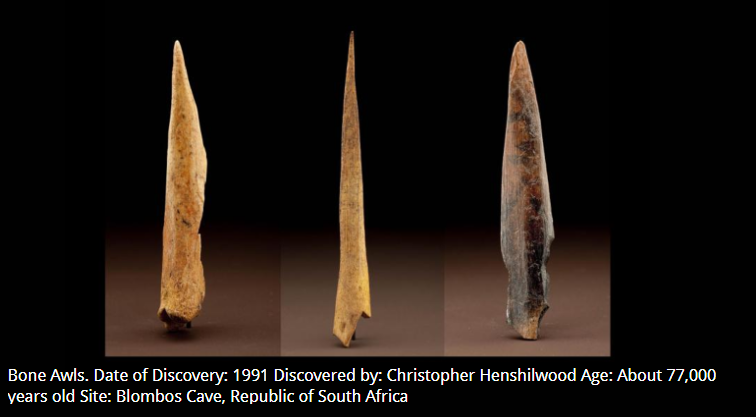

What tools are these? How old? Used for what?
They are the Bone Awls and are about 77,000 years old. They are used to make holes in clothes and are, obviously, made of bones.

What object is this? What does it show? When is it from?
It is incised Ochre. It has marks that may have been used to count/store info, showing some sort of information rather than decoration. SMITHSONIAN! It is from 100,000-66,000BCE.
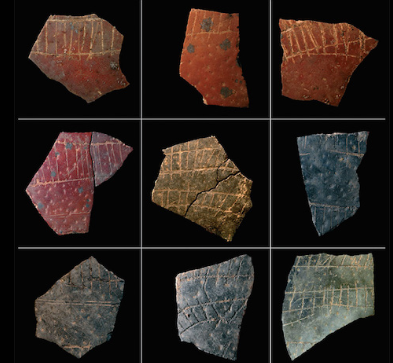
What are these objects? Used for? From?
They are fragments of engraved ostrich eggshells. They are likely also to record info and remember certain things, like time. It is from 60,000 BCE.
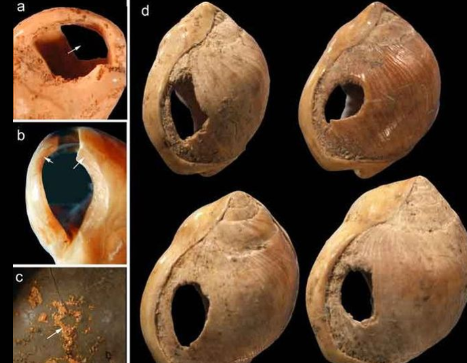
What are these objects? What do they show about early humans?
These are nassarius shell beads from the Blombos Cave, showing that early humans are capable of abstraction and creativity.

What is this? Where is it from? (C_ - M - - - - - - , Fr - - - - )
Shell bead necklace from 30,000 years ago in Cro-Magnon, France. These are from early humans before hominids.
What is Cro-Magnon and why is it important to the shell bead necklace?
It refers to early humans before hominids, and that is where this necklace was found.

What is this? When is it from? (time and where)
It is a neaderthal flute from 60,000 years BCE. It is the bone of a cave bear, and is from Cerkno, Slovenia.
What is a neanderthal?
They are hominids and close relatives who disappeared around 40,000 BCE, however it is being found that modern people have neanderthal ancestry in their DNA.
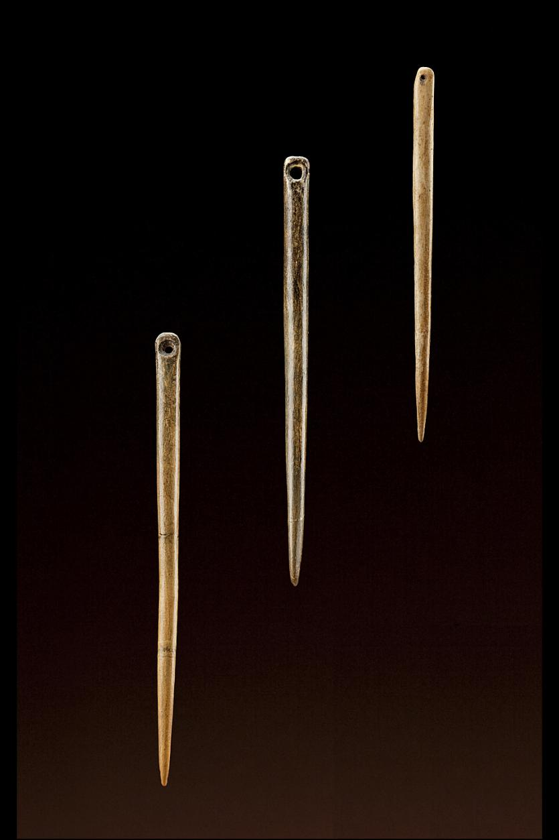
What is this? From where/what time? What does it show about humans at this time?
They are bone needles from 28,000-21,000 BCE, showing early humans evolving ability to create.

What is this? From when? Used for?

What is this? From when? What does it show?
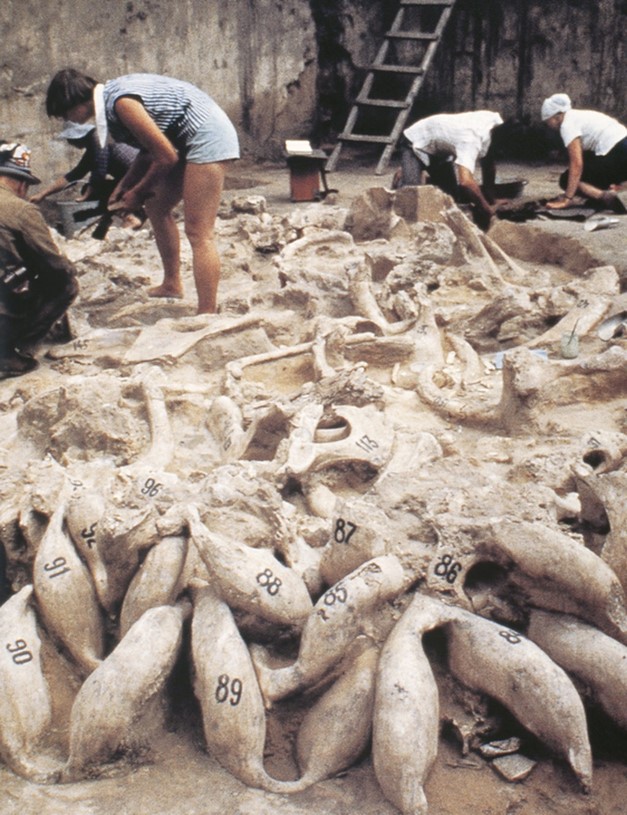

What is this? When is this from?
Mammoth-Bone Dwelling #4, shows creativity. From 15,000 BCE
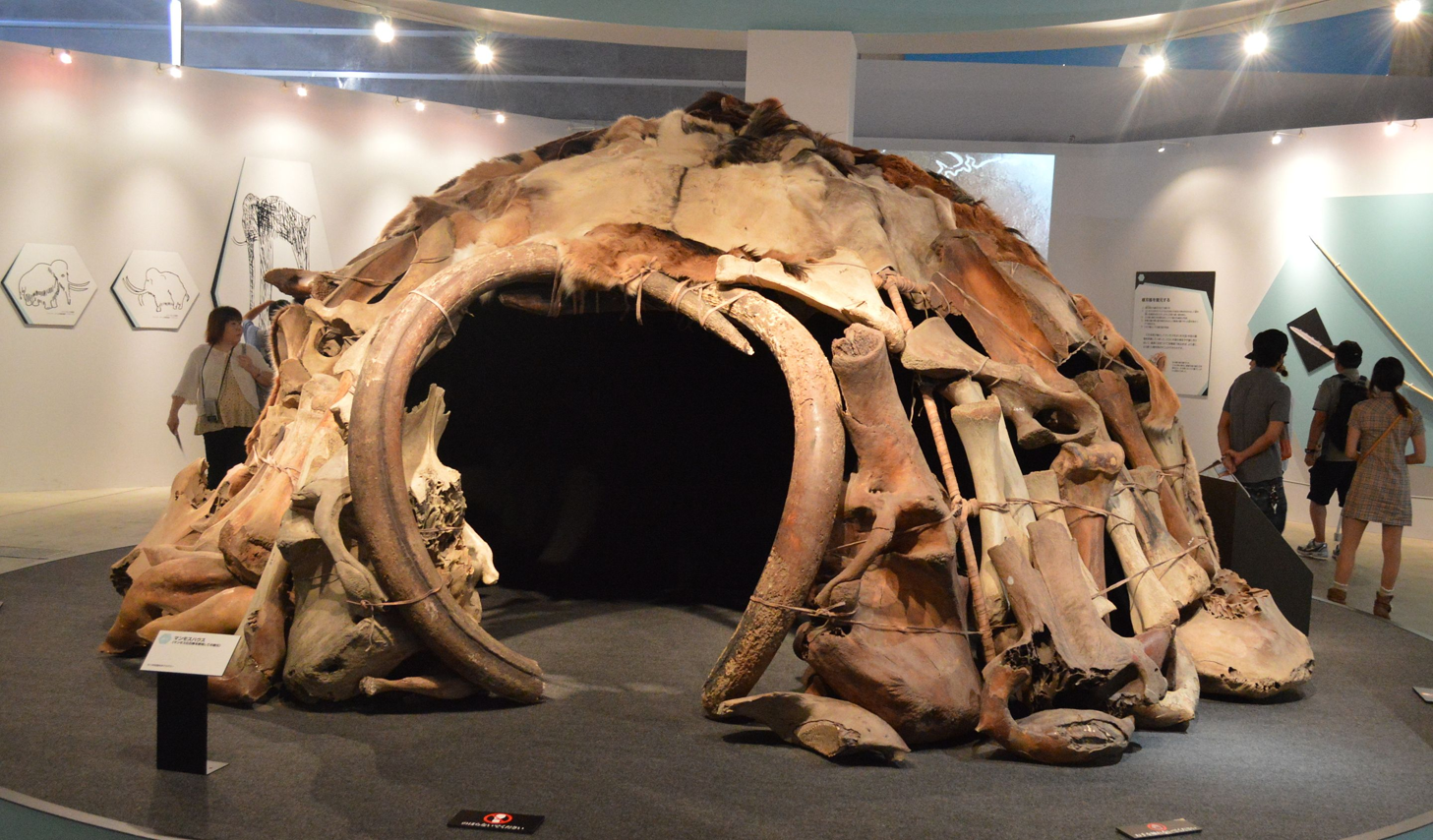

What is this? Made from?
It is a Mammoth House, made of bones and tusks of Mammoths.
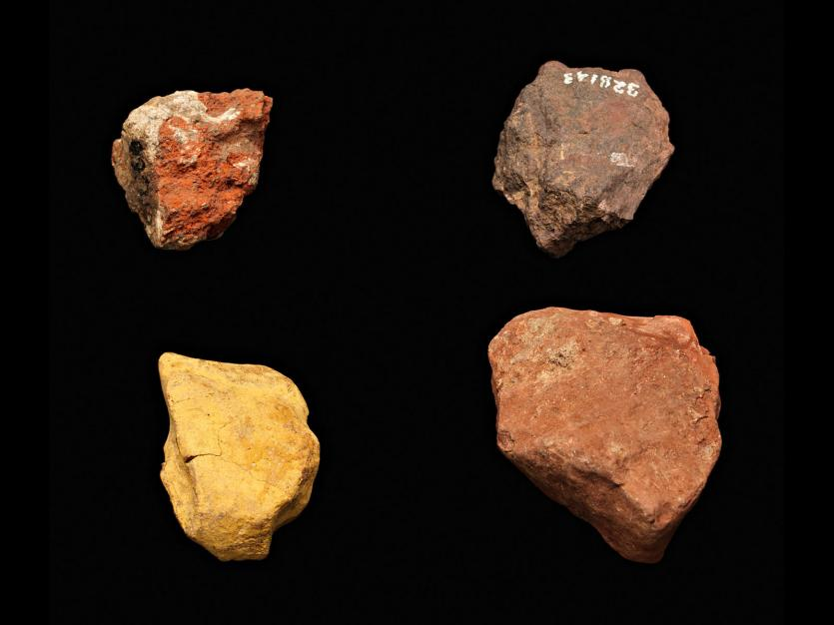

What is thiss? Found where? What does this tell us?
This is ochre that was found alongside the remains of 15 homo sapiens/modern humans that was likely used in a ritual.
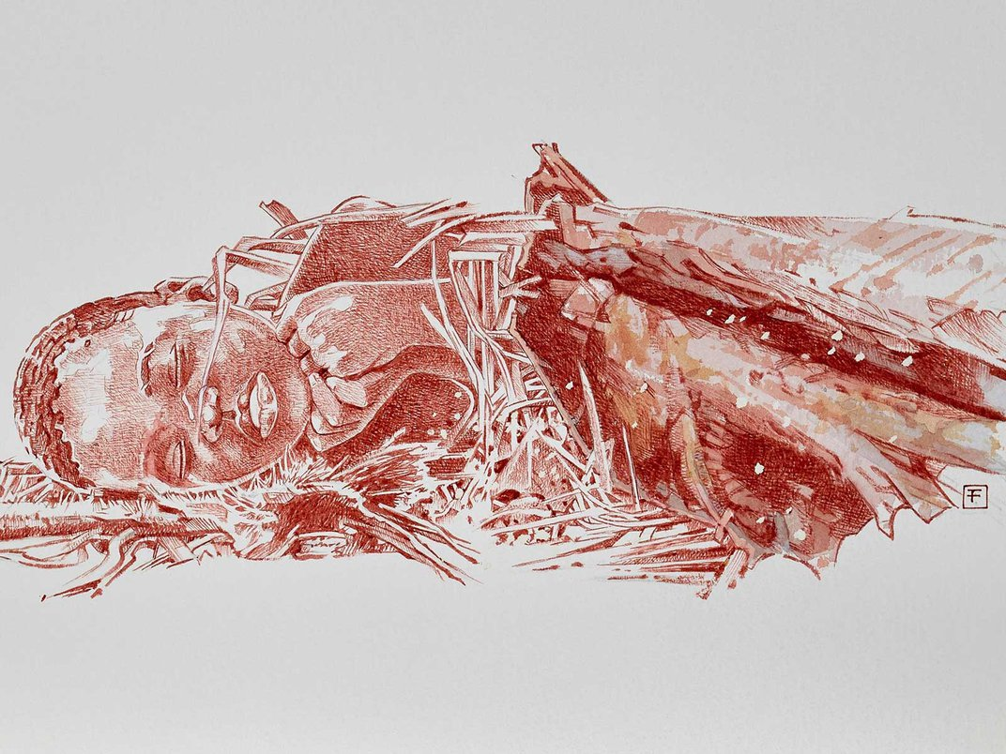

What is this? From? Where was he buried?
It is the interpretation of a 2 and a ½ year old child buried in the Panga ya Sadia cave in Kenya, from 76,000 BCE.
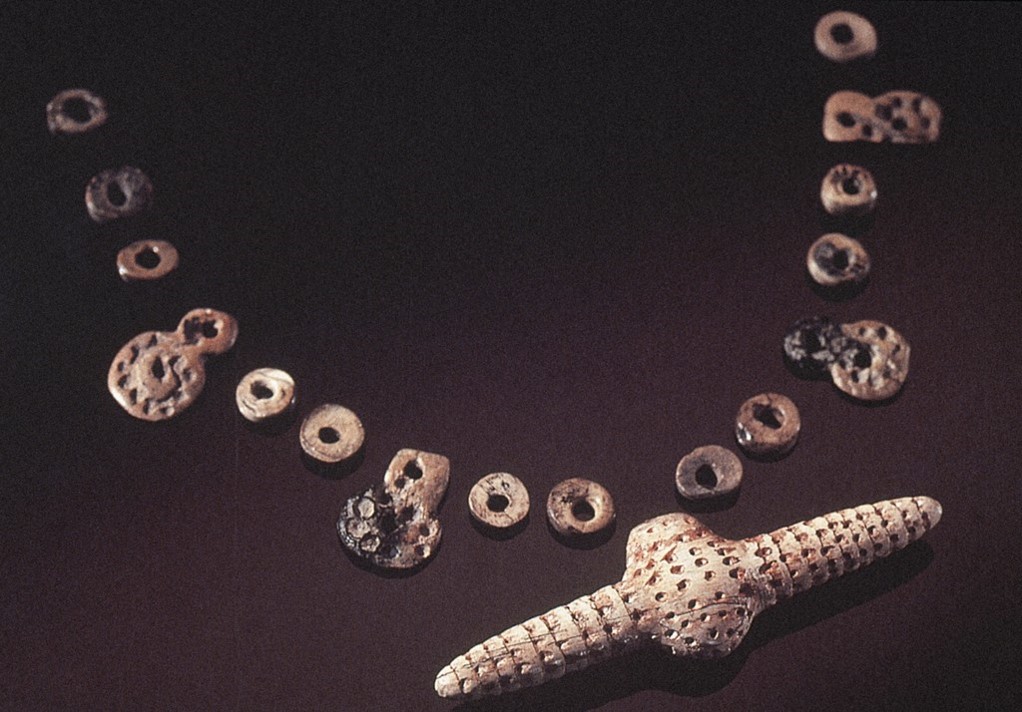
What is this? Suggests?
This is a mammoth ivory bead/pendant necklace found on an infant skeleton from 28,000-22,000 BCE, suggesting a sort of a ritual. They gave their nicest things to their children to bury them so they at least had something nice to carry with them.
Lower Paleolithic Dates
c. 2.6 million → 120,000 BCE1
Middle Paleolithic Dates
120,000BCE→40/35,000 BCE
Upper Paleoliothic Dates
40/35,000 BCE→14/10,000 BCE
Mesolithic Dates
14/10,000 BCE → 10/8,000 BCE
Pleistocene Dates (and peak! huge difference, low end of range)
2 million BCE-10,000 BCE, peak in 20,000 until 12,000 BC
Holocene Dates and is what?
Begins in 10,000 BCE and is the current era
Recognized in ____, the rock site in Canada is called _____, also known as Áísínai'pi is a sacred site in a mixed grassland prairie region on the northern edge of the Great Plains in Alberta. The Milk River Valley and several "coulees” dominate the topography of this cultural landscape, whose geological features include a concentration of ____ , with spectacular forms sculpted by erosion. The _____people (Siksikáítsitapi) have left engravings and paintings on the sandstone walls and landscape features, which bear witness to spirit messages. The landscape is considered to be sacred, and centuries-old traditions are perpetuated today in various ceremonies and in the respect in which the place is held.
2019, writing-on-stone, hoodoos, Blackfoot
Beginning of Human history, new mexico ancient footprints: findings, how they found it(method), significance and debate
Findings: They found old human footprints in New Mexico alongside large animals like mammoths. They found that they are 21,00-23,000 years old; much earlier than preconceived notions.
How: They dug into the ground to expose layers of old sediment and use radiocarbon dating on the seeds below these footprints
Significance: This shows that people coexisted with large ice animals in NA and challenges the idea that it was around 13,500 years ago.
Debate: Some argue that radiocarbon dating is not very accurate.
Footprints are a kind of evidence of behaviour often called a ____ fossil:
trace; geological evidence of biological activity
body fossils
fossilized remains from organism bodies
What can the sites of human footprints tell a scientist?
estimates of height, weight and gait as well as how many people made them.
features of the environment the footprints were formed (soft, hard, wet, dry?)
Aspects of environment that humans who made the footprints were living in, especially if left by other animals
-_____ Paleolithic or ____ Stone Age (2.6 million BCE - 120,000 BCE)
______ Paleolithic or ____ Stone Age (120,000 BCE – 40/35,000 BCE)
_____ Paleolithic or ____ Stone Age (40/35,000 BCE – 14/12,000 BCE)
______ Period (14/12,000 BCE - 10/8,000 BCE)
______ Period or Stone Age (2.6 million BCE -10,000 BCE)
______ Period or Modern (10,000 BCE-present)
Lower/early
Middle/Middle
Upper/Late
Mesolithic
Pleistocene
Holocene
The _____ geological epoch began around 2 million BCE and during that time the northern hemisphere was covered in glacial ice. The ice age peaked around 20,000 BCE during the ______ and lasted until 12,000 BCE during the ______ period. This ushered in the _____ epoch and the beginning of extensive human settlement. The art and visual culture of the ____ was strongly shaped by these environmental conditions.
A) Upper Paleolithic
B) Pleistocene
C) Stone Age
D) Mesolithic
E) Holocene
B - Pleistocene
A - Upper Paleolithic
D - Mesolithic
E - Holocene
C - Stone Age
Anatomically modern humans are:
Called Homo Sapiens Sapiens
only hominids to make art
Made objects that were useful and beautiful for practical and symbolic purposes
Were just like us
Killed off all the other hominids
1, 3, 4
The oldest evidence of human art and ingenuity comes from where?
Africa
Some scholars think cave art was created by and for who and why?
A variety of different humans for different reasons
What did the prehistoric cave art mean to thos who created them?
We dont know!
Experts strongly believe that the Woman (Venus) of Willendorf was made as a ____ ___ that helped women to become _____
fertility totem to help them become pregnant
In the past, experts believed that ____ cave art, was the pinnacle of paleolithic art. Yet recent discoveries in ___ and ___ have shown us that these earlier ideas were biased. Today, with the benefit of ____ and other dating technologies, we continue to expand the timeline of Pleistocene art. With new ____ and more open minds, experts are challenging old ideas about the evolution of human civilization.
Indonesia
Radio-carbon dating
Australia
archaeological evidence
European
-European
-Indonesia
-Australia
-Radio-carbon dating
-Archaeological evidence
The term "Pleistocene visual culture" is becoming popular with art historians, anthropologists, and archeologists because:
a. it de-centres the naturalistic style that many earlier experts saw as more aesthetically important
b. It is less Western-centric and more inclusive of other regions around the world
c. it better emcompasses the variety of mark-making, decorative practices, and artifacts made during this period
d. it places less importance on the temporal periods that are only applicable in certain parts of the world
All the above!