Bus 101 Information Systems Midterm
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Moore’s Law
The number of transistors per square inch on an integrated chip doubles every 18 months
Moore’s Law Implications
Computers are getting exponentially faster. The cost of data processing is approaching zero.
Metcalfe’s Law
The value of a network is equal to the square of the number of users connected to it
Metcalfe’s Law Implications
More digital devices are being connected together. The value of digital and social networks is increasing exponentially.
Nielsen’s Law
Network connection speeds for high-end users will increase by 50% per year.
Nielsen’s Law Implications
Network speed is increasing. Higher speeds enable new products, platforms, and companies.
Kryder’s Law
The storage density on magnetic disks is increasing at an exponential rate.
Kryder’s Law Implications
Storage capacity is increasing exponentially. The cost of storing data is approaching zero.
Bell's law
Today’s highly successful business could be bankrupt quickly because technology changed and it didn’t.
How Can Intro to MIS Help You Learn Non-Routine Skills? (Systems Thinking)
Model system components and show how components’ inputs and outputs relate to one another
Ability to discuss, illustrate, critique systems; compare alternative systems; apply different systems to different situations
How Can Intro to MIS Help You Learn Non-Routine Skills? (Abstract Reason)
Ability to make and manipulate models
Learn how to use and construct abstract models
How Can Intro to MIS Help You Learn Non-Routine Skills? (Collaboration)
People working together to achieve a common goal, result, or work product
How Can Intro to MIS Help You Learn Non-Routine Skills? (Ability to experiment)
Make reasoned analysis of an opportunity; develop and evaluate possible solutions
Difference between IT and IS
You cannot buy an IS: Can buy, rent, lease hardware, software, databases, and predesigned procedures
IS involves IT, people, and procedures.
Information
Knowledge derived from data.
Meaningful context.
Processed data, or data processed by summing, ordering, averaging, grouping, comparing, or similar operations.
Characteristics of Data
Accurate, timely, relevant (to context/subject), sufficient, worth its cost
2 key characteristics of collaboration
Successful collaboration
People working together to achieve a common goal
Feedback and iteration
Importance of critical feedback
members learn from each other
provide constructive criticism
Be willing to express different ideas
Avoid groupthink
Hackman’s Criteria for Judging Team Success
Successful outcome
Improve team capability over time
Meaningful and satisfying experience
4 primary purposes of collaboration
Become informed
Share data & communicate interpretations
Develop & document shared understandings
Make decisions
Solve problems
Manage projects
Requirements for a collaboration information system
Hardware
Software
Data / metadata
Procedures
People
Requirement for making decisions
Share decision criteria, alternative descriptions, evaluation tools, evaluation results, implementation plan
Requirement for solve problems
Share problem, solution alternatives, cost/benefits, alternative evaluations, solution implementation plan
Requirements for manage projects
Support starting, planning, doing, and finalizing project phases
Collaboration tools to improve team communication
Virtual Meetings
Skype, Google Hangouts, etc
Shared content w/ version control
Microsoft Sharepoint
large/complex app for collaboration
Five Forces Determine Industry Structure
Bargaining power of customers
Threat of substitutions
Bargaining power of suppliers
Threat of new entrants
Rivalry
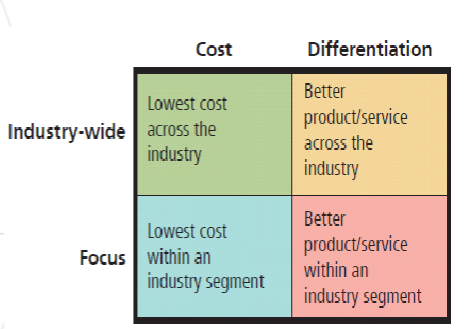
Porter’s Four Generic Competitive Strategies
Industry-wide
Cost
Focus
Differentiation
Primary Activities of the value chain
inbound logistics
operations/manufacturing
outbound logistics
sales and marketing
customer service
inbound logistics (value chain)
receiving, storing, and disseminating inputs to the products
operations/manufacturing (value chain)
transforming inputs into the final products
outbound logistics (value chain)
collecting, storing, and physically distributing the products to buyers
sales and marketing (value chain)
inducing buyers to purchase the products and providing a means for them to do so
customer service (value chain)
assisting customers use of the products and thus maintaining and enhancing the products’ value
Using IS to create competitive advantages
Enhance existing products
differentiate products
lock in customers
raise barriers to market entry
increase profit margins by decreasing costs and decreasing errors
Ex: maintain customer account data (IS collects info and saves customer time by automatically filling in part of form)
package & information delivery system: Helps customer to select delivery address and generate shipping labels
Why use a database?
Organize and keep track of things. If there are multiple themes.
Rows and columns are equivalent to…
Records and fields
Components of a database
tables or files + relationships among rows in tables + metadata
Database Management System (DBMS)
program to create, process, administer a database. licensed from vendors (IBM, Oracle, Microsoft, etc)
Processing the database
DBMS Process Operations
Read
insert
modify
delete data
Structured query language (SQL): international standard used by nearly all DBMS

Forms (database)
view data; insert new, update existing, delete existing data
Queries (database)
Search using values provided by user
Reports (database)
Structured presentation of data using shorting, grouping, filtering, other operations
Application programs (database)
Provide security, data consistency, special purpose processing (ex: handle out-of-stock situations)
Entity-Relationship Data Model
Entities
Something to track (order, customer, item, donation)
Attributes
Describe characteristics of entity (OrderNumber, CustomerNumber, PhoneNumber)
Identifier
Uniquely identifies one entity instance from other instances (StudentIDNumber)
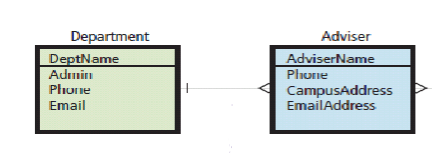
1:N (DB Relationship)
One department may have many advisers, but an adviser may be in only one department
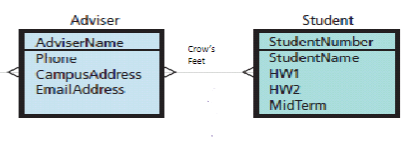
N:M (DB Relationship)
Adviser may have many students, and one student may have many advisers
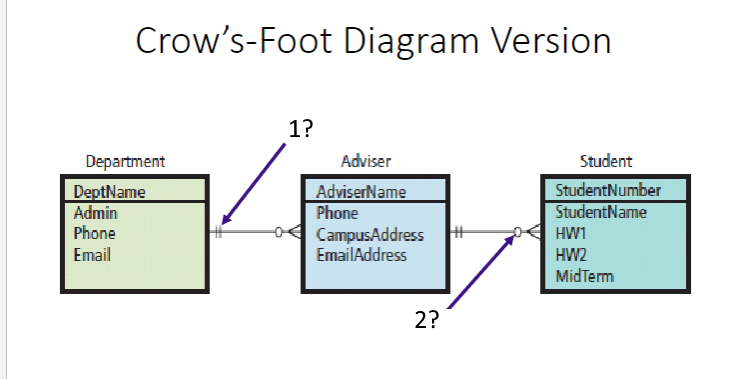
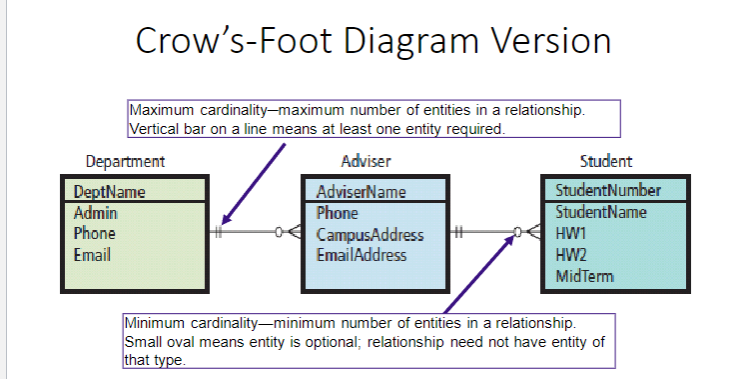
Crow’s-Foot Diagram (What do the arrows mean)
1: Maximum cardinality─maximum number of entities in a relationship. Vertical bar on a line means at least one entity required.
2: Minimum cardinality—minimum number of entities in a relationship. Small oval means entity is optional; relationship need not have entity of that type
Database Normalization
Converting poorly structured tables into 2 or more well-structured ones
Goal: construct table w/ single theme or entity
purpose: minimize data integrity problems

Cloud
elastic leasing of pooled computer resources over the internet
elastic: automatically adjusts for unpredictable demand, limits financial risks.
pooled: same physical hardware, economies of scale.
Benefits of the cloud
lower costs
ubiquitous access
improved scalability
elasticity
virtualization technology
internet-based standards enable flexible, standardized processing capabilities
In-House Hosting Benefits
control of data location
in-depth visibility of security/disaster preparedness
In-House Hosting Negatives
significant capital required
significant development effort
difficult to accommodate fluctuating demand
ongoing support costs
maintenance costs
obsolescence
SaaS - software as a service (cloud service)
users are employees and customers. allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps over the Internet (ex: iCloud)
PaaS - platform as a service (cloud service)
users are app developers/testers. software and hardware that provides an operating system on which developers can create and deploy solutions without administrating the underlying system software. (ex: AWS)
IaaS - Infrastructure as a service (cloud service)
users are network architects and system admins. It provides scalability, servers, data storage, and network hardware upon which a company can install and manage its operating system and database management to host its applications on the cloud. (ex: Amazon EC2)
content delivery network (CDN)
stores user data in many different geographical locations and makes data available on demand
specialized type of PaaS
CDN Benefits
decreased loadtime
reduced load on origin server
increased reliability
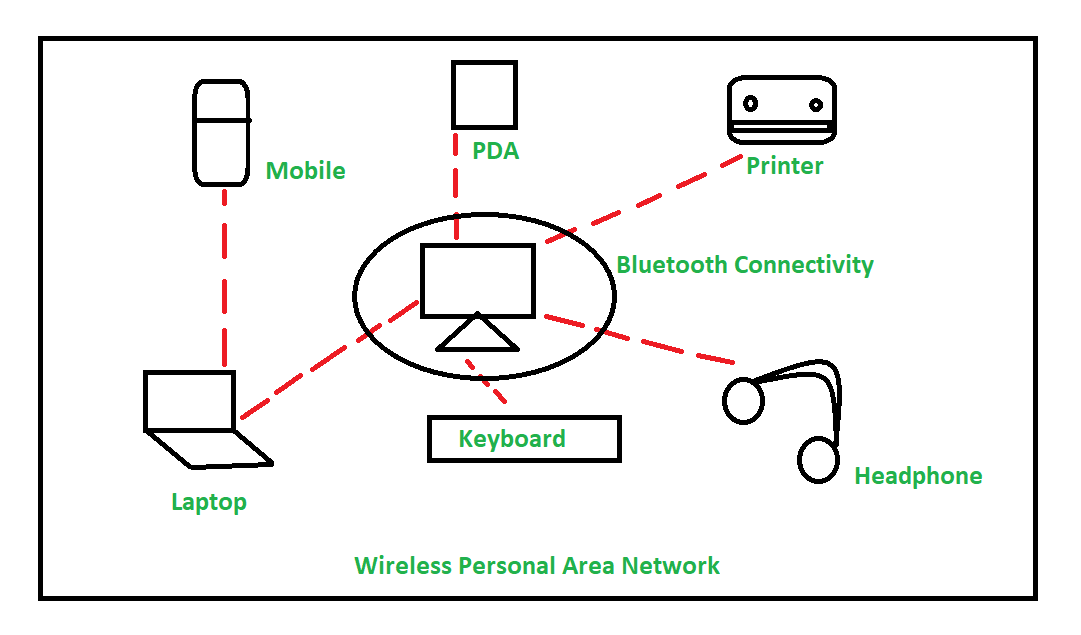
Personal area network (PAN)
Devices connected around a single person
Local area network (LAN)
computers connected at a single physical site
Wide area network (WAN)
Computers connected between two or more separated sites
Router
Device that forwards data packets along networks. A router is connected to at least 2 networks located at gateways, the places where two or more networks connect. Use headers and forwarding tables to determine best path for forwarding the packets, and use protocols such as ICMP to communicate with each other and configure the best route.
Switch
Device that filters and forwards packets between LAN segments. LANS that use switches to join segments are called switched LANs or, in the case of ethernet networks, switched ethernet LANs
Hub
common connection point for devices in a network. Commonly used to connect segments of LAN. Contains multiple ports. When a packet arrives at one port, its copied to all other ports so that all segments of LAN can see all packets
Switches vs routers
Switches create a network. Routers connect networks.
Domain Name System (DNS)
unique name affiliated with a public IP address. multiple domain names for same IP address.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
internet address protocol, such as http://
Public IP address
identifies a unique device on internet. assigned by ICANN. one public IP address per LAN.
Private IP address
identifies a device on a private network, usually a LAN. Assignment is controlled by LAN. Eliminates registering public IP with ICANN. Protects against direct attack.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
communications standard for delivering data and messages through networks
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
a mechanism for creating a secure connection between a computing device and a computer network, or between two networks, using an insecure communication medium such as the public Internet.
Structured Processes
formally defined, standardized processes that involve day-to-day operations.
Dynamic Processes
flexible, informal, and adaptive processes that normally involve strategic and less specific managerial decisions and activities.
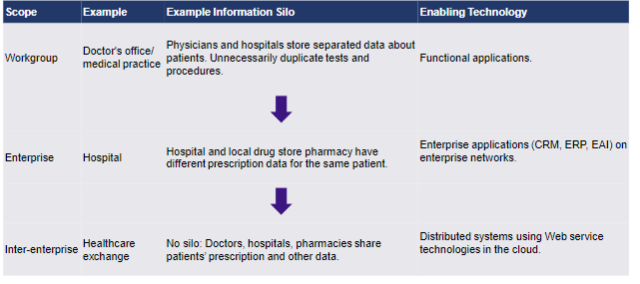
Workgroup
Support one or more _____ processes. 10–100 users; procedures often formalized; problem solutions within group; workgroups can duplicate data; somewhat difficult to change (ex: doctors office)
Enterprise
Support one or more _______ processes. 100–1,000+ users; procedures formalized; problem solutions affect enterprise; eliminate workgroup data duplication; difficult to change (ex: hospital)
inter-enterprise
Support one or more _______ processes. 1,000+ users; systems procedures formalized; problem solutions affect multiple organizations; can resolve problems of duplicated enterprise data; very difficult to change (ex: healthcare exchange)
information silo problems
data duplicated
data inconsistency
data isolated
disjointed processes
lack of integrated enterprise information
inefficient (decisions made in isolation)
Solving problem of information silos
integrate into single database
revise applications
Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
Integrated data, enterprise systems create stronger, faster, more effective linkages in value chains.
difficult, slow, expensive
requires high-level and expensive skills/time
Customer relationship management (CRM)
suite of applications, database, set of inherent processes. manage all interactions with customer through four phases of customer life cycle. supports customer-centric organization.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
software system that helps you run your entire business, supporting automation and processes in finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, services, procurement, and more.
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
connects system islands
enables communicating and sharing data
provides integrated information
provides integrated layer on top of existing systems while leaving functional application as is
enables gradual move to ERP
True ERP Have Application that Integrate:
supply chain
manufacturing
CRM
Human resources
Accounting
challenges of implementing and upgrading to ERP
collaborative management
requirement gaps
transition problems
employee resistance
new technology
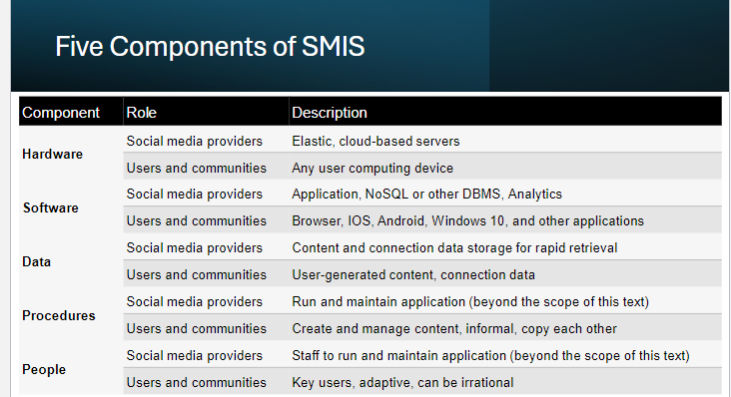
Social media information system (SMIS)
sharing content among networks of users
3 SMIS Roles
Social media providers
FB, Google, etc
Users
individuals/organizations
Communities
Mutual interests that transcend geographic boundaries
Five Components of SMIS
Hardware
Software
Data
Procedures
People
Social CRM
Customers craft own relationship.
Wikis, blogs, discussion lists, frequently asked questions, sites for user reviews and commentary, other dynamic content.
Customers search content, contribute reviews and commentary, ask questions, create user groups, etc.
Not centered on customer lifetime value.
How do social networks add value to businesses
Progressive organizations have social media
encourage customers and interested parties to leave comments
risk - encouraging excessively critical feedback
klout score - measure of individuals social capital
Earning revenue from social media
transform interactions w/ customers, employees, and partners into mutually satisfying relationships with them and their communities
you are the product (renting your eyeballs to an advertiser)
monetization
Revenue models for social media
Advertising
pay per click
freemium
offers user basic service for free, charge for premium features
sales
apps and virtual goods, donations, affiliate commissions
Enterprise Social Networks (ESN)
software platform uses SM to facilitate cooperative work of people within an organization. improve communication, collaboration, knowledge sharing, problem solving, decision making.