CMPP: Hemolytic Anemias Part 2
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
porphyrin ring
Fe2+
what is included in the heme portion of hemoglobin?
2 alpha chains
2 beta chains
--> 4 globin polypeptide chains
what is included in the globin portion of hemoglobin?
4
one hemoglobin molecule can carry how many oxygen molecules?
alpha, beta, gamma, delta
types of globin subunits
Methemoglobin
Fe3+ containing hemoglobin that cannot combine oxygen.
alpha2/gamma2
--> majority of Hgb after 14 wks gestation
fetal hemoglobin is made of what globin subunits?
after 6 mo old
when does fetal hemoglobin transition into adult Hgb
2 alpha globin genes (4 alleles) -- chromosome 16
single beta globin gene (2 alleles) -- chromosome 11
what is the "genetic makeup" of hemoglobin?
Oxygen dissociation curve
represents how easily hemoglobin gives up its O2
loading, higher, discourages
--> this occurs during processes in which the cells are good on oxygen
a left shift in the oxygen dissociation curve favors oxygen ________, has a _______ O2 affinity, and _________ O2 release
unloading, lower, encourages
--> this occurs in states in which there is a high metabolic demand (illness, acidotic), so more oxygen is needed to be given up, and CO2 must be collected due to a high pCO2
a right shift in the oxygen dissociation curve favors oxygen ________, has a _______ O2 affinity, and _________ O2 release
Bohr effect
states that the affinity fo normal hemoglobin for oxygen is inversely related to acidity and carbon dioxide concentration
THEREFORE:
> affinity for oxygen, decreased acid/CO2
< affinity for oxygen, increased acid/CO2
in utero -- fetal hemoglobin is better at holding onto O2, so, babies leech off of mom's lower affinity HgA1, so they can get oxygen
-->fetal Hb oxygen affinity allows for transfer of oxygen between mother's blood and developing fetus
what is the clinical significance of fetal vs adult hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
blood test used to identify types of hemoglobin present in sample; quantifies how much of each hemoglobin type is present
hemoglobin is negatively charged -- electrical current allows them to sort themselves by different charges
band pattern reviewed to determine type and quantity of hemoglobin present
how does hemoglobin electrophoresis work/separate Hgb?
Thalassemia
collection of disorders with a disrupted ratio between alpha ad beta chain production (reduced or absent production of one of the globin chains) that is autosomal recessive; has a high prevalence in Greek, Italian, Middle Eastern, Asian, African (Mediterranean sea)
excess unpaired globin chains precipitate inside RBC precursors --> premature hemolysis occurs
how does the absent/reduced production of one of the globin chains affect the RBC?
2, 16, insoluble, beta
alpha globin comes from ___ genes on chromosome __. free alpha chains are ______, and they occur in ______ thalassemia
single, 11, soluble, alpha
beta globin comes from a _____ gene on chromosome __. free beta chains are _____, and they occur in _____ thalassemia.
microcytic
what is the expected MCV range for thalassemia?
iron deficiency anemia
what is the #1 cause of microcytic anemia?
if the microcytic anemia was caused by an iron deficiency, RDW would be high, if it was caused by something genetic (thalassemia), it would be low
why does RDW help to narrow the diagnosis of a microcytic anemia?
Target cells
cells with a dark center with a clear ring between the dark center and the periphery of the cell; characteristic of thalassemia
Alpha thalassemia
Diseases in which there are insuffiecient alpha-globin chains due to gene deletions, which leads to an excess of beta chains in adults and an excess of gamma chains in infants
tetramers, unstable, precipitate
in alpha thalassemia, excess beta chains can form _____, while they are soluble, they are ______ and can ________ within the cell
alpha chains
are alpha or beta chains more toxic?
microcytic -- low volume due to chronic destruction of RBCs
hypo chromic -- less amount of Hb per cell so less color
what are some characteristics of the RBCs in alpha thalassemia?
Basophillic stippling
basophilic granules dispersed in RBCs; indicates disrupted erythropoiesis; dots are an accumulation of RNA fragments
hemolytic anemias
alpha or beta thalassemia
lead poisoning
in what conditions does basophilic stippling occur?
Wright stain
what stain is used to identify basophilic stippling?
Alpha thalassemia trait
also known as silent carrier (aa/a-); have an asymptomatic presentation and normal hematologic findings
DNA analysis (can be found incidentally if another family member has a more serious case of thalassemia)
how is alpha thalassemia trait diagnosed
prophylactic folic acid supplement
how is alpha thalassemia trait treated
Alpha thalassemia minor
aa/-- OR a-/a-; asymptomatic; can see target cells on peripheral smear; can have mild Anemia
prophylactic folic acid supplement
treatment for alpha thalassemia minor
Hemoglobin H disease
a-/--; HbH tetramers result from excess beta chains
high, left reduced
HbH tetramers have a _____ affinity for oxygen (____ shift), which results in a ________ability to supply O2 to tissues
readily oxidized -- hemolyze in times of oxidative stress
how is HbH more unstable than HbAI
at birth neonatal jaundice and anemia
Hemoglobin H disease presents when with what symptoms?
hemolytic anemia, iron overload, hepatosplenomegaly
--> due to unstable nature, disruption to iron absorption, and risk for sequestration of blood cells
patients with Hemoglobin H disease are susceptible to what symptoms and why?
HbF
Alpha2 Gamma2
ineffective erythropoiesis and blood transfusions for tx
why is there a risk for iron overload with alpha thalassemia intermedia
avoid oxidative stress
minimize infixes (vaccinate)
prophylactic folic acid supplementation
follow labs
blood transfusions for severe cases (but be careful, as these patients can become transfusion dependent and will need iron chelation)
splenectomy -- SEVERE cases
treatment for Hemoglobin H disease
alpha thalassemia major
condition in which the patient is unable to make ANY alpha chains; cannot synthesize HbA, HbF, HbA2
Hb Barts
tetramer consisting of 4 gamma globulins in which the O2 affinity is 10x greater than HbA; therefore binding O2 but cannot transport it to tissue; NOT COMPATIBLE WITH LIFE, as fetal demise occurs typically in late second/early third trimester
survival possible with intrauterine transfusions, chronic transfusions and stem cell transplant
treatment for Hb barts
Beta thalassemia
impaired production of beta chains; defect in beta globin gene on chromosome 11; this leads to an excess of insoluble alpha chains.
unstable, precipitate immediately, within the bone marrow
alpha chains are _____ and __________ within the RBC, which destroys RBC precursors ________________.
6 months
symptoms of beta thalassemia begin around...
fetal hemoglobin is gamma/alpha -- don't start producing beta until this age
why does beta thalassemia begin showing symptoms at 6 months?
Beta thalassemia minor
defect in one beta allele that causes one to be an asymptomatic carrier; heterozygous
ranges from asymptomatic, marked microcytosis with a disproportionately mild anemia, and target cells
clinical presentation of beta thalassemia minor
RBC count is HIGH in beta thalassemia minor
Retic count is normal to slightly increased in beta thalassemia minor
how to differentiate beta thalassemia minor from iron deficiency anemia
because the cells are so microcytic they need more oxygen, so, more RBCs are produced to compensate for the lack of oxygen being carried/transported by the defective cells
why is RBC count elevated in beta thalassemia minor?
no specific tx -- may occasionally need transfusion if pregnant
watch for iron tx -- only if they have a true iron deficiency!
treatment for beta thalassemia minor
Beta thalassemia intermedia
thalassemia in which symptoms are present but mild; anemia is present but not initially transfusion dependent
iron overload (releasing more iron to make more blood cells)
extra medullary hematopoiesis and therefore hepatosplenomegaly
hemolysis
in Beta thalassemia intermedia, ineffective erythropoiesis can result in...
Folic acid supplementation
monitor and support any progression of anemia -- may need transfusion during growth spurts, pregnancy, and oxidative stress
NOT transfusion dependent, but can become
monitor for iron overload due to repeated transfusions/abnormal iron absorption -- iron chelation
splenectomy reserved for SEVERE cases
Beta thalassemia intermedia tx
Cooley's Anemia (Beta Thalassemia Major)
thalassemia that results from 2 defective beta alleles, and absent beta globin production leads to excess unpaired alpha chains that are unstable and precipitate immediately within the RBC
intramedullary hemolysis (destruction of RBC precursors)
intravascular hemolysis
what causes the profound anemia associated with beta thalassemia major?
erythroid hyperplasia (cells made much more rapidly)
extra medullary hematopoiesis (cells are made elsewhere)
how does the body attempt to compensate for the profound anemia associated with beta thalassemia major?
EPO, beta chain, expanding sites of hematopoiesis (extra medullary hematopoiesis)
Excess demand associated with Cooley's anemia results in excess ____ production. Hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow try to respond but cannot without ________ production. So, the body responds by....
Extramedullary hematopoiesis
expansion of hematopoiesis outside the medulla of the bone marrow
liver lymph nodes, spleen, diaphysis, shaft, and periosteum of long bones
common sites for extramedullary hematopoiesis
bony masses, pathologic fractures, or bone pain
Extramedullary hematopoiesis in the diaphysis, shaft, and periosteum of long bones can manifest as what symptoms?
6 months of age, since beta chains aren't being made until then
beta thalassemia major presents at...
pallor, jaundice, growth retardation, abdominal swelling
presentation of Cooley's anemia in those < 2y/o
delayed skeletal maturation due to extramedullary hematopoiesis
--> marrow space widens and osteoporosis occurs
why is there growth retardation associated with Cooley's anemia?
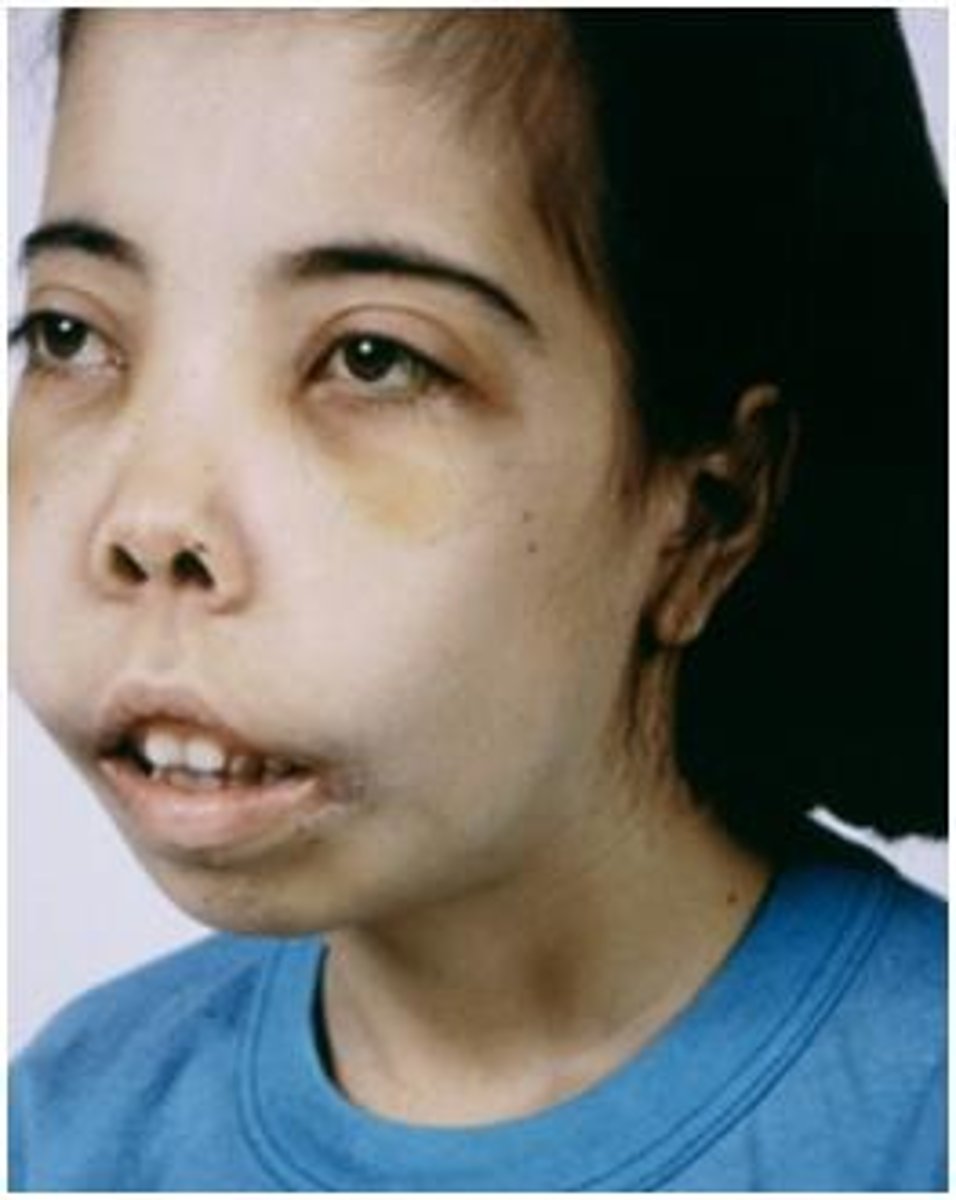
Chipmunk face
characteristic of beta thalassemia characterized by wide spaced eyes, prominent forehead, overgrowth of maxillae
hair on end appearance skull
what are the radiologic findings associated with beta thalassemia major?
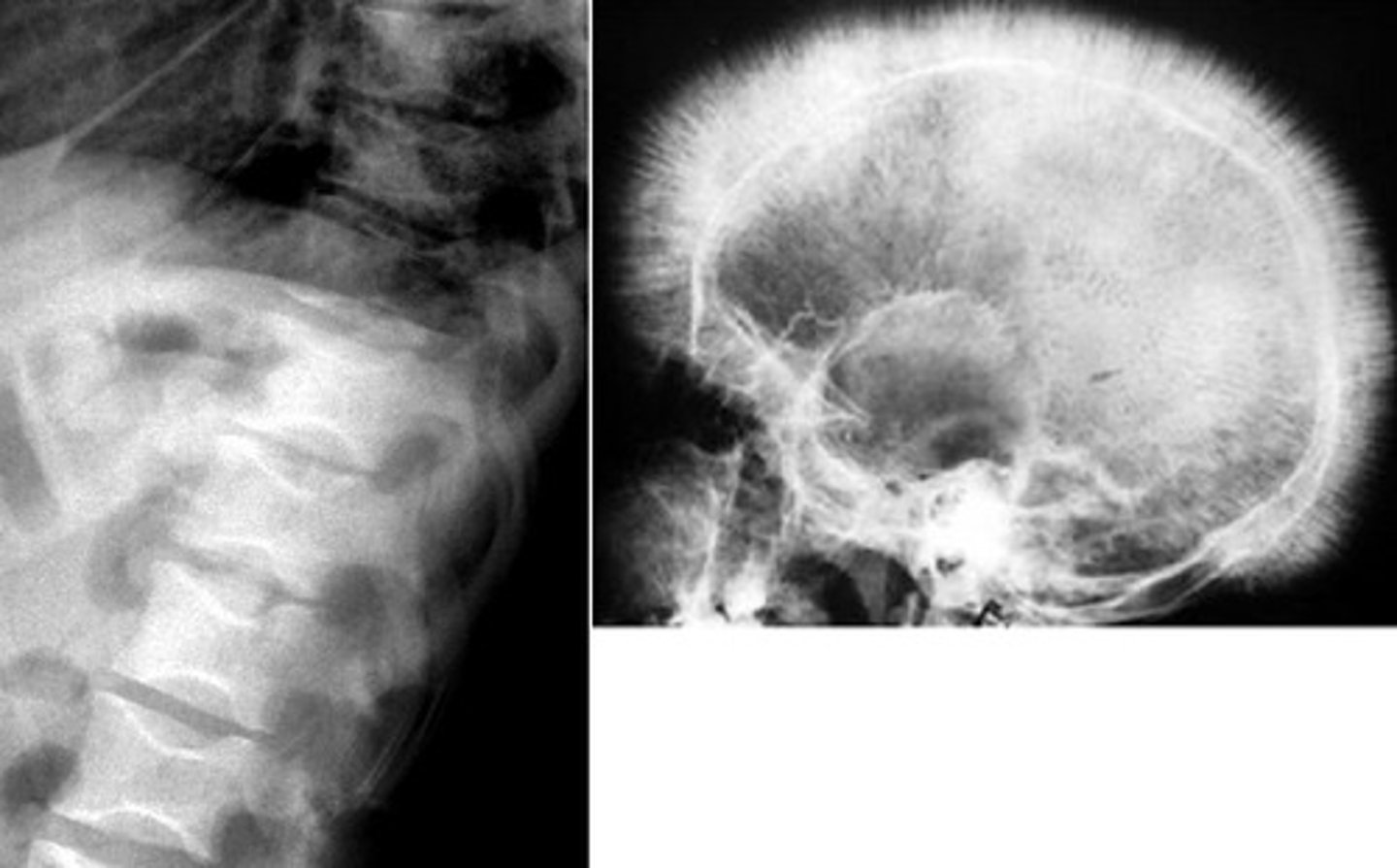
accentuated trabeculae due to bone marrow hyperplasia
why does hair on end appearance skull happen in beta thalassemia?
low - bone marrow is failing :(
elevated -- bone marrow is trying to make more and more blood, so it brings out more and more iron
Beta thalassemia major is a profound hypochromic microcytic anemia. Lab findings include a ___ reticulocyte count, and an ______ serum iron and ferritin
only HbF/HbA2 present since beta is not being made
--> would show donor blood if patient was getting transfusions
what are the Hb electrophoresis results associated with beta thalassemia major?
folic acid supplementation
chronic blood transfusions (transfusion dependent)
monitor complications -- iron overload (chelation), osteoporosis
splenectomy for SEVERE cases
bone marrow transplant
beta thalassemia major treatment
bone marrow transplant - reserved for severe cases
what is the ONLY CURE FOR BETA THALASSEMIA MAJOR
Iuspatercept (Reblozyl)
newly approved for transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia
promotes RBC maturation and makes RBCs more efficient
reduces transfusion requirements
Iuspatercept (Reblozyl) MOA
thromboembolism (DVT/CVA)
bone pain/arthralgias
adverse effects of Iuspatercept (Reblozyl)