Chapter 9 Microbiology
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Biotechnology
the use of microorganisms, cells, or cell components to make a product: Foods, antibiotics, vitamins, enzymes
Genetic modification
the alteration of an organism’s DNA to change or add traits, often used in agriculture, medicine, and research. Techniques include CRISPR and gene splicing.
Recombinant DNA technology
The insertion or modification of genes to produce desired proteins
Identify the roles of a clone in making recombinant DNA
population of genetically identical cells arising from one cell; each carries the vector
Identify the roles of a vector in making recombinant DNA
self-replication DNA molecule used to transport foreign DNA into a cell (plasmid)
Selection
selecting for a naturally occurring microbe that produces a desired product
Mutation
Mutagens cause mutations that might result in a microbe with a desirable trait
Restriction enzymes
cut specific sequences of DNA
Destroy bacteriophage DNA in bacterial cells
Methylated cytosines in bacteria protect their own DNA from digestion
Create blunt ends or staggered cuts known as sticky ends
List four properties of vectors
Carry new DNA to desired cells
Must be able to self-replicate
Plasmids and viruses can be used as vectors
Shuttle vectors exist in several different species and can move cloned sequences among various organisms
Explain how DNA technology can be used to treat disease and to prevent disease
Treat disease:
- Gene therapy: Corrects faulty gene
- CRISPR: Edits DNA to fix mutations
- Biopharmaceuticals: Produces medicines like insulin
Prevent disease:
- DNA Vaccines: Trigger immune responses
- Genetics Screening: Identifies disease risk
- Gene Editing: Increase gene resistance
Gene silencing
process where a gene is prevented from being expressed, meaning it doesn’t produce its protein
A population of cells carrying a desired plasmid is called a
clone
vector
southern blot
PCR
clone
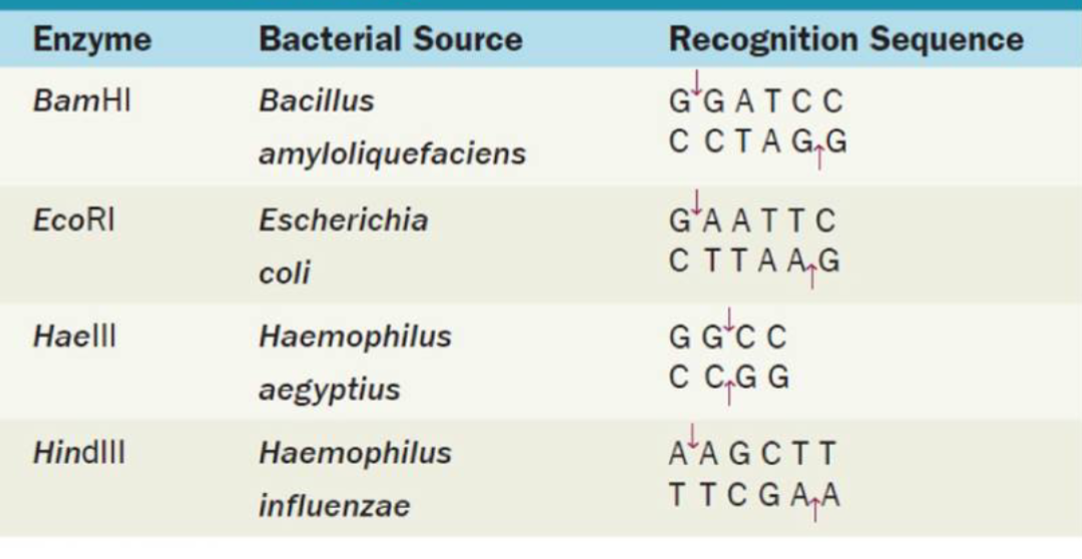
Which enzyme would cut this strand of DNA?
GCATGGATCCCAATGC
BamHI
Which of the following places the steps in the PCR procedure in the correct order?
1) Incubate at 94C to denature DNA strands;
2) Incubate at 72 for DNA synthesis;
3) Incubate at 60 for primer hybridization
1,3,2
A source of heat-stable DNA polymerase is
Thermus aquaticus
Sacchromyces cerevisiae
Bacillus thuringiensis
human
Thermus aquaticus
Biotechnology involves the
use of microorganisms to make desired products and the use of animal cells to make vaccines
development of disease-resistant crop plants
use of animal cells to make vaccines
use of microorganisms to make desired products, the use of animal cells to make vaccines, and the development of disease-resistant crop plants
use of microorganisms to make desired products, the use of animal cells to make vaccines, and the development of disease-resistant crop plants
Which of the following is NOT a desired characteristic of DNA vectors used in gene cloning procedures?
has a selectable marker
large size
self-replication
may replicate in several species
large size
The use of an antibiotic-resistant gene on a plasmid used in genetic engineering makes
the recombinant cell dangerous
the recombinant cell unable to survive
direct selection possible
All of the answers are correct
direct selection possible
While __ is/are responsible for the diversity of life, ___ is/are responsible for shaping a population with organisms possessing characteristics that enhance survival
mutations; selection
selection; mutations
properties; vectors
microbes; DNA
mutations; selection
TRUE/FALSE: In recombinant DNA technology, a vector is a self-replicating segment of DNA, such a plasmid or viral genome.
True