<NOT FINISHED> - Chapter 13 - CyberSecurity
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Why were security, privacy, and ethical concerns born from?
Born along with the introduction of information systems and technology in organizations
Widespread adoption of cloud-based solutions and the proliferation
of digital businesses, has done what?
Dramatically amplified threats of Security, privacy, and ethical concerns
A failure in security, privacy, or ethics can have
major consequences, potentially direct damaging effects (e.g., computer outages, disruptions to operations) and negative indirect effects (e.g., legal recourse, image damage)
digital security and risk management are not solely …what?
“IT issues”
What happened in WannaCry Example?
On May 12, 2017, the WannaCry ransomware rapidly infected hundreds of thousands of computers across banks, hospitals, firms, and other organizations worldwide. The attack lasted only a few days but caused damage estimated in the billions of dollars.
What happened in SolarWinds CyberAttack Example?
Systems using servitized digital resources face third-party vulnerability risks. In a major breach, hackers compromised the Orion software update suite of Texas-based IT firm SolarWinds, used by over 33,000 customers. Once clients installed the tainted updates, a backdoor was introduced into their networks. The breach went undetected for months, allowing attackers to access data from 18,000 networks—including Microsoft, Cisco, Intel, Nvidia, and US government agencies.
Digital infrastructure and resources must be secured against (2)
both internal and external threats
The internal threat is due to (2)
either ill-willed
careless personnel and is mitigated by setting security policies and training
Where do external threats come from?
The external threats come from hackers and take the form of
malware, intrusion attempts, and denial-of-service attacks.
How can internal and external threats be addressed?
By appropriate safeguards
Cybersecurity refers to
the set of defensive measures and policies an organization puts in place to mitigate threats to its technology infrastructure and digital assets
IT risk management is
the process by which the firm attempts to identify and measure cybersecurity risks and to devise the proper mitigation strategy
Computer systems are…(2) think woah
the infrastructure of developed economies
legitimate targets of terrorist attacks
Cybersecurity and IT risk management have come to managerial
attention because of
the increasing threat of cyberterrorism
“Game of Chess“ means?
offers a great metaphor between attackers
and the organization
Why should cybersecurity be on a manager’s radar?
Cybersecurity should be on managers’ radar because of the risk
of leaving it underfunded, unless managers get directly
involved in the threat assessment and mitigation process
What type of deliverable is cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is a negative deliverable
What does it mean by “Cybersecurity is a negative deliverable“
In other words, all the money spent on securing the firm’s IT infrastructure and the data repositories produces no revenue and no efficiencies.
It limits the possibility of future negative fallout.
It is difficult to take credit for it when all you have to show is that
nothing bad has happened.
The risk assessment process consists of
auditing the current resources,
- technological &
- human assets,
to identify the current set of vulnerabilities the firm is facing
Risk Mitigation…(2)
the process of matching the appropriate responses to the threats your firm has identified
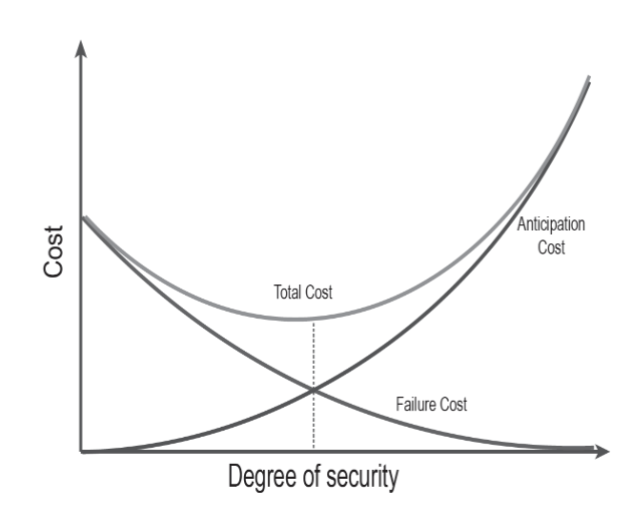
best trade-off between the degree of cybersecurity the firm
attains and the total investment in countermeasures necessary
to achieve it
What is a key vulnerability for firms integrating external servitized digital resources?
They increasingly rely on the “digital supply chain” without direct control over external resources—making them vulnerable to third-party risks, as seen in the SolarWinds case
What is the purpose of a risk audit in cybersecurity?
A risk audit provides the foundation for conducting a risk analysis by identifying potential hazards.
What does risk analysis aim to achieve?
Risk analysis attempts to quantify the hazards identified during the risk audit to assess their impact.
How should firms determine investment in cybersecurity safeguards?
Cybersecurity investment should be proportional to the severity of the threat and its potential negative effects.
Risk acceptance
consists of not investing in countermeasures and not
reducing the security risk → Higher potential failure costs while
minimizing the anticipation costs
Risk reduction
consists of actively investing in the safeguards designed to mitigate security threats → Higher anticipation costs while actively
reducing failure costs.
Risk transference
consists of passing a portion (or all) of the risks associated with cybersecurity to a third party (e.g., by outsourcing
security or buying insurance)
What are the main challenges of mitigation strategy?
Identify the optimal blend of the three strategies (Risk acceptance, reduction, transference)
Internal cybersecurity threats are posed by
by individuals who have direct access to the firm’s technology infrastructure or those who are permitted
Ex. A survey by Verizon: In 30% of companies, employees were the sources of cybersecurity incidents.
Intentional Malicious Behavior is
typically associated with unhappy or ill-willed employees who have a reason for leaking data or damaging a system
Careless Behaviour is
typically associated with ignorance of, or disinterest in,
cybersecurity policies.
Other examples of careless behaviour…
failing to modify default passwords
breaking the organization’s policy on Internet and web usage
not following guidelines about saving data on personal devices
failing to destroy sensitive data according to planned schedules
What is an intrusion in cybersecurity, and how do hackers typically execute it?
Intrusion refers to any situation where an unauthorized attacker gains access to an organization's IT resources. Hackers often exploit coding bugs or hidden software features to take control of entire systems or gain privileged access to sensitive company data
Social Engineering
trying to somehow convince legitimate users to
share some information
Phishing
consists of sending official-sounding spam (i.e., unwanted
e-mail) from known institutions (e.g., MasterCard)
Backdoors and Exploits
A backdoor is a code built into a software
program that allows access to the application by bypassing password
protection.
Why is delayed detection of an intrusion a major concern?
Because it allows the intruder to operate undetected over time, potentially executing multiple crimes.
What kind of data is at risk during an intrusion?
Private information and records, which the intruder may access and steal.
What must happen once an intrusion is discovered?
A thorough investigation is required to trace the origin and method of the breach.
What are the reputational risks if an intrusion becomes public?
If individuals’ private data is compromised and disclosure is legally required, the firm may suffer significant reputational damage.
Malicious code
refers to software programs that are designed to cause damage to IT assets
Virus
spreads by attaching itself to
legitimate, executable programs. Once
it runs, the virus replicates itself and
spreads to other programs. If the
infected files are shared by others,
their machines will be infected as well.
Trojan Horse
a computer program
that claims to deliver some useful
functionality, but executes a payload
similar to a virus
Worms
exploit cybersecurity holes in
network software to replicate
themselves
Spyware
is an unrecognized program
that monitors behavior, collects
information, and either transfers this
information to a third party or performs
unwanted operations
Ransomware
spreads as a harmless
attachment to e-mail messages, and
limits access to the user’s resources and
system, demanding a ransom in
exchange