Zahin, Nailah- APWH Unit 6 Flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:24 AM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
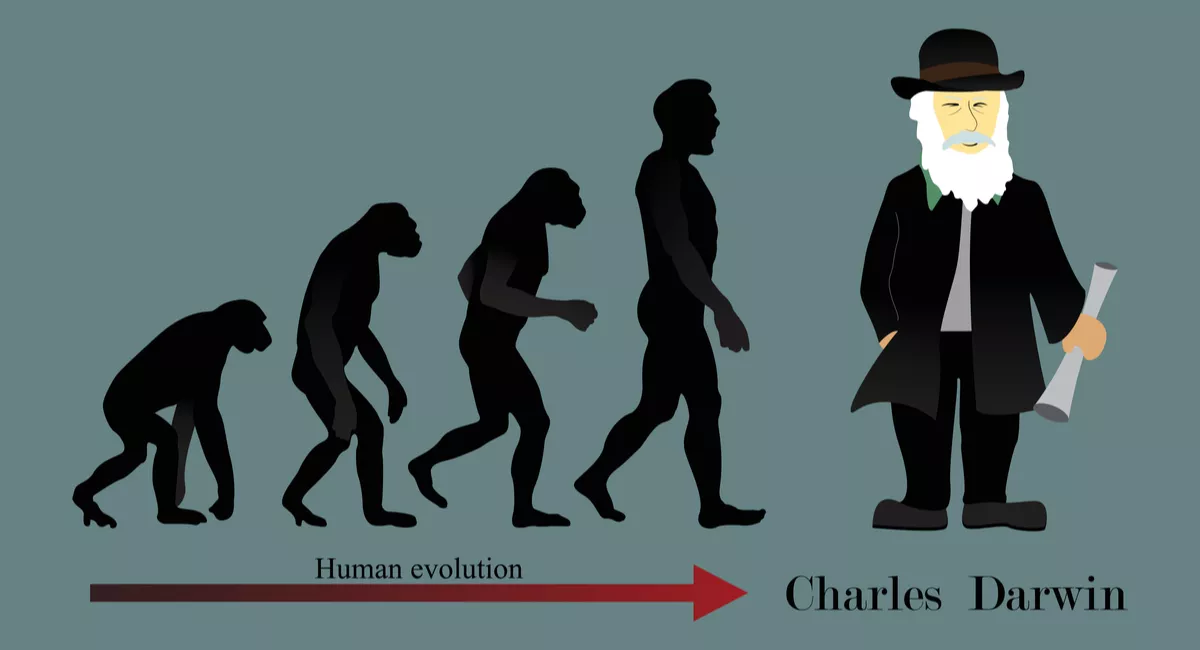
Social Darwinism 6.1
Social Darwinists believe in “survival of the fittest”—the idea that certain people become powerful in society because they are innately better.
1) Social Darwinism justified European Imperialism by allowing them to believe their superiority in the human race
1) Social Darwinism justified European Imperialism by allowing them to believe their superiority in the human race
2
New cards
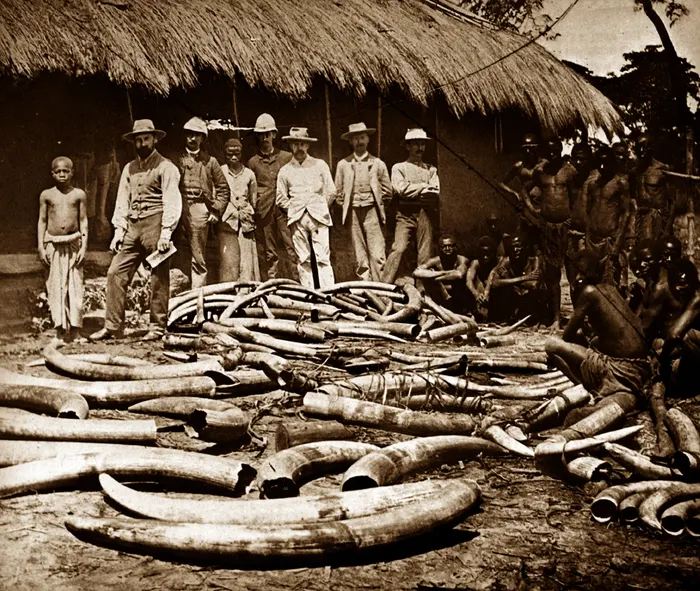
Belgian Congo 6.2
The Belgian Congo was a Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960.
2) State power during the Scramble for Africa shifted from the African leaders to European imperialism at the justification of social darwinism
2) State power during the Scramble for Africa shifted from the African leaders to European imperialism at the justification of social darwinism

3
New cards
Berlin Conference 6.2
The Berlin Conference marked the climax of the European competition for territory in Africa, a process commonly known as the Scramble for Africa.
2) The Berlin Conference shifted power from the African state into the divided and competitive hands of Western powers
2) The Berlin Conference shifted power from the African state into the divided and competitive hands of Western powers

4
New cards
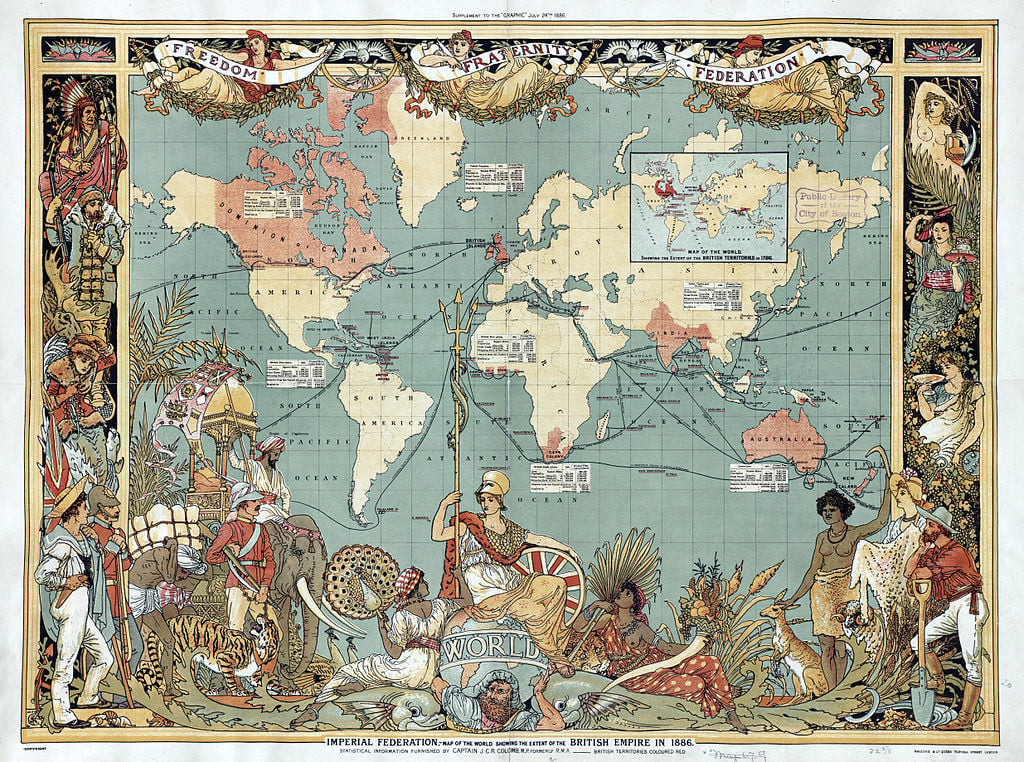
Settler Colonies 6.2
Settler colonialism is a type of colonialism in which foreign settlers move to and permanently reside on land already inhabited by Indigenous residents
2) Settler colonies are a type of imperialism in which power of a state goes from those of native residents to the foreign powers
2) Settler colonies are a type of imperialism in which power of a state goes from those of native residents to the foreign powers
5
New cards
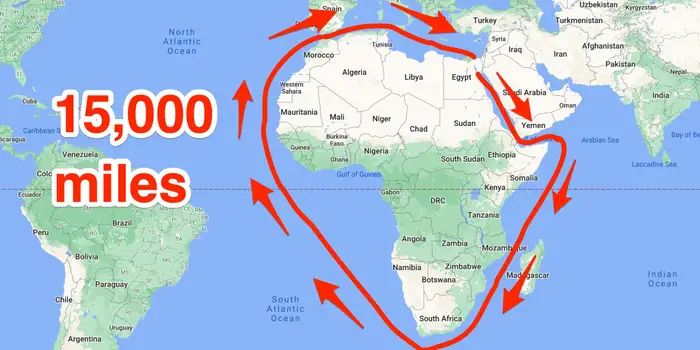
Suez Canal 6.2
The Suez Canal is a man-made waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea
2) The Suez canal, previously used by Asian countries for passage, was conquered by the British and shifted a large economical advantage into European control.
2) The Suez canal, previously used by Asian countries for passage, was conquered by the British and shifted a large economical advantage into European control.
6
New cards
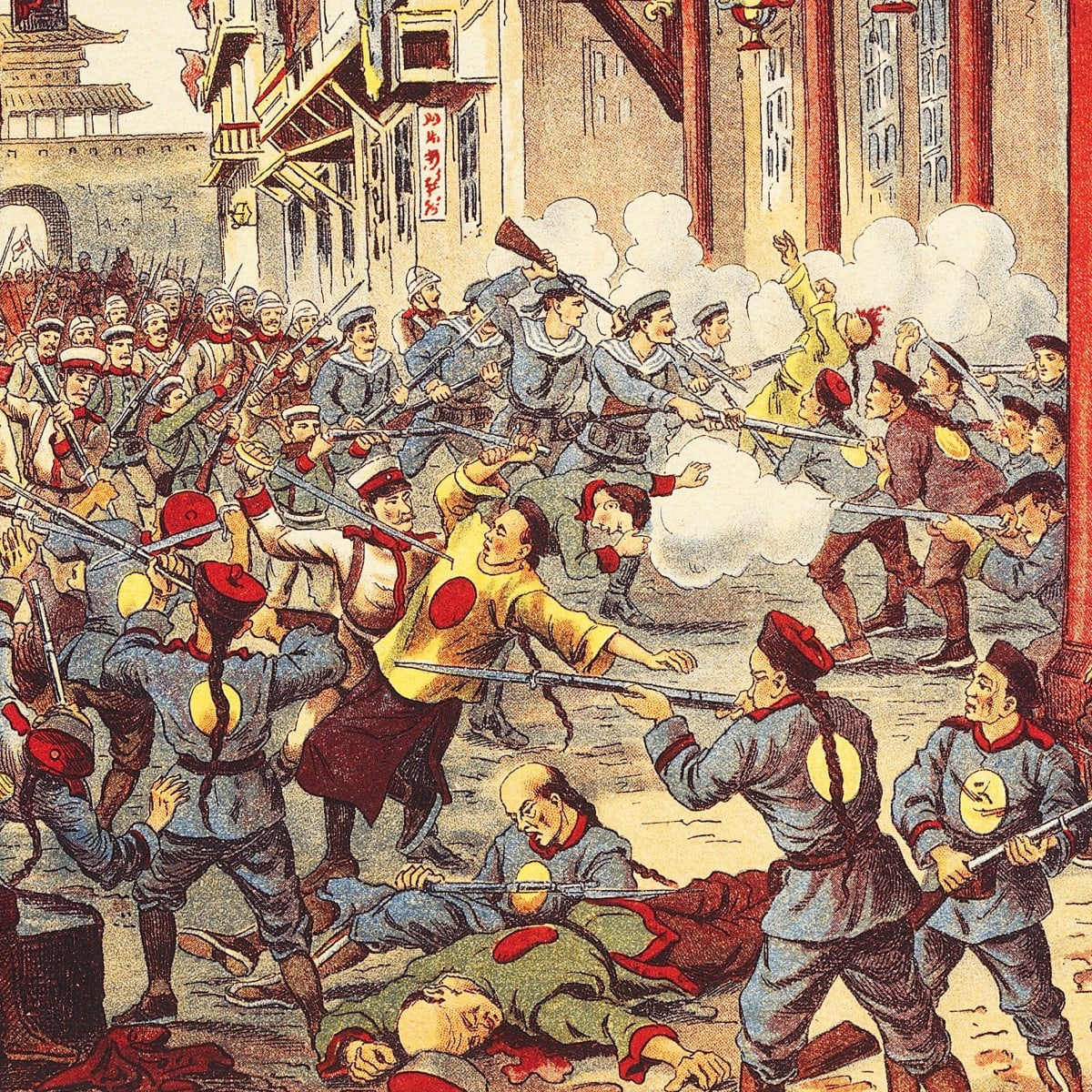
Boxer Rebellion 6.3
The Boxer Rebellion was an uprising against foreigners that occurred in China begun by peasants but eventually supported by the government.
3) The Boxer rebellion led to a weakened state of the Qing Dynasty and led to the end of the dynastic cycle with the Republic of China being developed.
3) The Boxer rebellion led to a weakened state of the Qing Dynasty and led to the end of the dynastic cycle with the Republic of China being developed.

7
New cards
Creation of Zulu Kingdom 6.3
Military campaigns resulted in widespread violence and displacement, and after defeating competing armies and assimilating their people, Shaka established his Zulu nation.
3) Internal rebellions in the african kingdoms influenced state building by the creation of the zulu kingdom through migrations of tribes and local leaders
3) Internal rebellions in the african kingdoms influenced state building by the creation of the zulu kingdom through migrations of tribes and local leaders

8
New cards
Indian Rebellion of 1857 6.3
Indian Mutiny, also called Sepoy Mutiny was a widespread but unsuccessful rebellion against British rule in India led by the Sepoy peasants.
3) The Sepoy rebellion led to European state building with external conflicts to imperialism with the shift from indirect to direct control of the political state of India
3) The Sepoy rebellion led to European state building with external conflicts to imperialism with the shift from indirect to direct control of the political state of India

9
New cards
Tupac Amaru Rebellion in Peru 6.3
The Rebellion of Túpac Amaru II was an uprising by mestizo rebels aimed at overthrowing Spanish colonial rule in Peru.
3) The natives’ rebellions on Spanish imperialism led to a colonial standpoint of future rebellions and reshaped colonial Peru for the indigenous community
3) The natives’ rebellions on Spanish imperialism led to a colonial standpoint of future rebellions and reshaped colonial Peru for the indigenous community

10
New cards
Xhosa Cattle Killing Movement 6.3
the Xhosa, a South African people, slaughtered roughly four hundred thousand of their own cattle to drive out British imperialist powers in the kingdom
3) Xhosa cattle killing both internally and externally destroyed the Xhosa kingdom through deaths and famine after the rebellion and destruction of stable nourishment.
3) Xhosa cattle killing both internally and externally destroyed the Xhosa kingdom through deaths and famine after the rebellion and destruction of stable nourishment.

11
New cards
Export Economy 6.4
Exporting is the practice of producing a good or service in one country and selling it to consumers in another country
4) Environmental factors such as the proximity to natural resources and water passages allowed for the accessible cross country exportation system
4) Environmental factors such as the proximity to natural resources and water passages allowed for the accessible cross country exportation system

12
New cards
Economic Imperialism 6.5
Economic imperialism is using economic means to influence or control a foreign country or territory
5) Economic imperialism including the transnational corporations grew the global economy by expanding the market for exportations and manufacturing
5) Economic imperialism including the transnational corporations grew the global economy by expanding the market for exportations and manufacturing

13
New cards
Opium Wars 6.5
The Opium Wars were two conflicts waged between China and Western powers during the mid-19th century over the illegal selling of British imported Opium in China’s economy.
5) The Opium Wars contributed to the global economy by providing a further method of British economic imperialism and trade market
5) The Opium Wars contributed to the global economy by providing a further method of British economic imperialism and trade market

14
New cards
Chinese and Indian Indentured Servitude 6.6
The Indian and Chinese indenture system transported millions of Indians and Chinese to various colonies of European powers to serve as an intensive work force.
6) While the plantation economy grew and the need for raw materials progressed, indentured servitude was used to sustain the agriculture
6) While the plantation economy grew and the need for raw materials progressed, indentured servitude was used to sustain the agriculture

15
New cards
Migrant Workers 6.6
A migrant worker is a person who migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work
7) Migrant workers were required in parts of the industrialist world and led to large waves migration to sustain the economy of manufacturing and exportations
7) Migrant workers were required in parts of the industrialist world and led to large waves migration to sustain the economy of manufacturing and exportations

16
New cards
Chinese Exclusion Act 6.7
The Chinese Exclusion Act was a United States law prohibiting all immigration of Chinese laborers for 10 years.
8) Migration affected the society of receiving societies as citizens were threatened by the foreign presence and the availability of jobs and resources
8) Migration affected the society of receiving societies as citizens were threatened by the foreign presence and the availability of jobs and resources

17
New cards
Ethnic Enclave 6.7
An ethnic enclave is an area with high ethnic concentration and groups of similar cultures in a secluded area
8) Ethnic enclaves included groups of people that remained and spread their culture, creating many syncretic foods and social groups
8) Ethnic enclaves included groups of people that remained and spread their culture, creating many syncretic foods and social groups

18
New cards
White Australia Policy 6.7
The White Australia policy is a term encapsulating a set of historical policies that aimed to forbid people of non-European ethnic origin from immigrating into Australia.
8) Migrations affected the receiving societies and promoted anti-immigration acts and increased acts of racism toward non-white groups of people
8) Migrations affected the receiving societies and promoted anti-immigration acts and increased acts of racism toward non-white groups of people
