Kidneys Part 1
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UT 302 - Abdomen 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
Where are the kidneys located?
In the retroperitoneum at about T12-L4
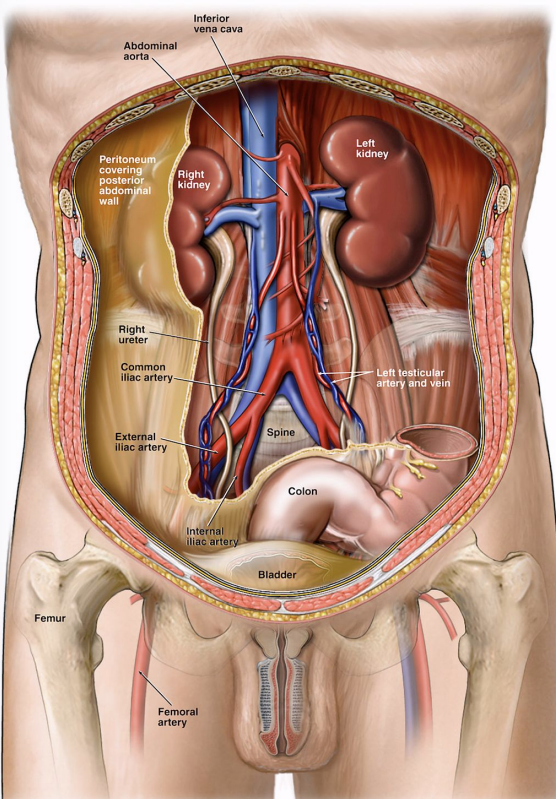
Where is the right kidney with respect to the liver and gallbladder?
It is posterior and inferior
T/F: the right kidney is higher than the left kidney by 2-8 cm, due to the liver placement
False
Where is the left kidney with respect to the spleen?
It is inferior and medial
T/F: the kidneys can demonstrate 3-4 cm of excursion when a patient changes from a supine to an erect position
True
Where are the adrenal glands with respect to the kidneys?
They are superior, anterior, and medial
The right kidney is ___ to the left kidney by 2-8 cm, due to the liver placement
inferior
What are the main functions of the kidney?
Excretion and filtration of waste
Synthesis of erythropoietin (EPO), active form vitamin D (calcitriol), and glucose (from glutamine)
Regulation of blood volume and blood pressure
What are some wastes that the kidneys filter?
Urea
Drugs
Creatinine
Bilirubin
How do the kidneys regulate blood volume?
By conserving or eliminating water
How do the kidneys regulate blood pressure?
By secreting renin, angiotensin, and aldosterone (RAAS system)
The kidneys filter ___ liters of blood each day, removing ___ liters of toxins, wastes and water in the process
200; 2
T/F: vitamin D is not important for bone health
False
What is erythropoietin (EPO) and why is it important?
Healthy kidneys synthesize EPO
EPO sends a signal to the body to make more red blood cells
If kidney function is impaired, they can't make enough EPO
If there is not enough EPO, the body doesn't know to make enough RBCs
What is the average kidney weight?
130-150 g
What is the average kidney length?
10-14 cm
What is the average kidney width?
5-7 cm
What is the average kidney height (AP)?
3-5 cm
Kidney anatomy/embryology
Start to develop in the 3rd week of embryo life
Develop from columns of mesoderm
Nephron development begins at 8 weeks GA
Kidneys migrate from the pelvis to the abdomen at 6-9 weeks GA
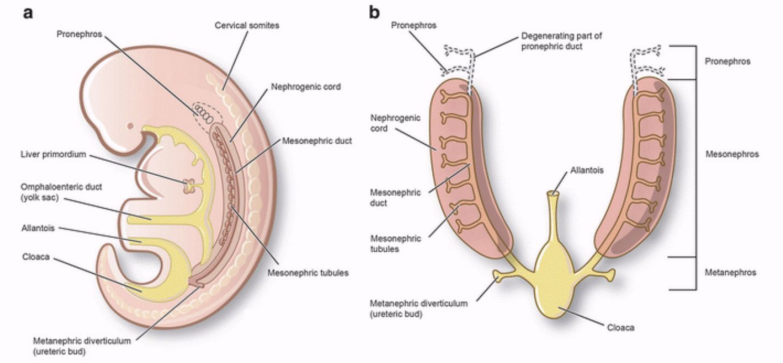
What are the 3 successive intervals of kidney development?
Pronephros (forekidney)
Mesonephros (midkidney)
Metanephros (permanent kidney)
Pronephros (forekidney)
A transitory, non-functioning structure, beginning of 4th week of gestation
Mesonephros (midkidney)
Late in the 4th week of gestation
This structure provides function while the permanent kidney continues to develop
Metanephros (permanent kidney)
Develops during the 5th week
What is the functional unit of the kidney and what does it do?
Nephrons are the functional unit of the kidney and they produce urine
Kidneys are reddish brown organs with ___ lateral borders and ___ medial borders
convex; concave
The kidneys are protected and stabilized by 3 outer layers which are …
Renal fascia (AKA Gerota’s fascia)
Superficial layer
Adipose capsule
Middle layer
Renal capsule
Deep layer
How does the renal capsule appear on US?
Appears as a strong continuous linear, echogenic reflector surrounding the renal cortex
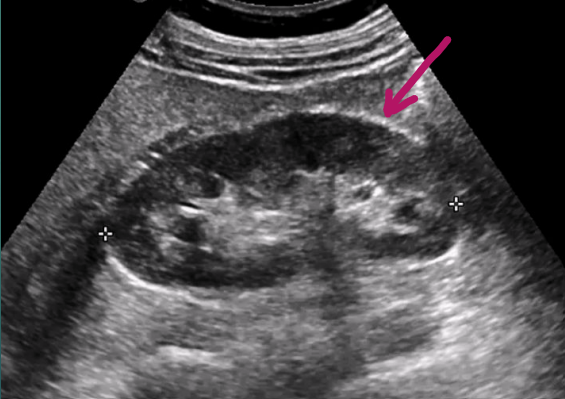
Gerota’s fascia is the ___ layer, and it encloses the kidney, capsule, and perinephric fat
superficial
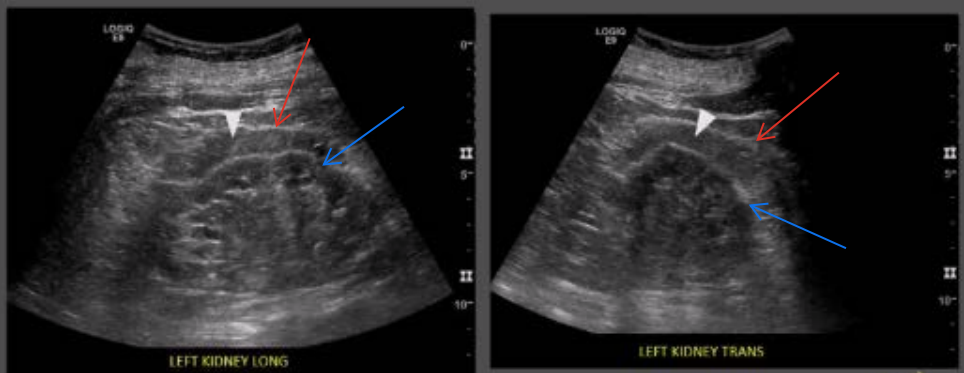
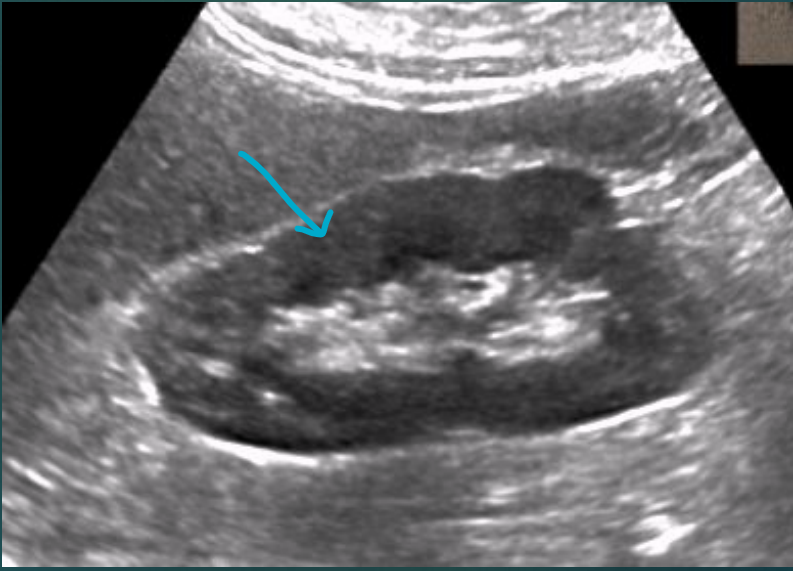
What are the white arrow heads pointing to?
Perinephric fat
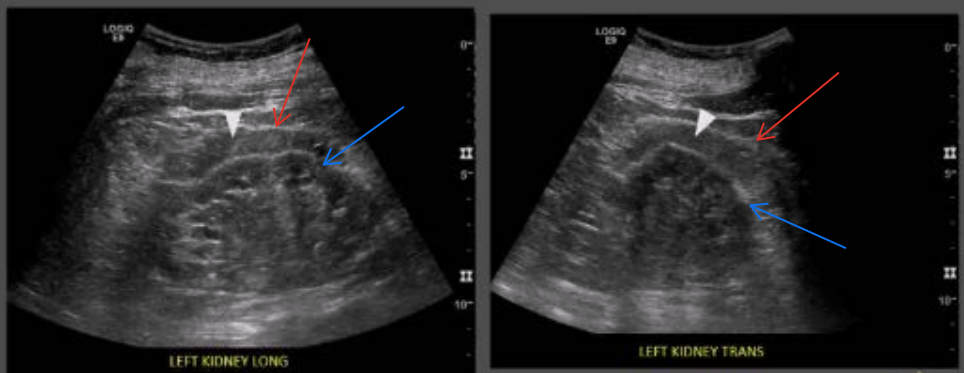
What are the red arrows pointing to?
Gerota’s fascia
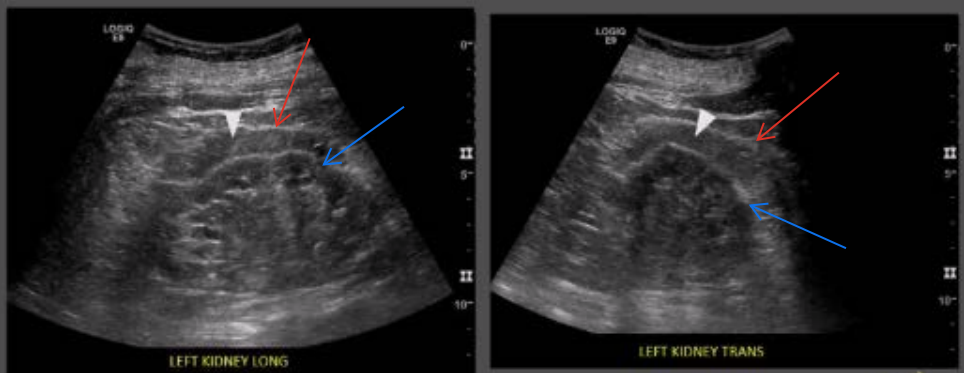
What are the blue arrows pointing to?
Renal capsule
What is the functional section of the kidney called?
Parenchyma
What is the functional section of the kidney (parenchyma) composed of?
Renal Cortex
Most nephrons here
Renal Medulla
Renal Pelvis
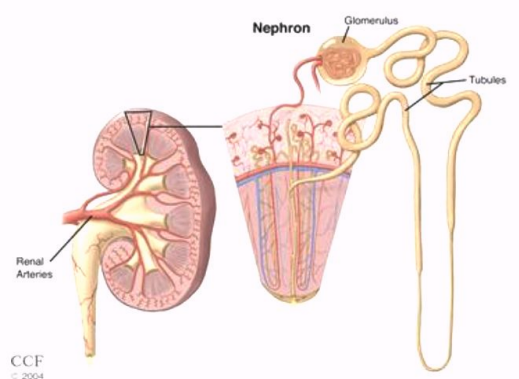
Where are most of the nephrons located in the renal parenchyma?
In the renal cortex
What is the anatomy of a nephron?
Composed of a glomerulus and a tubule
Glomerulus filters wastes and excess fluids
Tubules modify the waste to form urine
Cleaned blood returns back to the circulation via a renal vein
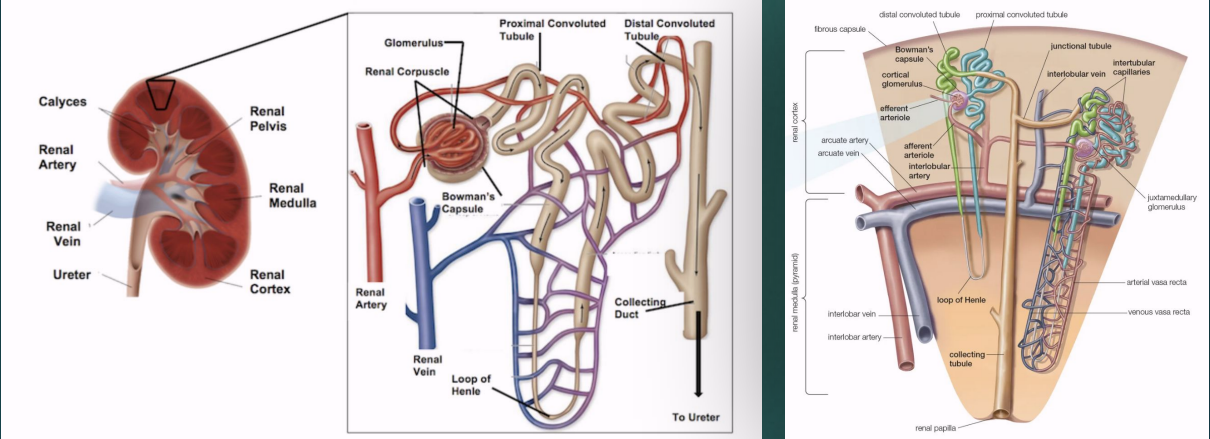
The glomerulus and convoluted tubules of the nephron are located in the renal , while the collecting ducts are located in the renal _ pyramids
cortex; medullary
The renal ___ surrounds the sinus
parenchyma
The renal ___ is the site of urine formation, and it contains nephrons
cortex
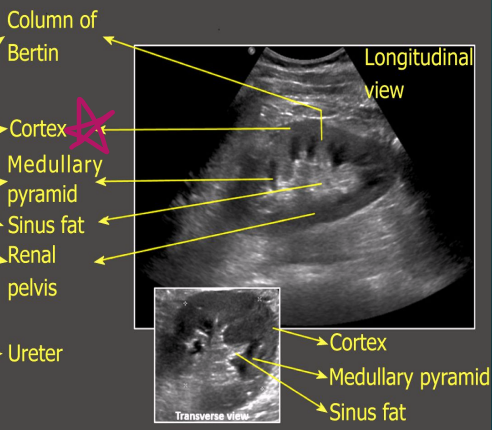
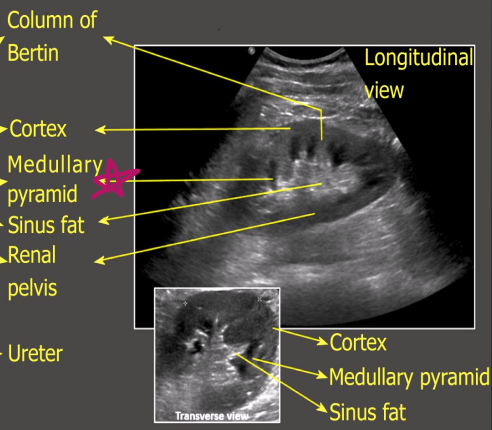
The renal ___ contains pyramids that pass urine to minor calyces
medulla
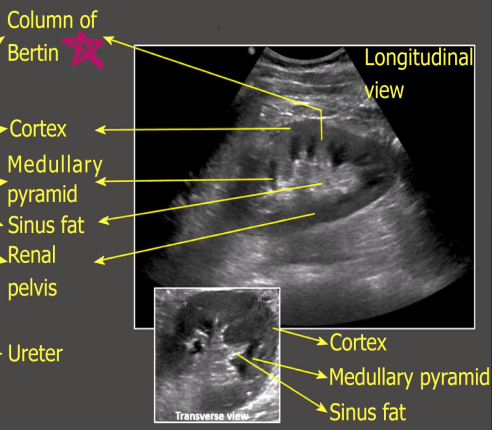
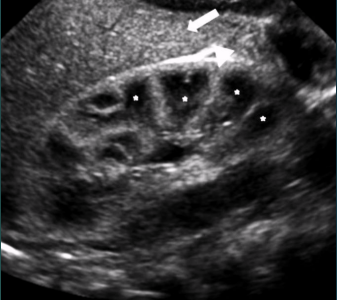
What structure separates the medullary pyramids?
Columns of Bertin
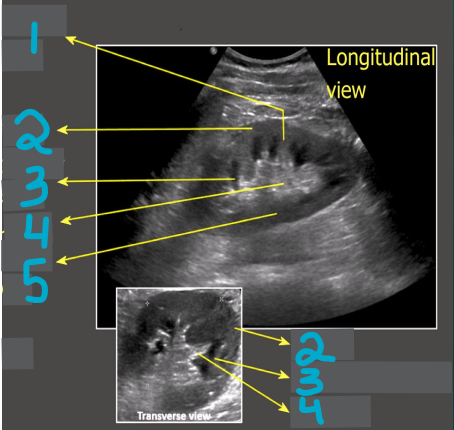
1
Column of Bertin
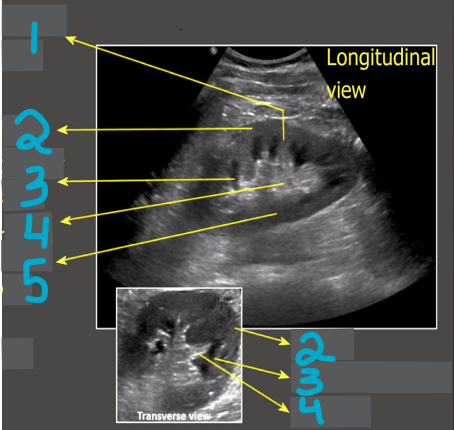
2
Cortex
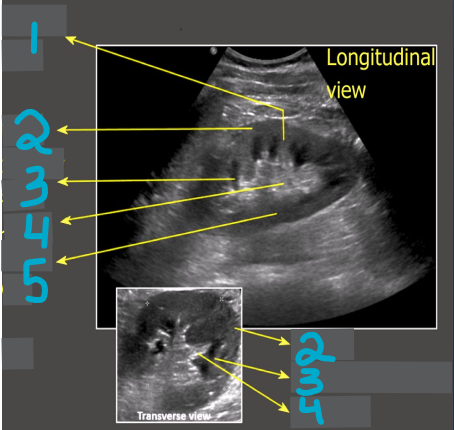
3
Medullary pyramid
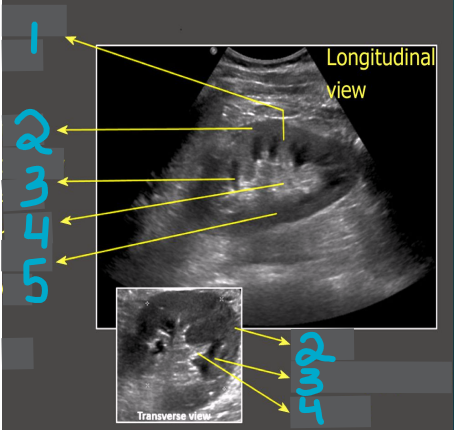
4
Sinus fat
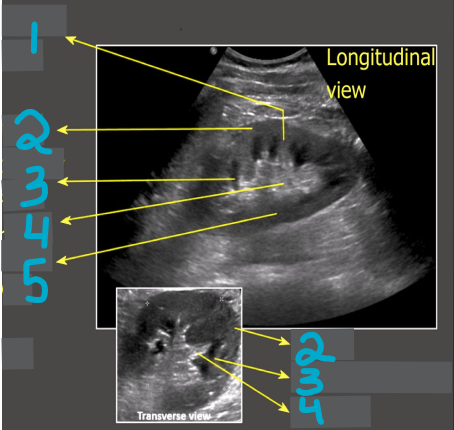
5
Renal pelvis
What does the renal cortex look like on US?
Normal renal cortex has homogeneous echotexture in adults and children
It is hypoechoic to the liver, spleen, renal sinus
It can still be considered normal if it is isoechoic with liver & spleen
In neonates, the renal cortex is normally isoechoic or hyperechoic compared to the adjacent liver or spleen
A hyperechoic cortex is ___ and should make the sonographer think renal disease
abnormal
Renal cortex
Extends from the renal capsule to the base of pyramids
Extends between renal pyramids forming renal columns (AKA columns of Bertin)
Which kidney is normal and which is abnormal?
Left: normal
Right: abnormal (they are hyperechoic)
Renal medulla
The inner portion of the renal parenchyma
Consists of cone-shaped renal pyramids (inner reddish brown region)
Cones are mostly urine collecting tubes
What does the shape of the pyramids in the renal medulla consist of?
The base (wider end) faces the renal cortex
The renal papilla (narrower end) faces the renal hilum
The pyramids are separated by the columns of Bertin
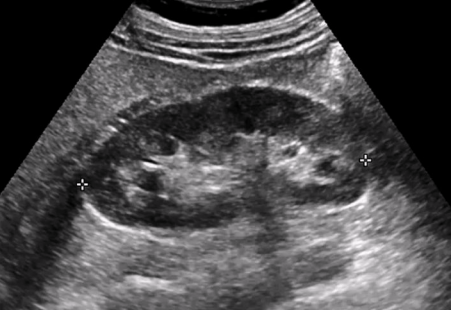
What do neonate kidneys look like on US?
What does medullary nephrocalcinosis look like on US?
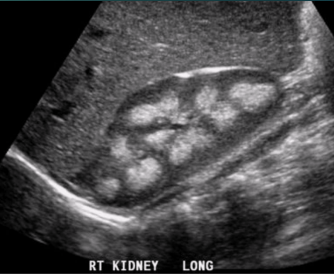
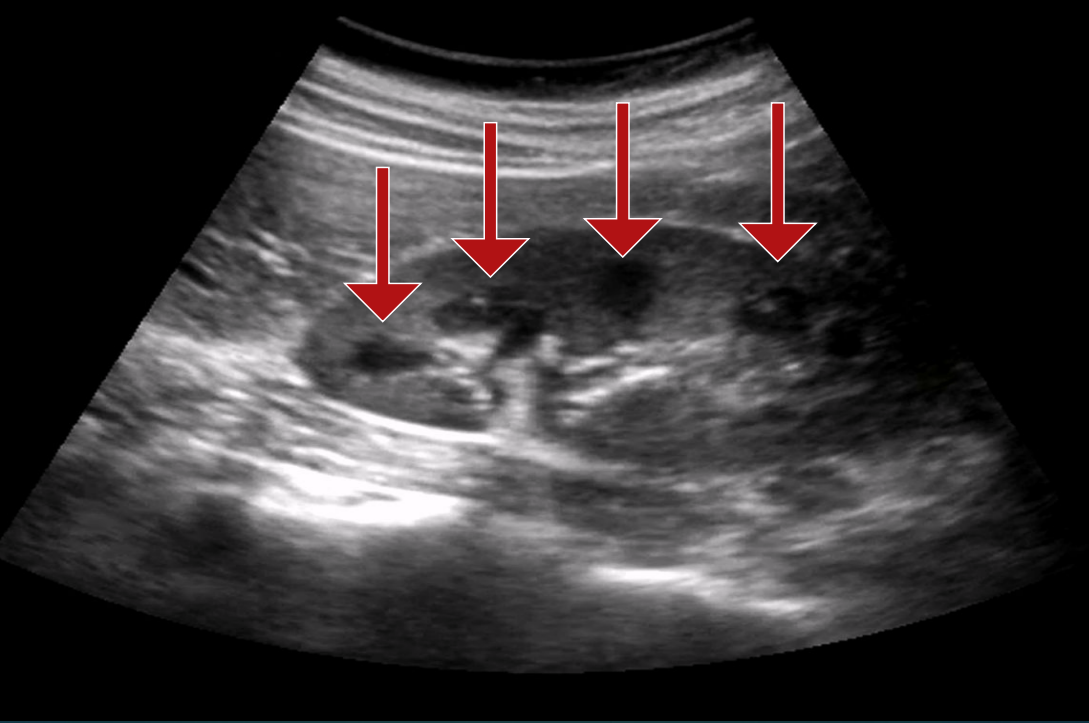
How do renal medullary pyramids appear on US?
Cone-shaped or heart-shaped
Hypoechoic compared the cortex
Larger in children
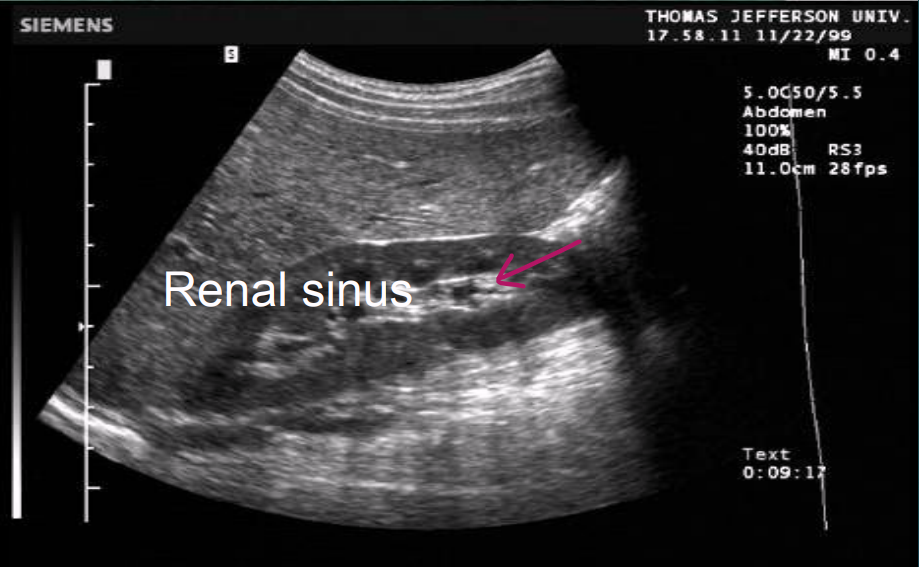
How does the renal sinus appear on US?
Intense, compact zone of homogeneous central echoes.
Hyperechoic
The echo intensity is caused primarily by hilar adipose tissue, secondary to blood vessels and the collecting system
What is the renal hilum?
Indentation near the center of concave medial border of the kidney where the following structures enter and leave:
Blood vessels
Arteries enter
Veins leave
Lymphatic vessels (take fluid out of kidney)
Ureter (exit)
Nerves (PSNS and SNS can regulate)
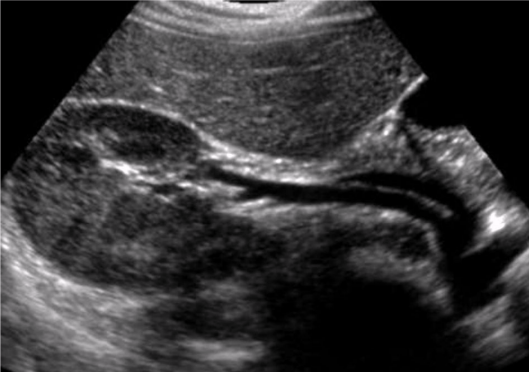
What does this trans image demonstrate?
Shows the renal artery and vein at the renal hilum
What is the renal pelvis?
Large cavity formed by calyces
Flat and funnel-shaped
Continuous with the ureter leaving the pelvis
Medial to hilum
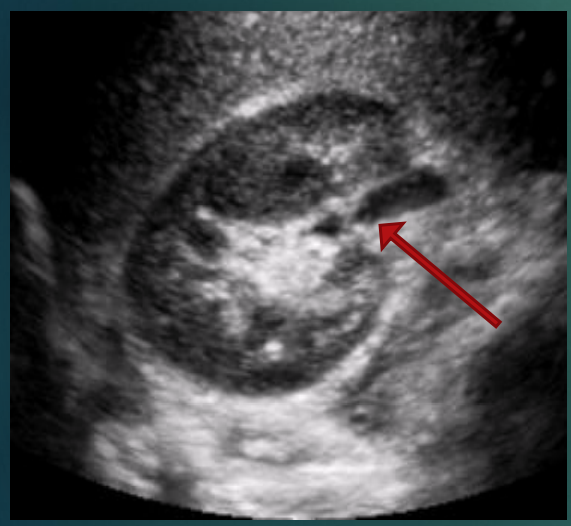
What does this image demonstrate?
Mild hydronephrosis
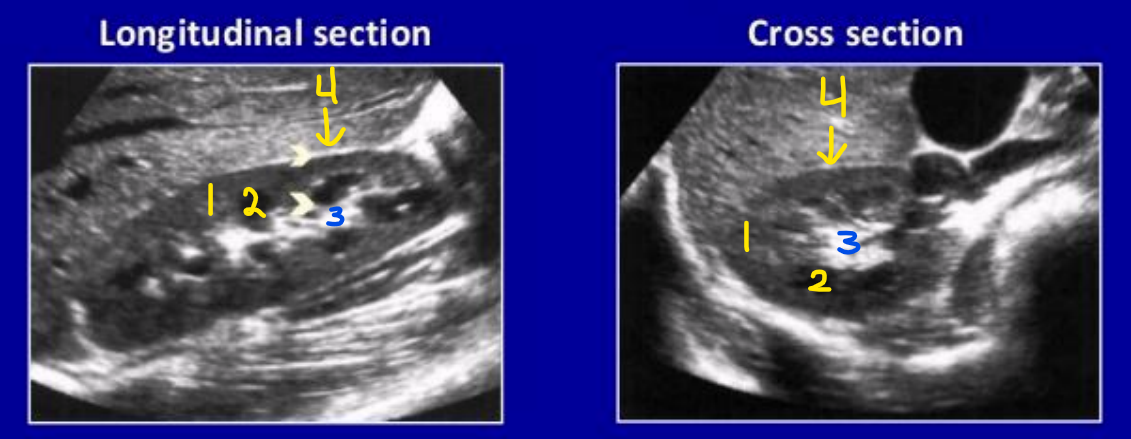
What is number 1? Describe its echogenicity compared to the liver
Renal cortex
Hypoechoic to the liver
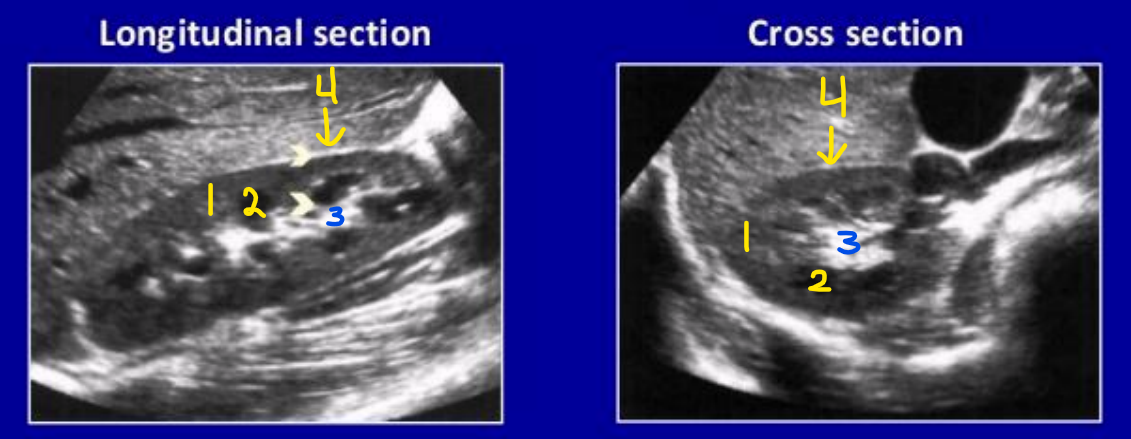
What is number 2? Describe its echogenicity compared to the renal cortex
Renal medullary pyramids
Hypoechoic to the renal cortex
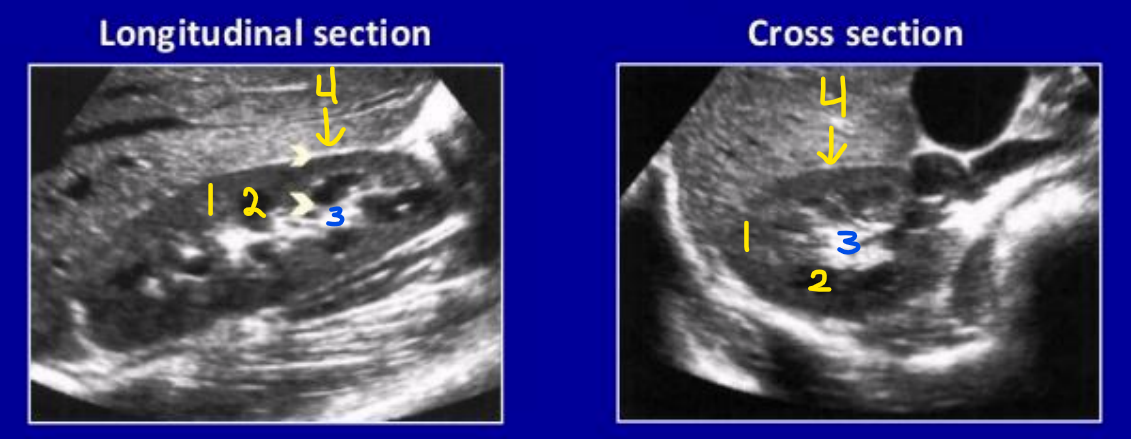
What is number 3? Describe its echogenicity compared to the renal cortex
Renal sinus
Hyperechoic to the renal cortex
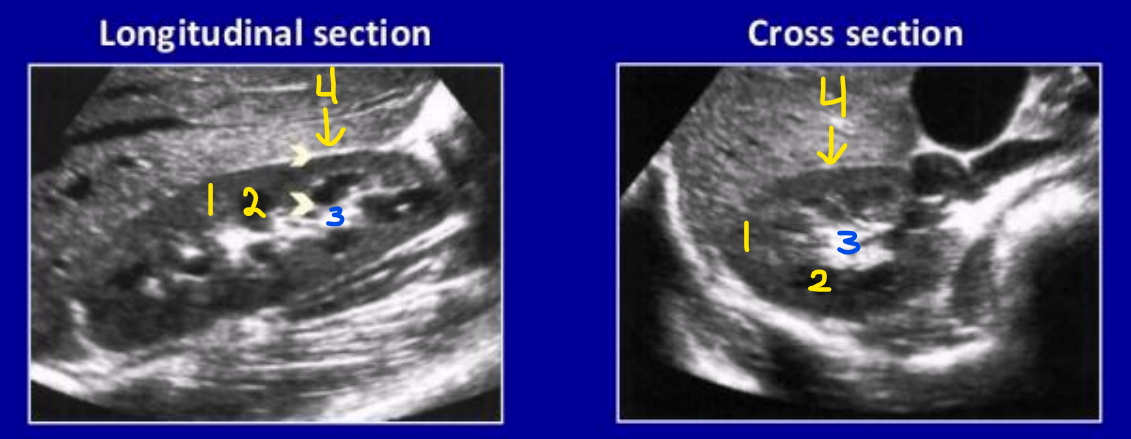
What is number 4? Describe its echogenicity compared to the renal cortex
Renal capsule
Hyperechoic to the renal cortex
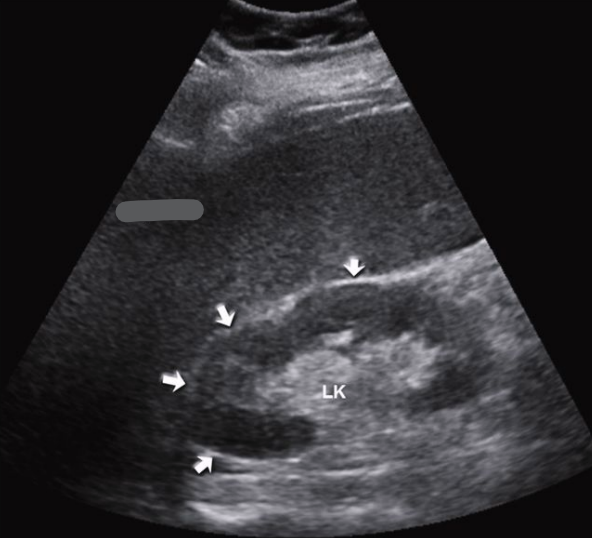
Is this the right or left kidney?
Right kidney
Is this the right or left kidney?
Left kidney
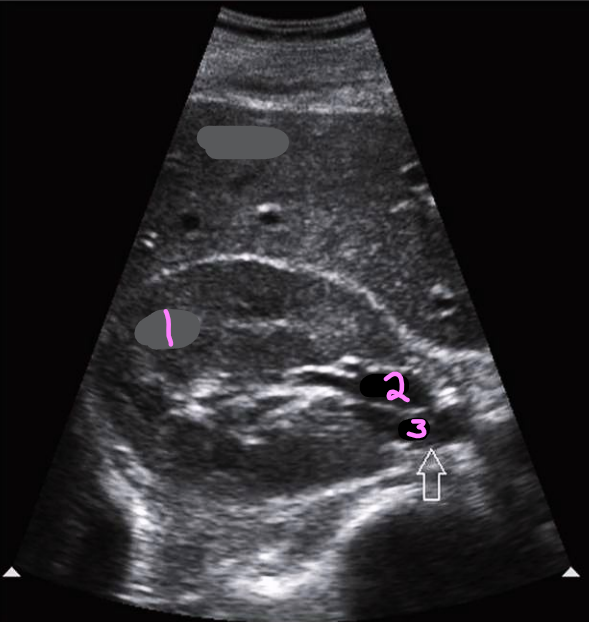
Label this trans kidney image
R kidney
R renal vein
Ureter
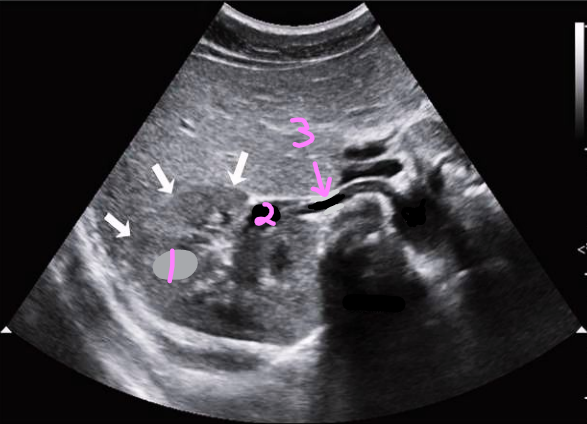
Label this trans kidney image
R kidney
R renal vein
R renal artery
The renal arteries branch ___ to the SMA at the lateral aspect of the abdominal aorta
inferior
Right renal ___ is typically longer than the left
artery
What is the path of the right renal artery?
It courses transversely across the crus of the diaphragm and posterior to the IVC, RRV, the head of the pancreas, and the inferior portion of the duodenum
Right renal ___ is typically shorter than the left
vein
What is the path of the right renal vein?
It courses anterior to the RRA and enters the right lateral aspect of the IVC at a slightly lower transverse plane than the LRV
What is the path of the LRV?
Courses from the left kidney hilus, passes anterior to the LRA, crosses over the aorta anteriorly and passes posterior to the SMA before entering the medial aspect of the IVC
The renal artery transports ___ blood from the heart and aorta into the kidney
oxygenated
The renal vein transports ___ blood from the kidneys to the IVC and heart
deoxygenated
Blood flow from the renal hilum to the parenchyma and renal columns involves …
the renal artery dividing into segmental arteries, branching, entering the parenchyma and passing through the renal columns (into) interlobular arteries
What is the path of blood flow into the kidney via the renal artery?
Renal artery
Segmental arteries
Interlobar arteries
Arcuate arteries
Interlobular arteries
Afferent arterioles
Nephrons (in cortex)
What is the path of blood flow out of the kidney via the renal vein?
Nephrons
Interlobar veins
Arcuate veins
Interlobar veins
Renal vein
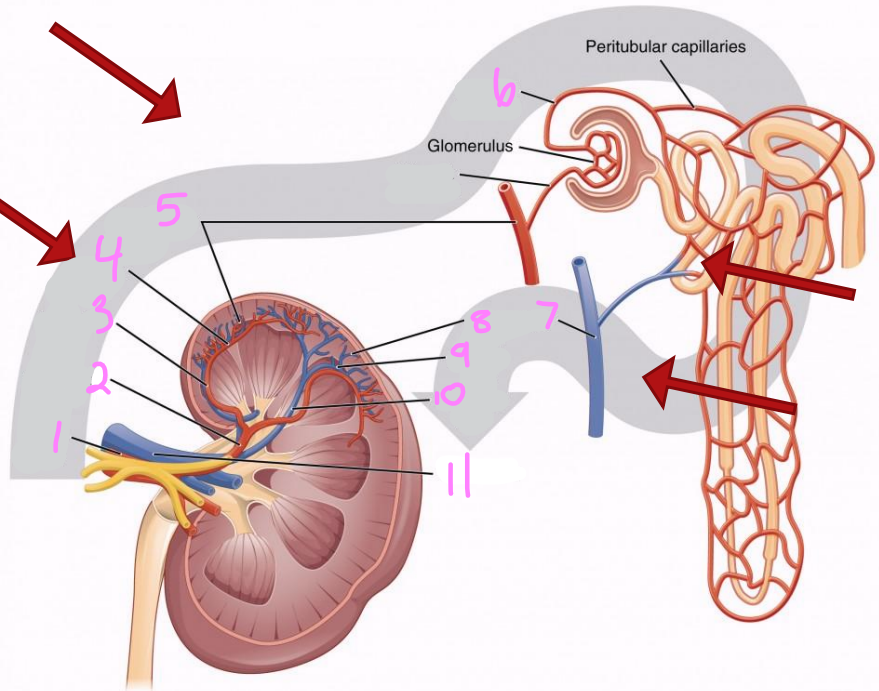
1
Renal artery
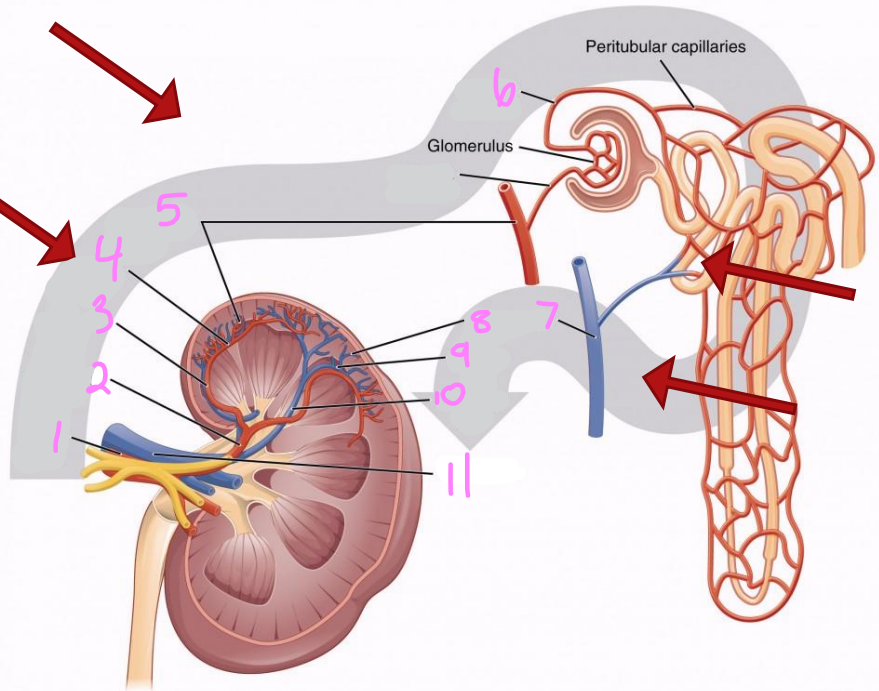
2
Segmental artery
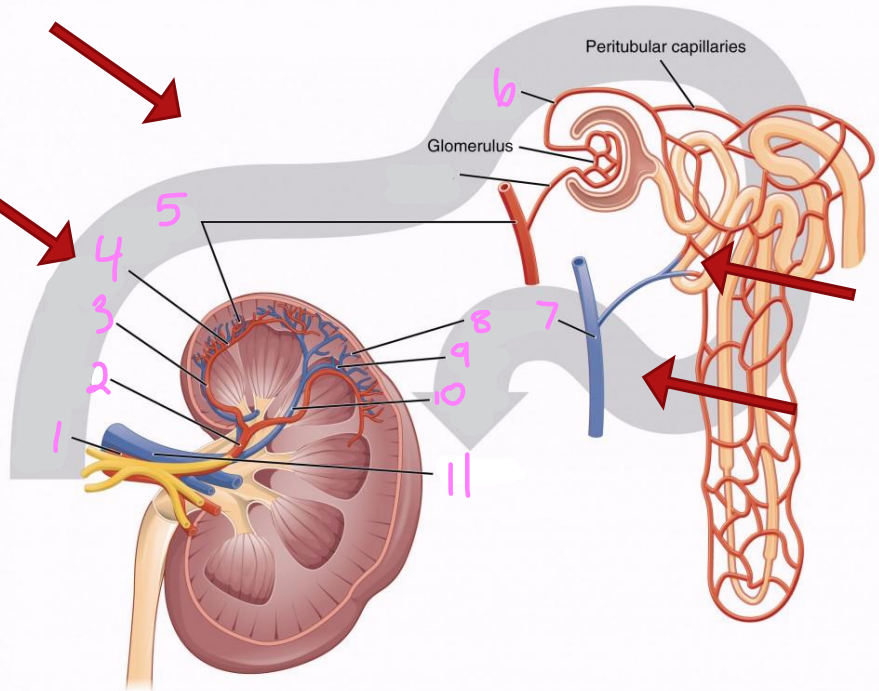
3
Interlobar artery
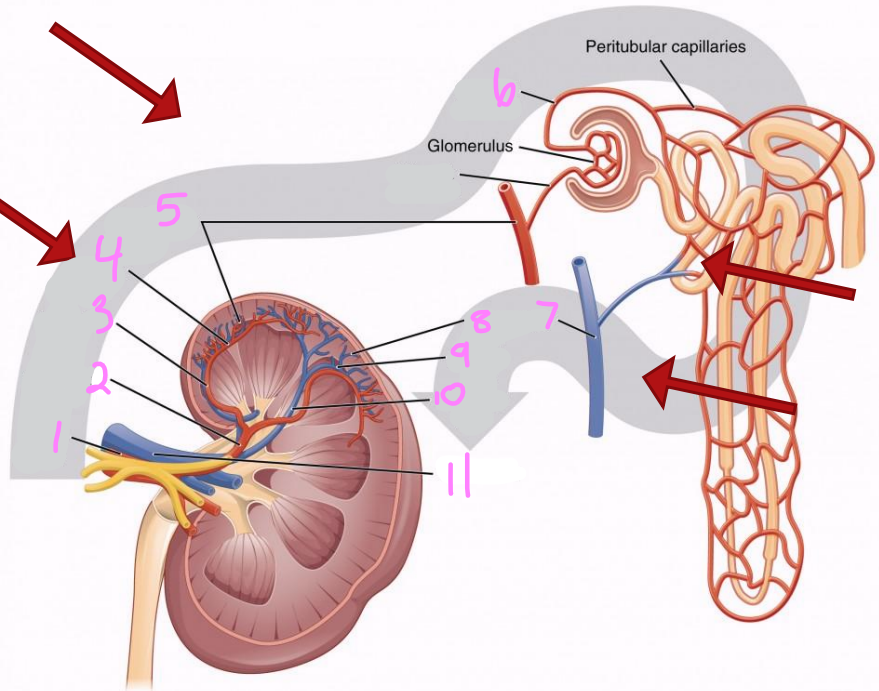
4
Arcuate artery
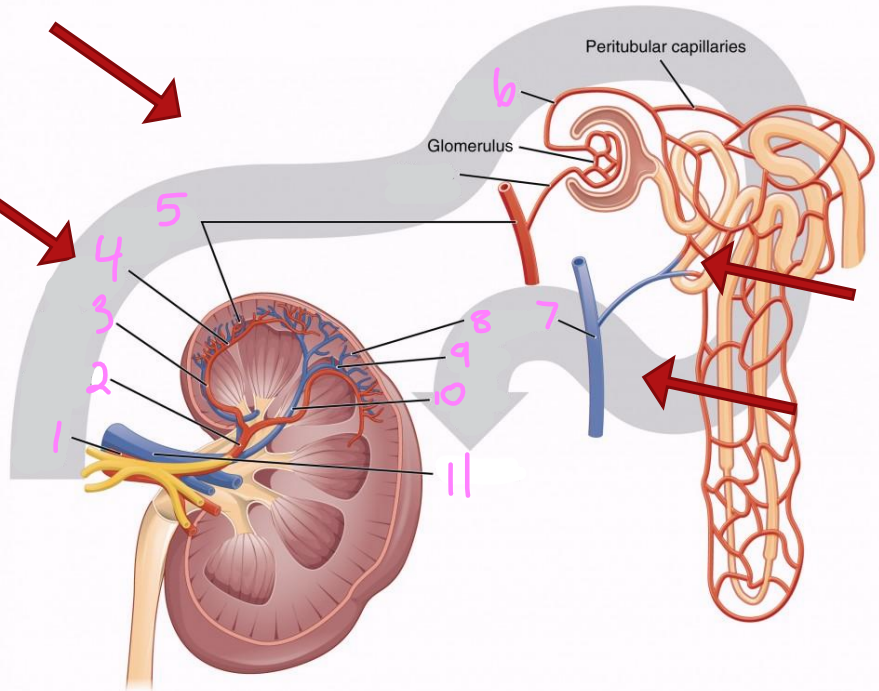
5
Interlobular artery
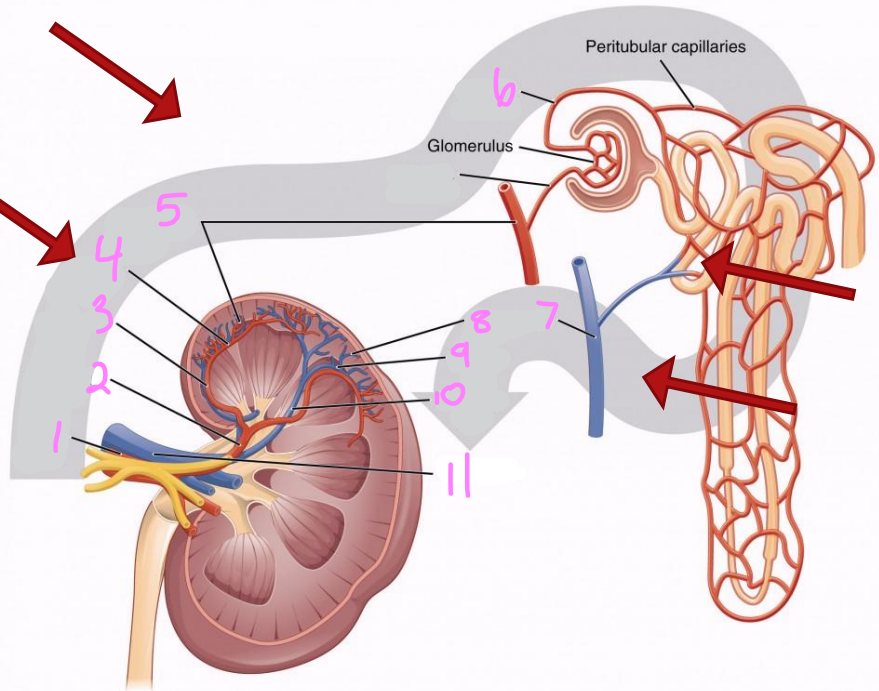
6
Efferent arteriole
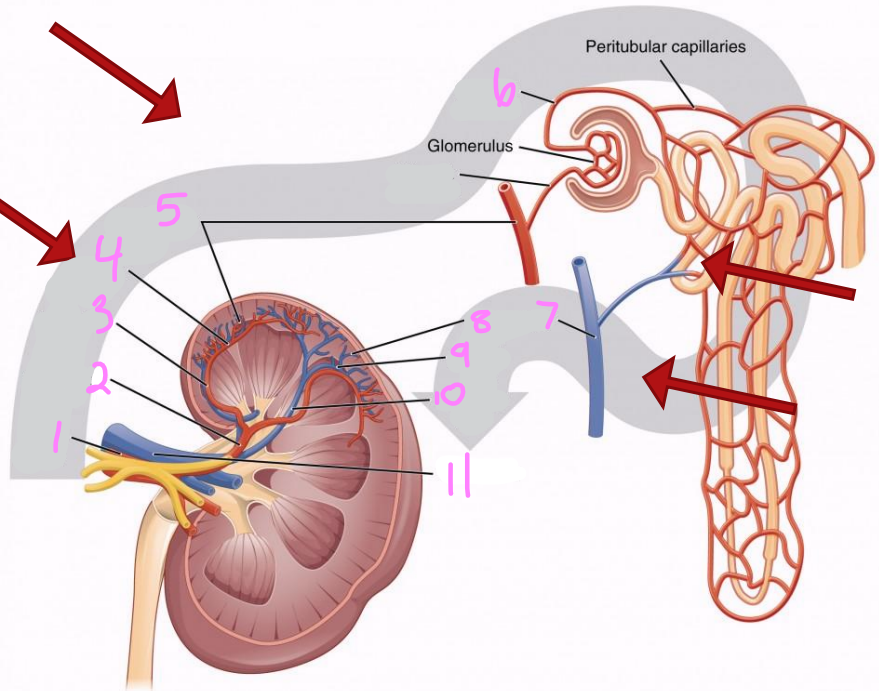
7 & 8
Interlobular vein
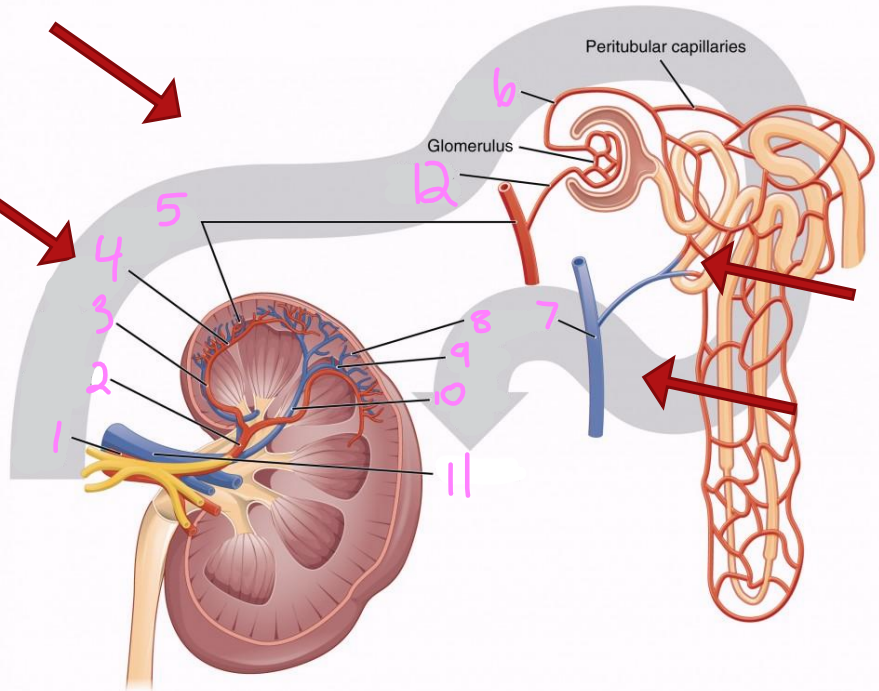
9
Arcuate vein
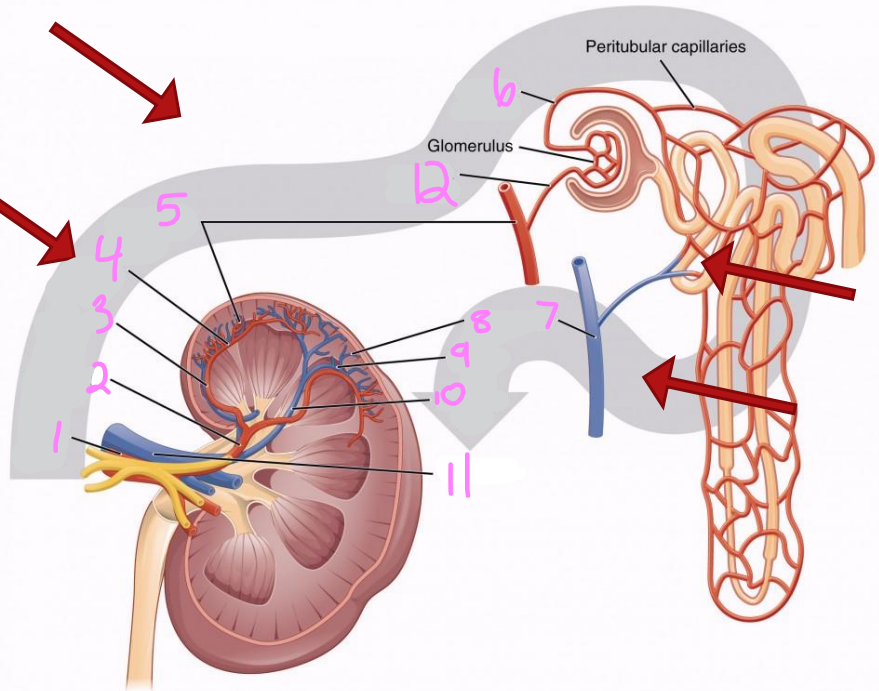
10
Interlobar vein
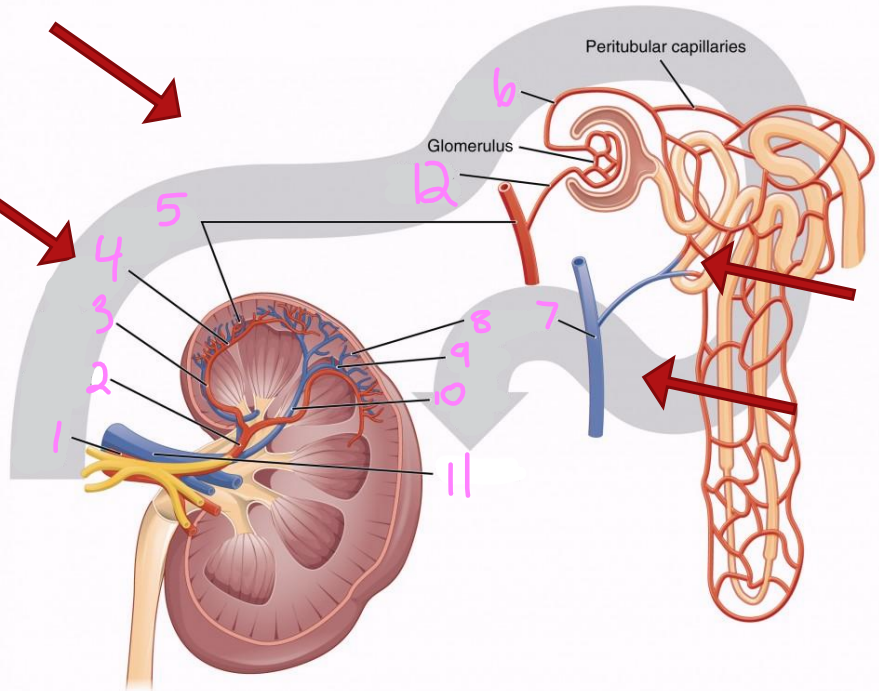
11
Renal vein
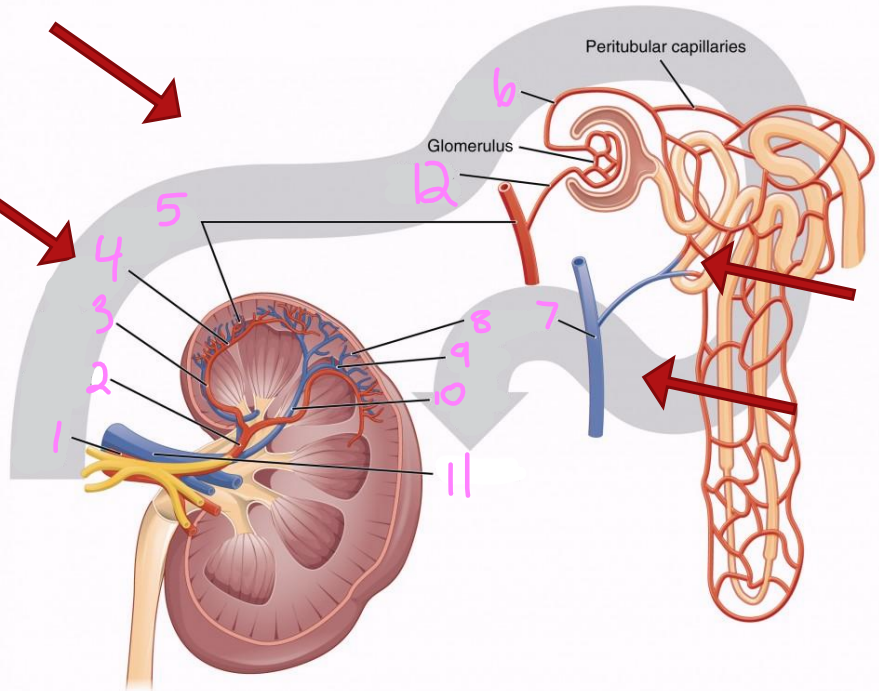
12
Afferent arteriole
What are the main organs of the urinary system?
Kidneys
Ureters
Urinary bladder
Urethra
What are the ureters, and what is their function?
Muscular ducts that connect the kidneys to the bladder
Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder
What is the main function of the urinary bladder?
Temporarily store urine
What is the urethra, and what is its main function?
Exit tube
Discharge urine from the body
What is hydronephrosis?
Dilation of the renal collecting system.
Includes
Dilation of the renal pelvis (pelviectasis)
Dilation of major & minor calyces (caliectasis)
Dilated proximal ureter (hydroureter)
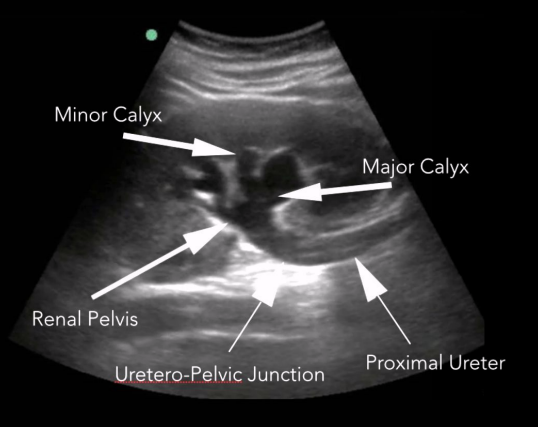
Is the collecting system typically visible on US?
Should not really be visible unless an obstruction is present, though the renal pelvis may be somewhat prominent in certain normal patients
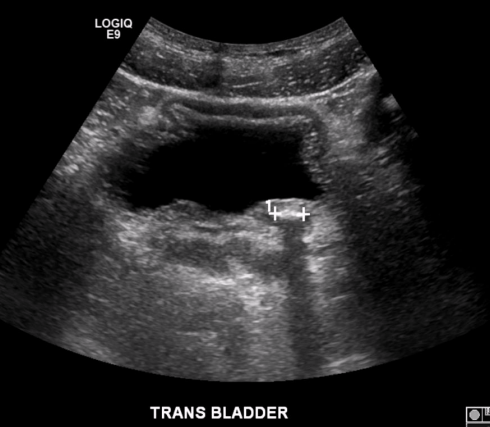
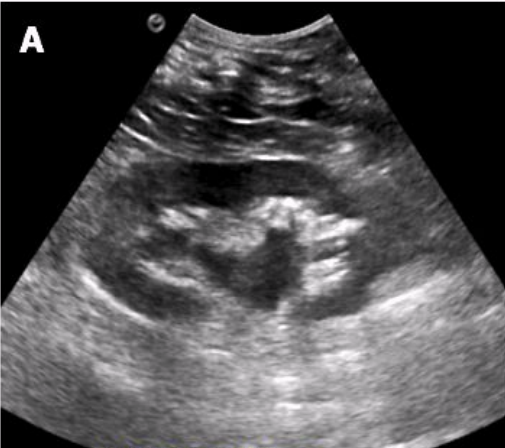
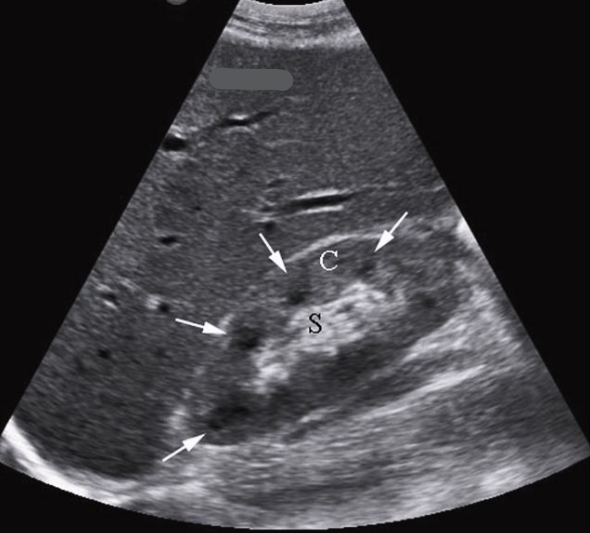
What pathology is present in this image?
Stone in distal ureter
How are the kidneys scanned?
Patient prepped like an abdomen study, plus a full bladder
Patient is scanned in supine, LLD, and RLD
Scan both kidneys
Compare the renal parenchyma to the liver (right) and spleen (left)
Kidney should appear slightly hypoechoic or isoechoic to these structures
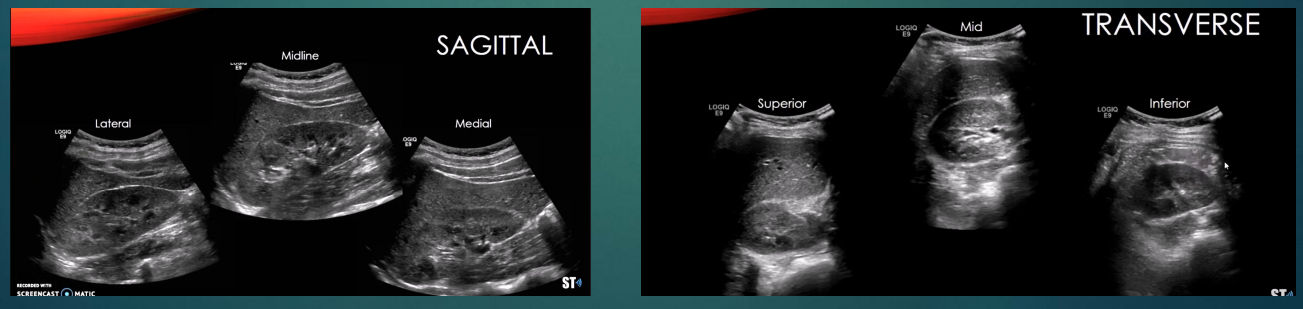
Take longitudinal images, sweeping through the entire kidney (lateral/mid/medial)
Take transverse images, sweeping through the entire kidney (superior to inferior)
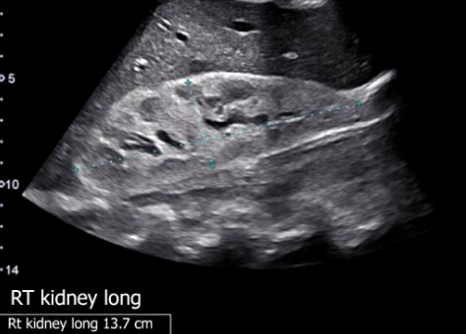
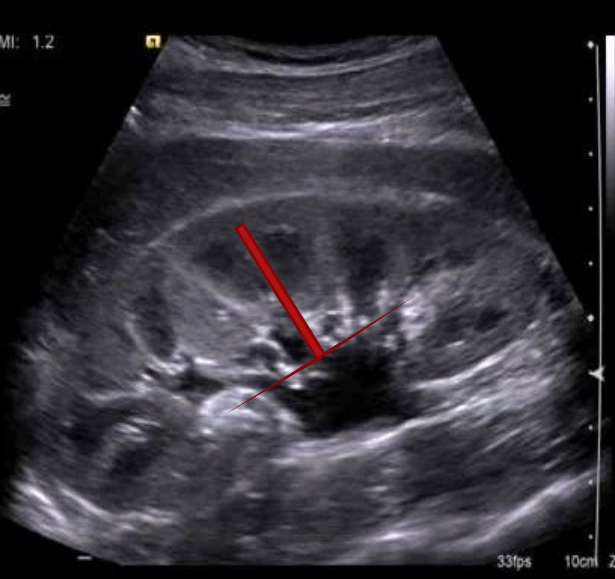
Measure the kidney in long and transverse
Not included in all protocols
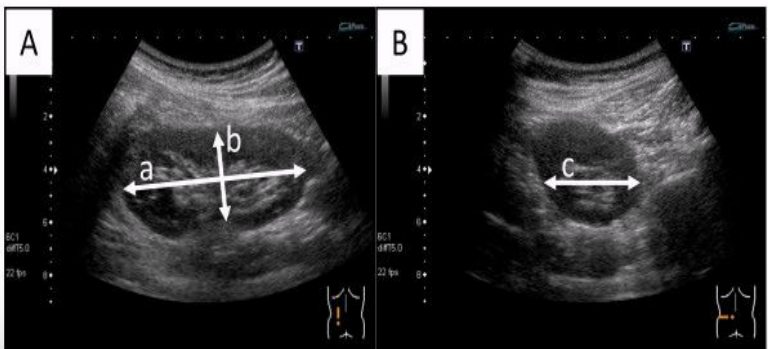
What does this image demonstrate?
How to measure the kidneys in transverse and longitudinal
The shape and contour of a normal kidney appear ____ and have internal lobes
smooth
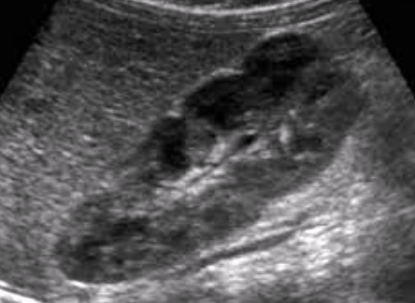
Is this a normal adult kidney?
No