Ch. 3: Igneous Rocks. the Origin and Evolution of Magma, and Intrusive Activity
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
magma
creating by melting of rock above a subduction zones or oceanic ridges - molten rock
magma consist of
liquid (ions of elements), solid
(crystals of silicate), and gaseous components (water
vapor, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide)
rock
naturally formed, consolidated materials usually composed of grains of one or more minerals
rock cycle
rock and minerals are changing through time, driven by internal and external heat engines of E in a sort of equilibrium
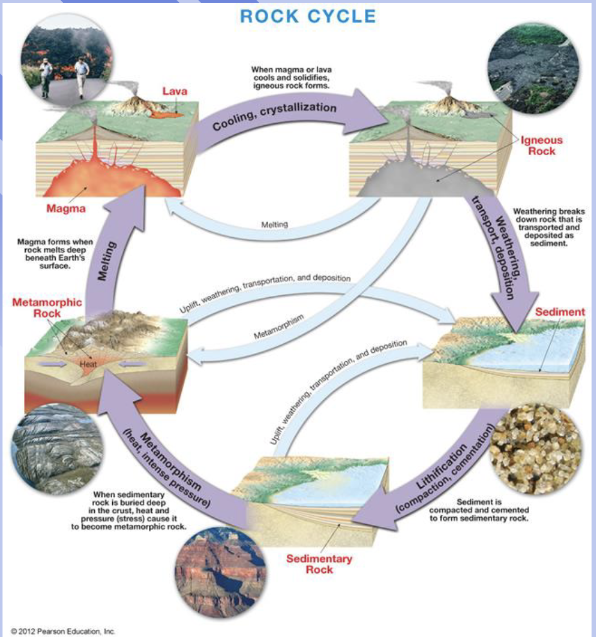
What Makes the cycle move
The cycle begins with magma
» Magma forms from melting Earth’s crust and upper
mantle
» Less dense magma rises toward the surface
» Over time magma cools and solidifies – crystallization
» This can be beneath the surface (extrusive) or following a
volcanic eruption, at the surface (intrusive igneous rock)
igneous rock
less dense magma rises and cools
What is weathering
The process that breaks down rocks and minerals into smaller pieces through physical, chemical, or biological means.
igneous rock exposed @ surface get weathered into
sediment
lithification
the process of converting sediment into solid rock through compaction and cementation.
Sediments transported to low areas are buried and hardened into
sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rock heated and squeezed at depth to form
metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock may heat up and melt to form
magma
igneous rock: intrusive
when magma solidifies underground = ex:granite
igneous rock: extrusive
when magma solidifies @ (on) E's surface (lava) = ex:basalt
Convergent Plate Boundary
where two tectonic plates collide, often leading to subduction and volcanic activity. This boundary is characterized by the descent of one plate beneath another, resulting in the formation of mountains, trenches, and associated igneous activity.
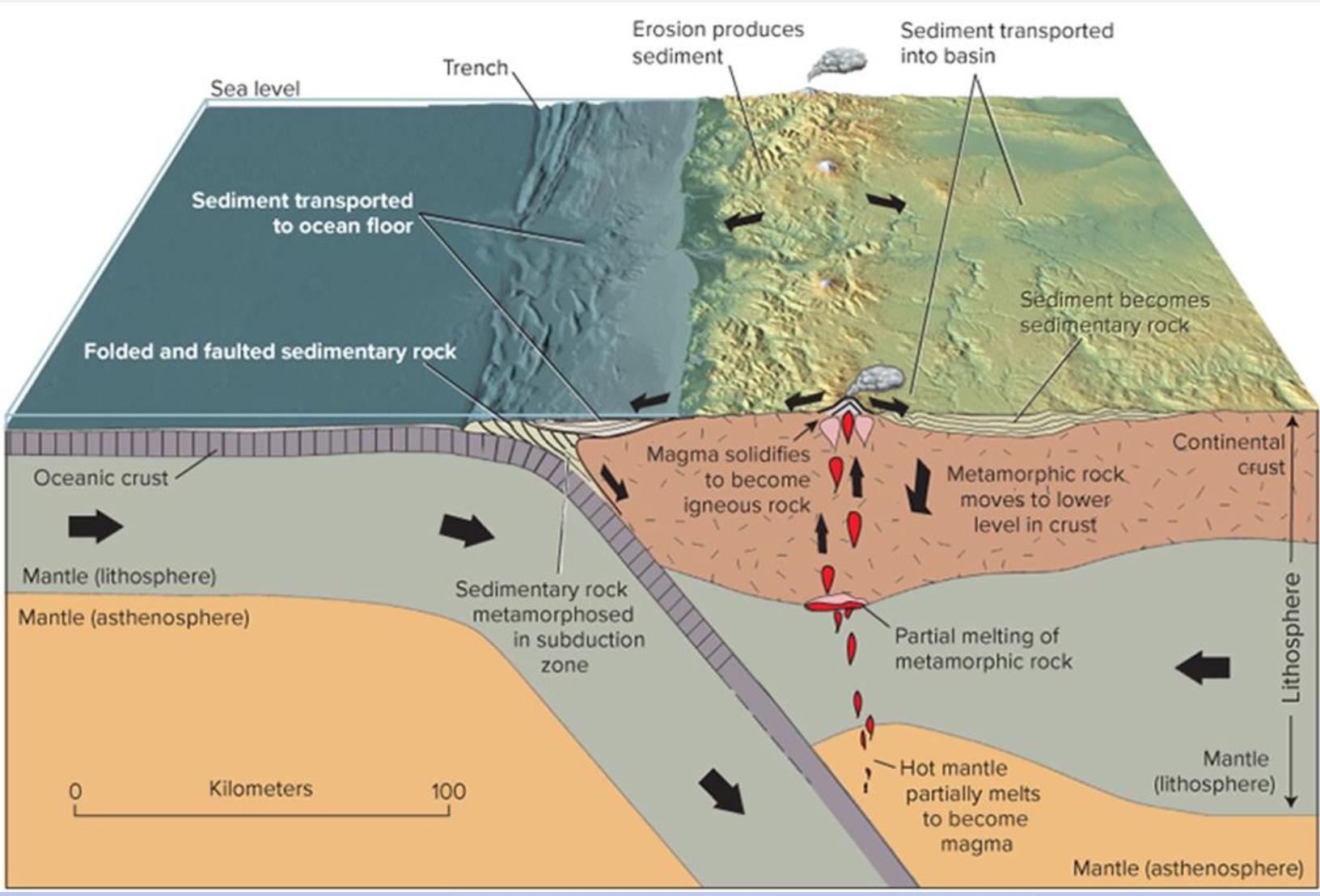
Rock cycle at a convergent plate boundary
Magma forms in melting zone above
subduction zone
Magma migrate upwards to surface
Eruption at surface, solidified into igneous
Exposed rock subjected to weathering
Sediment transported, deposited, lithify into
sedimentary rock
Tectonic forces push it deeper, and deeper
Heat and pressure causes sedimentary rock to
recrystallize to for metamorphic rock
As metamorphic rock is push deeper, may get
to the zone of melting – magma produced
The magma produced rises, erupt as a to the
surface, completing the cycle
Rate of Cooling SLOW
results in larger crystal sizes in igneous rocks. This occurs during the slow solidification of magma beneath the Earth's surface, allowing time for crystals to grow. (>1mm)
Rate of Cooling FAST
results in smaller crystal sizes in igneous rocks. This occurs when lava cools quickly on the Earth's surface, not allowing sufficient time for crystal growth. (<1mm)**
randomly distributed atoms
in solidified lava. This structure forms when cooling occurs so rapidly that there is no opportunity for atomic arrangement, resulting in a glassy texture.
chemical composition
refers to the specific elements and compounds that make up an igneous rock. It influences the rock's properties, behavior during crystallization, and overall classification.
Texture
refers to the size, shape, and arrangement of crystals in an igneous rock, which can vary based on the rate of cooling and the environment of formation.
Crystalline Rocks
made up of interlocking
crystals (e.g. quartz and feldspar). Size of grain or
crystal determine by rate of cooling & viscosity
Glassy Rocks
composed primarily of glass and
contain few, if any, crystals
Fragmental Rocks
composed of fragments of igneous material
Crystalline Rocks Types
Aphanitic and Phaneritic
Aphanitic
describes a type of igneous rock with a fine-grained texture, where individual crystals are not visible to the naked eye, typically formed from rapid cooling of lava.
Phaneritic
A type of igneous rock characterized by a coarse-grained texture, where mineral crystals are large enough to be seen with the naked eye.
Crystalline Rocks Textures
Pegmatitic and Porphyritic
Pegmatitic
describes an igneous rock texture that features exceptionally large crystals, typically formed from slow cooling in a magma chamber.
Porphyritic
A type of igneous rock texture characterized by large crystals, called phenocrysts, embedded in a finer-grained or glassy matrix, indicating varied cooling rates during formation.
phenocrysts
with the larger —————— having formed first during slow
cooling underground
groundmass
the smaller —————— forming during more rapid cooling at the Earth’s surface
Glassy Textures
Glassy and Vesicular texture
Glassy
contains no crystals at all and is formed by extremely rapid cooling of the magma. ex Obsidian
Vesicular texture
contains cavities (vesicles) in extrusive rocks resulting from gas bubbles that were in the lava. Scoria and pumice are examples. ex Pumice
Fragmental Texture
Pyroclastic Texture
Pyroclastic Texture
Debris such as ash, pumice, or crystalline rock fragments consolidate(accumulate and are cemented) to form new rock. Tuff (small) and Volcanic Breccia (large) are examples of rocks formed from explosive volcanic eruptions.
granite: intrusive igneous
cool slowly deep beneath E's surface and are typically coarse-grained (most crystal >1mm)
basalt: extrusive igneous
cools quickly @ or near E's surface and are typically fine-grained (most crystals <1mm) -often w/vesicles or not shown
silica (SiO2) contents
determines mineral contents and general color of igneous rocks
felsic (silicic)
- >65% silica
-contains light-colored minerals high in silica, Al, Na, K
-ex: intrusive/extrusive = granite (coarse) /rhyolite (fine)
intermediate rock or andesitic
- 55% and 65 % silica
-have silica contents between mafic and felsic rock
-ex: intrusive/extrusive = diorite (coarse) /andesite (fine)
mafic rock
- 45% and 55% silica
-contains dark-colored minerals high in (magnesium, iron, and calcium)
- gabbor (coarse) /basalt (fine)
ultramafic
- <45% silica by weight
-composed of almost entirely of dark-colored ferromagnesian materials
-ex: extrusive = peridotite (coarse) /komatiite (fine)
3 ways to identify Igneous Rocks
Extrusive Intrusive Composition and Texture
intrusive rocks exist in bodies or structures that penetrate or cut through pre-existing
country rock
two types of intrusive rock bodies
shallow and deep intrusive
intrusive bodies
are given names based on their size, shape and relationship to country rock
Shallow intrusions
-Form <2 km beneath Earth's surface
-Chill and solidify fairly quickly in cool country rock
-Generally composed of fine-grained rocks
Deep intrusions: Plutons
-Form at considerable depth bneath E's surface when rising blobs of magma (diapirs?) get trapped w/in the crust
-Crystallize slowly in warm country rock
-Generally composed of coarse-grained rocks
three types of shallow intrusives
volcanic necks, dikes, and sills
shallow intrusive: volcanic necks
formed when magma solidifies in throat of volcano
shallow intrusive: dikes
tabular intrusive structure that cuts across any layering in country rock (not parallel to any layering) - are discordant
shallow intrusive: sills
Tabular intrusive structure that parallels layering in country rock - are concordant
two types of deep intrusives
plutonic rocks and plutons
plutonic rock
igneous rocks that crystallize at great depths >several kilometers, coarse grained, slow cooling
two types of plutons
stocks and batholiths
plutons
large, irregular shaped discordant igneous bodies. Commonly granitic
plutons: stocks
small plutons with <100 sq. km of exposed area
plutons: batholiths
large plutons or group of plutons w/outcrop area >100 sq. km.
how magma forms
from minerals being melted
conduction
the transfer of heat through direct contact between materials.
convection
the transfer of heat through fluid motion, causing magma to rise and cool.
Decompression Melting
is the process where a decrease in pressure allows magma to form from solid rock without the addition of heat.
how magma forms :two type of minerals being melted
heat for melting rocks and geothermal gradient & partial melting
heat for melting rocks
heat moves upward (by conduction and convection) from the very hot (>5000°C) core through the mantle and crust
geothermal gradient & partial melting
This is the rate @ which temperature increases w/increasing depth bneath the surface (about 3⁰C per 100 meters = 30⁰C/km).
how magma forms: Factors that Control Melting Temperatures (2)
1. Pressure (decompression melting...in mantle @ spreading ridges - partial melting of mantle peridotite)
2. Hot water under pressure (flux melting) at subduction zone
Pressure (decompression melting...in mantle @ spreading ridges - partial melting of mantle peridotite)
Melting point of minerals increases w/increasing pressure
Hot water under pressure (flux melting) @ subduction zones
Water bcomes increasingly reactive @ higher temps. @ sufficient pressures and temps., highly reactive water vapor can reduce the melting point of rocks by over 200°C
Bowen's Reaction Series
sequence in which minerals crystallize from a cooling basaltic magma
How Magmas of Different Compositions Evolve by the processes
differentiation, assimilation, magma mixing, and partial melting
differentiation
the changing of magma composition by the removal of denser early-formed ferromagnesian minerals by crystal settling
assimilation
occurs when a hot magma melts and incorporates surrounding country rock = changing the chemical composition of the magma
magma mixing
-involves mixing of silica and mafic magma to make intermediate composition
-bcuz of their significant temp. differences, two magma not mixed throughly -> end up w/blobs of finer grained gabbro included in the felsic magma
-but the intrusion has an overall intermediate composition
partial melting
Only part of the rock melts... Under increasing temp. a rock will bgin to melt in a sequence progressing upward through Bowen's reaction series
igneous activity
occurs primarily @ or near tectonic plate boudaries
mafic igneous rocks formed
-commonly @ divergent
-decompression melting: increased heat flow and decreased overburden pressure produce mafic magmas from partial melting of the asthenosphere @ 50km depth
intermediate igneous rock formed
-commonly @ convergent
-partial melting of basaltic oceanic crust produces intermediate magmas
flux melting
happens @ convergent and the subducted oceanic crust releases water into the overlying asthenosphere, lowers its melting temp.
Crystal Settling
is a process where denser crystals formed from cooling magma sink to the bottom of the magma chamber, which can lead to the differentiation of the magma composition.
Mafic magmas
are typically hotter than felsic magmas.
Felsic magmas
are typically formed when mafic (basaltic) magma undergoes
magmatic differentiation
Mantle Plume
is a column of hot rock rising from deep within the mantle, leading to volcanic activity at the surface.
diapir
A type of rock formation where magma rises through the Earth's crust, causing the overlying rock layers to rise and fold.
phenocryst
a large crystal embedded in a finer-grained matrix of an igneous rock, indicating slow cooling.
porphyritic
describing an igneous rock texture characterized by large crystals (phenocrysts) surrounded by a finer-grained groundmass, indicating a complex cooling history.
Chill Zone
the area of an igneous rock where the temperature drops rapidly, typically around the edge of a magma body, resulting in finer-grained texture.