A1: Abdominal muscles
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANA124
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
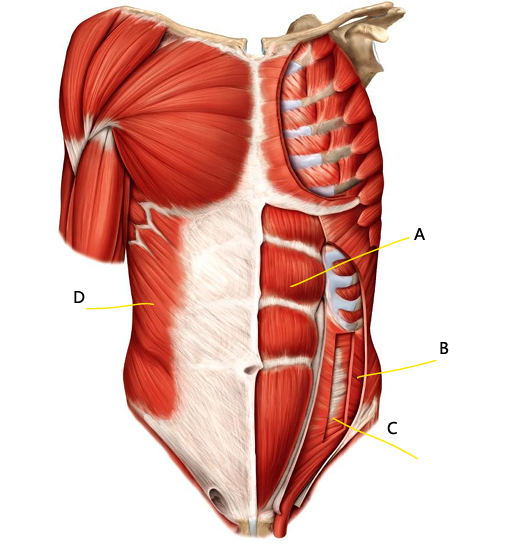
What is A?
rectus abdominis
What is B?
internal oblique
What is C?
transversus abdominis
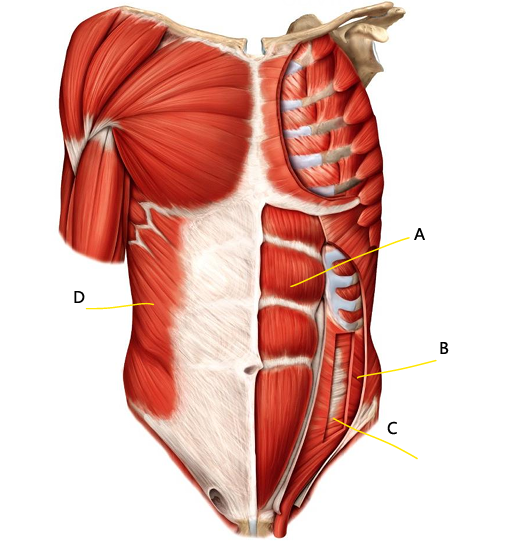
What is A?
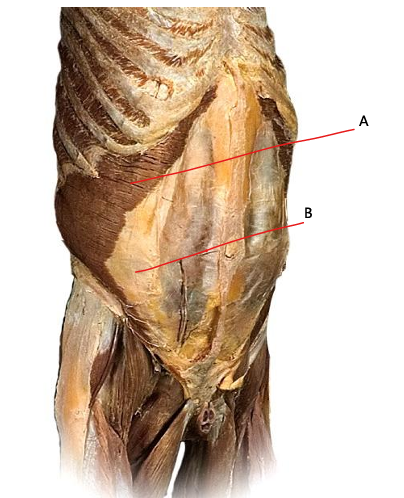
external oblique
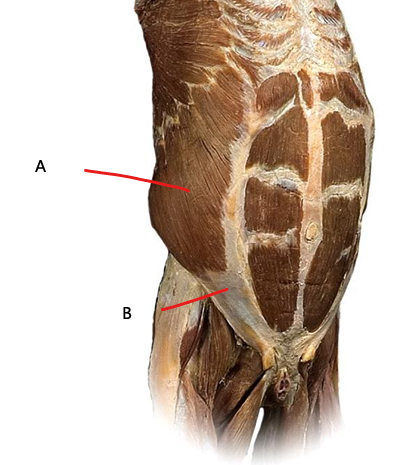
What is B?
aponeurosis of external oblique
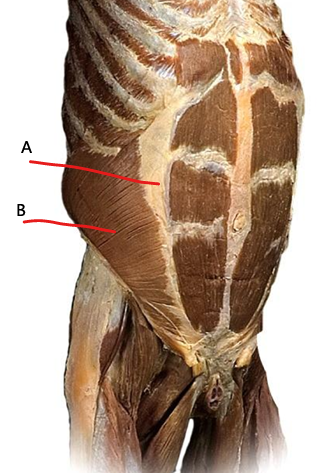
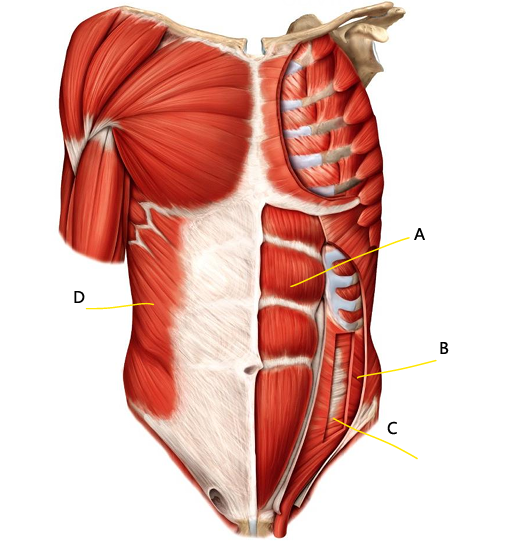
What is A?
aponeurosis of internal oblique
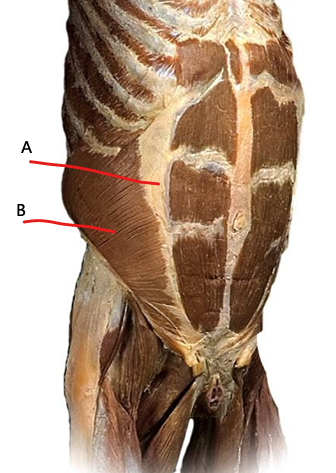
What is B?
internal oblique
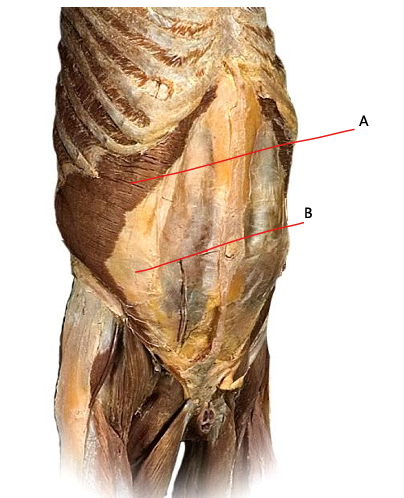
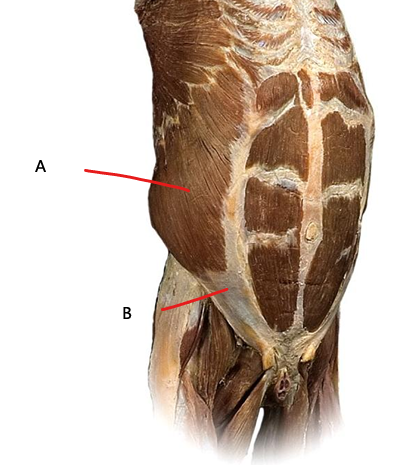
What is A?
transversus abdominis
What is B?
aponeurosis of transversus abdominis
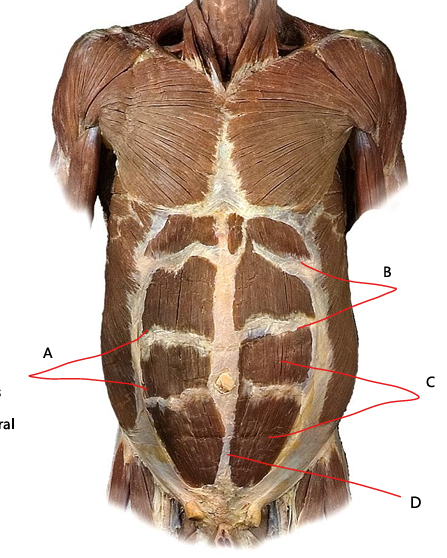
What is A
linea semilunaris
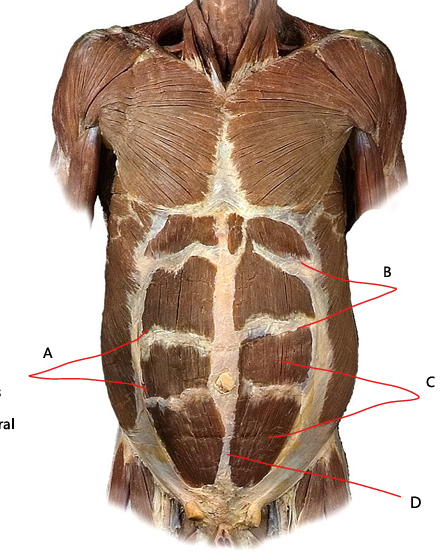
What is B
tendinous intersections
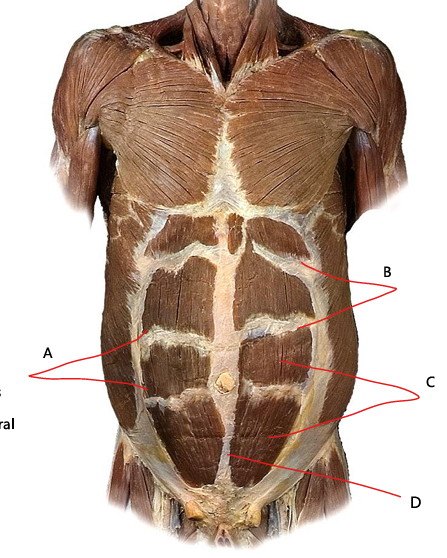
What is C
rectus abdominis
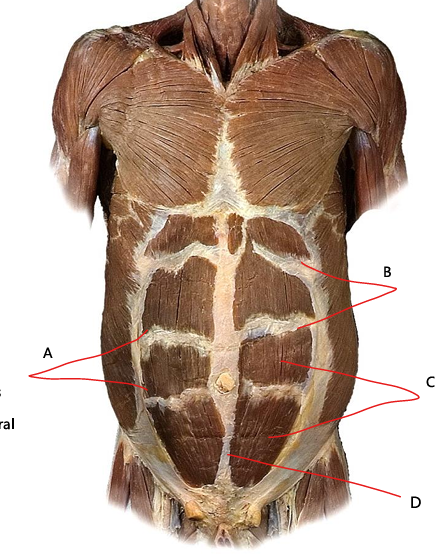
What is D?
linea alba
location of linea alba
vertical line formed by right and left sheath meeting in the middle
location of linea semilunaris
the most lateral edge of rectus sheath/abdominis
external oblique origin
lower 8 ribs
insertion of external oblique
iliac crest and linea alba
unilateral action of external oblique
rotation and side flexion
bilateral action
flexion of lumbar spine
innervation of external oblique
thoracic spinal nerves
internal oblique origin
lumbodorsal fascia, iliac crest, lingual ligament
insertion of internal oblique
costal cartilages of last 3 ribs, linea alba
unilateral action of internal oblique
rotation and side flexion
bilateral action
flexion of lumbar spine
innervation of internal oblique
thoracic spinal nerves
transversus abdominis origin
lower 6 CC, lumbodorsal fascia, iliac crest, inguinal ligament
insertion of transversus abdominis
linea alba
transversus abdominis actions
increase abdominal pressure, support back
innervation of transversus abdominis
thoracic spinal nerves
rectus abdominis origin
pubic crest
insertion rectus abdominis
costal cartilages 5-7 and xiphoid process
rectus abdominis actions
flexion of lumbar spine and compress abdominal contents
function of tendinous interactions
allows you to do more refined flexion ie. belly dancing
3 layers of rectus abdominis muscle
external oblique, internal oblique 1/2, transversus abdominis muscle
location of lingual ligament
attached btw public tubercle and anterior superior iliac spine
lingual canal function
passage way for spermatic cord/round ligaments of uterus to pass through.
deep ring
deficit in the transversalis fascia
superficial ring
opening in the fibers of external oblique muscle
peritoneum
lining of abdominal wall
greater omentum
double layer of visceral (covers organs)
lesser omentum
peritoneum from stomach to transverse colon
mesentery:
double layer from stomach to liver