AP HUG - Unit 1 (Thinking Geographically)
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Human Geography
The study of the physical features of the world and of human activity as they affect/interact with one another.
Physical Geography
The branch of geography dealing with natural features and processes, such as: rocks and minerals, landforms, soils, animals, plants, water, atmosphere, rivers and other water bodies, environment, climate and weather, and oceans.
Carl Sauer
Father of human geography. He was the first to study human patterns and the "why of where" ("Why are those people living there? Where did they migrate from? How has the environment shaped their cultural practices?").

Two Geographical Perspectives
1. Spatial perspective
2. Ecological perspective
-While the spatial perspective is about patterns and location, the ecological perspective is about interactions between humans and nature.
Spatial Perspective
A geographical perspective that focuses on where things are located, how they are arranged on Earth's surface, and why those patterns exist.
Ecological Perspective
A geographical perspective that looks at the relationship between people and the environment.
-It explores how humans adapt to, depend on, and change their surroundings, such as how farmers irrigate land in dry areas or how pollution affects local ecosystems.
Latitude
Lines that run horizontally on a map and measure North/South.
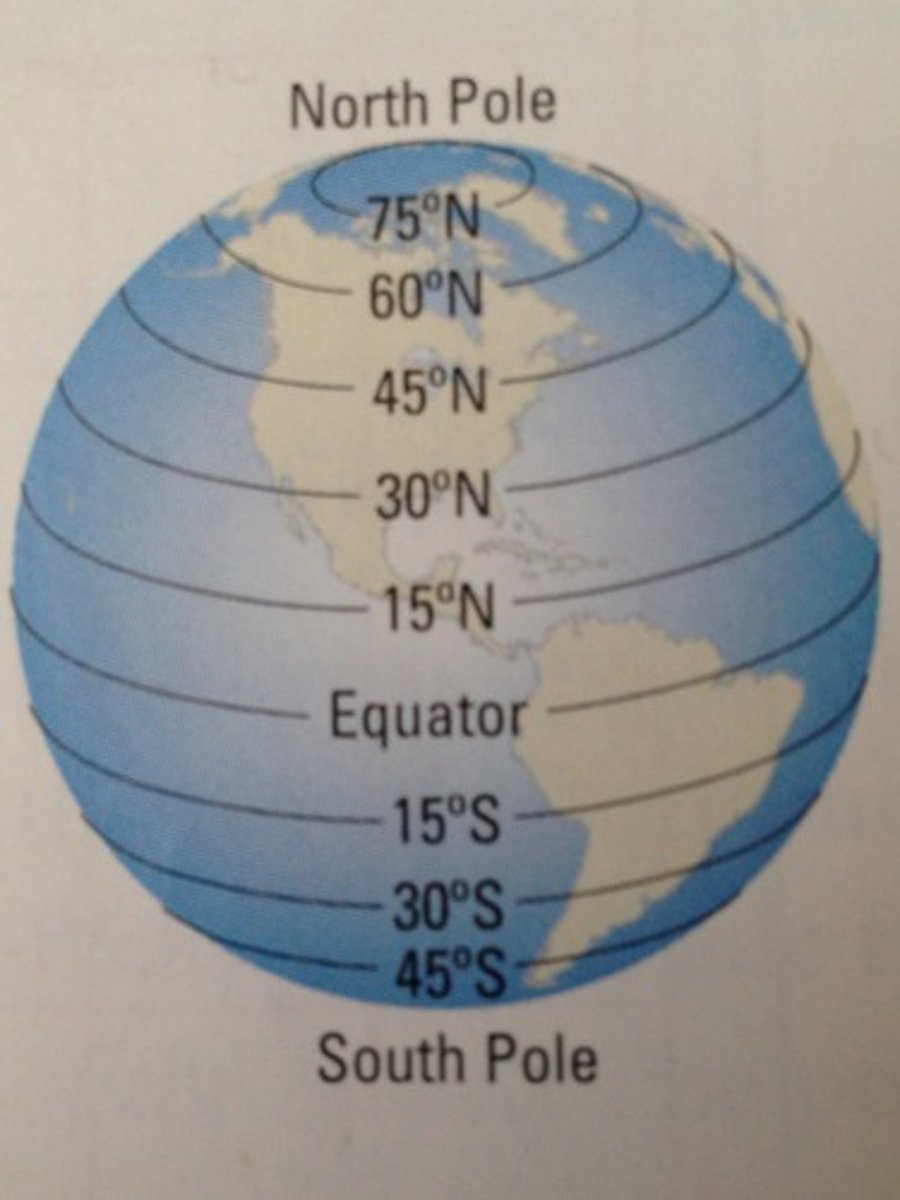
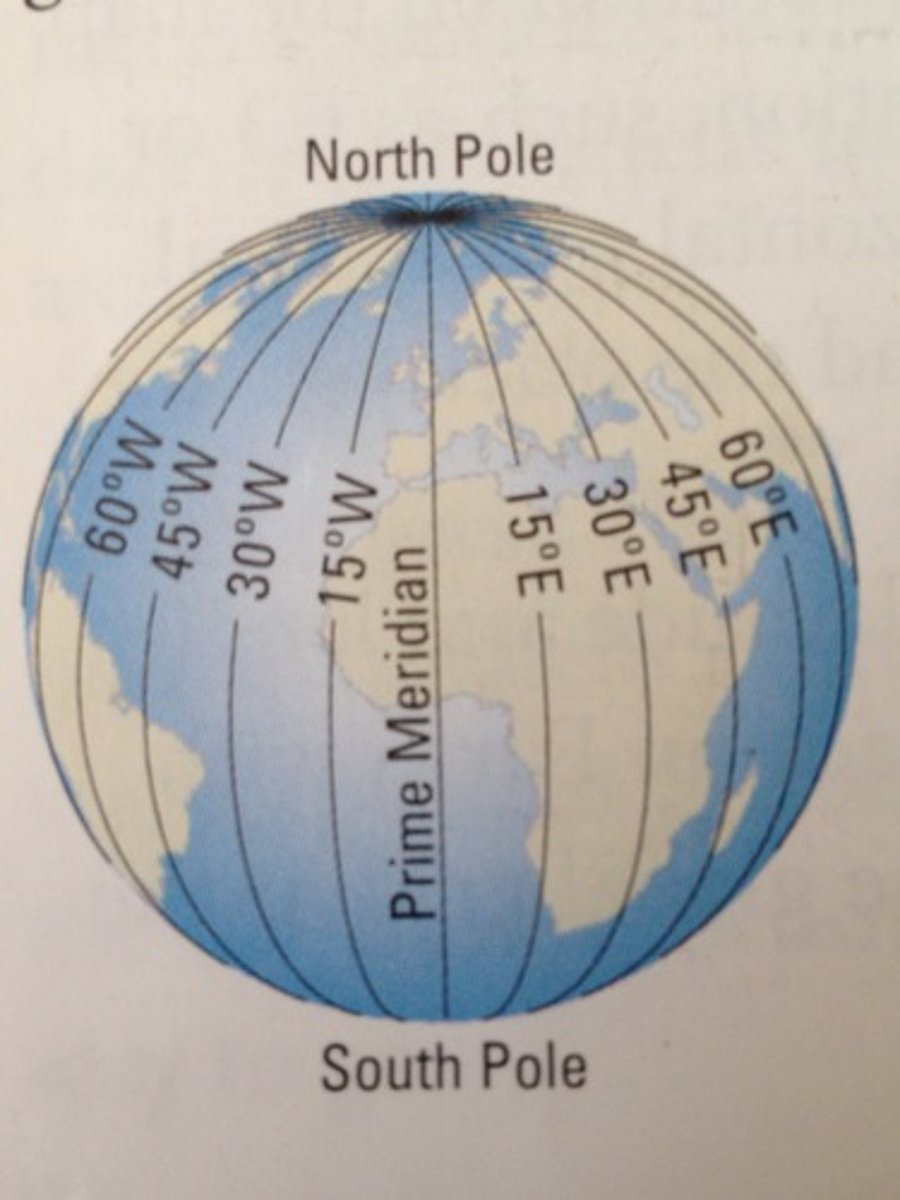
Longitude
Lines that run vertically on a map and measure East/West.
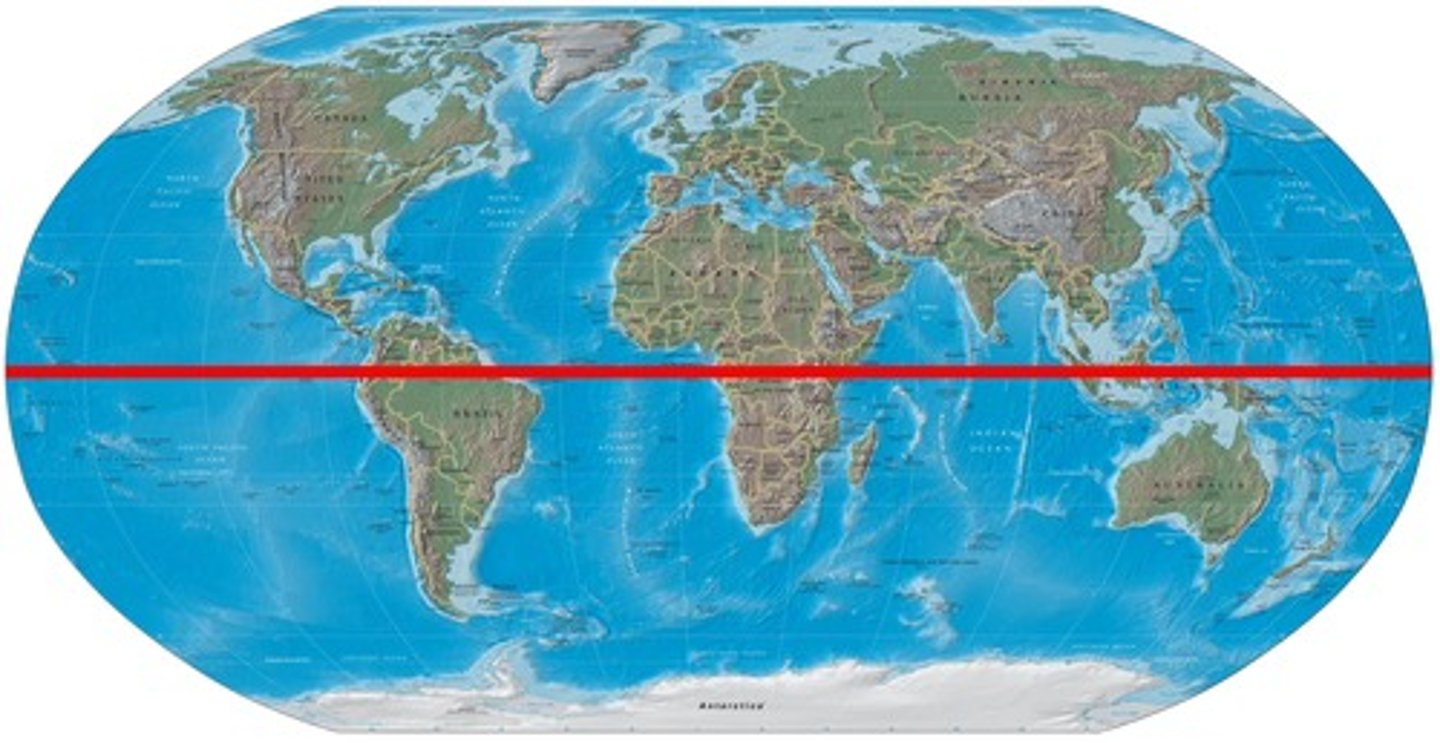
Equator
An imaginary HORIZONTAL line drawn around the middle of the earth, dividing the earth into northern and southern hemispheres, at 0 degrees latitude.
Prime Meridian
An imaginary VERTICAL line at 0 degrees longitude
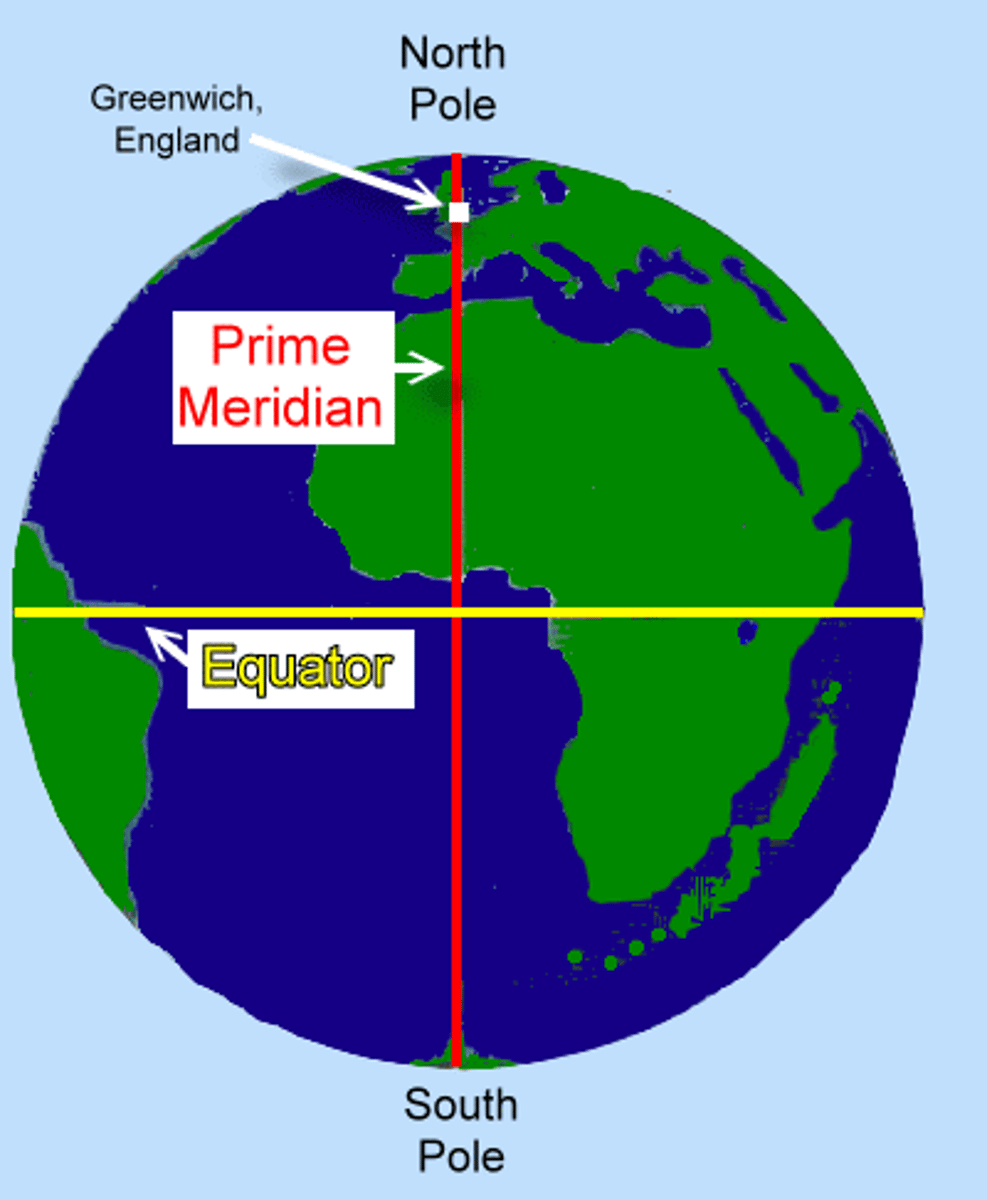
Absolute Location
Describes the exact position of a place on Earth using a coordinate system, typically latitude and longitude.
Relative Location
Describes where a place is in relation to other places like nearby landmarks.
Absolute Distance
The exact measurement of space between two points, typically expressed in standard units such as meters, kilometers, or miles.
Relative Distance
Distance measured in terms such as time, effort, or cost, rather than a fixed measurement.
Cartographer
A person who makes maps.
Reference Maps
Maps that tell us what is where.
Thematic Maps
Maps that tell us what it's like / how it's like in a specific area.
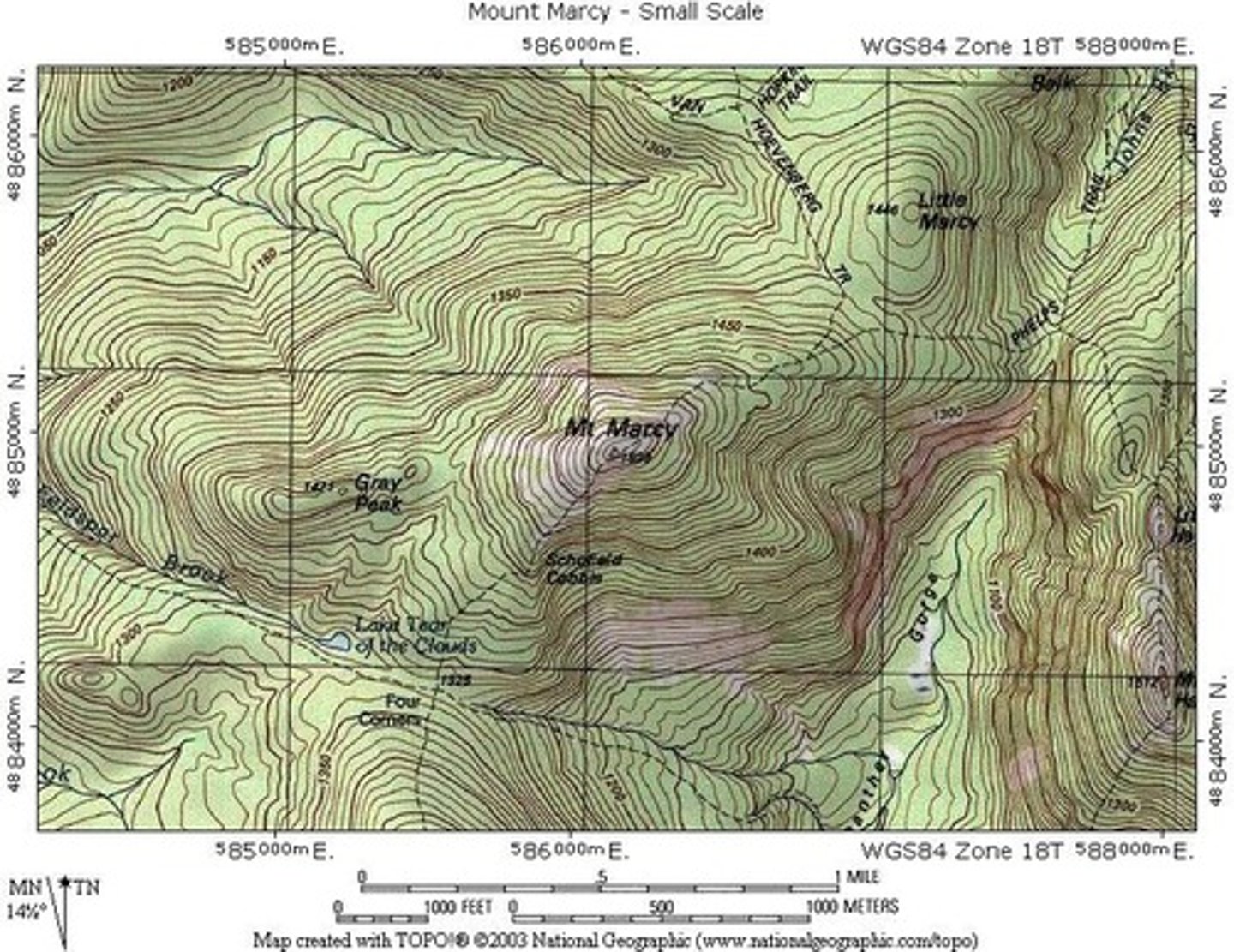
Topographic Map
A reference map that shows the surface features of an area.
-Strength: Shows accurate location of things.
-Weakness: Doesn't show what / how a place is like.
6 Types of Thematic Maps
1. Choropleth
2. Cartogram
3. Isoline
4. Dot distribution
5. Flow Map
6. Proportional/Graduated Symbol Map
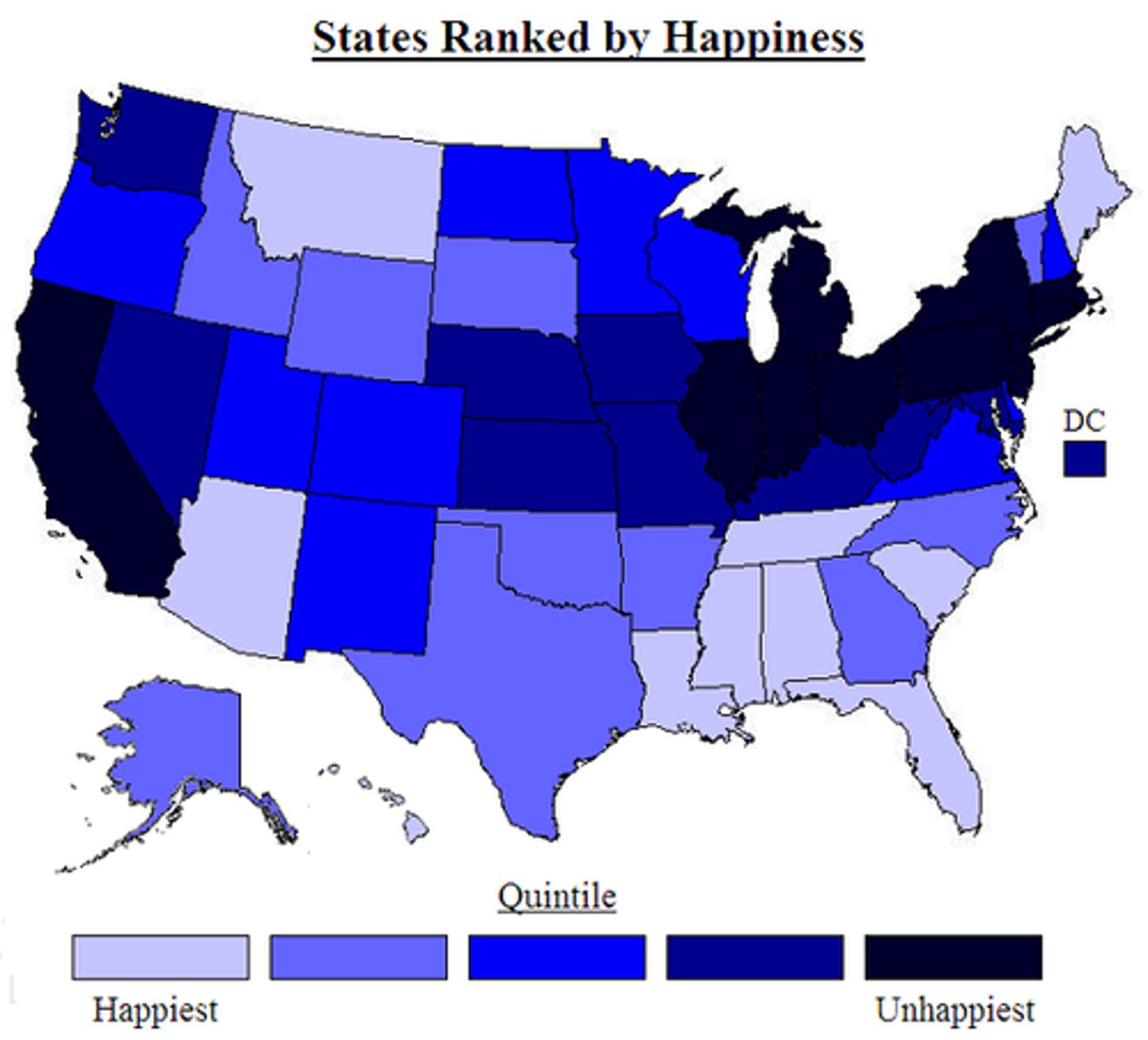
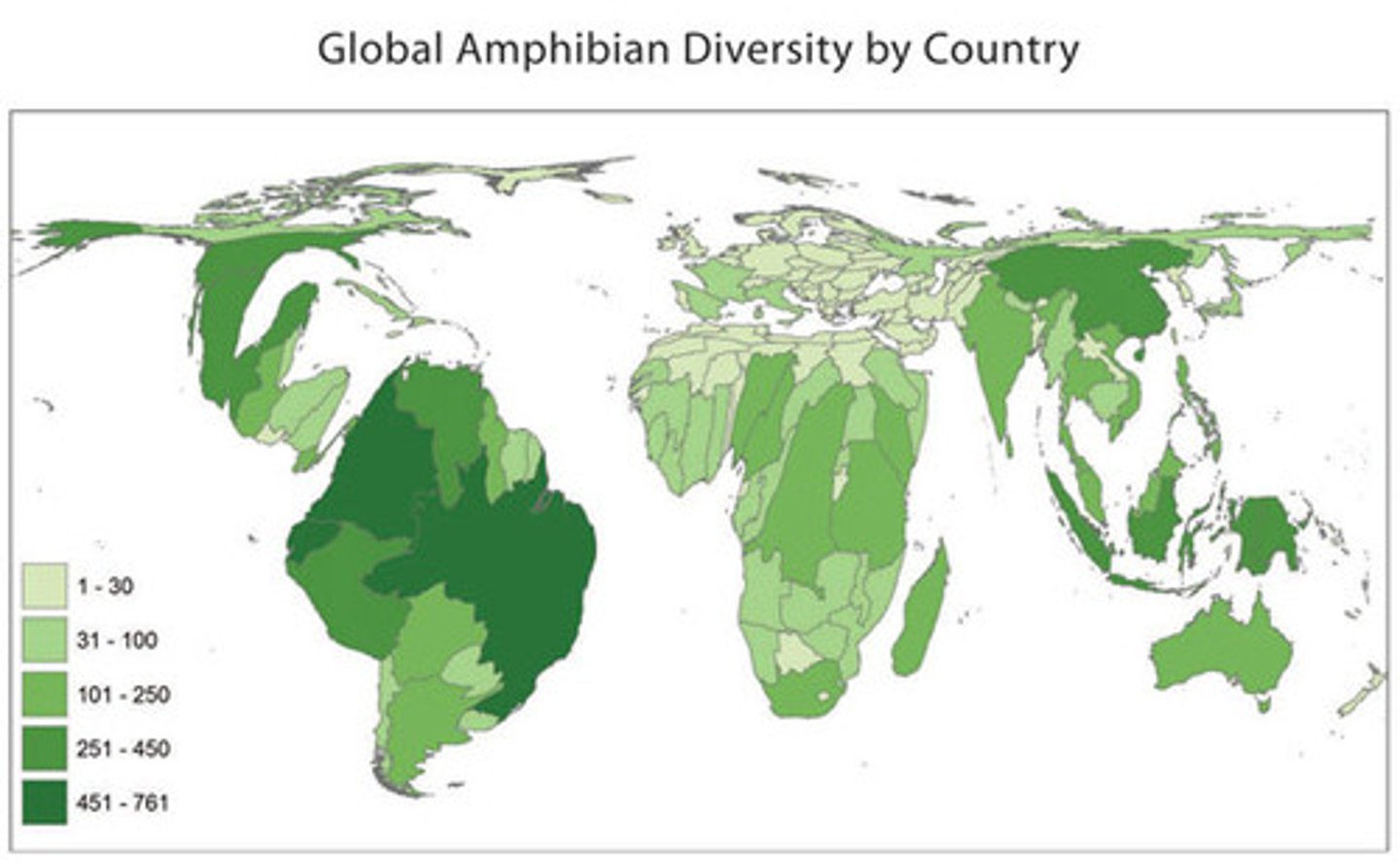
Choropleth Map
A thematic map that uses colors/shading to represent quantifiable data.
-Strengths: Shows great density, visually easy to see.
-Weaknesses: Doesn't show accurate distribution, not specific enough, can be misleading.
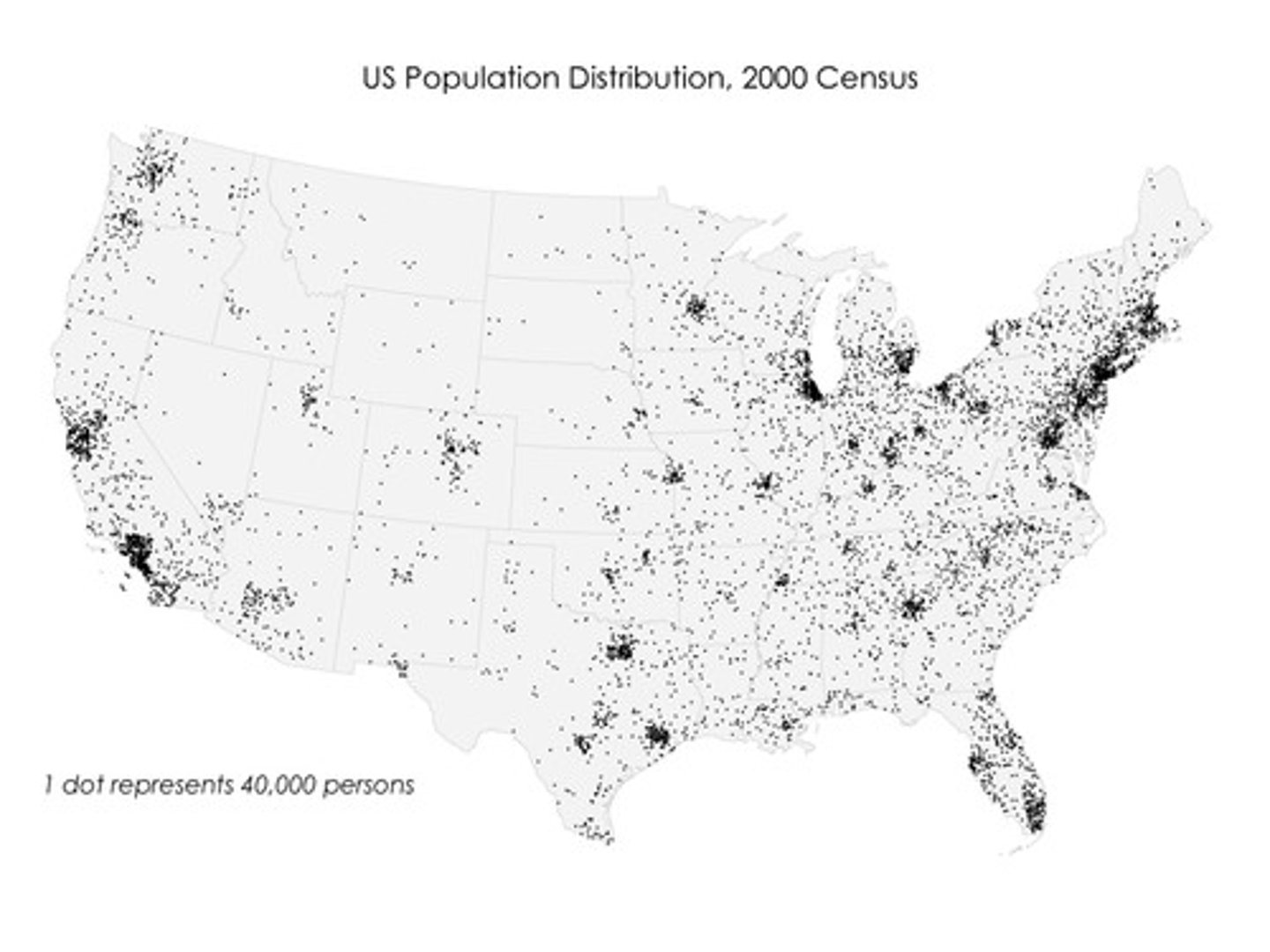
Dot Distribution Map
A thematic map where dots are used to demonstrate the frequency of a particular value.
-Strength: Shows accurate distribution.
-Weaknesses: Doesn't show accurate density because dots can be too close together to the point where you can't see individual dots.
Isoline Map
A thematic map that uses lines to connect points of equal value, such as elevation, temperature, or rainfall. It helps us visualize patterns and gradients across a geographic area.
-Strength: Shows areas that are similar in some feature (i.e., weather).
-Weakness: Can be very difficult to interpret if colors are not used.
Cartogram Map
A thematic map that distorts the appearance of places on a map to represent their value.
-Strength: Visually very clear and easy to interpret.
-Weakness: If a place has too small of a value, it may be hard to find on the map.
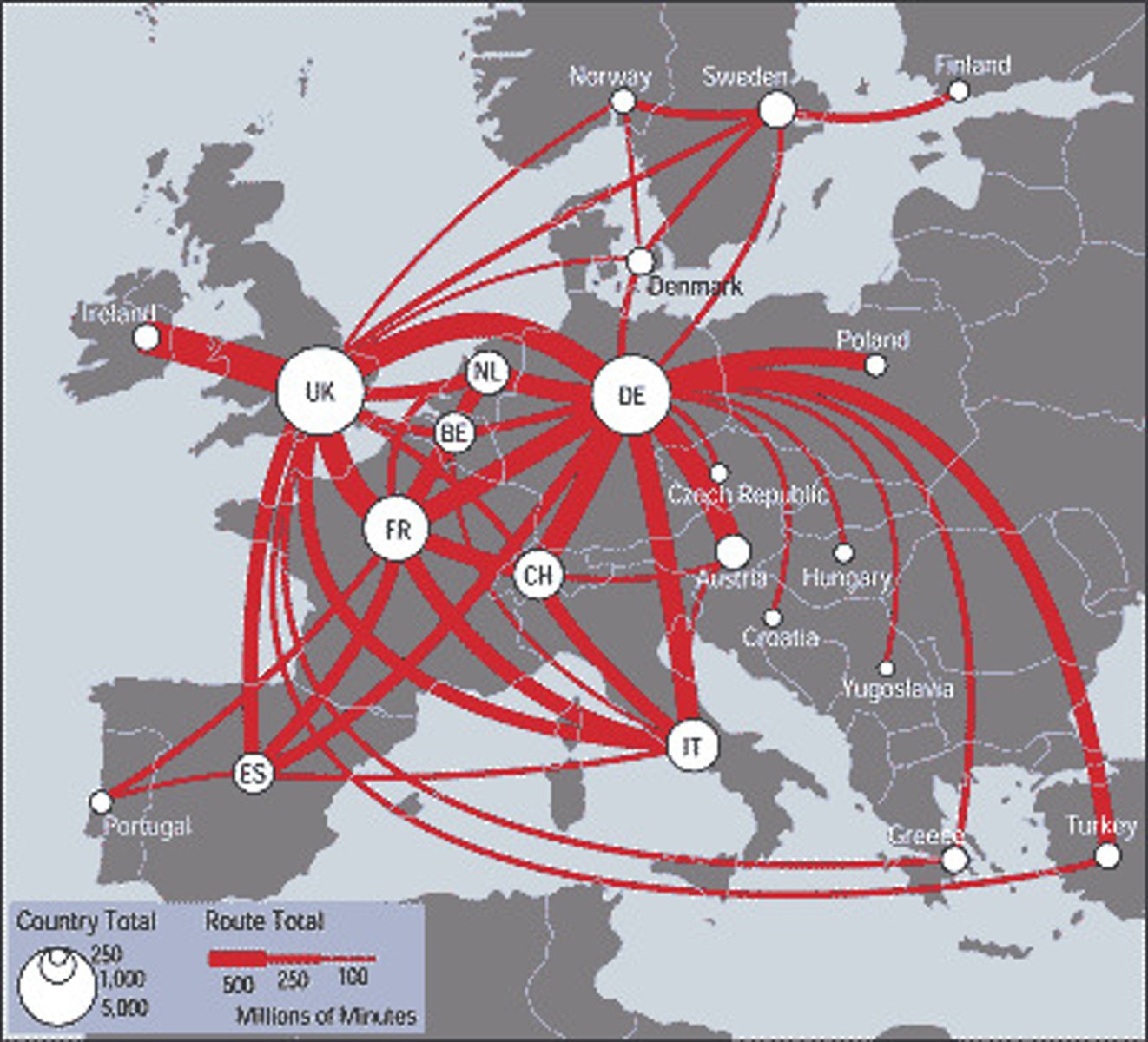
Flow Map
A thematic map that shows the direction of movement of a value like trade, or migration, or ocean currents.
-Strength: Mostly easy to interpret visually.
-Weakness: If there is too much data on the map, it can be hard to follow specific flows.
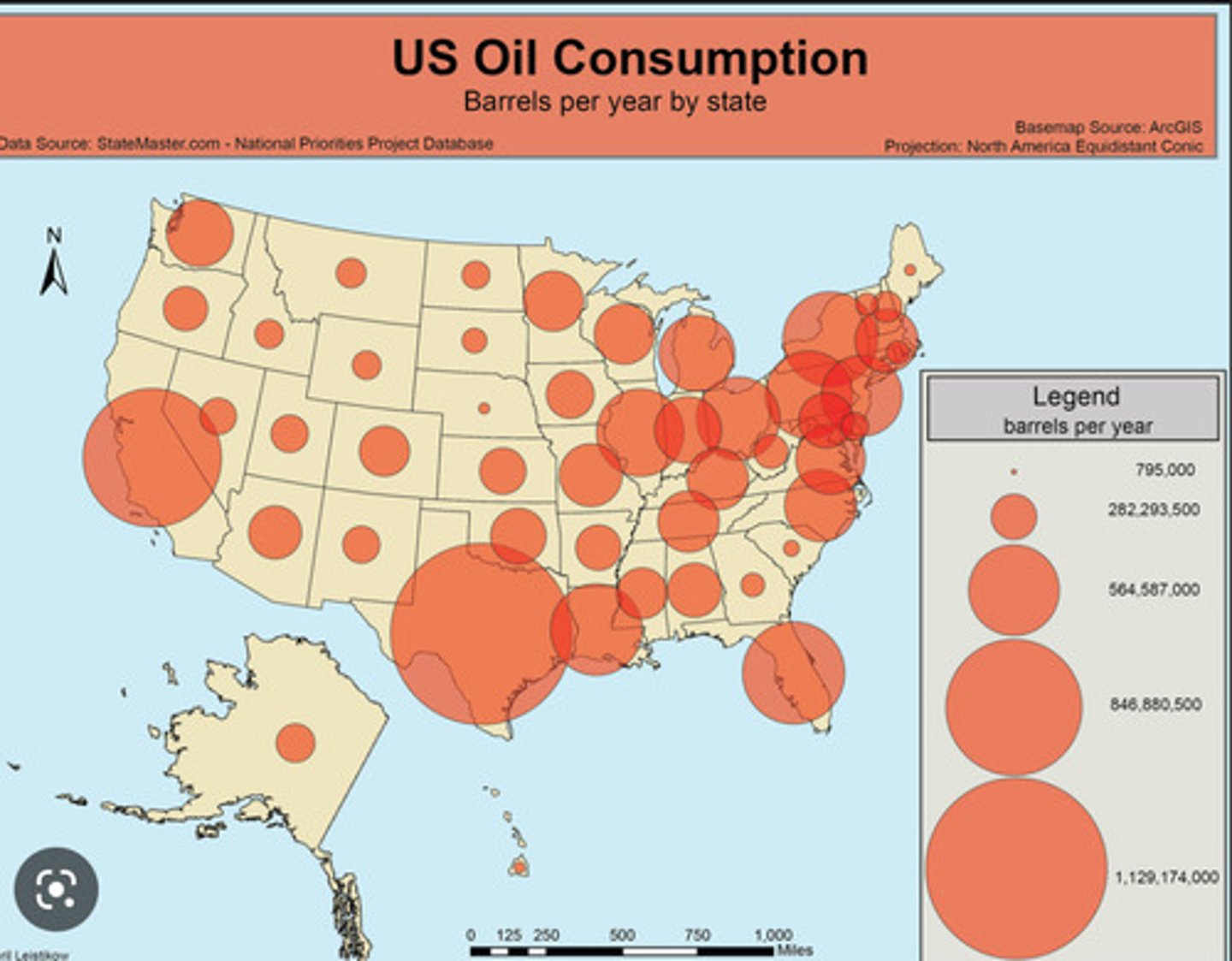
Proportional/Graduated Symbol Map
A thematic map that features symbols proportional to the size of the actual value.
-Strength: Shows accurate distribution.
-Weakness: Can be too clustered when the symbols are located too close to each other.
Site vs. Situation
-Site: Where cities are, where a country’s border is, where mountain ranges, lakes, and rivers are.
-Situation: How things are in a given place.
Map Projection
A way of representing the spherical Earth on a flat surface.
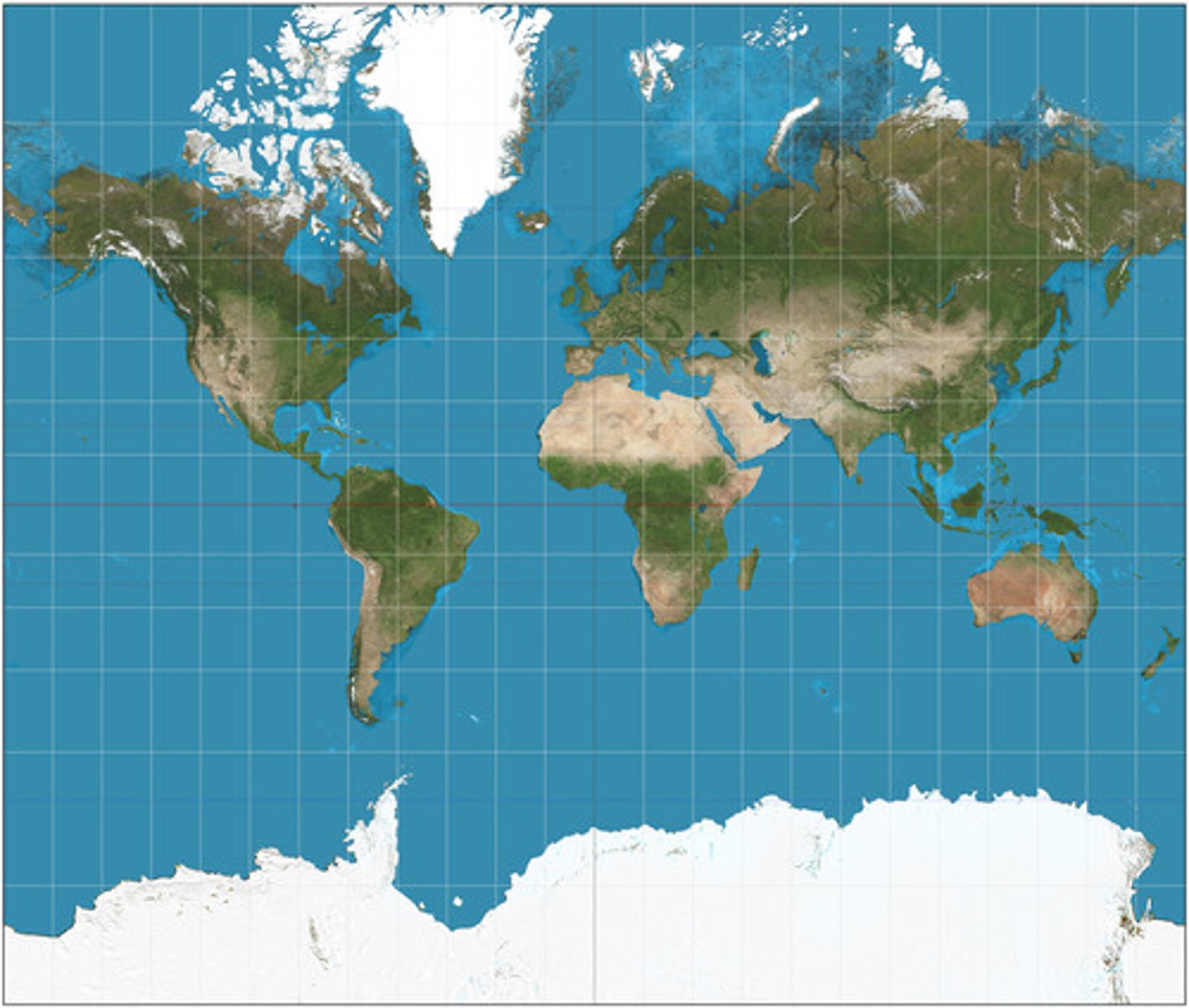
Distortion
An inaccuracy in shape, location, direction, or distance created when trying to form a map.
5 Types of Map Projections
1. Mercator Projection
2. Robinson Projection
3. Goode Homolosine Projection
4. Fuller Projection
5. Peters Projection
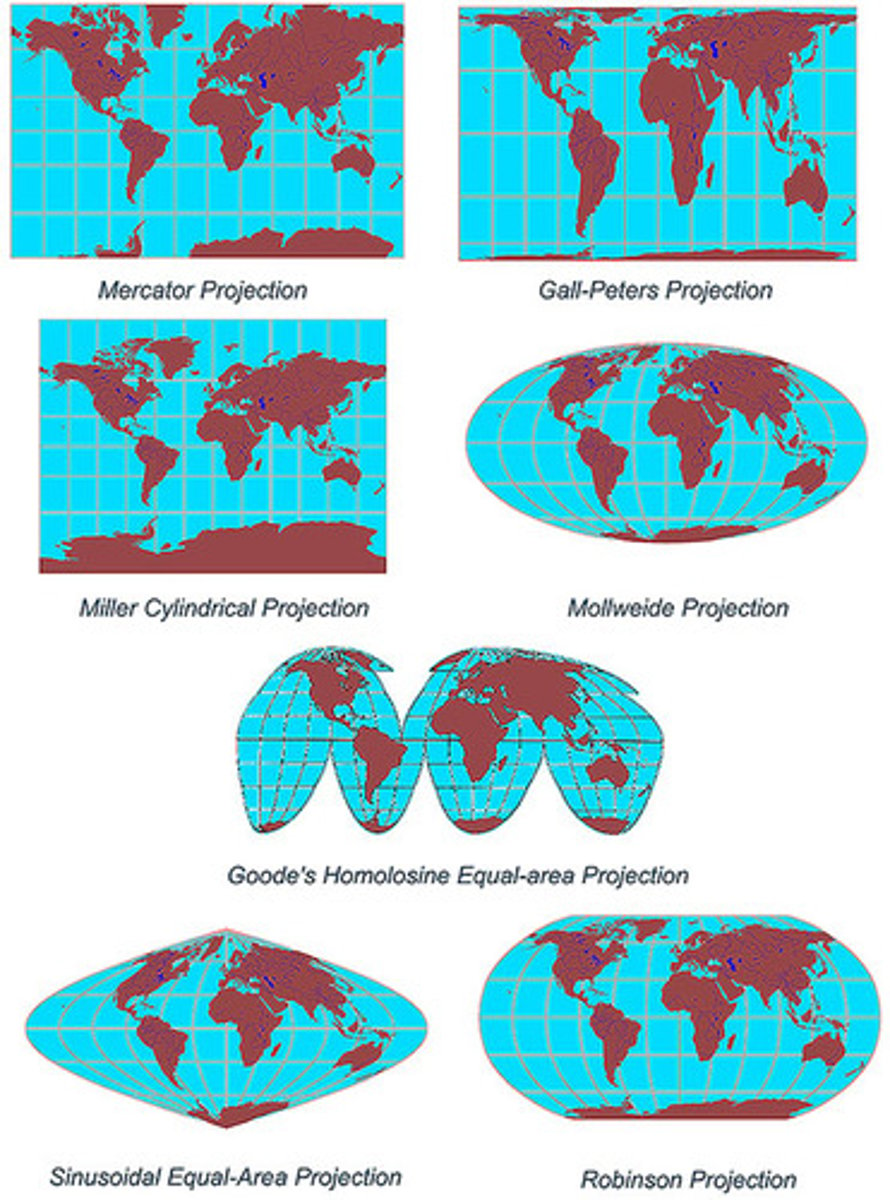
Mercator Projection
A type of map projection that includes:
-Distortion of poles
-Parallel lines of latitude and longitude
-Sizes are inaccurate, shapes are accurate
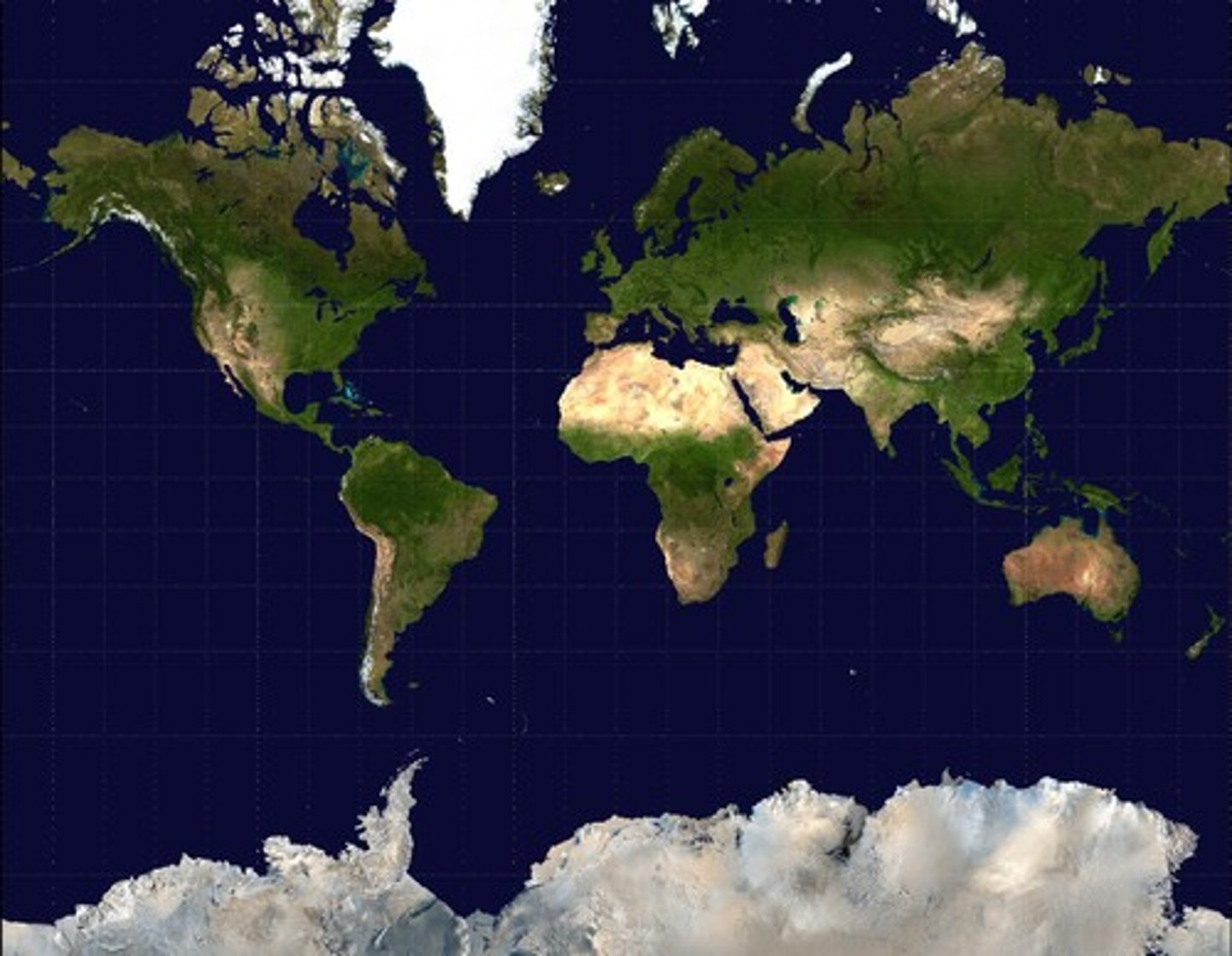
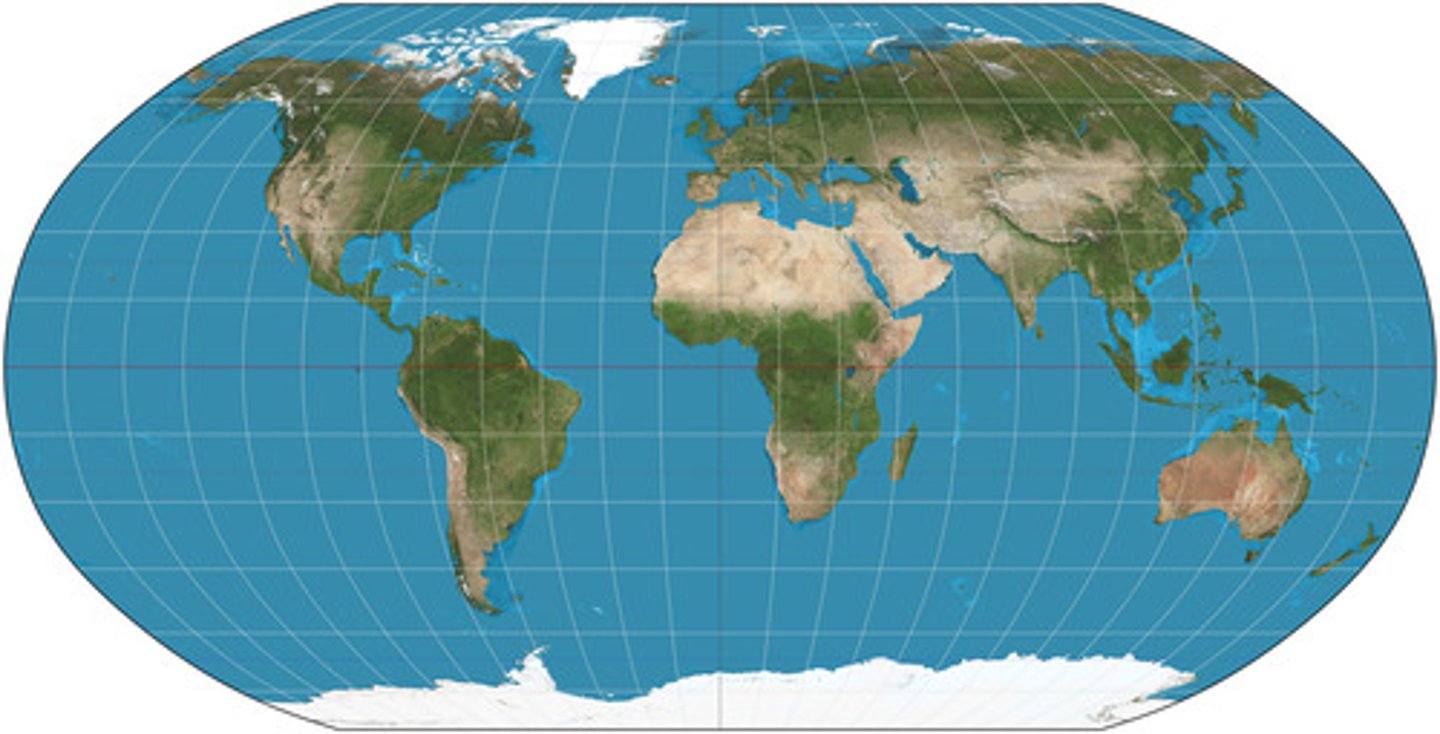
Robinson Projection
A type of map projection that includes:
-Distortion of North/South poles
-Accurate sizes AND shapes
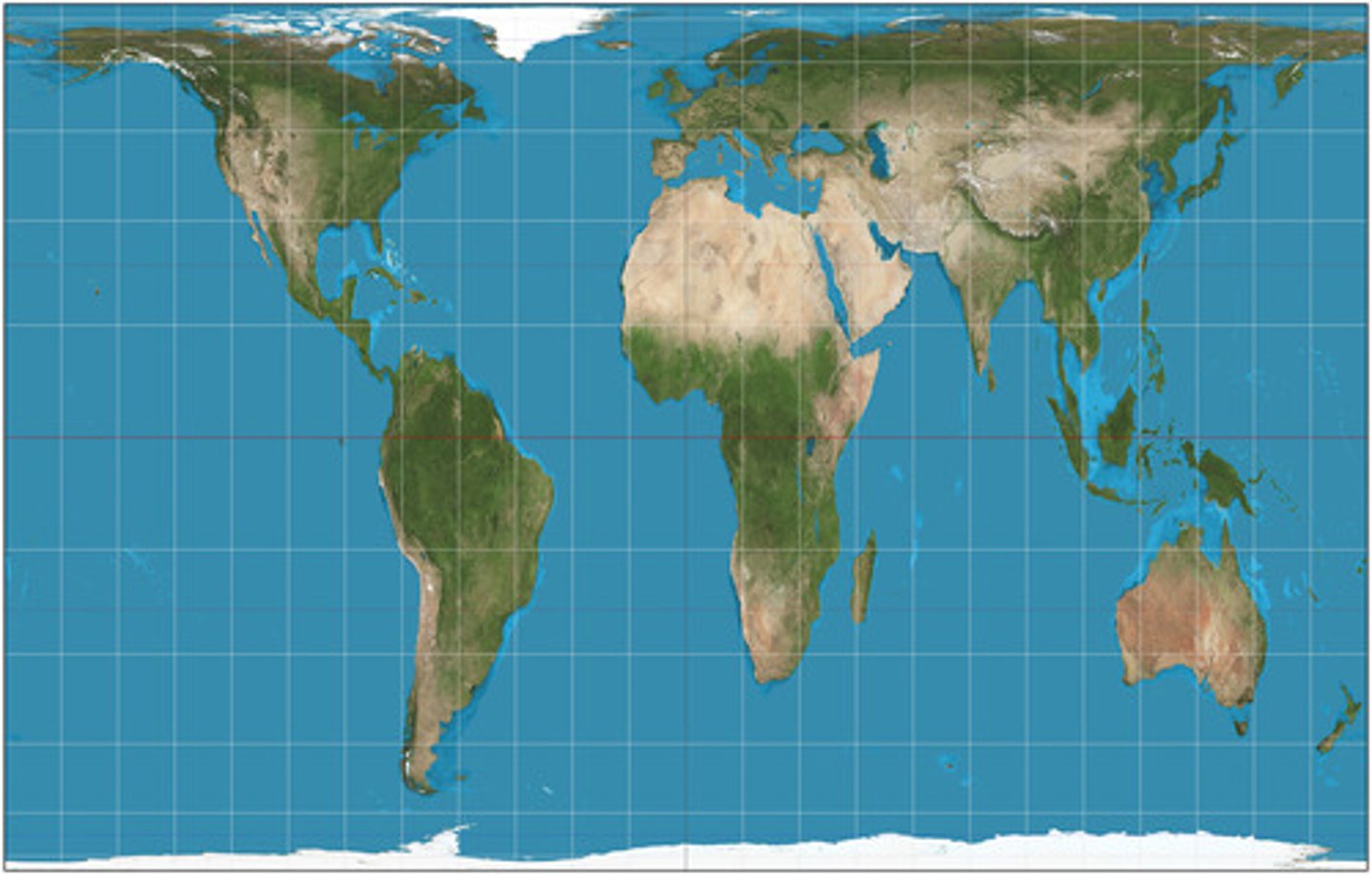
Goode Homolosine Projection
A type of map projection in which size and shape are accurate, but map is interrupted.
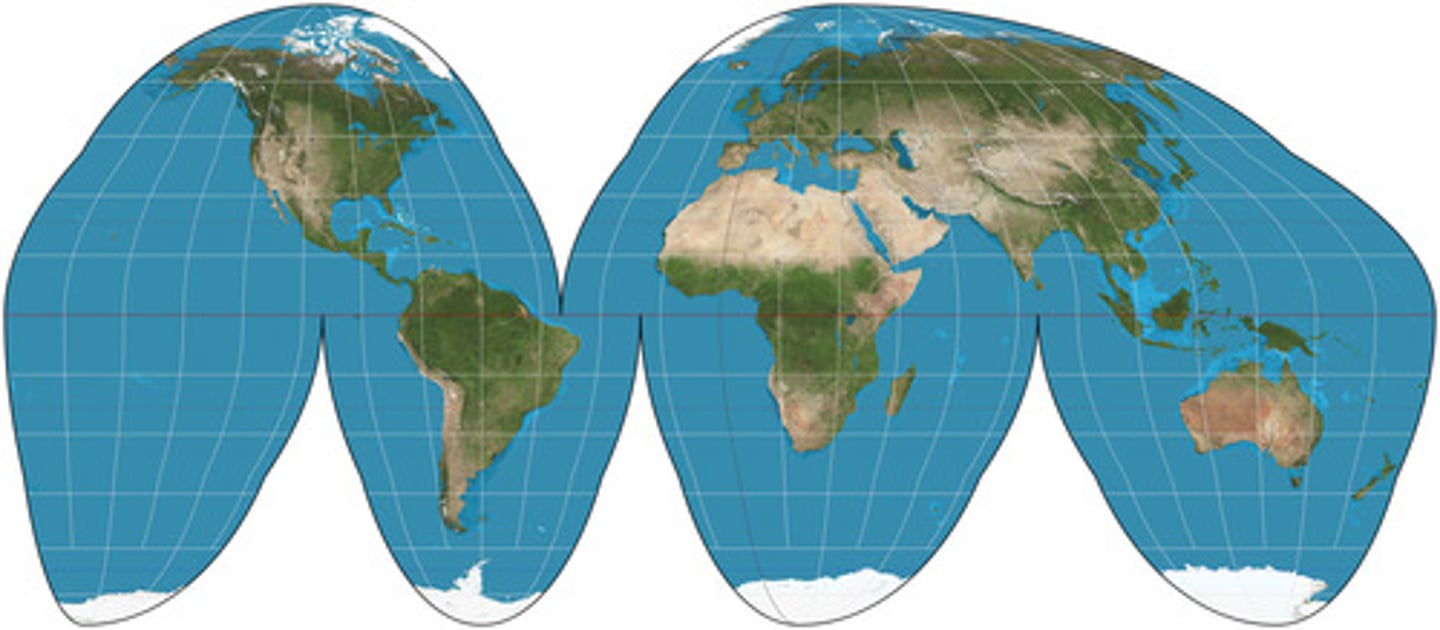
Fuller Projection
A type of map projection that doesn't follow East/West directions.
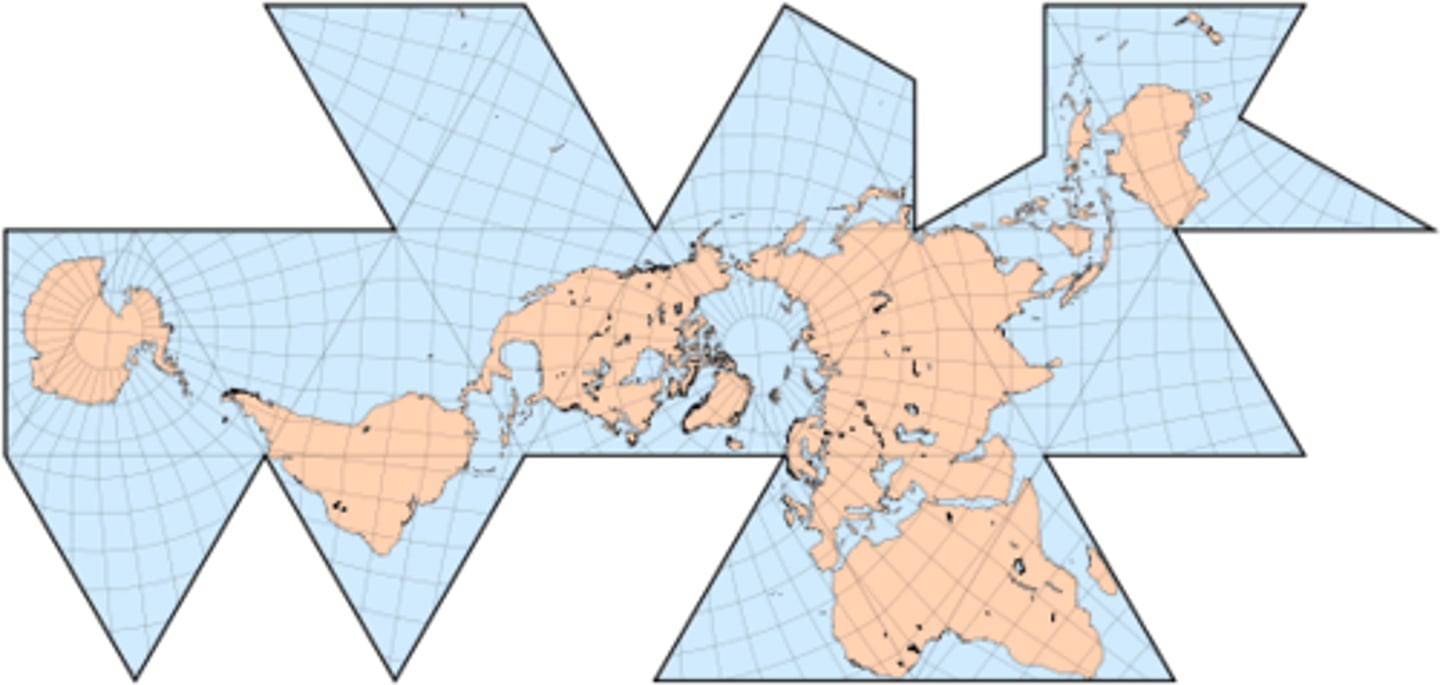
Peters Projection
A map projection purposely centered on Africa in an attempt to treat all regions of Earth equally.
-Shape is distorted, but size is accurate.
Mental Maps
Subjective maps in our minds shaped by personal experiences, cultural background, and social context.
Density
The number of individuals or objects per unit area or volume.
Clustered
A pattern where many people/objects occur closely together in one place.
Dispersed
Refers to the way something is spread out or arranged over a geographic area.
Space
The physical gap or interval between two objects or locations on the Earth's surface.
Pattern
The geometric arrangement of objects in space.
-Can be linear, centralized, random, etc.
Flow
Describes the movement of people, goods, information, or ideas between places.
Scales of Analysis
Refers to the level of which you are studying maps (how zoomed in or zoomed out).
Includes:
-Local
-National
-Regional
-Global
Interdependence
The idea that two locations are dependent on each other because of a flow that connects them through space.
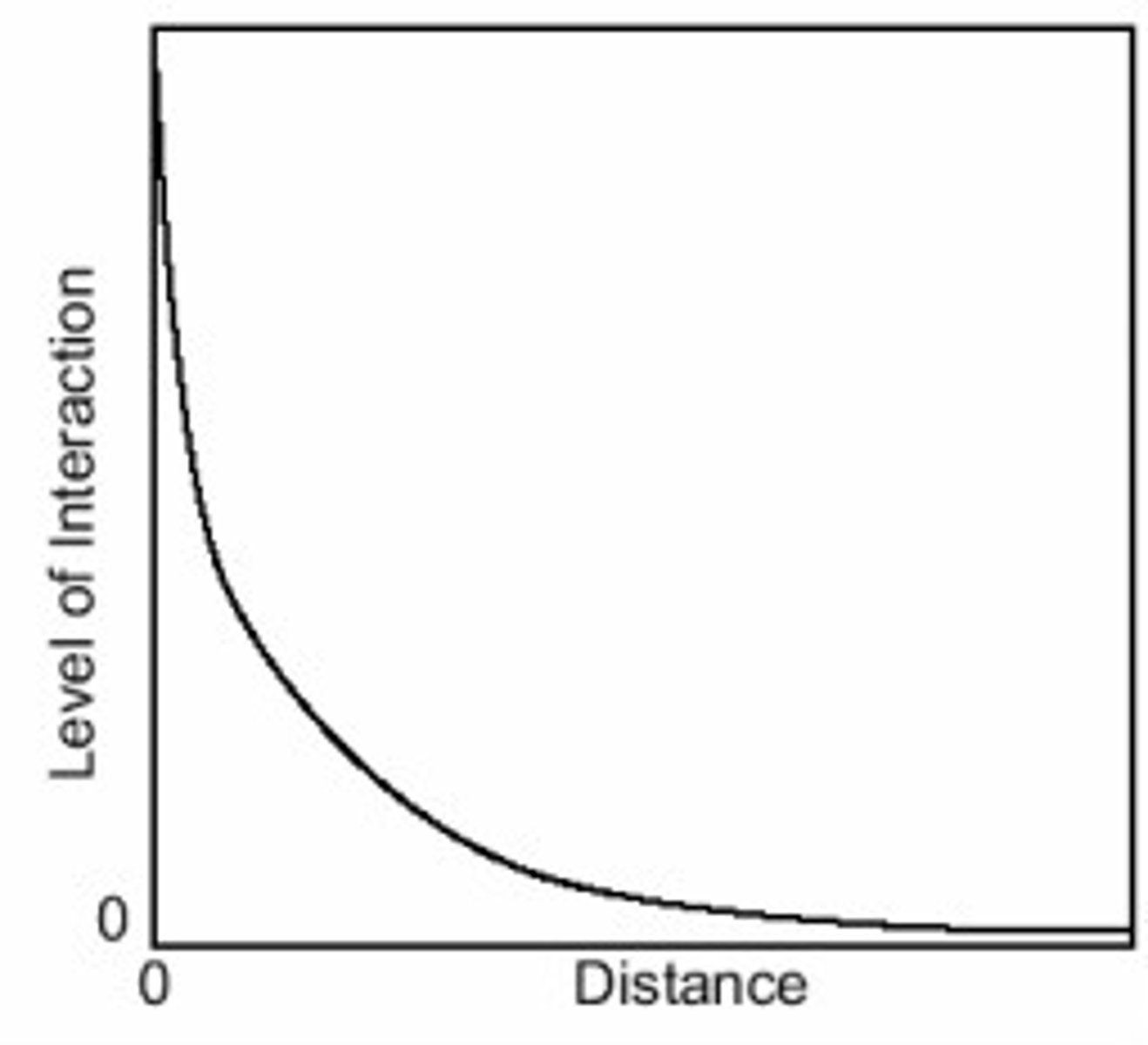
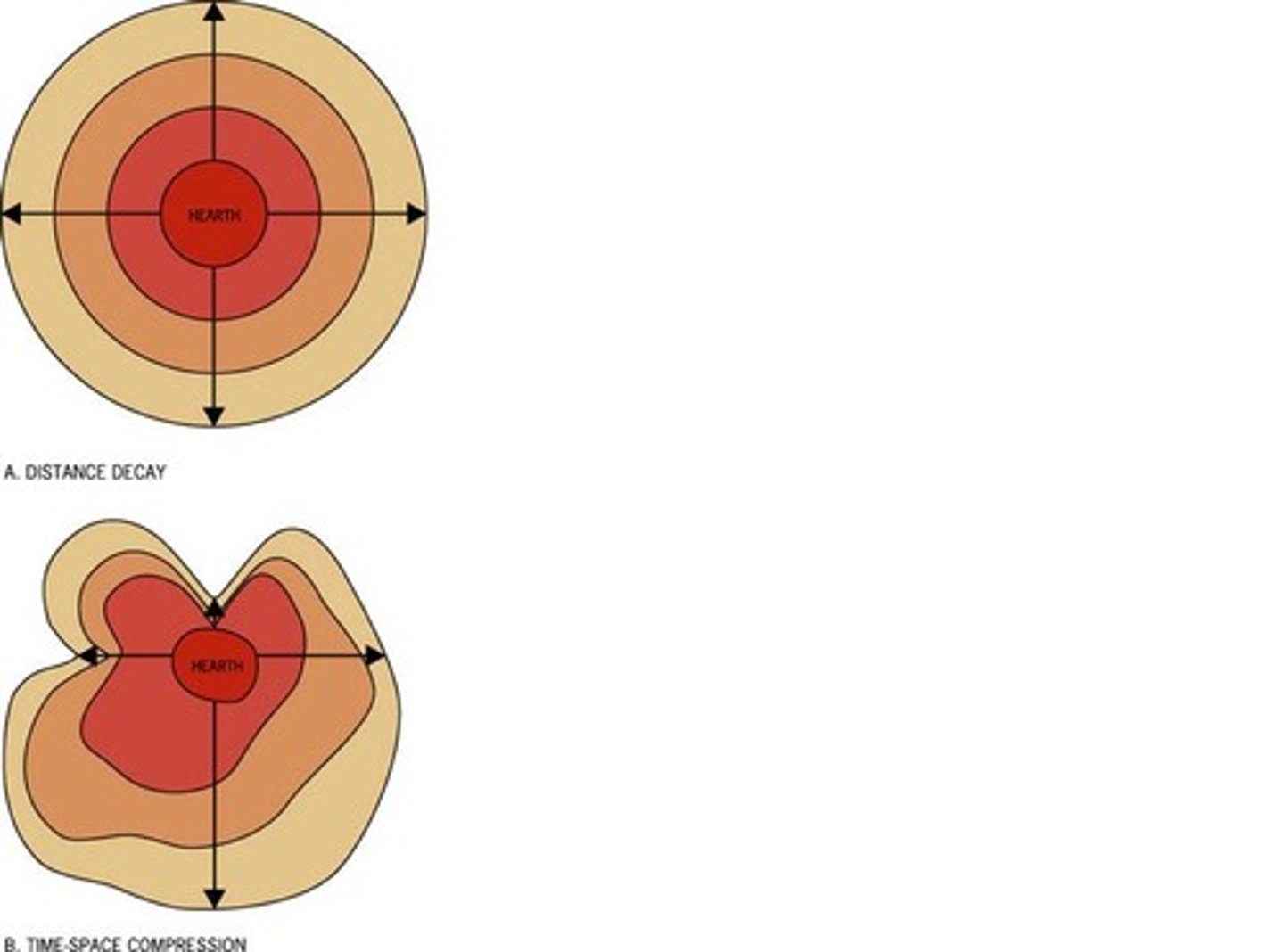
Distance Decay
The lack of connection, or communication between people from far away places.
-Caused by friction of distance (the farther apart two places are, the more effort, time, or money it takes to interact or move between them).
Time-Space Compression
The reduction of time it takes for a person, idea, or product to get from one place to another, thus connecting more places around the world regardless of distance.
-The opposite of distance decay.
Diffusion
How something spreads from one place to another over time.
5 Types of Diffusion
1. Hierarchical Diffusion
2. Reverse Hierarchical Diffusion
3. Stimulus Diffusion
4. Relocation Diffusion
5. Contagious Diffusion
Hierarchical Diffusion
Spread of an idea from people or places of power or influence to others
Reverse Hierarchical Diffusion
When a cultural trait spreads from lower levels of society or small towns to larger urban centers or elites.
Stimulus Diffusion
When the main idea spreads, but the new adopters change it a bit to fit the context of their area.

Relocation Diffusion
When people move to a new place and bring their culture or ideas with them.
Contagious Diffusion
Rapid, widespread diffusion of a characteristic through a population.
-E.g.: Like how a disease spreads or a viral video on TikTok.
"Why of the where"
Explanations for why a spatial pattern occurs, concluded from collections of data.
Large Scale Maps
Zoomed in maps for GREATER detail.
Small Scale Maps
Zoomed out maps for SMALLER detail.
Local Level of Analysis
Data collected from a specific city or town.
-E.g.: Alexandria
Regional Level of Analysis
Data collected across countries that are located close to each other or across areas within a country that are close to each other.
-E.g.: Northern Africa (small scale) or Upper Egypt (large scale)
National Level of Analysis
Data collected from a country.
-E.g.: Egypt
GLOBAL Level of Analysis
Data is collected from around the world.
-E.g.: Map of the world
GLOCAL Level of Analysis
Glocal = Global + Local
It recognizes that what happens locally can be shaped by global forces, and vice versa. It's about understanding how a local place is connected to the global system.
-E.g.: The question about where/how COVID-19 originated locally is just as important as understanding its global impacts on the economy.
4 Types of Regions
1. Formal Region (aka Uniform or Homogenous)
2. Functional (aka Nodal)
3. Perceptual (aka Vernacular)
4. Border Region / Transition Zones (aka Border Zone)
Formal Region (aka Uniform or Homogenous)
A geographical area inhabited by people who have one or more traits in common
Functional (aka Nodal)
A geographic area that has been organized to function politically, culturally, economically, or socially as one unit.
Perceptual (aka Vernacular)
A geographic area that is perceived to exist by its inhabitants based on the widespread acceptance and use of a regional name.
Border Region / Transition Zones (aka Border Zone)
A geographic area where cultures overlap at a political border and blend into a recognizable border culture.
Regional Identity
Identification with a group of people within a region.
Qualitative Data
Data often collected through interviews, observations, etc., rather than focusing on numbers.
Quantitative Data
Numerical data
Models
Representations of reality that help to explain, describe, and sometimes even predict events.
Types:
-Spatial models: Maps, globes, etc.
-Non-spatial models: Theories that use words, graphs, tables and charts.
Census
Official count or survey of a population.

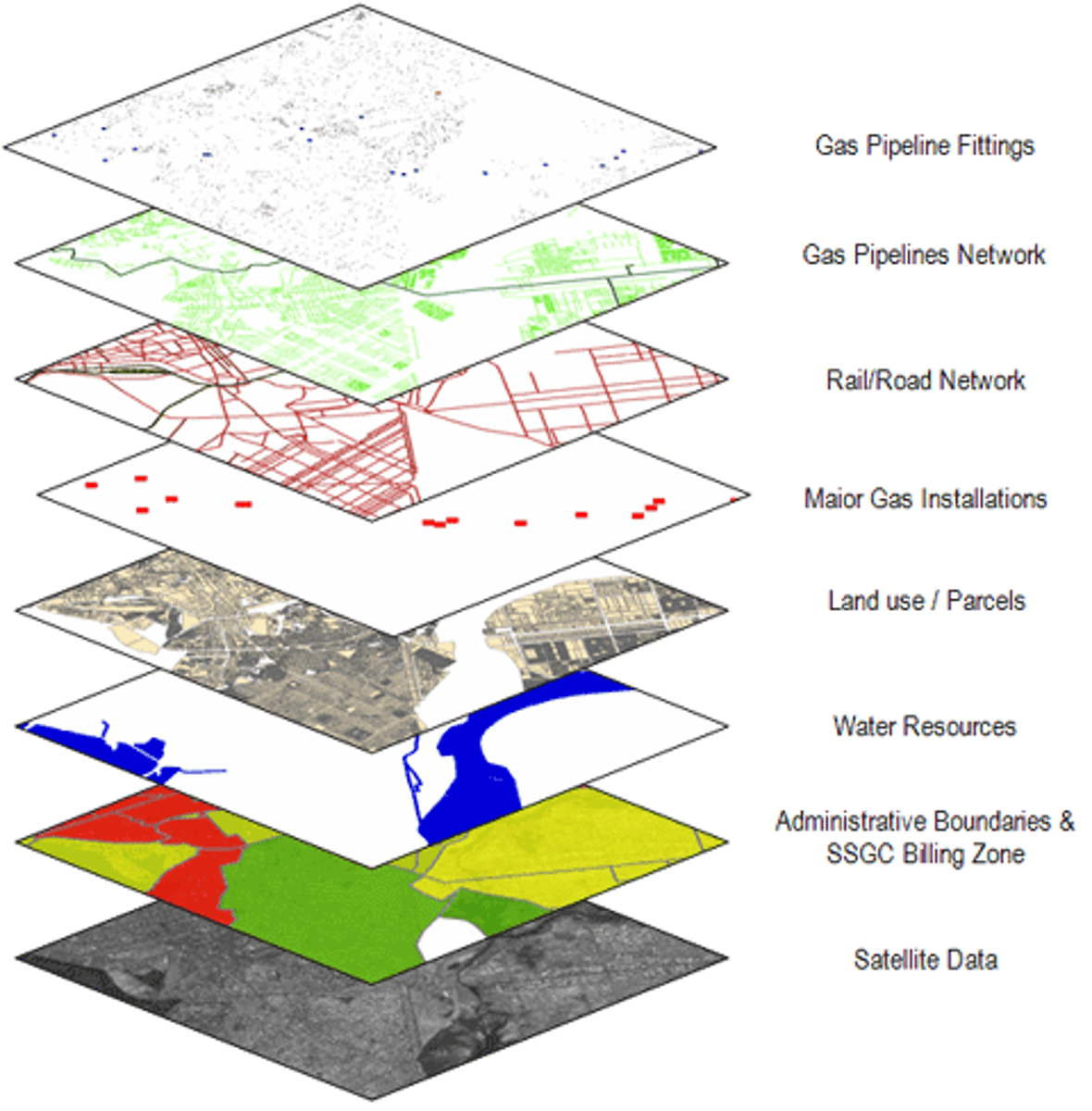
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Computer systems that collect, analyze, store and display geographic data.
-Layer multiple maps on top of each other for complete depiction of areas.
Geospatial Data
Any information about a specific location on earth., including coordinates, addresses, or zip codes, and is used to analyze patterns and processes on the human landscape (like population density or traffic patterns).
Remote Sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from satellites, drones/airplanes with cameras, or other long-distance methods.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information anywhere on Earth.
Environmental Determinism
The idea that the physical environment—especially climate and terrain—determines the patterns of human culture and societal development.
Possibilism
Viewpoint that argues that while the environment provides certain constraints, humans have the ability to adapt and choose among different possibilities to shape their own societies and cultures.
-It highlights human agency, innovation, and cultural factors in development.
Sustainability
The concept of living in a way that allows the Earth to sustain its resources rather than deplete them.
