Chapter 7
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Valance Electrons are
Electrons that reside in the outermost shell of a atom
how do you find the Valance electrons
Main group is found on the group number of PT
how do you find the Valance electrons for transition metals
e- in the last and d-subshels are counted as VE unless the d-subshell is full. if the 3d shell is not full then counted but if at 10 then shell before is counted
How do you find the Valance Electrons for main group elements
group number on PT ex: halogens = 7VE
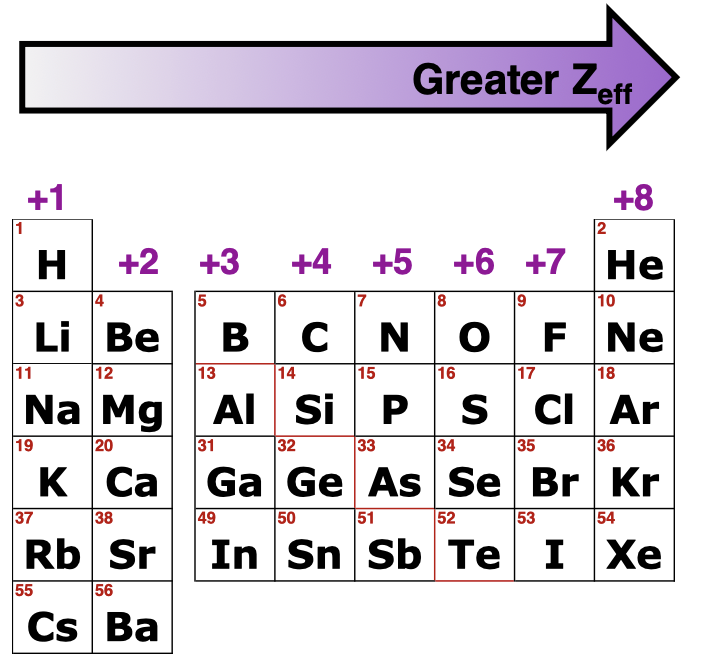
Effective Nuclear Charge (Zeff) is what
electrons, protons, how the charges interact. how the net positive charge that an electron “sees” from the nucleus.
How are VE and e- interact
VE shield from nucleus by core electrons
how are e- reacting to other e-
the e- are going to be repulsed by other e-
how are e- and protons in the nucleus
e- are attracted by p+ in the nucleus
How are VE and other VE interact
VE shield other VE (only weakly)
What do you calculate Zeff
Zeff= Z(number of protons)-S(shielding factor core electrons)
VE in mg calculate the Zeff
Z-S= 12 protons - 10 core electrons) = +2 (actual Zeff is +3.3)
Trends for Zeff (Z-S) (Z protons - S shielding factor)
Increases Left to Right across the row and small increase Top to Bottom
Number of core e- (s) stays the same but the p+ (Z) increases, Z-S is the same down a group but larger electron cores don’t shield as well
Atomic Radius (Size) is what
Distance from Center of the nucleus to the outermost VE in an atom
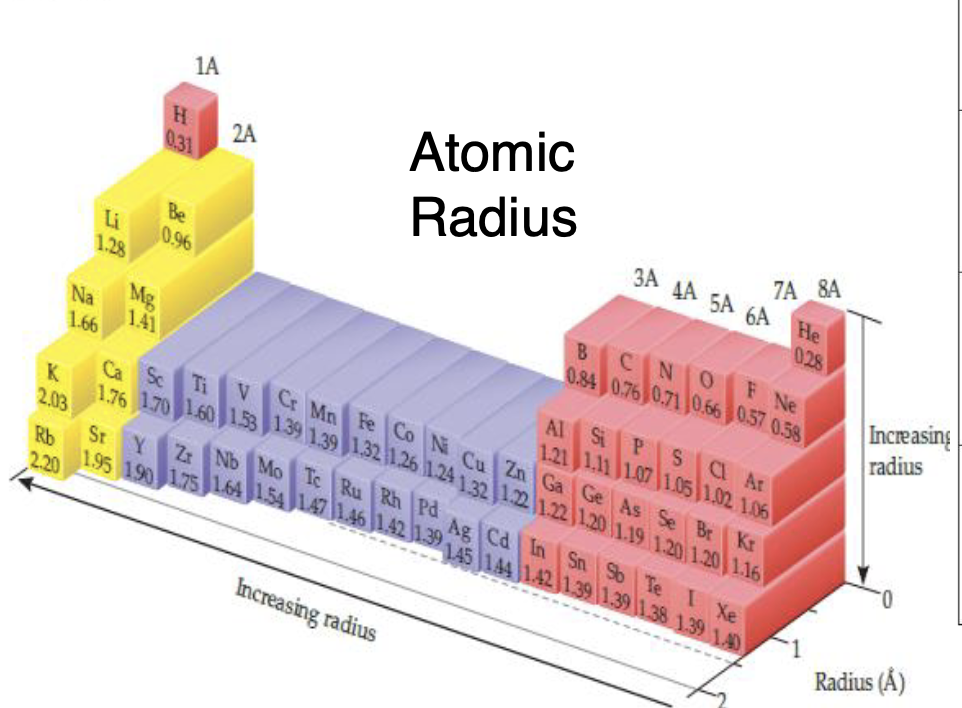
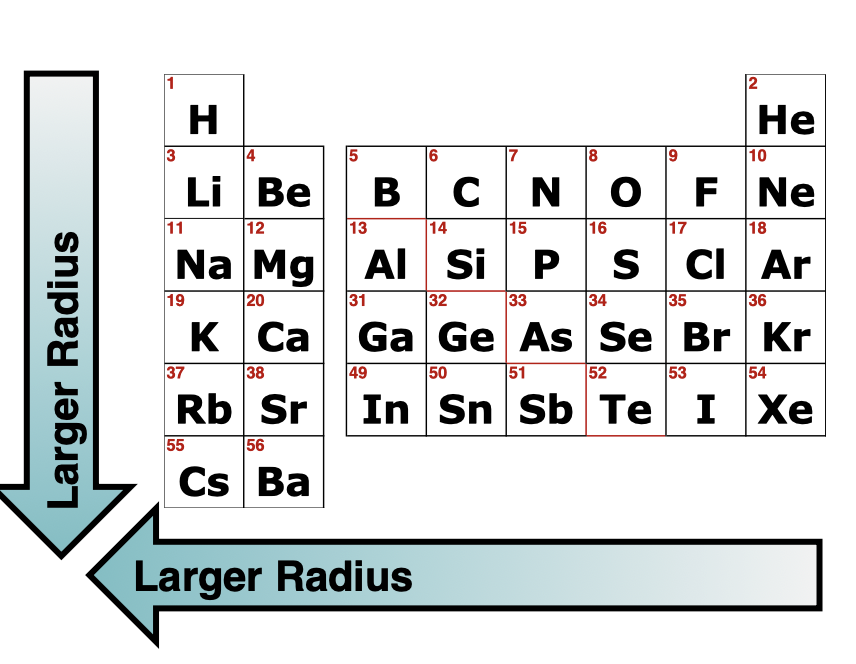
Trends in Atomic Radius
Increases Right —> Left, Increases Top—> Bottom
Trend in Atomic Radius for Cations:
Cations: remove electrons +, always smaller compared to parent atom
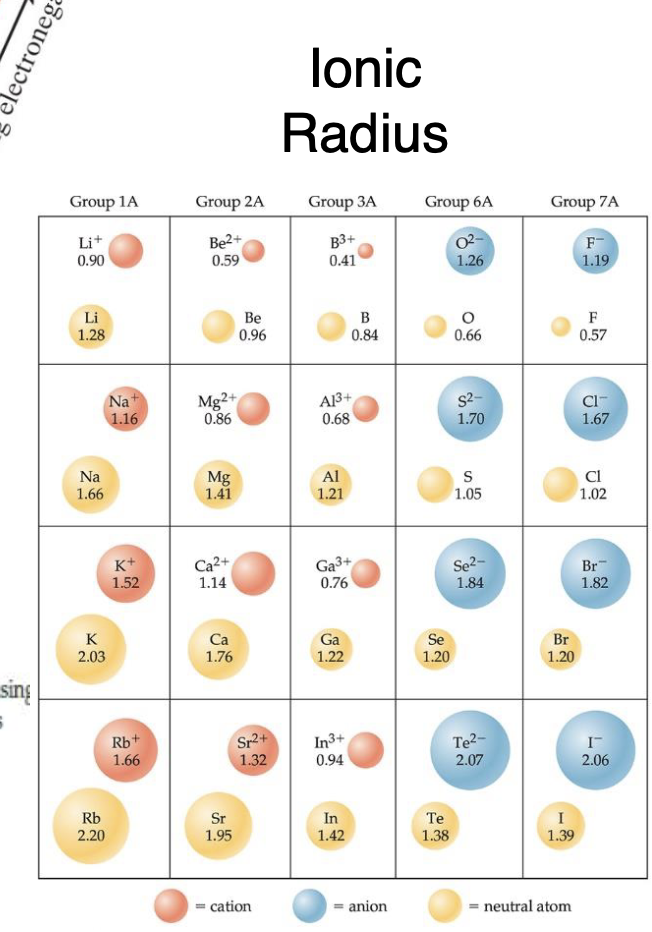
Cation + Atomic Radius Example: Ca2+<Ca means what
removed e- = making them a smaller size, removing VE means remain one’s are closer to the nucleus
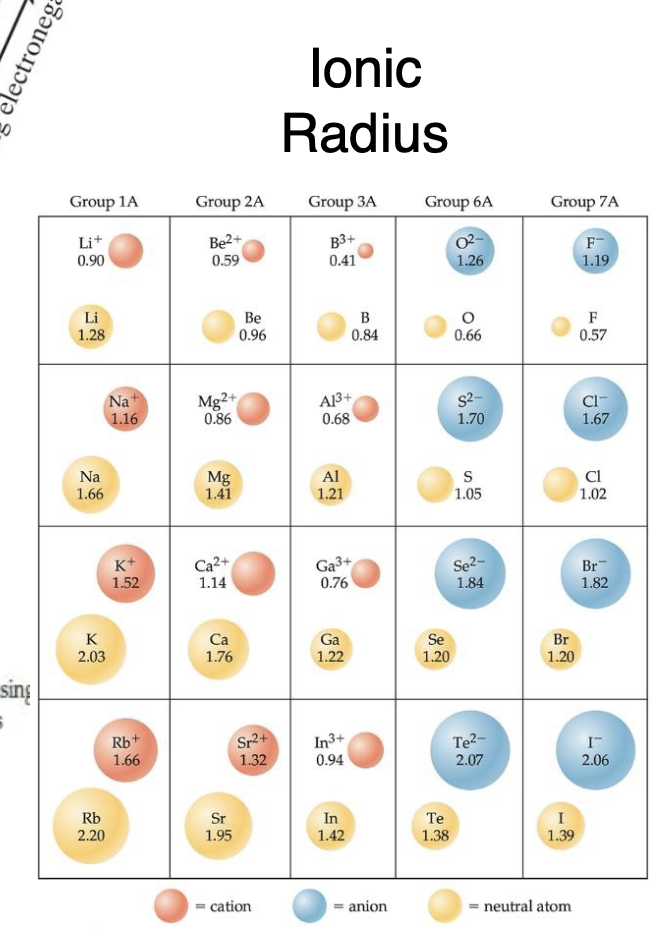
Trend in Atomic Radius for Anions:
- adds electrons, means larger than parent atom, adding VE means no extra protons to attract them means they drift farther away
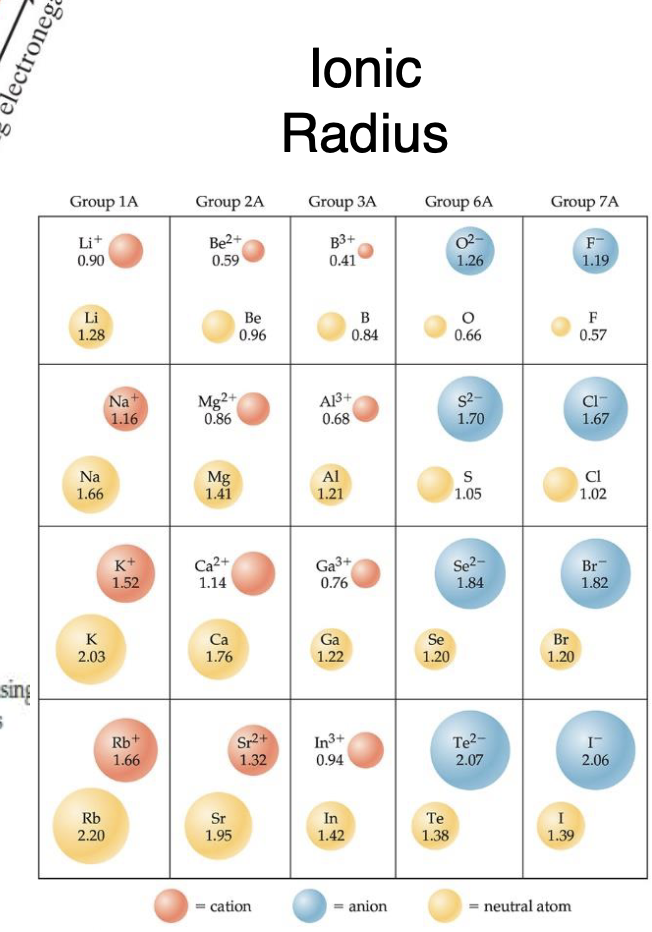
Anion + Atomic Radius Example:
Cl- > Cl the electrons mean no extra protons to attract and means they drift away
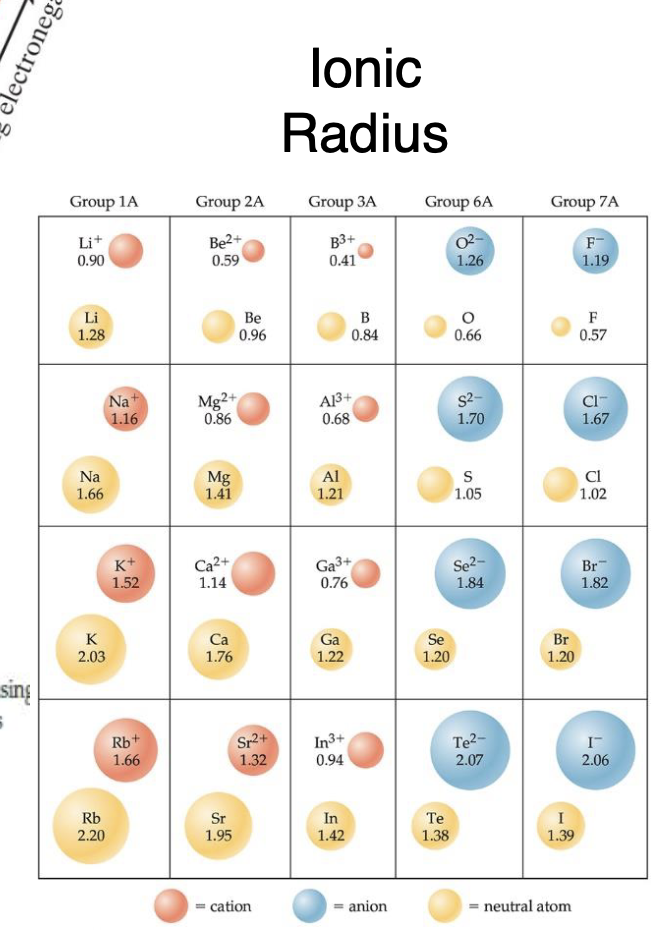
What is isoelectronic
same number of electrons series, ion that is largest so
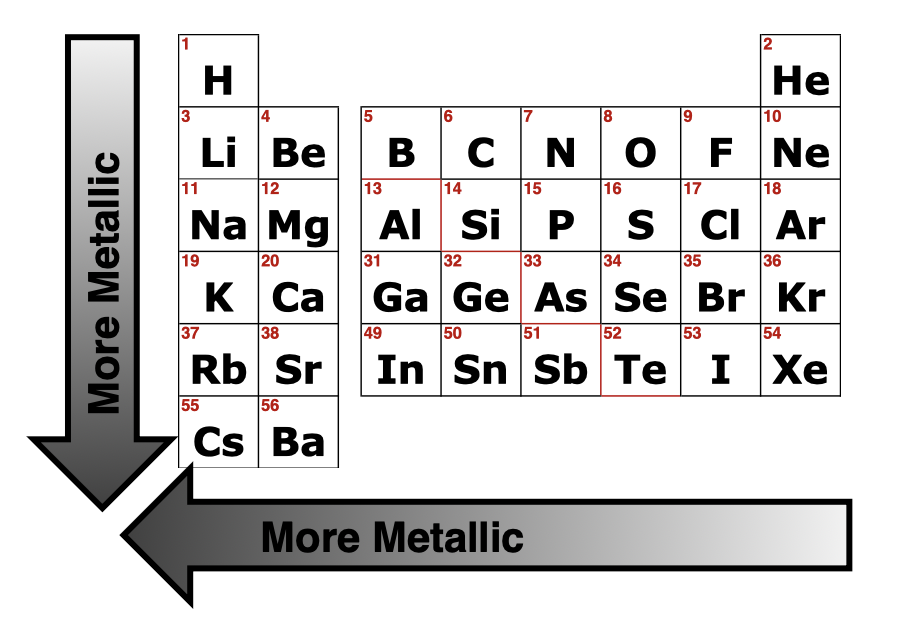
What is Metallic Character
Metals tend to lose electrons
easy to oxidize
form (+) ion
react with O2 to form basic oxides
React with H2O to form hydrogen gas and heat
Metallic character reaction H2O to form hydrogen gas and heat is what reaction
exothermic 2Na (S) +2H2O —> 2NaOH + delta H<O exothermic
Trends in Metallic Character
Increases from Right to Left (hold on VE gets weaker), Increases Bottom to Top ( atomic radius decreases so VE is closer to the nucleus and bound more tightly)
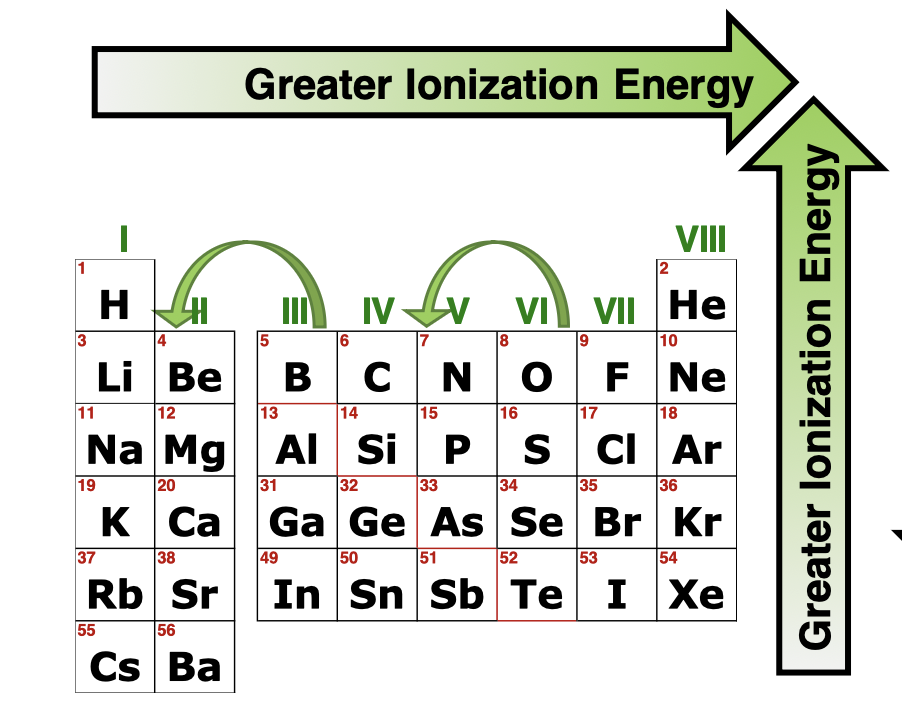
Ionization Energy (IE) is what
Energy required to remove an e- from a gaseous ground state atom or ion
Trends in Ionization
Increases Left to Right( Zeff increases so VE is bounded more tightly), Increases Bottom to Top( Atomic radius decreases so VE is closer to the nucleus and bound tighter )
Example of Ionization
E (g) —> E+(g)+ e- (IE)
What are the exceptions in Ionization
Be>B and N>O it is easier to remove 2nd ionization instead of first
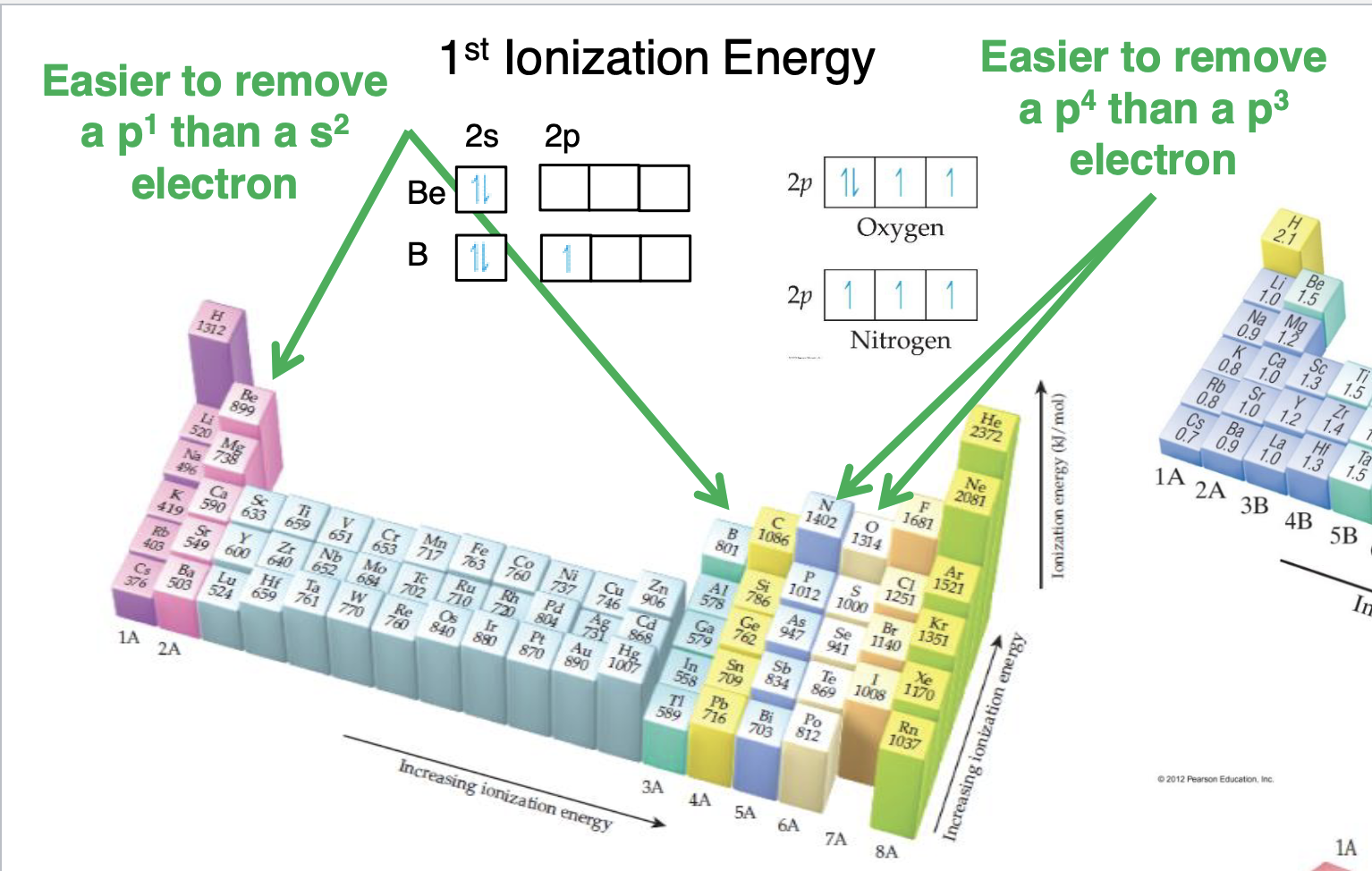
What is done for 2nd ionizaiton
2nd ionization energy are much larger to remove than the 1st and it takes a LOT more energy to remove core electrons
Electron Affinity (EA) is what
the affinity/willingness of a gaseous ground-state or ion to add e- and adding an e- usually releases energy so EA one are usually negative
example of electron Affinity
E(g)+ E- —> E -
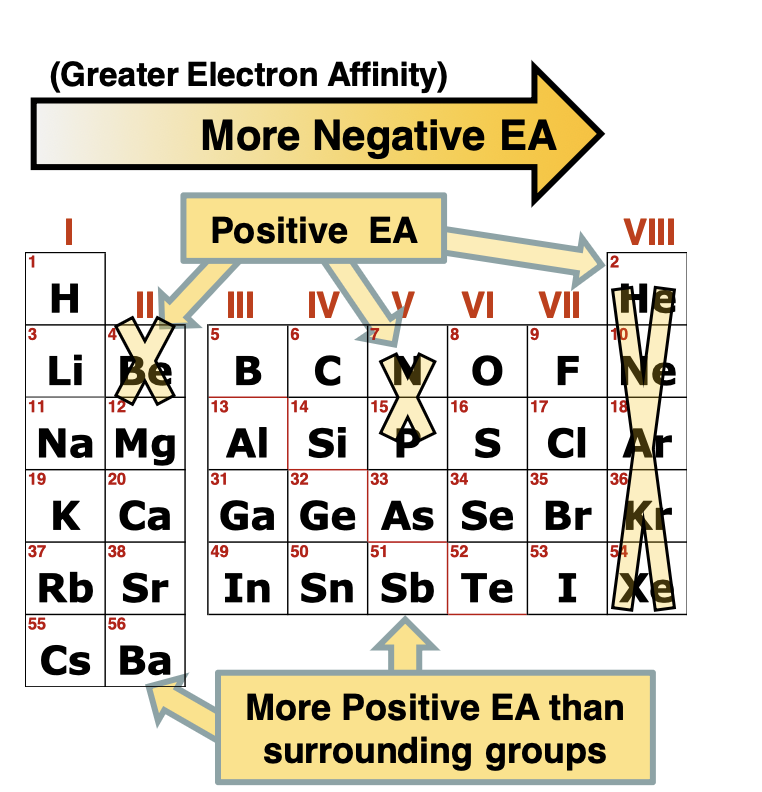
Trends in electron affinity
Increase Left to right, electron values are more negative, further right more likely to fill an energy shell
Exceptions in Electron Affinity
Nobel gasses have postive EA ( hard to add e- when already full s and p shell)
Group 2 (Be, mg) have more positive EA, harder to add e- to a full s-subshell
Group 5 (N,P) have more positive EA, harder to add e- to a half full p subshell
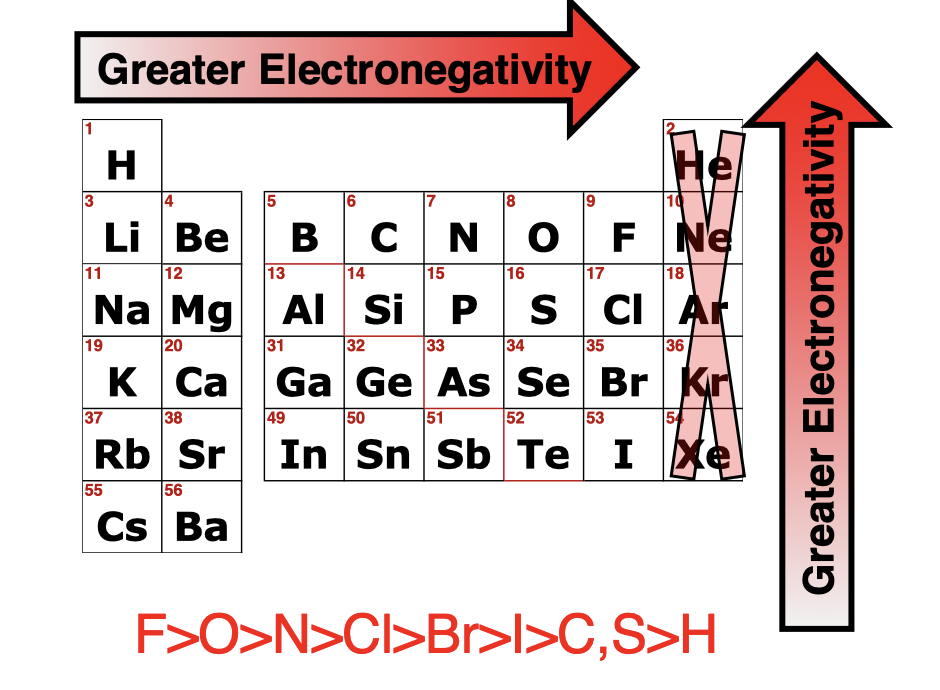
what is electron negativity
a measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons when it's bonded to another atom
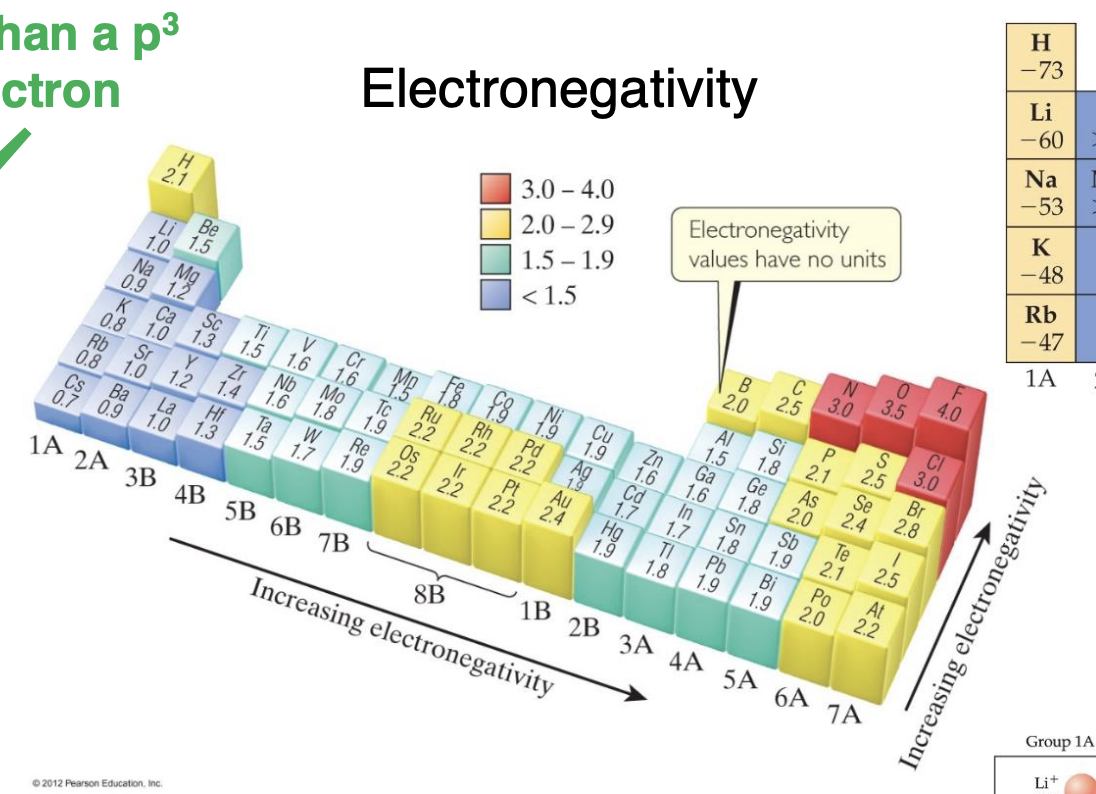
Trends in electron negativity
Increases Left to Right, and Increases from Bottom to Top