NMR and IR Spectroscopy
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What does NMR stand for?
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
What are the two main ideas of NMR?
The nuclei has charge and can spin and the spinning charge generates a magnetic dipole
How are magnetic dipoles characterized?
By nuclear magnetic spin quantum number I
What does the quantum number I mean?
It’s a function of the number of protons and neutrons
What does quantum numbers I=0, I=1/2, I>1/2 mean?
0 means there’s no spin so there’s no interaction with the applied magnetic field
½ means the nuclei are NMR visible examples include 1 H, 13 C
>1/2 means the nuclei are hard to observe in NMR examples include 2H, 14 N
Where are nuclei aligned in a magnetic field?
They’re aligned with the lower energy alpha spin state
What does delta E equal?
The energy difference between the alpha and Beta spin states
What does increasing the applied magnetic field equal?
It equals increasing delta E between the spin states
What does it mean when the nucleus is in Resonance with the applied magnetic field?
It means the nuclei can absorb energy and flip from the alpha spin state to the beta spin state
What are deshielded/downfield nuclei?
These protons have a large effective magnetic field where it comes into resonance at a higher frequency
What are shielded/upfield nuclei?
These protons have a smaller effective magnetic field where it comes into resonance at a lower frequency
What do electronegative atoms do toward nuclei?
They withdraw electron density from the Carbon and Hydrogen atoms which deshields them
What does deshielding or lesser shielding mean?
It means more of the applied magnetic field strength is experienced and higher frequency is absorbed.
What is the schematic of an NMR spectrometer?
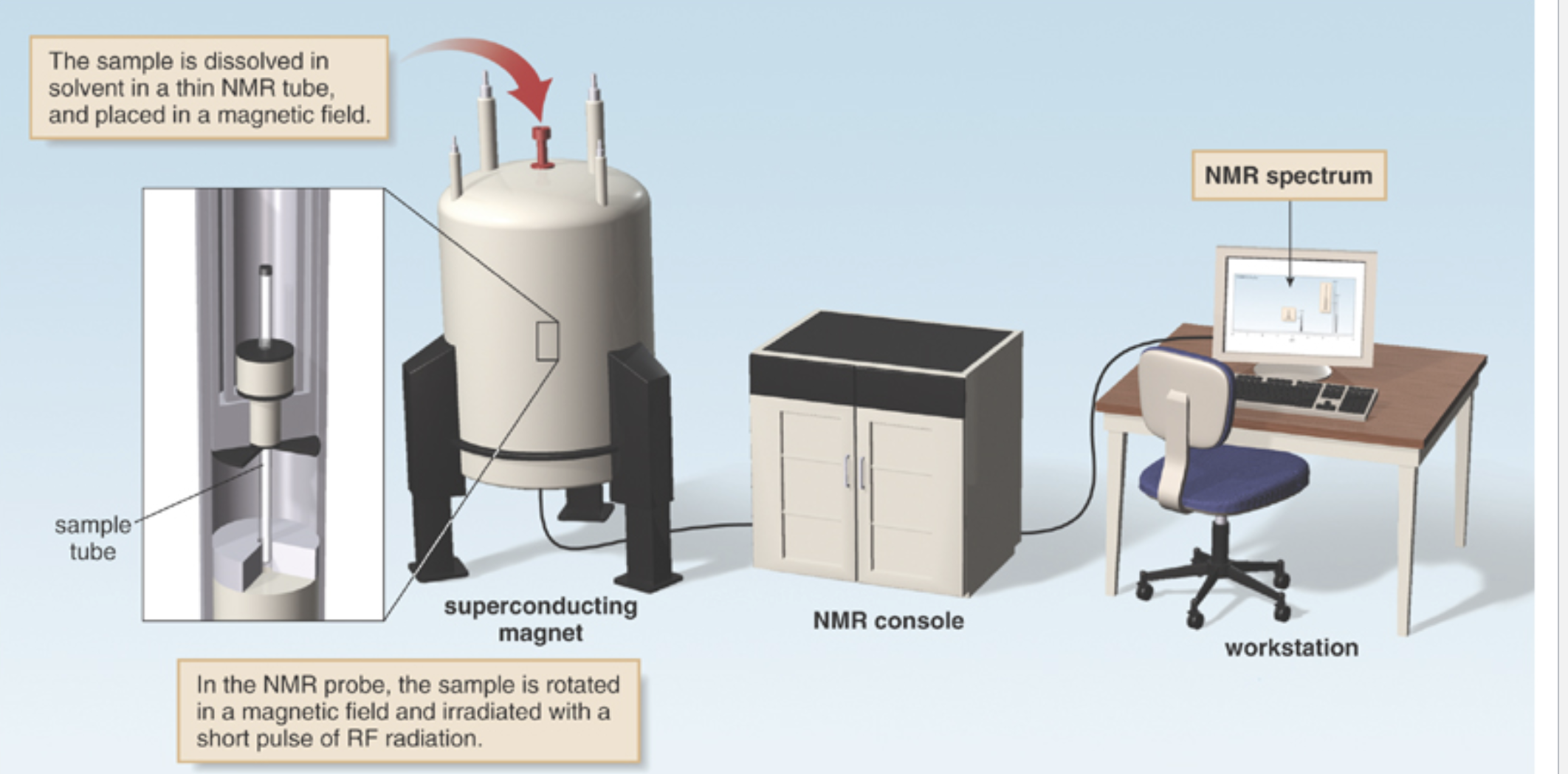
What does the NMR spectrum plot?
It plots the intensity of an observed NMR signal against the frequency measured relative to a reference compound
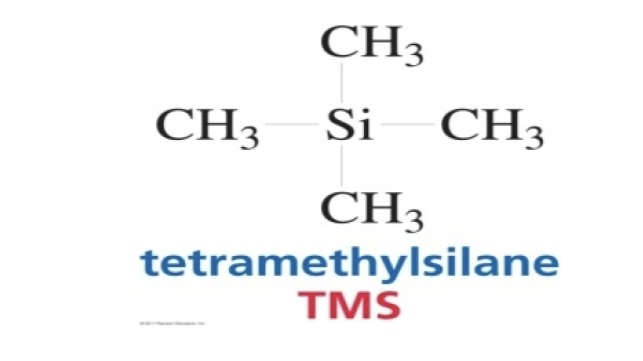
What is the reference compound for a NMR? And its structure?
Tertamethylsilane (TMS)
What is the NMR solvent used?
Deuterated chloroform (CDCl3)
Why do we use deuterium instead of hydrogen?
Because if there was hydrogen it would show really high peaks
What are the advantages of TMS?
-It has 12 equivalents of Hydrogens
-The NMR Signal due to the protons in TMS appear as a singlet at 0 ppm
-It’s low boiling and inert
What is the equation for degrees of unsaturation? And what do the number correspond to?
2(# C + 2 + # N - # X - # H) / 2
-1 du= 1 ring or 1 double bond
-2 du= 2 double bonds 1 ring and 1 double bond, 2 rings, or 1 triple bond
-4 du= benzene ring
What are the features of a 1 H NMR spectrum? And what do they tell you about a compounds structure?
-Size of area under the peak of NMR signals=shows number of identical protons in an environment
-Number of signals=shows different groups of non-equivalent protons
-Position of signals=shows the kind of protons for the signal
-Spin-spin splitting of signals=shows the number of neighboring protons
What are chemically equivalent protons?
Protons in the same environment and they don’t split each other’s signals
What do chemically in-equivalent protons give?
They give more than one peak
When does spin-spin splitting happen?
It happens between non-equivalent protons on the same carbon or adjacent carbons (splitting into n+1 peaks)
-splitting isn’t observed for protons separated by more than 3 sigma bonds
What is unique about OH protons?
They do not split and they do not split the NMR signal of adjacent protons, so the signal appears as a singlet.
What does an Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy do?
It’s used to detect functional groups present
How do IR absorptions happen?
They arise due to stretching and bending of covalent bonds in molecules
What does 100% transmittance mean in IR? What about 0%?
-100% means all light is transmitted, none absorbed
-0% means no light is transmitted, all is absorbed
What is the fingerprint region used for?
It’s used for structure elucidation by spectra comparison, where it distinguishes between different compounds if they have the same functional group
What are the four regions of the IR spectrum in order from increasing energy and wavenumber?
Single bonds, Double bonds, Triple bonds, Bonds to hydrogen
Which type of region is apart of the finger print region?
The single bonds
What is the stretching IR absorption for anhydride?
1820 and 1760 cm-1