Ch. 14 Natural Radioactivity
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Natural Radioactivity, nuclear reactions, radiation measurements, half life, med app, nuclear fission and fusion
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
radioactivity comes from…
unstable nuclei
unstable nuclei are (1)…
found in C, H, and elements w/ atomic #’s 20+
Unstable nuclei are… (2)
defined as nuclei which nuclear forces can’t offset the repulsions between protons
Unstable nuclei are… (3)
radioactive, emitting small particles of energy called radiation to become more stable
Radiation may take form of…
alpha, beta particles, positrons, or pure energy like gamma rays
radioisotopes are… (1)
isotopes of an element that emits radiation
radioisotopes are… (2)
one or more isotopes of an element
radioisotopes are… (2)
including the mass number in its name
atomic symbol iodine-131 is a radioisotope with…
mass number 131 and atomic number 53
alpha particles are identical to…
a helium nucleus
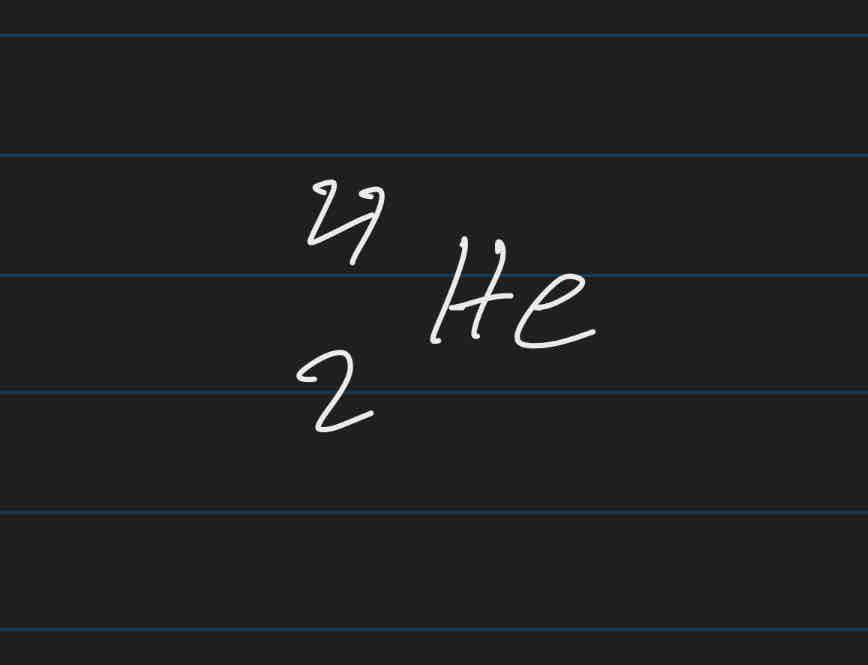
Beta particles
High energy electrons
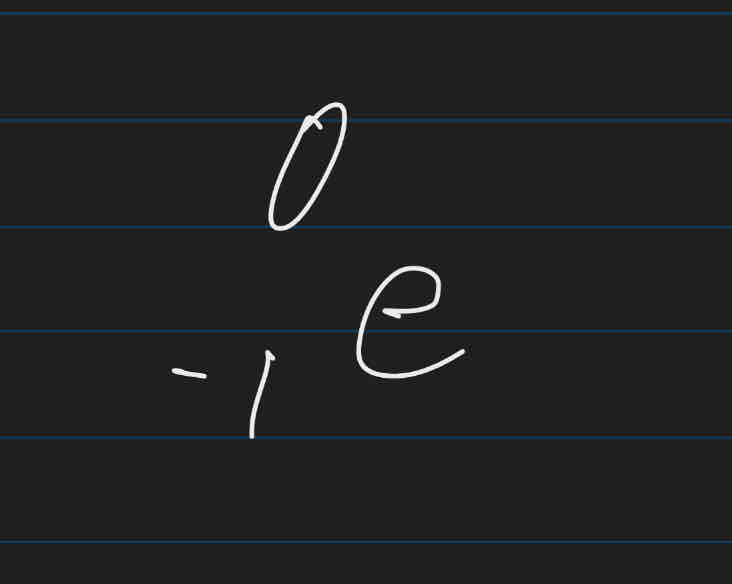
Positrons
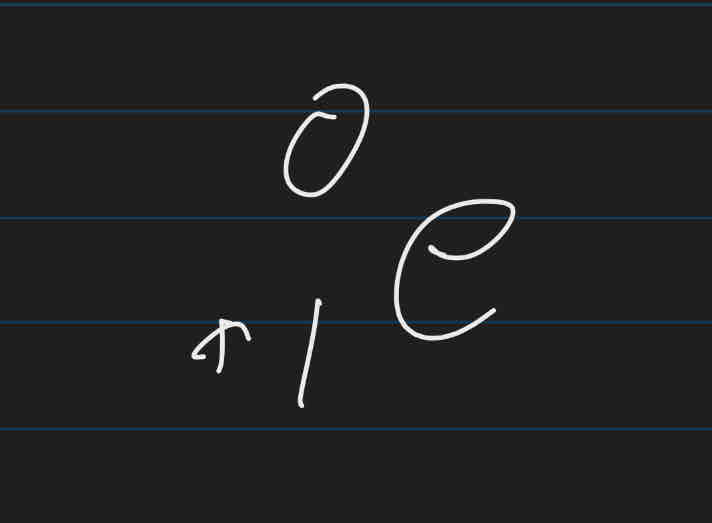
Gamma rays
Pure energy
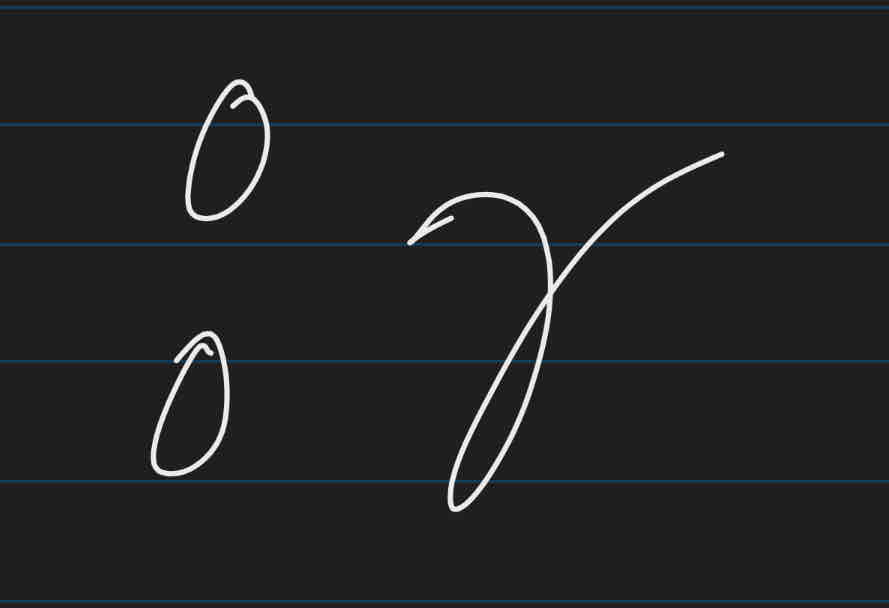
radioactive decay
nucleus breaks down by emitting radiation
alpha decay
form a new nucleus with a mass number decreased by 4 and atomic number decreased by 2
beta decay
mass number of new nucleus remains, atomic number increases by 1
positron emission
proton converted to neutron and positron, mass remains but atomic number decreases by 1
gamma radiation
energy emitted from unstable nucleus, numbers remain the same
radioactive isotopes are produced…
when stable nucleus convert to radioactive nucleus by bombarding it with small particles aka transmutation
Geiger counter
detects alpha, beta, and gamma rays, uses ions produced by radiation to create an electrical current
rem (radiation equivalent in humans)
measures alpha particles in the body, high-energy radiation, and gamma rays
alpha particles, if entered the body…
cause extensive damage in tissue
high-energy radiation causes…
more damage than alpha particle, includes beta particles, high-energy protons, and neutrons that travel into tissue
gamma rays cause…
damage bc they travel a long way through body tissue
biological damage (rem) =
absorbed dose (rad) x factor
activity
curie (Ci), becquerel (Bq)
Half-life
radioisotope’s time for radiation level to decay to one-half of OG value
decay curve
illustrates amount of time thats needed for one half of substance to be converted into a different element
nuclear fission
a large nucleus bombarded with a neutron making an unstable isotope
atomic energy
unstable isotope splits and release large amounts of energy
fusion reactions
occur at extremely high temps, combining small nuclei into large ones, release large amounts of energy