Film & Media Studies Midterm
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
180 degree rule
A guideline in film making that states that two characters in a scene should maintain the same left/right relationship to one another.
magic lantern
An early type of image projector that used painted glass slides to create images.
cinema of attractions
A term describing early cinema that focuses on spectacle and visual novelty rather than narrative.
chronophotography
A technique that captures a sequence of movements in a series of photographs.
composition
The arrangement of visual elements in a work of art
continuity editing vs. discontinuity
Continuity editing aims to create a seamless flow of action
narrative vs. spectacle
Narrative refers to the story being told
deep focus
A cinematographic technique that allows objects in both the foreground and background to be in sharp focus.
depth of field
The distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image.
dialectical montage
cutting together conflicting or unrelated images to generate an idea or emotion in the viewer
diegetic / nondiegetic
diegetic sound originates from within the story's world and is heard by the characters, such as dialogue, a character playing a guitar, or a car radio.
non-diegetic sound originates outside the story world and is only heard by the audience, including a film's musical score, a narrator's voice-over, or added sound effects
eyeline match
a cut that follows a shot of a character looking offscreen with a shot of a subject whose screen position matches the gaze of the character in the first shot
framing
the technique of arranging visual elements within the camera's frame to guide the viewer's attention and convey meaning

German expressionism
a silent film movement from early 20th-century Germany that uses exaggerated, distorted visuals to convey subjective emotions and psychological states rather than realistic depictions
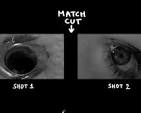
graphic match cut
a cinematic transition that connects two different shots by matching their visual composition, using similar shapes, colors, or outlines to create a seamless and meaningful link between scenes
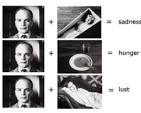
Kuleshov effect
a film editing principle where viewers derive more meaning from the interaction of two or more sequential shots than from a single shot in isolation

Lumière and Méliès
Lumière films are defined as early, realistic documentaries of everyday life, often single-shot and with a stationary camera
Méliès films are defined by their fantastical, narrative-driven stories and pioneering use of special effects like dissolves and double exposures, transforming cinema into a medium of illusion
medium specificity
the idea that the medium itself—film and its unique properties like projection, movement, and close-ups—has distinct characteristics that shape its art and meaning

compositing
the process of combining visual elements from separate sources into a single, seamless image or sequence
mise-en-scene
All of the elements placed in front of the camera to be photographed: the settings and props

onscreen/offscreen space
onscreen space in film is the area within the camera's frame, while offscreen space is all the unseen area outside the frame but still part of the film's world
photographic realism
a style that aims to represent reality as closely as possible, striving to look like an unedited photograph or recording by making the camera and its effects unnoticeable
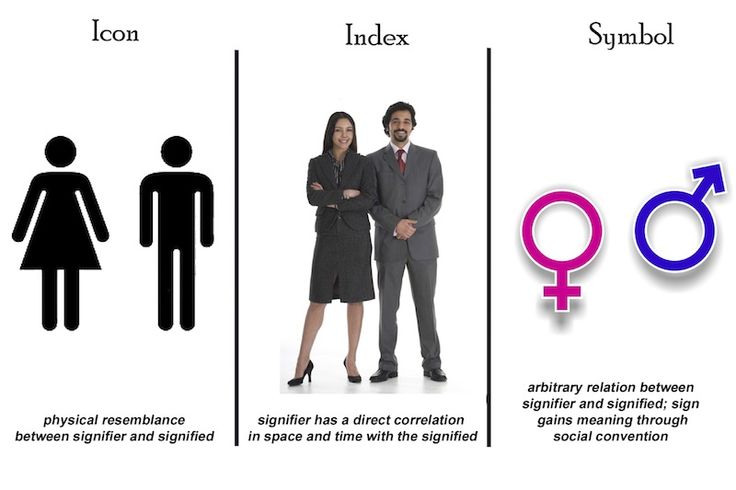
symbol / icon / index
icons are signs that visually resemble what they represent
indices have a direct, causal connection to what they represent
symbols have an arbitrary relationship that is learned through cultural convention
point-of-view cutting
a camera angle that shows a scene from a character's perspective, making the audience see through their eyes
shot size (long shot, medium shot)
shot size refers to how much of a subject is visible within the frame, ranging from close-ups to long shots. A long shot shows a subject's entire body and places them within their environment, while a medium shot typically frames the subject from the waist up
shot/reverse-shot
filmmaking technique where a camera cuts back and forth between two characters in a conversation, showing each character's perspective and creating the illusion of a single, continuous dialogue.

Soviet montage school
a film editing technique developed in 1920s Soviet Russia that uses the juxtaposition of shots to create meaning and evoke emotional and intellectual responses from the audience
subjective camera
hows a scene from a character's personal point of view, immersing the audience in their perspective to create an emotional connection and show their mindset
wide-angle vs telephoto lens
A wide-angle lens offers a broad field of view to capture expansive scenes, making distant objects appear smaller and keeping both near and far elements in focus, while a telephoto lens provides a narrow field of view to magnify distant subjects, creating a compressed perspective and isolating details, often with a shallower depth of field to blur the background
pro-filmic
a term used in film studies to describe the "reality" or world that is arranged and filmed in front of the camera
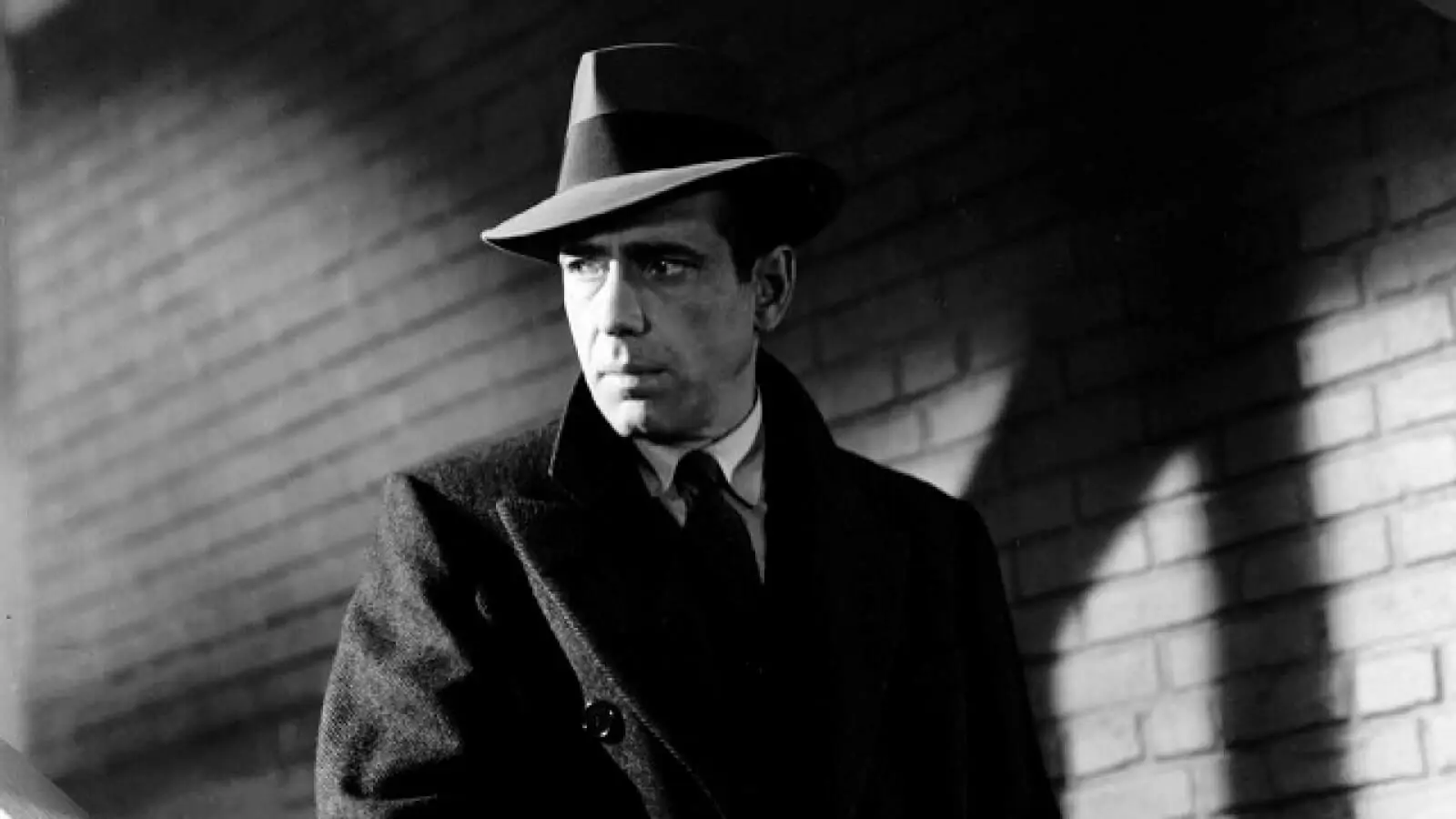

chiaroscuro
a lighting technique that uses strong contrasts between light and dark to create a sense of volume, depth, and drama
fidelity
the extent to which a film's sound is perceived as accurate to its source or how closely a film adaptation follows its source material
acousmetre
off-screen voice in film
puzzle film
a genre characterized by complex, non-linear, or obfuscated storytelling that requires the viewer to piece together the narrative and its clues
restricted vs. omniscient narration
estricted narration limits the audience's perspective to what a single character knows and perceives, while omniscient narration allows the narrator (and audience) to have a god-like perspective, knowing the thoughts and feelings of all characters and seeing events that a single character is unaware o
Steadicam
a camera stabilization system that creates smooth, fluid camera movements by mechanically isolating the operator's motion
referential meaning/explicit meaning/implicit meaning/symptomatic reading
summary, stated, implied, deeper
expansion vs. elision
elision shortens on-screen time by omitting story details, expansion artificially lengthens it to emphasize a moment
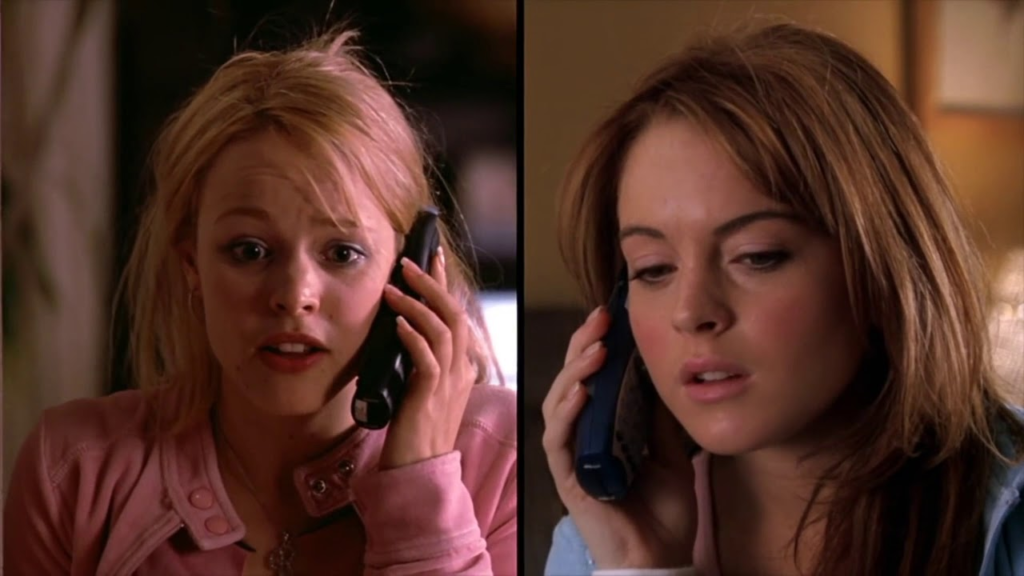

cross-cutting
an editing technique where the editor switches back and forth between two or more distinct scenes or actions, often in different locations, to create the impression that they are happening at the same time or in a simultaneous timeline
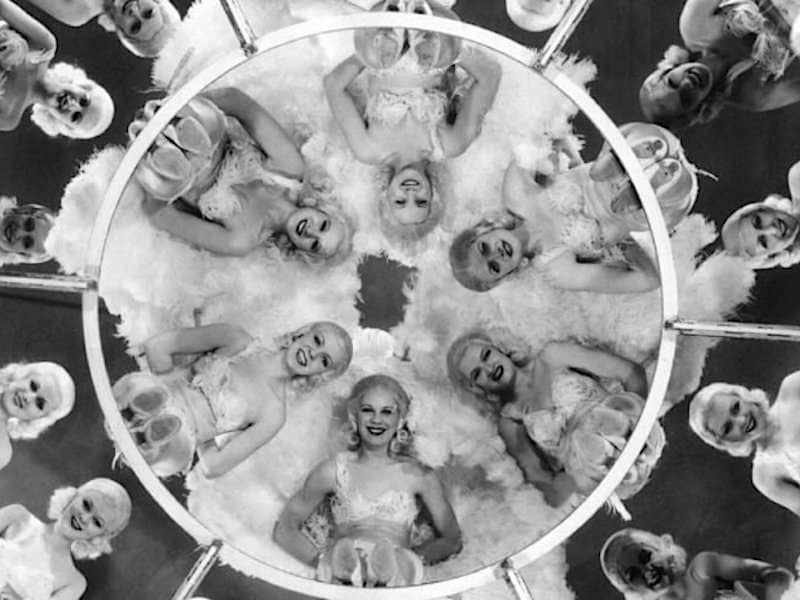

Busby Berkeley
a musical featuring elaborate, large-scale dance numbers characterized by overhead shots that arrange dancers into geometric and kaleidoscopic patterns, often using props like pianos and waterfalls
jump cut
an abrupt transition from one scene to another