Chemistry-Corrosion
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Redox
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Corrosion
When an uncombined metal decomposes into one of its more stable compound
Condition/ requirement for corrosion
Metal surface free from protective films e.g paint/oil
Suitable oxidising agent present
something high on the SRP table
Solution containing ions for conducting charge
Chemical formula for rust
Fe2O3.H2o
Products of corrosion
Soluble products
Sparingly soluble products
Soluble products
readily dissolve and washed away leaving holes or pits in the metal
Sparingly soluble products
Form layers which are not washed away
2 types
Coherent coatings - stay in one piece to form a continuous coating on the metal surface (Zn&Al in air) This stops further corrosion i.e protective coatings such as Al2o3 on Al (uniform coating of Al2o3 on Al)
Incoherent coatings - flaky powdery or peel off the metal surface e.g the oxidation of Fe2+. Corrosion can occur below this layer
Al and Mg are _________
Strong reducing agents with high oxidation potential value, so in the presence of suitable oxidising agent such as o2 in the presence of h2o, these metals readily undergoes oxidation to produce Al3+ and Mg2+ respectively
Instead of corrosion use ______
Oxidation of metal
Formation of rust requires____?
iron
oxygen
presence of water
Rust is composed of ___? Chemical formula
hydrated iron(III) oxide - Fe2o3.nH2o
Initial oxidation of iron equations
Oxidation of iron at the anodic site
Reduction of o2 in acidic or non acidic conditions
Precipitation of Fe(OH)2

Further reduction of Fe(OH)2

Dehydration of Fe(OH)3

Prevention of corrosion
Surface protection
Plating with metal that has a lower oxidation potential
Sacrificial anodes
Cathodic protection
Surface protection
prevents o2 or h2o from being in direct contact with iron
Less reactive
Weaker reductant/ reducing agent
Plating with a weaker reductant than Fe
weaker reductant has lower oxidation potential and does not get oxidised easily
a scratch on the surface will lead to an increase in the rate of oxidation than uncoated Fe
Sacrificial anode
Galvanising (plating with zn)
connecting the iron to a piece of metal that is a stronger reductant than iron
Can be easily replaced after consumed using a wire
Ships hull/ buried pipes
Why isn’t Na, Ba, Ca or K used as a sacrificial anode
Oxidise too rapidly, depleting themselves before effectively protecting the metal structure
Sacrficial anode definition
it is a piece of metal that is connected to Fe that has higher oxidation potential than the metal being protected from oxidation and so oxidises in preference to the metal being protected
iron/steel to be protected, connected by a conducting wire to a stronger reductant than Fe
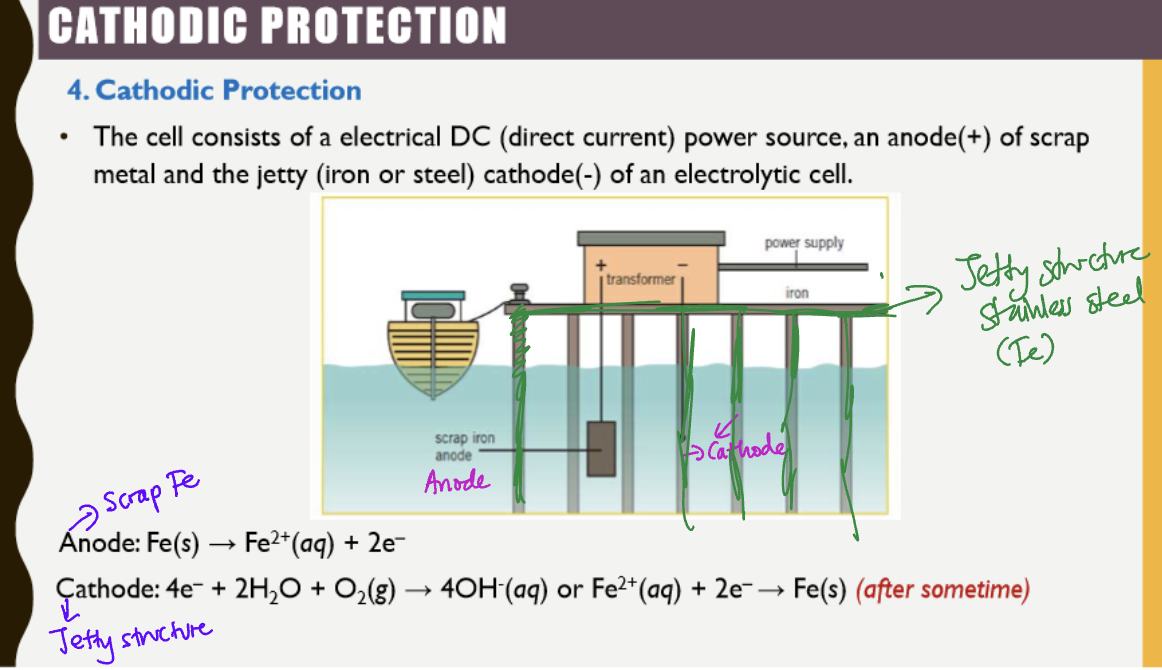
Cathodic protection requirements
electrical DC current power source
Anode of scrap metal (+ve)
Jetty (cathode of electrolytic cell)
Cathodic protection
Fe structure is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply making it the cathode in an electrochemical cell preventing the oxidation of Fe in jetty structure
at cathode, O2 is reduced in the presence of h2o and forms OH-
iron scrap is connected to the +ve terminal of the power supply made as anode
Acts as an electrolytic cell
Non-spontaneous reaction
Iron scrap
refers to discarded iron metals like old railways
What would happen if a lower oxidation potential than Fe was used for cathodic protection?
Higher voltage will be required to provide a potential difference in the electrode potential value
If higher voltage not used
the iron to be protected will undergo oxidation at a faster rate due to positive p.d in electrical potential
the purpose of a conducting wire during sacrificial anode
to provide a path for electron flow
Cathodic protection equations