Exam 1
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
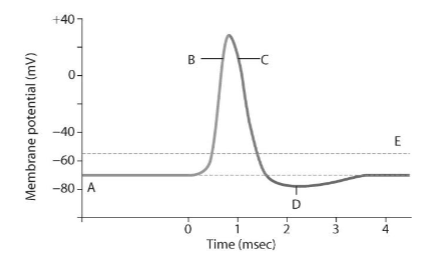
What is the resting membrane potential?
-70
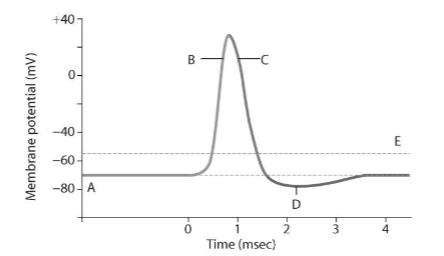
What is the threshold it must reach to start an action potential?
-55
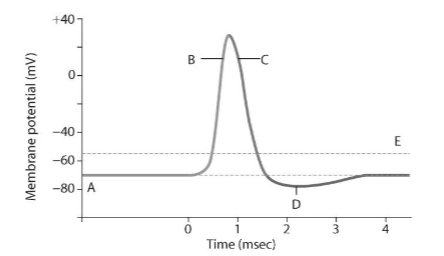
What happens during depolarization?
Na in
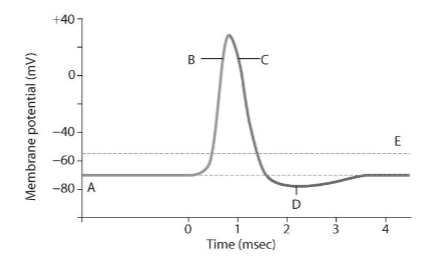
What is the value of the spike?
+30
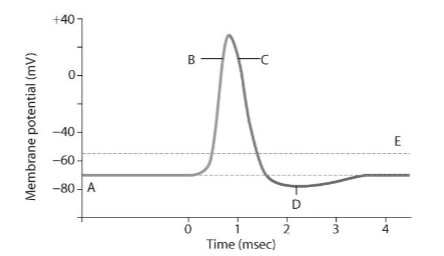
What happens during repolarization?
K out
What binds to a chemically gated sodium channel that results in an end plate potential on a skeletal muscle?
acetylcholine
What does an action potential cause when is travels down the axon and reaches the terminal axons?
influx of calcium
What does the influx of calcium cause the synaptic vesicles to do?
to bind to the membrane
What binds to troponin, releasing tropomyosin off actin binding sites?
calcium
What are carbs ingested as?
polysaccharides
What are carbs digested as?
monosaccharides
What is the primary enzyme that breaks down carbs?
amylase
Where does the breakdown of carbs begin?
saliva
What are proteins ingested as?
polypeptides
What are proteins digested as?
amnio acids
What is the primary enzyme that breaks down protein?
protease
Where does the break down of protein begin?
stomach
What are fats ingested as?
triglycerides
What are fats digested as?
fatty acids and monoglycerides
What is the primary enzyme that breaks down fats?
lipase
Where does the break down of fats begin?
pancreas
What is a fact about the phosphagen system?
no oxygen needed, fuels activities that last less than 15 seconds, uses stored ATP
What is a fact about glycolysis?
no oxygen needed, occurs in the cytoplasm, makes pyruvate and lactate, fuels the krebs cycle
What is a fact about the krebs cycle?
needs oxygen, occurs in the mitochondria, makes carrier molecules
What is a fact about the electron transport chain?
needs oxygen, occurs in the mitochondria, makes ATP
What is the pH of someone in acidosis?
low
What is the pH of someone in alkalosis?
high
If someone is in acidosis, do they want to reabsorb or secrete HCO3?
reabsorb
If someone is in acidosis, do they want to reabsorb or secrete H?
secrete
If someone is in alkalosis, do they want to reabsorb or secrete HCO3?
secrete
If someone is in alkalosis, do they want to reabsorb or secrete H?
reabsorb
What are the components of the central nervous system?
brain and spinal cord
What are the components of the peripheral nervous system?
cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and sensory organs
Where is the origin of preganglionic fibers for parasympathetic?
cranial and sacral
Where is the origin of preganglionic fibers for sympathetic?
thoracic and lumbar
Where is the location of ganglion for parasympathetic?
near effector organ
Where is the location of ganglion for sympathetic?
near spine
What are the main parts of the brain?
cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and diencephalon
What are cranial meninges?
membranes that cover and protect the CNS (dura, arachnoid, and pia)
What are the four lobes of the cerebrum?
frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
speech, thought, and muscle control
What is the function of the parietal lobe?
sensation interpretation
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
recognition center
What is the function of the occipital lobe?
visual center
What is the function of Wernicke’s area?
language comprehension
What does someone sound like if they have an issue with Wernicke’s area?
jumble response, takes a moment to respond
Where is Wernicke’s area?
temporal lobe
What is the function Broca’s area?
speech production
What does someone sound like if they have an issue with Broca’s area?
slow, stutter, broken speech
Where is Broca’s area?
frontal lobe
What is the function of the cerebellum?
fine motor movements, posture, and balance/coordination
What are the parts of the brainstem?
midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
What is the function of the midbrain?
connect cerebrum to spinal cord, visual and auditory reflexes, and wakefulness
What is the function of the pons?
bridge that connects cerebrum to cerebellum, respiratory center, deep sleep, and multiple cranial nerves
What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
connect spinal cord to brainstem, cardiovascular control center, respiratory rhythmicity center
What is the diencephalon?
contains the thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus
What is the function of the thalamus?
relay information to appropriate parts of brain and connected to limbic system
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
thirst, body temperature, sex drive, and weight control
What is the function of the epithalamus?
pineal gland
What is the Limbic System?
group of structures that establish emotions and facilitate memory
What does the limbic system consists of?
hypothalamus, thalamus, hippocampus, and amygdala
What is the Circle of Willis?
flow of blood, provides collateral for the brain
What are the main arteries the circle of willis is derived from?
vertebral and internal carotid
What is the venous drainage from the brain?
transverse to sigmoid to internal jugular vein
What are the ventricles of the brain?
cavities in the brain that produce, transport, and remove CSF
What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid functions
protection, buoyancy, and chemical stability
What is the flow of the ventricles?
Lateral ventricles to Interventricular foramina to Thrid ventricle to Cerebral aqueduct to Fourth ventricle
What are cranial nerves 1-4?
olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear
What are cranial nerves 5-8?
trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear
What are cranial nerves 9-12?
glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, hypoglossal
What are the functions cranial nerves 1-4?
sensory, sensory, motor, motor
What are the functions cranial nerves 5-8?
both, motor, both, sensory
What are the functions cranial nerves 9-12?
both, both, motor, motor
What are the four parasympathetic nerves?
oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
What is the function of olfactory nerve?
smell
What is the function of optic nerve?
vision
What is the function of oculomotor nerve?
pupil constriction and near vision
What does the oculomotor nerve innervate?
superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, inferior oblique
What is the function of trochlear nerve?
to innervate the superior oblique
What is the function of trigeminal nerve?
sensory: around eyes, forehead, mouth, check, anterior 2/3 of tongue, lower jaw
motor: mastication
What are the divisions of the trigeminal nerve?
opthalmic, maxillary, mandibular
What are the muscles of mastications for the trigeminal nerve?
temporalis, masseter, medial pterygoid, and lateral pterygoid
What is the function of abducens nerve?
lateral rectus (eye gaze)
What is the function of facial nerve?
sensory: tast from anterior 2/3 of tongue
motor: muscles of facial expressions and lacrimal and salivary gland secretion
What are the five branches of the facial nerve?
temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical
What is the function of glossopharyngeal nerve?
sensory: taste for posterior 1/3 of tongue and pharynx
motor: pharynx and parotid salivary gland
What is the function of vagus nerve?
sensory: taste to root of tongue, pharynx, larynx, heart, lungs, and abdominal organs
motor: pharynx and larynx, visceral smooth muscles and cardiac muscles
What are the roots of the accessory nerve?
cranial and spinal
What is the function of the pathways of the accessory nerve?
motor: pharynx, trapezius, and stemocleidomastoid muscles
What is the function of hypoglossal nerve?
motor: intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles
What are the tongue muscles that the hypoglossal nerve innervates?
palatoglossus, styloglossus, genioglossus, and hypoglossus
What is the endocrine system?
series of glands that secrete hormones which impact bodily functions
What does the endocrine system help control?
metabolism, growth, and reproduction
What are the glands affected by the endocrine system?
pituitary, adrenal, thyroid, pancreas, parathyroid, testes, and ovaries
What hormone does the pituitary gland release?
growth hormone
What hormone does the adrenal gland release?
glucocorticoids
What hormone does the thyroid gland release?
thyroid hormone
What hormone does the pancreas release?
insulin
What hormone does the parathyroid release?
parathormone
What hormone does the testes release?
testosterone