MOD 5 - Pelvic Fractures
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
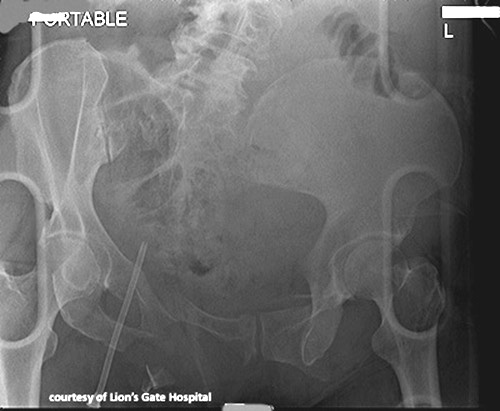
Stable Pelvic Fractures (DERTC)
a fractured pelvis that can withstand normal forces without deformation; involve a single break along the peripheral margins
MOI = moderate trauma to the pelvis
Reduction of the fracture and surgical intervention, with a screw or plate
Neurological problems leading to bladder problems, post-surgical bowel obstruction
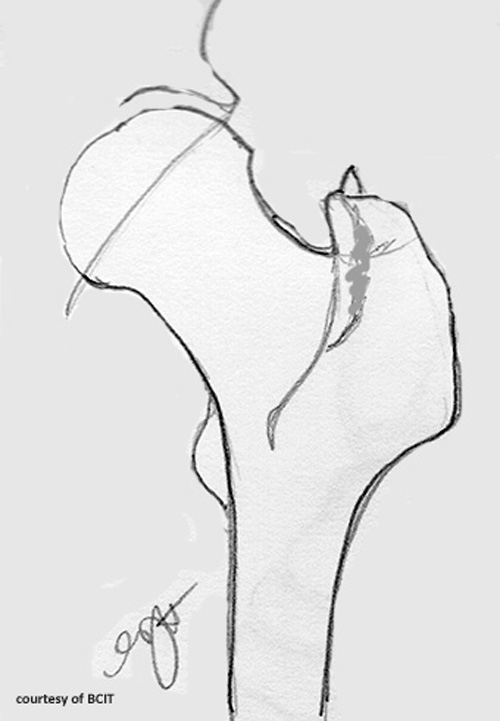
Avulsion Fractures (DERTC)
seen mostly in young athletes, considered stable fx, can occur in the ASIS, AIIS, the ischial tuberosities and GT/LT.
MOI = forceful contraction of the muscle
rest and reduction of activity
generally heal well
Unstable Pelvic Fractures (DT)
with breaks in the anterior and posterior arches of the pelvic ring; categorized according to the MOI
high risk of morbidity due to increased blood loss
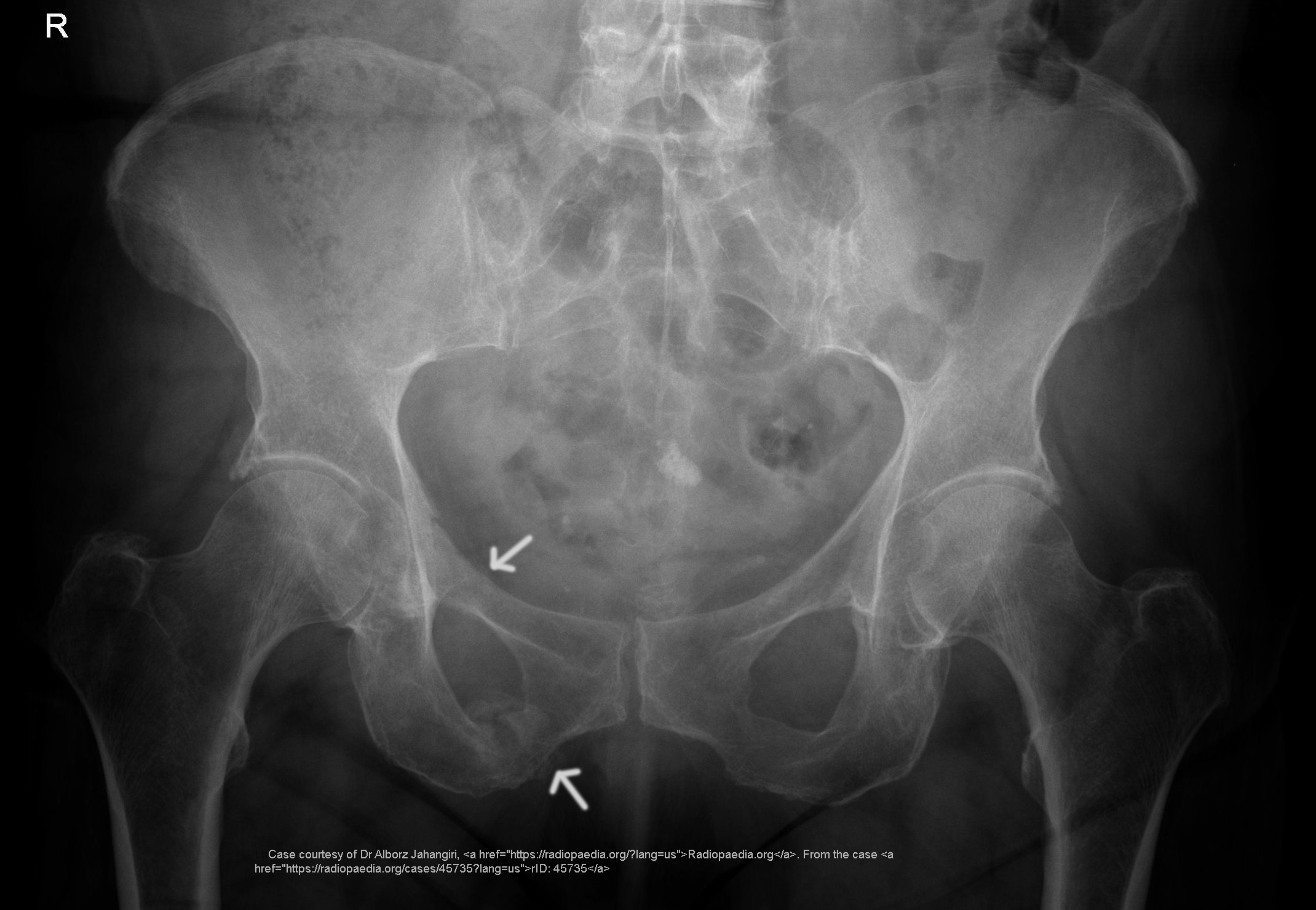
Anteroposterior Compression (DERTC)
results in a “sprung” or "open book" pelvis which is a widening of the pubic symphysis and anterior sacroiliac joints
MOI = extreme force applied to the pelvis in an AP or PA direction
Surgical plating may be required if there are associated genitourinary injuries
Hemorrhage, genitourinary and rectal injuries
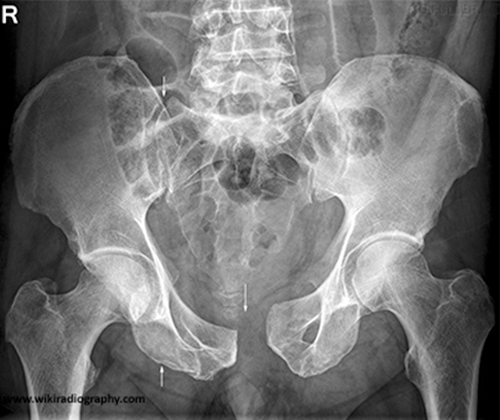
Lateral Compression of the Pelvis (DETC)
ilium wings folding, sacral fractures, SI joint widening; superior and inferior pubic rami fractures associated
MOI = mild to moderate trauma, with the force being applied in a lateral to medial direction
Surgical intervention, external fixation
Vascular injuries, genitourinary injuries, or neurological damage
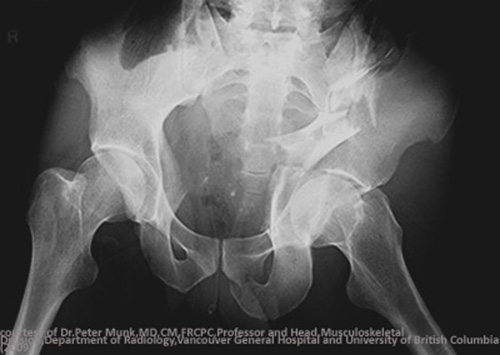
Most common type of pelvic fracture
Lateral Compression
Vertical Shearing of the Pelvis (DETC)
highly unstable and result in fractures along the axis, pubic rami, SI joints and sacrum; associated heavy bleeding
MOI = severe axial force, for example, a fall from a height
Surgical intervention
Ongoing low back pain. Some pelvic obliquity with or without a limp. Poor function related to nerve injuries
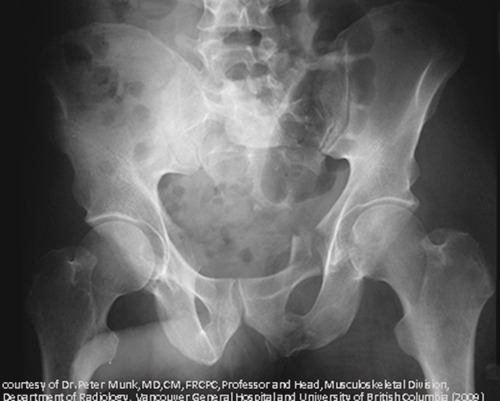
Combined Mechanical Force Fractures (DETC)
These fractures often include head and chest injuries as well as injuries to the abdomen and extremities
MOI = combination of forces from various directions.
Stabilization of the pelvic ring
Ongoing pain, neurological damage.