Lecture 6- resin composites
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Resin Composites – Applications (Uses in Dentistry)
Direct Restorations
Placed directly in the cavity (anterior & posterior).
Includes Class I–V restorations.
Indirect Restorations
Lab-processed, then cemented.
Inlays, onlays, veneers, crowns.
Base-Up / Build-Up
Core build-ups under crowns.
Replace large missing tooth structure.
Sealants
Preventive application for pits and fissures.
Cements
Used as luting agents for indirect restorations (inlays, onlays, veneers).
Repair of Restorations
Add composite to fix chipped or defective existing restorations.
Provisional Restorations
Short-term crowns, bridges, or fillings.
Delivery Forms
Single paste (light-cure): syringes, compules (single dose).
Dual-paste (chemically/dual-cured): automix or manual mix.
Composite
compound of two or more materials with properties superior/intermediate to individual constituents.
Composition of composite (5)
resin matrix, filler particles, coupling agent, Optical Modifiers, Initiators/Accelerators
1) Resin matrix is made up of (3)
Bis-GMA (hard, solid)
UDMA
TEGDMA (runny/flowable)
*resin material is hydrophobic must keep composite dry to work
2) Filler Particles:
Quartz, silica, lithium aluminum silicate, zirconia, barium/strontium/zinc/ytterbium glasses.
Improve strength, reduce shrinkage & water sorption.
without filler particles resin chains will curl up -> swells
3) Coupling Agents:
Silanes → bond inorganic filler particles to resin matrix.
4) Optical Modifiers:
Pigments, opacifiers, fluorescence, opalescence → match enamel/dentin shades.
5) Initiators/Accelerators:
Chemical: benzoyl peroxide + amine
Light: camphorquinone (blue ~468 nm), Lucirin TPO (violet ~370 nm), phenylpropanedione
Dual-cure = combination
Polymerization
a chemical process where small molecules, called monomers, link together to form long chains of larger molecules, called polymers
Free radical chain reaction (double bond breaks → reactive site).
50–70% (not all monomers react) bec now maxtrix is more hard less free space
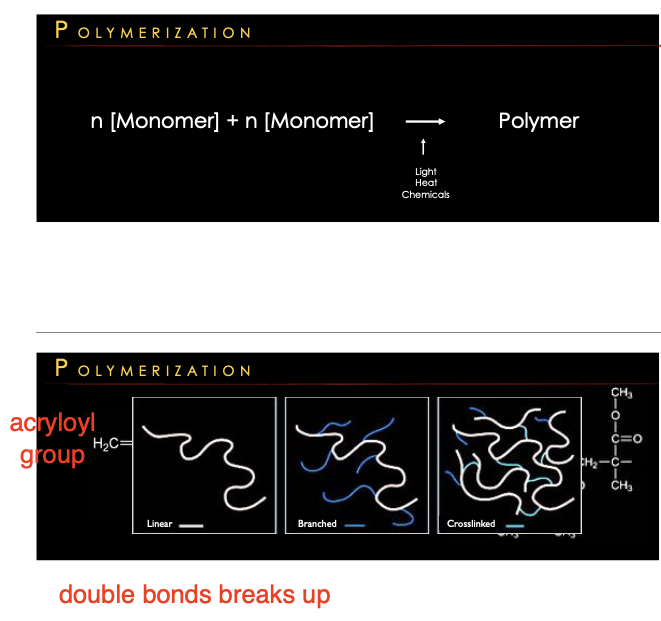
Polymerization stages: (3)
initiation → propagation → termination
Polymerization Issues:
Problems:
Oxygen-inhibited layer (soft, unpolymerized surface).
Inhibition by eugenol (temp fillings) or peroxide (bleaching).
Shrinkage:
Always occurs; direction depends on cavity shape and bonded walls (C-factor).
Higher C-factor = more stress/debonding risk.
Oxygen-inhibited layer is formed by:
the atmosphere has oxygen that reacts with free radicals in the composite
Two options with oxygen inhibited layer:
Remove: (best because OIL is bad) when surfaces of restorations exposed to air (done building up)
Leave: surface will be covered with more layers (NOT done with build up) *Overfill slightly → polish later
Polymerization shrinkage:
Stress can debond at margins, cause staining, sensitivity.
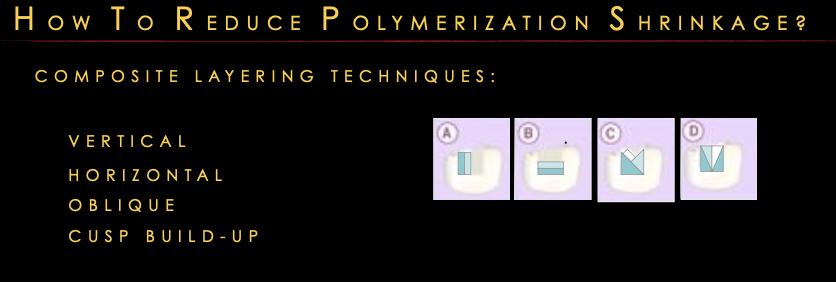
Reduced by:
Smaller filler size
Special monomers
Soft-start curing lights
Incremental layering (2 mm layers, low C-factor).
c-factor 5/1 highest stress in class ___&___ c-factor 1/6 lowest stress in class ___
I & V, VI
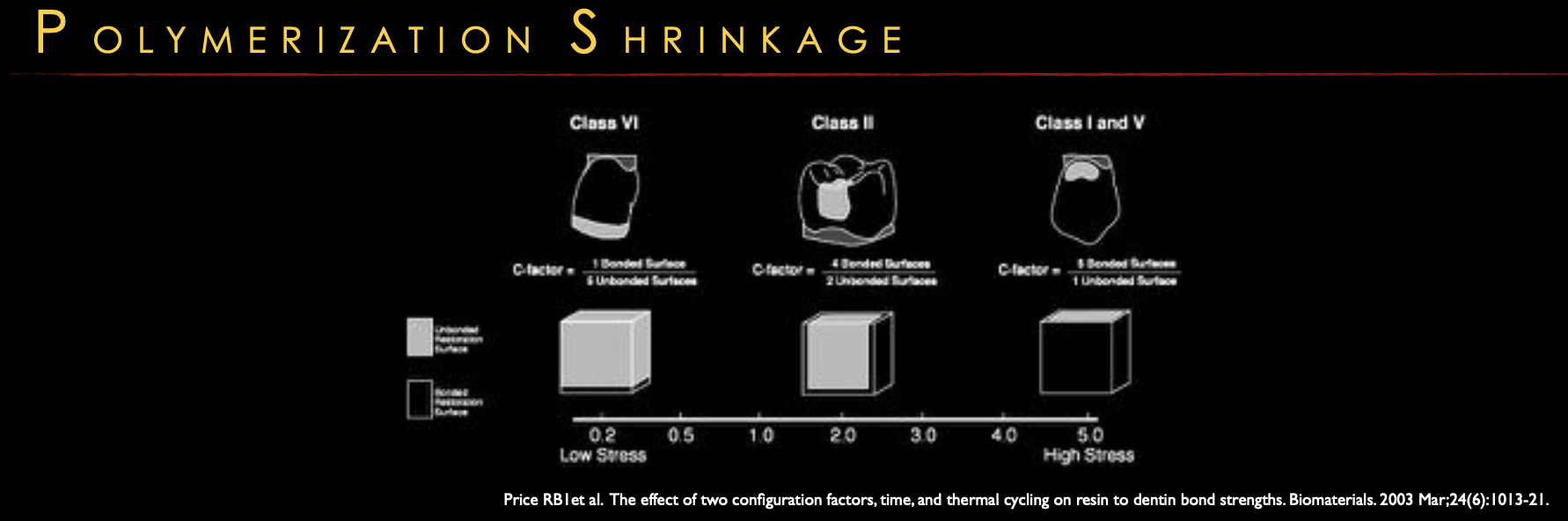
C- Factor
ratio of bonded / unbonded surfaces
lower C factor = lower stress
less walls = less likely to break because no air in between
Layering techniques
vertical, horizontal, oblique, cusp build-up
*b has high c factor lots of stress on the walls so not very good technique
Types of Filler Composites
Macrofilled: >5 µm, 60–80% wt.
Microfilled: 0.04–0.6 µm, 35–85% wt., very good polishable.
Hybrid: 0.04–15 µm, 70–80% wt.
Fine/Microhybrid: 0.04–1 µm, 70–80% wt.
Nanohybrid/Nanofilled: 0.002–0.075 µm, ~75–79% wt., strong + great polishable.*
*we use nanofilled
Shade & Optical Properties
Shade guides → dentin & enamel shades.
Fluorescence: absorbs energy, emits longer wavelength.
Opalescence: scatters shorter wavelengths, gives natural look.
Opacity: resistance to light passage; increases with age.
Spectrophotometer: objective shade mapping.
Light Curing
Blue light (~468 nm) used for polymerization.
Curing modes: standard, high power, extra power, polywave.
Barriers: sleeves, films for infection control.
Important: match light wavelength with composite’s initiator system.